PSY 101 Chp.1-3
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
What is the Barnum/Forer Effect?
When people think a general description applies to them specifically.
Define Subjective Validation.
The belief that two things have a correlation due to how a situation is structured, often leading individuals to see personal relevance in general statements. Often used by horoscopes, mediums, etc.
What is Pseudo-psychology?
A belief system based on folk wisdom or superstitions that appears scientific but does not adhere to the scientific method.
What is the scientific study of behavior and mental processes?
Psychology.
What does Karl Popper’s definition of science emphasize?
Science seeks to disconfirm hypotheses while pseudoscience looks to confirm them.
List the common characteristics of pseudoscience.
Un-falsifiability, absence of self-correction, unclear language, reliance on anecdotes, and not being peer-reviewed.
What is the CRAAP Test?
A framework to evaluate information sources based on Currency, Relevance, Authority, Accuracy, and Purpose.
What are the four main goals of psychology?
Description, Explanation, Prediction, and Change.
What is Deductive Reasoning?
A type of reasoning in which results are predicted based on a general statement or premise.
What is the definition of a hypothesis?
A tentative and testable statement about the relationship between two or more variables.
What does empirical research involve?
Testing hypotheses through observation and experimentation.
Describe Descriptive Research.
A method of observing and recording behavior in natural conditions, providing insights but lacking control over variables.
What is the difference between correlation and causation?
Correlation indicates a relationship between variables, while causation implies that one variable directly affects another.
Define the term 'illusory correlation'.
The belief that a relationship exists between two variables when in fact there is none.
What is Experimental Research?
A controlled scientific procedure involving the manipulation of variables to determine cause and effect.
What is Random Assignment in research?
A method where all participants have an equal chance of being placed in experimental or control groups to minimize bias.
What is the function of the Central Nervous System (CNS)?
To process and organize information, consisting of the brain and spinal cord.
Differentiate between Afferent and Efferent Nerves.
Afferent (sensory) nerves carry information from the body to the brain, while Efferent nerves carry information from the brain to the body's muscles.
Compare and contrast the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems.
The sympathetic system arouses the body (fight or flight), while the parasympathetic system calms the body (rest and digest).
What is the role of Glial Cells?
To support, nourish, and protect neurons while also aiding in communication between them.
Explain the process of neurotransmission.
Neurotransmitters are released from terminal endings of neurons, facilitating communication between neurons through chemical signals.
What does the all-or-nothing law pertain to in neurons?
It refers to the principle that action potentials occur at full strength or not at all once the threshold is crossed (-55mV), with variations only in frequency.
What is inductive reasoning?
Conclusions are drawn from observations.
What is the C for in the CRAAP test?
Currency, as in when the information was published.
What is the R for in the CRAAP test?
Relevance, as in the importance of the information for your needs (target audience)
What is the A for in the CRAAP test?
Authority, referring to the source's credibility and expertise on the topic.
What is the second A for in the CRAAP test?
Accuracy, which refers to evaluating the credibility and reliability of the source.
What is the P for in the CRAAP test?
Purpose, which refers to the reason the information exists and its intended use.
What are the steps of the scientific method?
The steps of the scientific method include observing a phenomenon, forming a hypothesis, testing with empirical research, drawing conclusions through data analysis, and evaluating the theory (peer-review/publishing).
What are the characteristics of the nervous system?
Complexity, integration, adaptation, and electrochemical communication.
What are the sub-categories of the peripheral nervous system (PNS)?
Somatic and autonomic. Somatic is responsible for voluntary actions while the autonomic is involved in involuntary actions such as breathing.
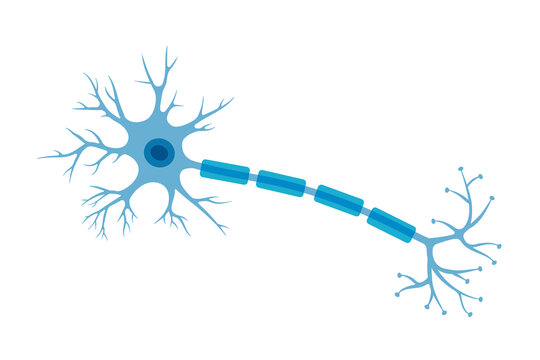
What are the structures of a neuron?
From left to right it’s dendrites, cell body, axon, and terminal buttons.
Lesion Studies
Method to localize brain functions by damaging/removing parts of the brain and observing effects.
Neural Networks
Interconnected pathways of nerve cells that strengthen with use and integrate sensory input and motor output.
Frontal Lobe
Part of the brain involved in intelligence, personality, and voluntary muscles, including decision-making and self-control.
Wernicke’s Area
Region in the left temporal lobe involved in language comprehension.
Corpus Callosum
Axons connecting the two hemispheres of the brain, facilitating communication between them.
Neurogenesis
The process of developing new neurons over time, often used in recovery from brain damage.
Electroencephalogram (EEG)
Electrical recording of brain-activity in different regions using a cap and nodes
CT, PET, MRI, fMRI
Methods of brain imaging that either give structural and/or functional information about the brain
Hindbrain structures & function
Made up of the pons, cerebellum, and medulla. The hindbrain works to control life-sustaining functions such as breathing, heart-rate, balance, reflexes, etc.
Midbrain structures & function
Made up of the reticular formation and the substantia nigra. Together they control stereotyped movement patterns (ie walking), sleep, and level of arousal (alertness/calmness).
Forebrain Structures & Function
Includes the cerebral cortex, thalamus, hypothalamus, and limbic system. Together they control higher-level functioning.
Cerebral Cortex
Is the outermost layer of the brain responsible for complex human behavior.
Parietal Lobe
Function: Spatial location, attention, and motor control.
Temporal Lobe
Processes hearing, language stimuli, verbal communication, and plays a role in memory.
Occipital Lobe
Processes and interprets visual stimuli
Left Hemisphere
Contains Broch’s and Wernicke’s area. Overall is responsible for verbal processing, speech, and grammar.
Right Hemisphere
Responsible for spatial perception, visual recognition, and emotion.
Collateral Sprouting
A method of brain damage repair where nearby neurons take over the function of the damaged ones.
Substitution of Function
A function is taken over by secondary structures that were involved in the function already when the primary structures are damaged.
Brain Tissue Grafts
The implantation of stem cells into the area of brain injury so they specialize/convert into the type of cells that were damaged so they can take over their function.
Association Areas
“Quiet areas” in the cerebral cortex involved in integrating, interpreting, and acting on information from other parts of the brain
Motor Cortex
The edge of the frontal lobe before parietal lobe is the motor cortex. The motor cortex is responsible for helping in fine motor function.
Somatosensory Cortex
It’s in the front of the parietal lobe and is responsible for us receiving and interpreting touch.
Resting Potential
Stable, negative membrane potential (-70mV) with more potassium ions inside the neuron than sodium ions outside.
Depolarization
Occurs when a stimulus reaches the threshold potential (-55mV), causing voltage-gated sodium channels to open and sodium ions to rapidly influx.
Peak of Action Potential
The stage where the membrane potential reaches its most positive value, exceeding the sodium equilibrium potential.
Repolarization
The process where voltage-gated sodium channels close and potassium channels open, allowing potassium ions to exit, bringing the membrane potential back toward resting state.
Hyperpolarization
A brief period after repolarization where membrane potential becomes more negative than resting potential due to continued potassium efflux.