Integumentary High-Yield Clinical Sciences Flashcards
1/115
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Clinical Sciences, Sourced from emma_dip on Quizlet
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
116 Terms
What is albinism? symptoms, diagnosis
-congential recessive
-mutation in any enzyme needed or produce melanin or in proteins responsible for transport (ex. tyrosine or melanosomes)
Symptoms
-little or no colour in hair, eyes and skin
-eyes: light blue or translucent (look light blue or red), causes vision problems (focusing, depth perception, nystagmus, amblyopia - lazy eye)
-skin: can cause freckles, moles, lentigines and an icnreased risk of skin cancer
Diagnosis
-via clinical observations
-skin biopsy or hair bulb extraction showing decreased melanin
-definitive with genetic testing
What condition is albinsim related to?
Chediak higashi
What is pemphigus?
-autoimmune disease
-epidermal cells and mucous membranes attacked
-antibodies against desmogleins (bind skin cells)
-skin becomes fragile and fluid can collect between its layers which forms blisters
2 main types:
Pemphigus vulgaris
-m/c in US
-blisters in mouth, other mucosal surfaces, and skin
-develop within a deep layer of the epidermis
-often painful
*subtype of the disease called pemphigus vegetans = blisters form mainly in the groin and under the arms.
Pemphigus foliaceus
-less common
-only affects the skin
-blisters form in upper layers of the epidermis and may be itchy or painful
What causes ehlers danlos syndrome?
-defective collagen synthesis
-results in stretchy skin, easy bruising and flexible joints
1. Gene mutation
-in any gene that codes for collagen type (type of collagen affected determines type of EDS)
2. Protein mutation
-in TNXB which causes a defect in tenascin x protein which regulates production and assembly of certain collagen types, also controls flexibility
-results in classical like EDS
3. Enzyme mutation
-actaully in gene that codes for enzyme that assists in synthesis of collagen
Describe the 5 types of ehlers danlos
1. Classical (cEDS)
-mutation in COL5A1 and COL5A2 (codes for collagen type 5)
-autosomal dominant
-results in stretchy skin, easy bruising and flexible joints
2. Vascular (vEDS)
-mutation in COL31A (codes for type 3 collagen)
-weakens blood vessels
3. Classical Like (clEDS)
-defect in tenascin x protein
-hyperflexible joints
4. Kyphoscoliotic (ksEDS)
-defect in gene that codes for lysyl hydrolyase that assists in synthesis of collagen
-autosomal recessive
-classic symptoms plus early kyphoscoliosis
5. Musculocontractural (mcEDS)
-mutation that blocks proteolytic processing
-autosomal recessive
-classic symptoms plus scoliosis, slender features
What is epidermolysis bullosa? causes, symptoms
-inhereted
Causes
-decreased or dysfunctional hemidesmosomes (hold epidermis to dermis)
-keratin also lack mechanical stiffness (causing proteolysis, cellular stress, and cytolysis)
Symptoms
-fragile (thin and painful) skin and mucous membranes that blister easily
-minor mechanical friction results in blisters and wounds
-sx usually start in childhood (sometimes in adults)
-lesions often in high friction areas
-lesions can occur on internal tissues like GI
-lesions start as blisters -> erosions -> ulcers -> crusts -> scar
-damage can cause muscles and tendons to harden and shorten
-can also cause joint contractures and deformities
-can also have nail defects or no nails
-tooth decay and alopecia common
*increased risk of skin cancer
How is epidermolysis bullosa diagnosed? treated?
Diagnosis
-history, PE
-skin biopsy = immunofluorescense to see if decrease or missing hemidesmosomes // electron microscopy to identify structural defects
-genetic testing
Treatment
-no cure
-prevention by keeping skin cool and moist
-treat complications = wound care to prevent infections
-surgery to correct deformities if needed
What is alopecia areata?
-autoimmune -> attacks hair follicle
Risk factors
-AI = celiac, T1DM, RA
-family history
Symptoms
-patchy hair loss (usually circular or oval) on scalp
-rarely can affect hair on whole body
-amount of hair loss varies person to person
-thinning hair + hair loss
-may itch or burn
-white spots, thin, splitting and/or rough nails
Diagnosis
-scalp biopsy
-presentation
-bloodwork
What is bullous pemphigoid? causes, symptoms, testing, treatment
-m/c 60-80yo
-autoimmune
-likely result of genetics + meds - furosamide, captopril, penicillamine, NSAIDs, abx)
Causes
-IgG abs against dermal-epidermal basement membrane proteins (hemidesmosomes)
-Fab region on ab binds to dystonin (BPAG1) and type 17 collagen (BPAG2) on hemidesmosome and activates complement
-type 2 hypersensitivity
Symptoms
-pruritis, tense, subepidermal bullae formed when basement membrane splits from hemidesmosome (dermis and epidermis separate)
-Bullous pemphigoiD = Deep
-negative nikolskys sign = no bullae form when lateral pressure applied (dif than p. vulgaris which ruptures easy)
-often in flexors of forearms, axillar, med thighs, groin, abdo (often spares oral mucosa)
Testing
-immunofluorescense = linear deposition of IgG and C3 along basement membrane
-IgG anti basement membrane detectable in serum
-biopsy shows ab and complement
Treatment
-systemic corticosteriods
-topical steroids
-stop offending meds
What is psoriasis? causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment
-strong HLA association
-1-3% of world pop
-onset during adolescence or >60yrs
Causes
-excessive inflammation after immune response (following strep pharyngitis, HIV) causes chronic skin damage
-blood vessels dilate in dermis bringing more immune cells in
-neutrophils collect in stratum corneum
-keratinocyte production increases -> dont stick together properly and easily break
-results in thin basal layer and thicker rest of epiderm
-cell growth > sloughing off
-can also be caused by scratching the skin (keobners) or drugs like lithium, NSAIDs, alc or beta blockers
Symptoms
-well demarcated, flat, elevated erythematous papules that are salmon coloured
-plaques with silvery white scales (acanthosis)
-rash common in areas of trauma (elbows, knees, lower back)
-positive auspitz sign (pin point bleeding under scales)
-nail pitting
-may itch
* symptoms vary depending on type of psoriasis (plaque, gluttate, inverse, pustular, erythrodermic)*
Diagnosis
-biopsy
Treatment
-natural sunlight, UVB
-avoid offending drugs
-potent corticosteriods
-retinoids
-systemic treatment -> methotrexate, cyclosporine
-moisurizers and emollients
What is pemphigus vulgaris? causes, symptoms, testing, treatment
-40-60yo; m/c in jewish, med, asian
-likely result of genetics + herpes or captopril or certain abx
Causes
-IgG against epidermal desmoglein-1 (epithelial) AND/OR -3 (epithelial and mucosal)
-IgG binding causes protease release = desmosome breakdown
-breakdown results in acantholysis = cells let go of each other and form INTRAEPIDERMAL bullae
-basal cells adhered to membrane but rest of epidermis separates -> TOMBSTONING
-type 2 hypersensitivity
Symptoms
-vesicles and bullae develop on oral mucosa (90%), scalp, face, chest, axillae, groin, umbillicus
-positive nikolskys sign = bulla formation with rubbing over skin
-pemphigus vulgariS = Superficial
-asboe-hansen sign = pressure applied to bulla causes lateral extension
Testing
-immunofluorescebce shows IgG and C3 deposition intraepidermally = fish net appearance
-serum anti-desmoglein IgG antibodies
-skin biopsy = tombstone appearance
Treatment
-corticosteriods
-may be fatal unless treated with immunosuppress (methotrexate, cyclosporine)
-rituximab (prevents ab production)
What is vitiligo? causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment
-pigmentation disorder causing hypo or depigmentation
Causes
-autoimmune destruction or loss of function of melanocytes (ranges from local to extensive)
-associated with other AI disorders
-likely result of genetics and enviro triggers
-can also develop after skin trauma (keobner)
Symptoms
-streaks of depigmented hair, possibly eyes
-sections of hypopigmentation over extensor surfaces and periorificial areas (mouth, eyes, genitalia)
-2 types:
1. non-segmental
-often on hands, forearms, feet, neck, scalp, face
-m/c; any age
-symmetrical (both sides of body) distribution over multiple body sites
3. segmental
-often on skin near dorsal spinal cord roots and face (esp near trigeminal)
-m/c in kids
-along single spinal nerve
Diagnosis
-r/o other AI conditions (thyroid, addisons, T1DM)
-woods lamp to detect lesions
Treatment
-sun avoidance and protection
-topical steriods
-narrow band UVB phototherapy
What is lichen planus? causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment
-AI, antigen unknown
-30-60yo; m/c women
-acute or chronic inflammation in mucous membranes (oral LP if only here) AND/OR skin (cutaneous LP) (usually both)
Causes
-healthy keratinocytes present ag's on MHC1 = killed by CD8 T cells
-release cytokines which attract more CD8 to the area
-causes damage to surrounding cells (stratum basale and dermis)
-causes melanocytes to release melanin = hyperpigmentation
-damage eventually reaches stratum granulosum keratinocytes and causes them to increase in numbers and size = hypergranulosis
-can also be triggered by medication (lichenoid reaction)
Symptoms
-commonly affects wrists, ankles, nails scalp, mouth, vulva, glans)
-lesions develop in areas of scratching (koebners phenomenon)
-fine whitish reticular network visible in oral musoca 50% of time
-increased risk of developing squamous cell carcinoma
-6 P's: Pruritic, Polygonal, Planar (flat topped), Purple, Papules, Plaques
Diagnosis
-skin scrape or biopsy showing sawtooth dermal-epidermal junction
Treatment
-topical corticosteriods
-immunosuppressants (cyclosporin, methotrexate)
-retinoids for lichen planus in mouth
-phytotherapy for resistant cases
What is lichen sclerosis? symptoms, diagnosis, treatment
-likely AI bc associated with thyroid issues, pernicious anemia, diabetes; actual cause unknown
-m/c postmenopausal ,women 40-60yo, prepubescent girls
Symptoms
-discoloured, thin, itchy skin with scaly patch
-scratching can form blisters and sores
-small, white, shiny, slightly raised spots
-often affects neck, chest, upper back, torso, wrists, mouth
-ulcers, sores, inflammation, scarring, cracking
-dysuria, dyspareunia, tight foreskin, phimosis, penile discharge
Diagnosis
-symptoms
-biopsy
Treatment
-topical corticosteriods
-phytotherapy
-immunosuppressants
-surgery if needed
What is a pressure ulcer? risks, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment
-blood flow diminishes to an area = pressure -> ischemia -> necrosis
-localized skin, underlying tissue injury caused by unrelieved pressure +/- friction, shearing forces
-m/c affects bony prominences like sacrum, hips, heels, ankles
Risks
-reduced mobility (d/t disease, nerve damage, altered consciousness, old age)
-reduced perfusion (atherosclerosis, periph vasc dx, hypotens, smoking)
-factors affecting skin structure (malnutrition, protein def, skin moisture)
-diabetes
Symptoms
-ulceration
-fever, foul odor
-may be painful
-complications if biofilm formation on wound, infection, sepsis, fistulas, gangrene, malignant transformation (rare)
Diagnosis
-swab culture to determine tx in healing resistant ulcers
Treatment
-topical sulfadiazine creame
-debridement of biofilm
-dressing replacement
-negative pressure therapy
Differentiate scorpion, bedbug, snake and spider bites
Scorpion
-usually not life threatening
-may tingle/burn in area
-can cause serious sx like impaired swallowing, breathing, seizures, hypertension, drooling, etc -> hospital
-non urgent = clean site, apply ice or cold, elevate area, use antihistamines or steriods
Bedbug
-small, itchy, inflamed spots with dark middle in a line or cluster
-m/c on face, neck, arms, hands
-prevent and eliminate
-hosp if severe rxn
Snake
-puncture marks, red, swelling, bruising, bleeding, N/V/D, severe pain, decreased vision, low bp, inc hr, dec breathing, numbness and tingling
-hospital asap incase poisonous
-remove rings, watches, etc before swelling starts
-mark areas of injury
-NO ice or pain killers
-cover with clean, dry dressing
Spider
-usually harmless except for few species
-if poisonous like black widow = dec breathing, itching skin rash, sweating, muscle cramps, N/V, inc saliva, headache, droopy/swollen eyes
-blister or bulls eye wound, swelling, ulcer over site
-hospital if severe
-diagnose based on skin sx unless know the spider (no test)
-antivenom, sedatives, muscle relaxants
what should be done in the case of skin trauma?
Refer to ER
-open = bone, muscle or subcutaneous fat exposed
-labs done to determine severity of injury (CBC, CMP, ABG, UA)
How are pressure ulcers staged?
1. Stage 1
-nonblanchable erythema
-skin intact, localized
2. Stage 2
-partial thickness dermis loss
-red wound, serum filled blister, no skin sloughing
3. Stage 3
-full thickness tissue loss
-visible subcutaneous fat
-raised wound edges
-skin sloughs
4. Stage 4
-full thickness tissue loss
-bone, muscle, tendon esposed
-raised wound edges
-skin sloughs/eschar formation (dead tissue that forms over healthy skin before falling off)
Unstageable: filled with sloughed skin, scabs, diagnosis difficult
Deep tissue injury: nonblanchable erythema, skin separation, no skin disruption
How are burn injuries graded?
1. Stage 1
-limited to epidermis
-mild erythema
2. Stage 2
-partial thickness with dermal involvement
-red, moist injuries with blisters
3. Stage 3
-full thickness, extends to subdermal soft tissues
-white/brown-black, dry, leathery apperance
4. Stage 4
-extends to bone
-dark like charred tissue
What needs to be looked out for in skin trauma?
-if injury circumferential around limb = limb at risk
-infection = fever, localized pain, edema, erythema, crepitus, warmth, fluid collection
-fournier gangrene = perianal, retroperitoneal lesion or UTIs can cause -> spreads to skin, soft tissue of external genitalia and perineum = massive ulcer and tissue death/necrosis
refer to hosp
What is stasis dermatitis/varicose eczema? How is it managed?
-decreased bloodflow to an area (unhealthy valves, venous reflux, DVT) resulting in skin inflammation
-lighter skin appears itchy, dry, flaky, scaly
-darker skin appears dark brown/grey
-m/c in legs but can spread
**can progress to ulcer
-if weepy or discharges = emergency
Management
-stay active, elevate leg
-compression socks
-keep skin moisturized
-steriod creams if bad itch
-refer to MD if needed
What is seborrheic dermatitis? symptoms, treatment
dandruff
-possibly associated with Malassezia spp. (yeast)
-common in infants and puberty
-inc incidence and severity in immunocomp
Symptoms
-adults = yellow-white flakes, pruritis on scalp and underlying erythema
-children = generalized with flexural and scalp involvement
-newborn = cradle cap
-m/c on scalp, eyebrown, eyelashes, beard, body folds, trunk, genitalia
Treatment
-selenium sulfide or zinc pyrithione shampoo (head and shoulders)
What is actinic keratosis? causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment
-m/c in fair skinned in areas with long term sun exposure
-40-60% in adults >40
-HPV, immunocomp and/or disorders that decreased DNA repair increase risk
Causes
-prolonged UV radiation exposure damages the keratinocytes
-characteristic UV induced mutations in TP53 gene and deletion of gene coding for p16 tumor suppressor protein
-precursor to squamous cell carcinoma (2-5% of cases)
Symptoms
-begin as small, rough spots of various colours (pearly, grey-white, pink, flesh toned, dark tan or some combo)
-hyperkeratotic, easier felt than seen
-feels like sandpaper
-3-20mm in size but can enlarge to several centimeters
-m/con face, back of neck, scalp if bald, lips, sun exposed limbs
-recurs if scraped off
Diagnosis
-biopsy if resistant to treatment
Treatment
-excision always recommended
-liquid nitrogen, electrodessication and curettage
-topical therapy with 5-fluorouracil cream for 2-3 weeks
-phytodynamic therapy
What is basal cell carcinoma? causes, symptoms, testing, treatment
-m/c malignancy in humans
-M>F; m/c in elderly
Causes
-chronic exposure to UVB light (so >80% on face)
-occurs in sun exposed areas like face, upper lip
-locally aggressive (tangential growth), rarely metastasizes
-arises from basal cell layer of epidermis and infiltrates the underlying dermis
-increased risk of reoccurance if >20mm or any size on head, neck, hands, feet, genitals; poorly defined; recurrent; micronodular, morpheaform, sclerosing, mixed infiltrative, etc
Symptoms
-usually presents with lesion that chanegs in size and colour or wont heal
-skin coloured papule or nodule with rolled, pearly, telangiectatic boarder and depressed/eroded/ulcerated centre
-sides of the crater have telangiectatic vessels
-late stages = large, fungating -> local invasion
Testing
-biopsy (shave if shallow, punch or excisional if deep) showing fibrosis, clefting, inc mitotic activity, peripheral palisading, ulceration or deep invasion
Treatment
-shave excision with curettage and electrodessication
-cryotherapy
-topical therapy with 5-fluorouracil cream to inc immune response
-radiation (esp w elderly)
**most are slow growing and dont metastasize
Describe the 3 main types of basal cell carcinoma
1. Nodular
-m/c subtype (60%)
-classic, raised, pearly or waxy with rolled edges
-may have central ulceration
2. Superficial
-2nd m/c
-red and scaly
-looks like squamous cell, eczema, psoriasis
3. Infiltrative
-flat, white, scar like
-most aggressive subtype
*many other rare forms
What condition can increase the risk of developing basal cell carcinoma?
Xeroderma pigmentosum
-rare, autosomal recessive
-decreases the ability of body to repair DNA damage
-increases risk for many cancers
Albinism can also inc risk for skin cancer
What is a dysplastic nevi?
atypical mole
-acquired proliferation of atypical melanocytes
-may be hereditary
-can turn into melanoma, but melanoma can arise denovo
-having lots increases risk of melanoma
-result of combo genetics + family history + environmental factors like UV light
-ABCDE exam and monitoring
What is the ABCDE exam for moles?
1. A = Asymmetry
-melanoma often asymmetrical
-non-cancerous typically uniform and symmetrical in shape
2. B = Border
-melanoma often has undefined or irregular boarders
-non-cancerous moles usually have smooth, well-defined borders
3. C = Color
-melanoma often more than one color or shade
-benign are typically one color
4. D = Diameter
-melanoma growths normally larger than 6mm in diameter
5. E = Evolution
-melanoma often changes over time (in size, shape, colour)
Sens = 92%, spec = 100%
What skin cancer type favours the upper lip?
Basal cell carcinoma
B higher in alphabet than S
What is formed via UV radiation and damages keratinocytes?
Pyrimidine dimers
-DNA usually repaired but can leave transcriptional errors and mutations
-if errors/mutations in proto-onco or tumor suppressor genes = risk of skin cancer
What is the #1 risk factor for skin cancer?
UV radiation exposure
What skin cancer type favours the lower lip?
Squamous cell carcinoma
S lower in alphabet than B
What is a keratoacanthoma?
an umbilicated skin nodule that mimics basal cell carcinoma but appears over a short period of weeks
-regresses spontaneously
What are the 4 major subtypes of melanoma?
1. Superficial spreading
-prolonged horizontal growth phase
-good prognosis
2. Nodular
-nodule or lump
-early vertical growth phase
-worst prognosis
3. Lentigo maligna
-slow and lentiginous horizontal growth
-good prognosis
4. Acral lentiginous
-palms, soles, nailbeds
-darker skinned individuals
What is melanoma? causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment
-malignant tumor of melanocytes with an increased risk of metastasis
-leading cause of death d/t skin cancer
-median age diagnosis = 53
-m/c site = back in males, calves in females
Causes
-malignant neoplasm of melanocytes and nevus cells (pigment forming)
-mutation in BRAF V600E gene (codes for BRAF kinase) = proto-onco gene = uncontrolled growth signals
-mutation in CDKN2A tumor suppressor gene
Symptoms
-often asymmetrical with undefined or irregular boarders
-often more than one color or shade
-normally larger than 6mm in diameter
-often changes over time (in size, shape, colour)
-ABCDE mnemonic
-4 subtypes
Diagnosis
-excision biposy (including surrounding normal tissue, full depth of dermis) stains positive for S100
-tumor usually deeper than anticipated
Treatment
-excisional biopsy to remove (include surrounding normal tissue and full depth of dermis to prevent regression)
-chemotherapeutic, gene therapies, vaccines in metastatic
-radiotherapy as adjunct
-vemurafenib if BRAF mutation
Describe the risk factors and growth of melanoma
Risk factors
-numerous moles, family history, use of tanning booths
-blue eyes, fair/red hair, pale complexion, freckles, inc incidence of sunburn
Growth
-initial = radial, melanocytes proliferate within epidermis (low risk metastasis)
-secondary = vertical growth phase, malignant cells penetrate underlying reticular dermis (inc risk of metastasis)
*Breslows thickness (thickness of lesion) = most important prognostic factor for predicting metastasis*
What is squamous cell carcinoma? risks, symptoms, treatment
-primarily in elderly on sun exposed skin
Risks
-chronic sun exposure
-actinic keratosis
-arsenic exposure
-m/c complication during immunosuppressive therapy
-M>F
Symptoms
-usually present with chronic, non healing wound or abnormal growth
-indurated erythematous nodule/plaque with surface scale/crust +/- ulceration
-70% on head (forehead, scalp) and neck
-favours lower lip
-also often on external ear, periauricular region
*more rapid enlargement than BCC*
Treatment
-surgical excision (+ biopsy to diagnose)
-Mohs surgery (thin layers of cancer containing skin progressively removed and examined until only cancer free tissue remains)
-lifelong follow up bc more aggressive than BCC
*Bowen disease - SCC in situ*
What is merkel cell carcinoma? causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment
-rare and aggressive type of skin cancer
-merkel cells are neuroendocrine cells with nervous and endocrine system function (sit near nerve endings)
Causes
-develops in merkel cells in epidermis
-spreads quickly and commonly reoccurs
-inc risk with UV radiation exposure
-8/10 people have merkel cell polyomavirus (but most people with mcp dont develop merkel cell carcinoma)
Symptoms
-shiny or pearly lump on area of skin that commonly gets sun exposure (face, neck, arms, eyelids; can occur on legs or torso too)
-lump commonly size of dime
-dome shaped, raised
-firm, itchy, skin coloured or red, pruple, bluish-red
-tender or sore
-similar to pimple or insect bite
-commonly spreads to lymph nodes first
Diagnosis
-biopsy
Treatment
-Mohs surgery (thin layers of cancer containing skin progressively removed and examined until only cancer free tissue remains)
-wide local excision
-lymph node dissection
-chemo, radiation, immunotherapy if needed
What is an acrochordon? symptoms, treatment
-skin tag
-often in middle age or elderly
-typically in obese; F > M
Symptoms
-benign outgrowth of skin
-forms in areas where skin forms crease (eyelids, neck, axillae, groin)
-fibroepithelial polyp
-ranges from 1-10mm in size
-generally harmless and painless
-dont grow or change over time
Treatment
-removal by excision, electodessication or cryosurgery
What is a benign melanocytic nevus (nevocellular nevus)?
-benign neoplasms of melanocytes in contact with each other
-form small collections of cells known as nests
-commonly form during early childhood
-formation may be result of UV exposure
-very small percentage develop into melanoma
What is lichenification?
-thick, leathery skin with a bark like appearance
-usually result of constant scratching and rubbing
-with prolonged rubbing, epidermis hypertrophies resulting in thickening of skin and exaggeration of normal skin markings
-common consequence of atopic dermatitis and other pruritic disorders
What are sebaceous cysts? symptoms, treatment
-derived from epidermis of hair follicle that becomes filled with keratin and lipid debris
Symptoms
-round, yellow coloured
-mobile, slow growing
-firm and fluctuant nodule
-may rupture and produce a foul cheesy odor with creamy colour consistency
Treatment
-none
-surgical excision if infected
What is a lipoma? symptoms, diagnosis, treatment
-benign, fatty, soft tissue tumors that are slow growing
-lobulated masses enclosed by thin, fibrous capsule
-occur in 1% in population
-m/c in females than males
-being overweight does not increase risk
Symptoms
-rarely symptomatic
-no overall health impact
-small (1-3cm)
-felt just under skin
-moveable, painless
-soft, rubbery consistency
-remain same size or grow very slowly
-m/c on trunk and extremities but can be anywhere
Diagnosis
-clinical
-biopsy if atypical (painful, rapid growth, firm)
Treatment
-surgical removal if problematic
What is a xanthalasma? risk factors, symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment
-harmless, yellow growth that appears on or by the corners of your eyelids next to your nose
-formed by cholesterol deposits under skin
-can be sign of another condition (diabetes, hyperlipidemia, thyroid issues)
Risk factors
-overweight, smokers
-high cholesterol, diabetes
-high bp
-family history
**increases risk for heart disease, heart attack, atherosclerosis, high cholesterol
Symptoms
-yellow skin around eyes
-appearance varies, can be flat, bumpy, soft, firm
-may be uncomfortable
Causes
-high cholesterol (can be familial)
-diabetes
-weight gain
-thyroid issues (hypo)
-inflammation
-drinking too much alcohol
Diagnosis
-clinical
-bloodwork showing high cholesterol
Treatment
-doesnt go away on its own
-liquid nitrogen
-reduce cholesterol levels
What is seborrheic keratosis?
-m/c benign tumor in older individuals
Symptoms
-has 'stuck on' appearance
-initially = sharply defined, light brown flat macules
-evolves into uneven warty surface with waxy papule appearance
-colour can vary fom bown to dark brown or black
-slow enlargement with increasing thickness and pigmentation
-m/c on face, trunk, upper extremities (can occur anywhere except for palms or soles)
Diagnosis
-biopsy needed if diagnosis uncertain
Treatment
-none
-curettage or liquid nitrogen if needed
What is acanthosis nigricans? What should patients who present with this be screened for?
A brown to black, poorly defined, velvety hyperpigmentation of the skin
-m/c in fexural skin (neck, armpits, skin folds)
-associated with DM, obesity and other endocrine disorders and malignancy
-cutaneous marker of tissue insulin resistance
-must screen pt for diabetes
What is allergic contact dermatitis? symptoms, treatment
-type 4 hypersensitivity (cell mediated, delayed)
-ex. poison ivy, other allergens
Symptoms
-erythema with papulovesicular eruption
-swelling and pruritus
Treatment
-avoid allergen
-topical or oral steriods
What is irritant contact dermatitis? symptoms, treatment
-skin reaction to irritant
-non immune mediated
-ex. laundrydetergent, soap, acid/alkaline solvents, alcohols, oils
Symptoms
-erythema, dryness, burning, oozing
-acute: quick reaction with sharp margins (ex. acid/alkaline burns)
-chronic: slow to appear, poorly defined margins
Treatment
-avoid allergen
-topical or oral steriods
What is acne vulgaris? symptoms, treatment
-chronic inflammation of pilosebaceous glands
-usually around puberty, severity increases in teenage years and decreases in adulthood
-family history of severe, cystic acne inc risk
Symptoms
-inflammatory papules, pustules, nodules, cysts (pimples)
Noninflamed comedones:
-plugging of hair follicle by keratin debris
-open comedone = blackhead
-closed comedone = whitehead
Inflammatory type:
-d/t bacterial infection by P. acnes
-increased sebum production
-bacterial lipase produces irritating fatty acids causing inflammatory reaction
Treatment
Systemic antibiotics:
-mild = clindamycin (inhibits protein synth)
-moderate = doxycycline (inhibits protein synth)
-severe = isotretinoin (inhibits sebaceous gland function and regulates keratinization)
Hormonal therapy:
-oral contraceptives (reduce free testosterone levels in women)
What is urticaria? causes, symptoms, treatment
-hives
-pruritic elevations of the skin
Causes
-mast cell release of histamine
-type 1 hypersensitivity (IgE mediated)
-reaction to exposures to food/additives, insectstings, drugs, aeroallergens, physical contact
Symptoms
-transient, red, pruritic, edema, well demarcated wheals
-involving the dermis and epidermis
-last >24 hours
Treatment
-discontinue offending drugs, food, etc
-avoid asprin and other NSAIDs
-ER if signs of angioedema or anaphylaxis
-0.3-.05ml IM epinepherine if needed
-25ml IV or 50ml IM diphenhydramine
-oxygen
What is atopic dermatitis?
-eczema
-inflammation of skin, characterized by pruritis
-often affects kids, young adults
-1/3 have symptoms into adulthood
-family or personal history
Causes
-type 1 IgE mediated hypersensitivity
-epidermal barrier dysfunction
-triggers include irritants, sweating, stress, microbes (s. aureus)
Symptoms
-acute: erythematous rash w vesicles
-chronic: dry, thickened skin (hyperkeratosis), d/t chronic itching
-dry skin, prolonged severe pruritis
-inflammation, excoriations, lichenification secondary to continued scratching
-infants: face, scalp, extensor surfaces forearms
-children (>18months): flexural surfaces (back of knees, elbows, neck)
-adults: hands, feet, flexures, wrists, face, eyelids, neck
Diagnosis
-clinical
-can do skin biopsy or check serum IgE levels
Treatment
-avoid triggers
-enhance barrier function of skin with moisturizers to hydrate and decrease itching
-topical corticosteriods to decrease inflammation
What is a chalazion?
-retined sebaceous secretions leak into tissue causing chronic granulomatous inflammation of meibomian gland eventually leading to stye
-forms d/t blocked oil gland
-m/c on underside of upper eyelid but can occur on lower
Risk factors
-previous chalazion
-chronic blepharitis (eyelid inflammation)
-certain skin conditions, like dandruff (seborrheic dermatitis) or rosacea
-dry skin
-hormonal changes.
Causes
-gland obstruction = impissination (dec flow of secretions) = granulomatous inflammatory response = lipogranuloma inflammation = lesion forms on eyelid
Symptoms
-bump on eyelid (m/c upper)
-single, non tender firm nodule deep within lid
-mild irritation causing eye to water
-blurred vision
-swollen eyelid, erythema
-slow growing, may persist for months
Diagnosis
-clinical
Treatment
-warm compress
-good hygiene
-draining and steriods if needed
What is the difference between a chalazion and a stye?
chalazion = blocked oil gland, deeper than stye
stye = bacterial infection of oil gland
What is dyshidrotic eczema (dyshidrosis)? symptoms, diagnosis, treatment
-recurrent dermatitis
-m/c 20-40yo; F > M
-personal and/or family history of eczema or contact dermatitis
-people who recieve immunoglobulin infusions
-cause unknown but likely result of immune system, allergies and/or excessive moisture (ex. excessive hand sweating)
-not contagious
*cant find source confirming if IgE related but assume so?
Symptoms
-intensely pruritic
-small, firm, painful blisters
-typically involves palms and soles
-itchy, scaly skin on or around blisters
-increased sweat around blisters
-dry, cracked skin
Diagnosis
-allergy test
-biopsy
-blood test
Treatment similar to atopic dermatitis
-treat and prevent flares
-steriods
What is nummular eczema? causes, symptoms, diagnosis
-discoid eczema
-chronic, can last for weeks-months
-m/c in young females and older men
*cant find source confirming if IgE related but assume so?
Causes
-allergies
-bacterial infection
-exposure to rough fabrics
-dry skin or dry environments
-frequent bathing or showering with hot water
-skin trauma or injury (burn, scrape, bug bite)
-irritating and drying soaps
Symptoms
-circular, raised spots (coined shaped)
-itchy, ooze clear fluid
-crusty on top
-very itchy
-may burn or sting
Diagnosis
-clinical
-skin scrape
Treatment similar to atopic dermatitis
-treat and prevent flares
-steriods
What is pterygium? causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment
-surfer's eye
-rapidly growing fibrovascular lesion that can distort the cornea
Causes
-long-term exposure to UV light (m/c cause)
-eye irritation from hot and dry weather, wind and dust
Symptoms
-raised, fleshy growth
-can be unilateral or bilateral
-typically grows on the medial -> lateral side of the sclerae
-redness, swelling, itching of eye
-blurry vision or double vision (if grows onto cornea)
Early:
-slightly raised pink growth on eye
-red, irritated, swollen, dry, itchy or burning eyes
-feels like sand or grit in eye
-teary eyes
Late:
-increase in size and spread of lesion
-unpleasant appearance of eye (d/t size of the lesion)
Diagnosis
-slit lamp eye exam, visual acuity test, corneal topography
Treatment
-lubricating eye drops
-steroid eye drops
-surgery if vision is blocked, symptoms are not being relieved or cosmetic issues
What is dacryocystitis? causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment
-inflammation or infection of the lacrimal sac (tear sack)
-pathogens may differ between acute and chronic
-often in >40yo
Causes
-trauma (fractures or surgery on nose)
-medical conditions involving immune system/inflammation/infection
-unusual nasal structure
-tumors
-certain drugs (timolol, dorzolamide, pilocarpine, trifluridine, fluorouracil, docetaxel or radioactive iodine)
-retained punctal plugs (devices to help drain tear ducts)
Symptoms
-acute: starts and reolves quickly (<3 months)
-chronic: lasts >3months; linked to systemic and autoimmune conditions (granulomatosis with polyangiitis, sarcoidosis and SLE); often cormorbid with chronic conjunctivitis
-eye pain
-swelling around eye
-redness or skin darkening
-abscess or sore that may have pus in the inner corner of eyelids
-fever
Diagnosis
-eye exam
-testing discharge
-yellow dye in eye (see how long it takes to dissapate)
-imaging
-bloodwork
Treatment
-warm compress
-abx if bacterial
What is acne rosacea? causes, symptoms, treatment
-chronic, inflammatory reaction of pilosebaceous units of skin on the face
-hyperplasia of sebaceous gland
-m/c in fair skinned, 30-5yo, sources vary on which gender more commonly affected
-genetic predisposition
-triggered by warm weather, alcohol, spicy foods, stress, heat, cold, wind, sun
Causes
-unknown
-may be innate immune system dysfunction in response to bacteria or UV light = chronic inflammation
Symptoms
-pustules and flushing with burning sensation
-flushing, non-transient erythema and telangiectasia (can sometimes see vessels)
-m/c on cheeks, forehead, nose and chin
-causes ruddy complexion (persistant central facial erythema)
-intensity intermittent (remits and exacerbates)
-phymatous changes (irregular, nodular skin)
-hyperactive vascular response (may extend to eyes)
Treatment
-trigger avoidance
-avoid topical corticosteriods and makeup
-1st line = oral tetracycline and topical metronidazole, topical azelic acid
-oral retinoids, topical sulfur
What are the complications of acne rosacea?
-skin thickening
-scarring
-rhinophyma (enlarged, red, bumpy, bulbus nose)
-ocular rosacea (blepharitis)
What are the 6 types of acne rosacea?
1. Papulopustular
-similar to acne
-no comedones
2. Phymatous
-thick, oily skin
-mostly on nose
-m/c in males
3. Ocular
-common
-conjunctivitis, keratitis
-tearing, burning
-telangiactasias
4. Granulomatous
-papules around eyes, cheeks
5. Pediatric
-rare
-never phymatous
6. Neurogenic
-pain
-neurologic symptoms
What is erythema multiforme? causes, symptoms, dignosis, treatment
-immunologic reaction of skin
-type 4 hypersensitivity -> body attacks basale cells
Causes
-infection by mycoplasma pneumonia, HSV
-rarely triggered by drugs (sulfonamides, penicillin, phenytoin)
Symptoms
-vesicles, bullae (sometimes macules and papules) that have classic bulls eye pattern of concentric light and dark rings (typical target)
-bullseye: erythema surrounding central necrosis
-targeted lesions 2mm-2cm big
-located on palms, soles, extensor membranes of hands and forearms, mucosa
-bilateral and symmetric
-lesions last 2 weeks and heal w/o complications
-mild or major type
Diagnosis
-clinical
Treatment
-systemic with oral anti-histamines, antacids
-treat triggering infection
-eliminate offending meds
-oral acyclovir for 6-12 months if recurring HSV infection
-maintain hydration
What is iritis/keratitis? causes, risk factors, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment
-corneal inflammation causing corneal tissue destruction
-inflammatory response causing stromal damage from infection resulting in edema, infiltrates, necrotic ulceration, focal thinning, perforation
Causes
-infectious: bacteria, virus, fungus, parasites
-non infectious: inflammation
Risk factors
-contact lenses, recent keratoplasty
-immunocop
-occular steroid use
-often comorbid with sicca (dye eye), neurotrophic keratitis (lesion on CN V), certain AI conditions
Symptoms
-erythema
-periauricular lymphadenopathy
-discharge = watery (viral), mucopurulent (bacterial)
-corneal opacity, stromal infiltrate (yellow = bacterial; white = fungal)
-feels like something in your eye
Diagnosis
-fundoscopy
-corneal scrapings
-penlight
-physical exam (snellen)
-fluorescein dye (in cornea)
Treatment
-topical antimicrobials for offending agent
-control comorbidities
What is the most common cause of infectious blindness in western countries?
-herpes simplex keratitis
-usually HSV type 1
-triggered by stress, immunosuppression, fever
Symptoms
-pain, photophobia, blurred vision
-tearing, redness, eyelid edema
Diagnosis
-via observation of corneal lesion
Complications
-corneal scarring
Treatment
-refer
What is conjunctivitis? causes, symptoms, treatment
-inflammation of conjunctiva
-infection, inflamatoin = dilation of conjunctival tissue = conjunctival hyperemia = edema = inflammatory discharge
Causes
-infectious: bacterial, viral, chlamydial
-non-infectious: allergic, toxic (irritants, dust, smoke, etc)
Symptoms
-red eye
-itching, tearing, discharge
-crusting of lashes in the morning
-lid edema
-palpable preauricular, submandubular nodes
Treatment
-cool compress
-antibiotics if bacterial
Distinguish the types of conjunctivitis (4) and treatment for each
1. Allergic
-airbourne allergens (seasonal,etc)
-IgE mediated, local mast cell degranulation
-associated with asthma, hay fever, rhinitis, seasonal
-treatment = avoiding allergens, cool compress, antihistamine, mast cell stabilizers (cromolyn)
2. Viral
-very contagious (via direct contact)
-occular manifestationof systemic infection
-serious discharge, lid swelling, enlarged lymph nodes
-usually caused by adenovirus, HSV, VZV
-treatment = cool compress, self limiting (7-10 days)
3. Bacterial
-very contagious (via direct contact)
-purulent discharge, lid swelling, moderate tearing
-usually caused by s. aureus, s. pneumonia, h. influenze
-if sexually active, consider n. gonorrhea
-**c. trichomatis is m/c cause in neonates (can cause blindness in child)
-threatens vision
-treatment = broad spectrum abx (doxy)
4. Non-infectious
-mechanical, chemical insult
-treatment = remove/avoid agent
What is dermatitis herpetiformis? risks, symptoms, testing, treatment
-chronic condition
-manifested by pruritic papules, vesicles over the elbows, knees, buttocks, posterior neck, scalp and hairline
-result of celiac disease or gluten sensitivity
-m/c in 30-40yo w celiac disease
-M > F
Risks
-celiac disease/gluten sensitivity
-relative with dermatitis herpetiformis or celiac disease
-fam history of autoimmune like anemia, thyroid, vitiligo, Type 1 DM, alopecia areata, Addison’s
Symptoms
-skin rash: pruritic papules, vesicles over the elbows, knees, buttocks, posterior neck, scalp and hairline
-oral: pitting, discoloration or horizontal grooves on teeth; canker sores
-GI: gluten sensitivity or celiac disease and associated GI symptoms
Testing
-skin biopsy, blood test
-Immunofluorescence: granular IgA deposits along dermal papillae
-circulating anti-endomysial antibodies can be detected in all pts (gluten-sensitive enteropathy)
Treatment
-gluten free diet
-antibiotic (dapsone)
What is Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (TEN)? causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment
-rare, immune mediated
-type 4 hypersensitivity
-epidermal detachment
Causes
1. medications
-anticonvulsants (phenytoin, carbamazapine)
-antibiotics (sulfanamides)
-anti-inflammatories (sulfasalazine)
-certain NSAIDs
2. infections
-mycoplasma pneumonia
-HIV
-CMV
-herpes
Symptoms
-rapid onset pain and rashes
-flu like symptoms (cough, sore throat, fever)
-usually starts as atypical flat, dusky target lesions on palms and soles
-later will progress to erythema, ulcers and blisters over skin and mucosa
- >30% epidermal detachment (vs. steven johnson syndrome <10%; 10-30% detachment = overlap)
-extensive skin damage resulting in severe dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, and inc risk of infection
Diagnosis
-positive nikolsky sign
-CBC may show signs of infections
-blood culture
-CXR
-lung crackles if lung involvement
-definitive with biopsy
Treatment
-refer
-dicontinue offending meds
-wound care
-hydration
-pain management
-steroids, IV IG, abx if needed
Distinguish minor and major erythema multiforme
Minor
-mild
-triggered by infection
-targeted lesions on palms and soles
-symmetric spread to trunk
-NO or mild mucosal involvement
Major
-involves >2 mucosal sites (oral, ocular, genital m/c)
-usually triggered by mycoplasma, HSV or meds
-more severe than minor; rarely life threatening
-painful ulcers than can bleed
-lip crusting
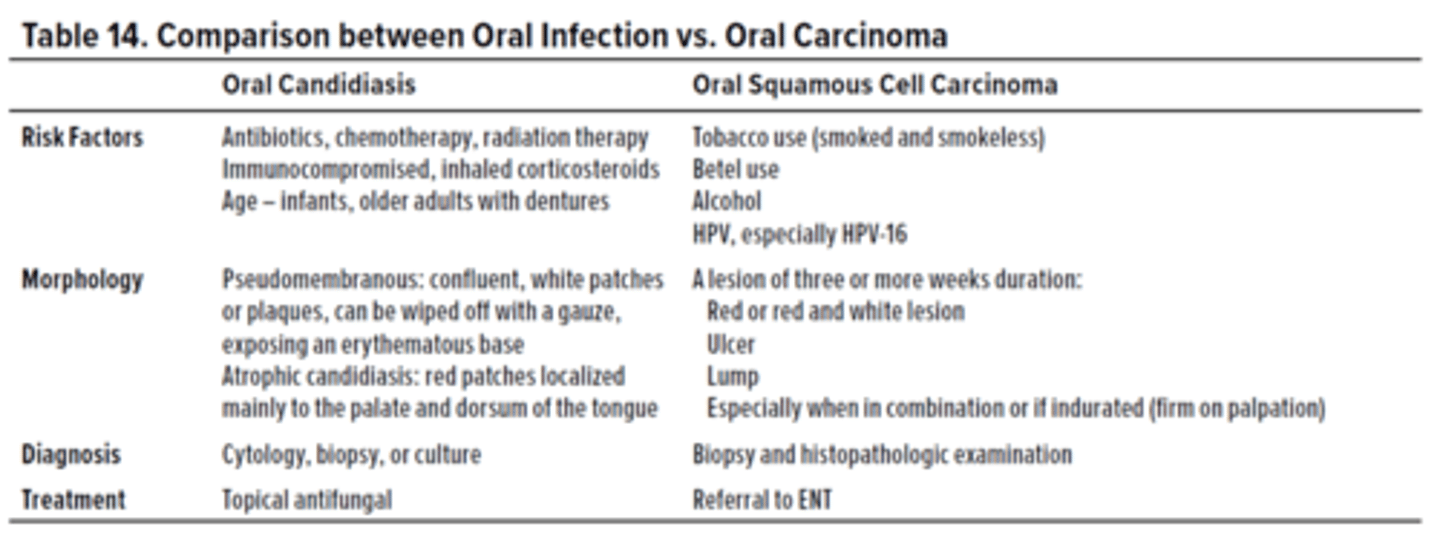
Differentiate between oral candidiasis and oral squamous cell carcinoma
What is candidal paronychia? treatment?
-m/c C. albicans
-affects periungual (toenail,fingernail) skin
-painful, red, swollen
Treatment
-topical agents
-if not effective, oral antifungals
Differentiate between folliculitis, carbuncles and furuncles
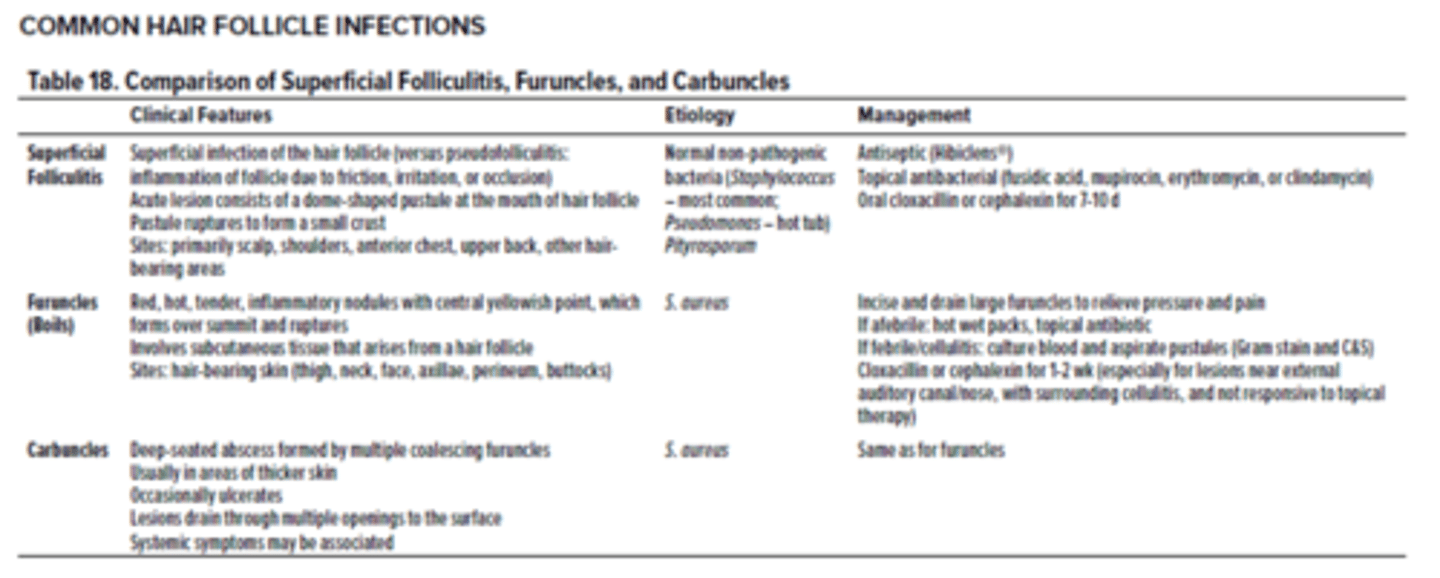
What are carbuncles? symptoms, treatment
-collection of furuncles that coalesce to form a large infected mass
-larger than a boil, may have multiple openings to drain pus onto skin
-m/c S. aureus
Symptoms
-deep seated abscess from multiple coalescing furuncles
-mass may not be able to drain bc so deep
-red, irritated and may be painful when touched
Treatment
-incise and drain to relieve pressure and pain
What is cellulitis? Risks, symptoms, testing, treatment
-inflammation of dermis and subcutaneous fat
-d/t bacterial infection; m/c Group A strep, B hemolytic strep, S. aureus, S. lagdunensis
Risks
-animal bites/trauma
-recent surgery
-peripheral vascular disease
-diabetes
-lymphedema
-cracked skin in feet/toes
Symptoms
-involves lower dermis and subcuteneous fat
-erythema with poorly elevated, indistinct boarders
-warmth, swelling, pain
-m/c in legs
-may have systemic symptoms (fever, chills, malaise)
-regional lymphadenopathy may be present; can lead to lymphangitis
Testing
-clinical
-bacterial culture to confirm
Treatment
-antibiotics (cephalexin 1st line)
-trimethoprim sulfamethoxazole if diabetic
What is folliculitis? symptoms, treatment
-superficial infection of fair follicle causing inflammation
-normal, non pathogenic bacteria (S. aureus m/c)
Symptoms
-dome shaped pustule at hair follicle
-pustule will rupture to form a small crust
Treatment
-topical antibacterial meds (mupironcin)
-antiseptic
What are furuncles?
-boils
-deep folliculitis, infection of hair follicle
-m/c caused by S. aureus
Symptoms
-painful, swollen area on skin d/t accumulation of pus and dead tissue
-m/c in areas with hair (thighs, neck, face, axillae, groin, buttox)
-red, hot, tender, inflammatory nodules
-yellow or white point at center of lump can rupture and drain pus
**can coalesce and turn into carbuncle**
Treatment
-topical antibiotics
-incise and drain to relieve pressure and pain
What is impetigo? Differentiate causes, symptoms, testing, treatment in nonbullous and bullour impetigo
-bacterial infection of superficial epidermis
-m/c bacterial skin infection
-3rd m/c skin disease in children
-highly contagious
Impetigo Vulgaris (NONbullous)
Causes
-group A strep, S. aureus, S. pyogenes
-m/c in preschool and young adults
-often d/t poor hygiene or neglected minor trauma
Symptoms
-acute purulent infection
-vesicle or pustule that ruputures and becomes yellow honey crusted exudate
-exudate covers erosion and is surrounded by erythema
-m/c on face, arms, legs, butt
-rapid spread follows by contiguous extensionor to distal areas through inoculation of other wounds from scratching
Testing
-gram stain
-culture lesion fluid
Treatment
-saline compress and topical antiseptic soak to remove crusts
-topical antibacterial (mupirocin)
-topical antibiotic (cephalexin)
Bullous Impetigo
Causes
-S. aureus
-m/c in neonates and older children
Symptoms
-small or large, superficial fragile thin walled bullae
-appear quicly and sponteneously rupture
-drain clear, yellow turbid fluid with no surrounding erythema
-lesions spread on face, trunk, extremeties, butt, groin
Testing
-gram stain and culture of lesion fluid
Treatment
-topical antibacterial (mupirocin)
-oral antibiotics
What is necrotizing fasciitis? causes, symptoms, testing, treatment
-rapidly progressive inflammatory infection of the fascia with secondary necrosis of subcutaneous tissues
-limb and life threatening = REFER TO ER ASAP
Causes
-surgical procedures, insect bites, IM injections, local ischemia in diabetics
-Type 1 = polymicrobial (aerobes and anaerobes - S. aureus, Bacteroides, Enterobacteriaceae)
-Type 2 = monomicrobial (m/c B hemolytic strep)
Symptoms
-pain out of proportion to clinical findings
-pain reaches past the boarder of erythema
-crepitus can be heard as anaerobes produce gas
-edema
-rapid spread of infection
-may appear well initially but will get very sick quickly
-skin turns blue and black (2ndary to thrombosis and necrosis)
-gangrene
Testing
-clinically = start treatment ASAP (dont wait for cultures)
-blood and tissue culture and sensitivity (C&S)
-Xray to visualize soft tissue gas
-serum creatine kinase may be extremely elevated = late sign of myonecrosis
Treatment
-IV fluids and abx (penicillin and clindamycin)
-Emerg surgical debridement to confirm diagnosis and remove necrotic tissue
-may require amputation
What is onychomycosis? symptoms, ddx, testing, treatment
-tinea unguium
-T. rubrum (90%) and T. mentagrophytes are m/c causes
-associated with HIV, DM, peripheral arterial disease
Symptoms
-crumbling, dystrophic nails
-yellowish, opaque with subungual hyperkeratotic debris
-nail raised and plate is white or yellow, tick and crumbly
-toenail usually precedes fingernail infections
DDx
-psoriasis, lichen planus, contact derm, traumatic onychodystrophy, bacterial infection
Testing
-microscopic exam of nail scrapings with KOH prep shows hyphae
-culture of scraping or clippings on sabourauds agar
-periodic acid schiff (PAS) stain of cliping
Treatment
-terbinafine antifungal most effective
-itraconazole
What is paronychia? causes, symptoms, treatment
-local infection and inflamamtion of soft tissue around fingernail (nail fold)
Causes
-commonly caused by injury to the area (ex. biting, picking hangnaill, trimming back cuticles, sucking fingers)
-acute infection usually = Staph
-chronic infection usually = Candida (also usually diabetic and w constant hand exposure to water)
Symptoms
-painful, red, swollen area around nail
-often at cuticle or site of hangnail/other injury
-nail may look detached, abnormally shaped or have unusual colour
Treatment
-warm compress 2-3x/day
-acute = warm compress and cephalexin; drain abscess if present
-chronic = antifungals
What is pediculosis? types, symptoms, testing, treatment
-lice
-can transmit infectious agents like Bartonella quintana and Rickettsia prowazekii
-m/c 3-11yo
Types
-Phthirius pubis = pubic
-Pediculus humanus capitis = scalp
-Pediculus humanus humanus = body (found in poverty, war; uncommon in most people)
Symptoms
-intense pruritic excoritations
-secondary bacterial infection and lymphadenopathy (d/t constant scratching)
-nits (louse eggs) can be seen on hair and clothing seams
-itching occurs when lice feed on blood (>1/day) via piercing skin with tiny needle like mouthparts (saliva excretion during this causes itching)
-cannot burrow in skin
Testing
-comb scalp thoroughly with a louse comb and examine for presence of living lice
-most effective method to detect
Treatment
-no product that assures 100% destruction of lice and nits after single treatment
-need combination of products to remove:
-Permethrin cream
-combing hair using dilute vinegar solution (removes nits)
-shaving hair so they have no place to hide
-wash clothing with detergent in hot water and machine dry
Name 7 different types of Tinea and what they cause
1. Tinea capitis
-round, scaly patches of alopecia
-ringworm of scalp
2. Tinea corporis
-ringworm (of body)
3. Tinea cruris
-jock itch
4. Tinea pedis
-Athletes foot
5. Tinea manuum
-uncommon
-blisters or dry scaly patch of infection on hand
6. Tinea unguium
-onychomycosis
7. Tinea barbae
-superficial inflammed annular lesions, pustules and crusting around hairs
What is Tinea capitis? symptoms, ddx, testing, treatment
-ringworm of the scalp
-infection involves hair shaft and follicles
-m/c in kids (mainly black), immunocompromised adults
-highly contagious
-often transmitted from barber, hats, theatre seats, pets
Symptoms
-round, scaly patches of alopecia
-hairs may be broken
-itchy scalp, eyelashes and eyebrows
-may have occipital lymphadenopathy
-Kerion (boggy, elevated, purulent, inflammed nodule/plaque) may form secondary to infection and result in scarring
DDx
-alopecia, psoriasis, seborrheic dermatitis, trichotillomania
Testing
-woods light exam of hair = green fluorescence
-culture of scales/hair shaft
-KOH prep of scales or hair shafts
Treatment
-terbinafline for 4 weeks
-oral antifungals to penetrate hair root
-adjunctive antifungal shampoos or lotions to prevent spread
What is Tinea corporis? symptoms, ddx, testing, treatment
-ringworm
Symptoms
-pruritic, scaly, round/oval plaque with active erythematous margin
-may have central clearing
-m/c on trunk, limbs, face
DDx
-granuloma annulare, pityriasis rosea, psoriasis, seborrheic dermatitis
Testing
-KOH prep of scales show hyphae
-culture of scales
Treatment
-topical clotrimazole, ketoconazole, miconazole, terinafline or ciclopiroxolaime cream BID 2-4 weeks
What is Tinea cruris? symptoms, ddx, testing, treatment
-jock itch
Symptoms
-scaly patch/plaque with well defined, curved border and central clearing
-pruritic, erythematous, dry/marcated
-starts medial thigh then spreads centrigulally to perineum, gluteal cleft, butt
DDx
-candidiasis (will involve scrotum and have satellite lesions)
-contact dermatitis
-erythresma
Testing
-culture of scales
Treatment
-terbinafline, itraconazole, fluconazole, ketoconazole if extensive
What is Tinea pedis? symptoms, ddx, testing, treatment
-athletes foot
-predisposing factors = heat, humidity, occlusive footwear
Symptoms
-pruritic scaling and/maceration of web spaces
-powdery scaling of soles
-acute = interdigital (esp 4th web space); red/white scales, vesicles, bullae, often with maceration
-chronic = non pruritic, pink, scaling keratosis on soles and sides of feet
-acute on chronic possible
DDx
-atopic dermatitis, contact dermatitis, dyshidrotic dermatitis, erythrasma, intertrigo, inverse psoriasis
Testing
-culture scales
Treatment
-terbinafline, itraconazole, fluconazole, ketoconazole if extensive
What is Tinea manuum? symptoms, ddx, testing, treatment
-usually associated with tinea pedis (primary infection of hand is rare)
Symptoms
-acute = blisters at edge of red areas on hands
-chronic = single, dry scaly patch
DDx
-atopic derm, contact derm, granuloma annulare, psoriasis
Testing
-culture scales
Treatment
-terbinafline, itraconazole, fluconazole, ketoconazole if extensive
What is Tinea unguium? symptoms, ddx, testing, treatment
onychomycosis
-associated with HIV, DM, peripheral arterial disease
Symptoms
-crumbling, dystrophic nails
-yellowish, opaque with subungual hyperkeratotic debris
-nail raised and plate is white or yellow, tick and crumbly
-toenail usually precedes fingernail infections
DDx
-psoriasis, lichen planus, contact derm, traumatic onychodystrophy, bacterial infection
Testing
-microscopic exam of nail scrapings with KOH prep shows hyphae
-culture of scraping or clippings on sabourauds agar
-periodic acid schiff (PAS) stain of cliping
Treatment
-terbinafine antifungal most effective
-itraconazole
What is Tinea barbae? symptoms, ddx, testing, treatment
Symptoms
-superficial, inflammed annular lesions
-pustules and crusting around hairs
-inflammatory kerion may occur and result in scarring hair loss
-predom affects men who work with animals
-m/c in beard area
DDx
-folliculitis, malignant lymphoma, sporotrichosis
Testing
-KOH prep of scales show hyphae
-culture of scales
Treatment
-terbinafline or itracanozole
What organism is the leading cause of skin and soft tissue infections? Name 5 that affect the skin
-S. aureus
1. Folliculitis
-least serious
-hair root follicle infection
2. Impetigo
-shallow, fluid-filled blisters that rupture, leaving honey-colored crusts
-may itch or hurt.
3. Abscesses (boils or furuncles)
-warm, painful collections of pus just below the skin
4. Cellulitis
-infection of skin and the tissue under it
-pain and redness
5. Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN)/SJS + scalded skin syndrome in newborns
-serious infections
-large-scale peeling of skin
What is rubella? causes, symptoms, testing, treatment
-german measles (milder than rubeola/measles)
Causes
-RNA togavirus (3 day measles)
-incubation = 14-21 days
-transmission = droplets
-MMR vaccine to protect
Symptoms
-Forchheimers spots = red spots on posterior soft/hard palate, develop at onset of rash
-appearance of pink, discrete, maculopapular rash lasting 1-5 days
-rash starts on hairline, rapidly spreads to neck, trunk and rest of body
-pruritic but disappears by the 3rd day
-painful postauricular lymphadenopathy
-polyarthritis in adults
Testing
-ELISA serology for IgM
-may not be detected for 4-5 days after rash onset
Treatment
-symptoms
-self resolves
What happens when a pregnant woman contracts rubella? What symptoms will be seen in mom? Baby when born? Testing? Treatment?
-contracted via respiratory droplets (highly contagious)
-transmitted transplacentally in 1st trimester
Symptoms for mom
-rash (exanthema) on face which spreads to trunk and extremities
-disappears after 3 days (3 day measles)
-low grade fever, post auricular or occipital lymphadenopathy
-joint pain
Symptoms for fetus/baby when born
-deafness (sensorineural)
-cataracts
-thrombocytopenia (blueberry muffin baby)
-hepatomegaly
-patent ductus arteriosus
Testing
-ELISA IgM that is 4x greater than IgG in acute
Treatment
-MMR vaccine after pregnancy (CANNOT give during preg bc live attenuated)
What is scarlet fever? causes, symptoms, testing, treatment
-scarletina
Causes
-toxin producing group A beta hemolytic strep (GABHS)
-GABHS found in secretions and discharge from nose, ears, throat and skin
-toxin causes pathognomonic rash d/t inflmmatory mediators leading to scarlet coloured rash
-GABHS replicates in tonsils and pharynx
-m/c in 5-15yo
Symptoms
-acute onset fever, sore throat
-24-48 hours after pharyngitis, erythematous rash develops on face and neck, then spreads to other parts of body
Rash
-sandpaper quality, non pruritic, non painful
-spares mouth but tongue has white exudate with studded prominent red papillae
-fades after 6 days, starts peeling (can last up to 10 days)
-white exudate on tongue disappears, tongue turns beefy red = strawberry tongue
Testing
-rapid strep test
-throat culture
Treatment
-penicillin, amoxicillin
What acronym is useful to remember the features of scarlet fever?
SCARLET
S = Sore throat
C = Circumoral pallor (white around lips)
A = group A strep
R = Rash
L = Lymphadenopathy
E = Erythrogenic toxin
T = strawberry Tongue
What is erythema infectiosum? symptoms, testing, treatment
-fifths disease
-d/t parvovirus B19 (erythrovirus)
-occurs in epidemics
Symptoms
-mild prodromal symptoms begin 1 week post exposure to parvoB19, last 2-3 days
-prodromal sx = fever, headache, sore throat, pruritis, arthralgias (flu like)
-classic slapped cheek appearance which typically fades over 2-4 days
-1-4 days after slepped cheek fades, erythematous maculopapular rash extends to trunk and proximal extremities
Testing
-diagnosis via clinical presentation alone
-ELISA = increased IgM
-western blot hybridization, PCR assay
Treatment
-self limiting
-symptom relief w NSAIDs
Describe the differences seen in rashes associated with roseola, rubeola, rubella, erythema infectiosum, scarlet fever, varicella, hand-foot-mouth disease
Roseola (human herpes virus 6 (DNA virus)
-non pruritic
-starts at neck, trunk then spreads out to face and extremities
-pink/rose colorued macules and maculopapules
-1-5mm in diameter
Rubeola (measles; paramyxovirus)
-non pruritic
-starts at hairline or mucous membranes (white spots on cheeks) and spreads down to face/neck/trunk
-no palm or sole involvement with rash
-erythematous, blotchy rash
-Koplik spots = grey/white papules on buccal mucosa
Rubella (german measles; RNA togavirus)
-pruritic but disappears by the 3rd day
-rash starts on hairline, rapidly spreads down to neck, trunk and rest of body
-Forchheimers spots = red spots on posterior soft/hard palate
-pink, discrete, maculopapular rash
Erythema infectiosum (fifths disease; parvoB19)
-possibly pruritic
-classic slapped cheek appearance
-after cheek fades, erythematous maculopapular rash spreads down to trunk and proximal extremities
Scarlet fever (toxin producing group A beta hemolytic strep)
-sandpaper quality, non pruritic, non painful
-erythematous rash on face and neck, then spreads down to other parts of body (fades and peels)
-spares mouth but tongue has white exudate with studded prominent red papillae -> strawberry tongue after
Varicella (chicken pox; VZV)
-pruritic
-often starts on trunk, then spreads out to face, scalp, conjunctivae, oral mucosa, extremities (inc palms and soles)
-progresses from macules to vesicles to pustules that burst
-lesions crust over
Hand-foot-mouth disease (coxsackievirus)
-possibly pruritic, painful
-erythematous lesions found on hands, feet, buttocks and genitalia
-lesions progress to vesicles that erode and become surrounded by erythematous halo
Herpangina (coxsackievirus A16, enterovirus 71)
-non pruritic
-multiple vesicles (grey with red base) or ulcers on soft palate and pharynx, surrounded by erythema
What is hand-foot-mouth disease? symptoms, testing, treatment
-acute viral illness
-via Coxsackievirus
-m/c in young children
-infection via fecal oral OR contact with skin lesions and oral secretions
-incubation 1 week
Symptoms
-sore mouth, throat, malaise
-macular lesions appear on buccal mucosa, tongue and/or hard palate = may be painful
-lesions progress to vesicles that erode and become surrounded by erythematous halo
-lesions = erythematous, tender macules or vesicles found on hands, feet, buttocks and genitalia
-fever within first 24-48 hours
Testing
-clinically
Treatment
-self limiting
-no meds generally needed
What is herpangina? symptoms, testing, treatment
-acute febrile illness
-arises from various enterovirus infections (coxsackievirus A16, enterovirus 71)
-spreads via fecal oral; can spread via respiratory or fomites
-m/c in newborns-young adults in summertime
-incubation 4-14 days
Symptoms
-50% asymptomatic
-fever (101-104), malaise
-multiple vesicles or ulcers on soft palate and pharynx, surrounded by erythema
-vesicles = gray papulovesicles with erythematous base
-sore throat and pain on swallowing
Testing
-diagnosis = clinical
Treatment
-none effective
-self resolves
What is roseola? symptoms, treatment, complications
-human herpes virus 6 (DNA virus)
-unclear transmission; incubation = 5-15 days
-m/c viral exanthema in kids <2yo
Symptoms
-high fever (>39.5/103) lasting 3-5 days
-fever may cause febrile convulsion/seizures**
-cough, nasal congestion
-fever resolves abruptly, then rash appears
Rash
-pink/rose colorued, non-pruritic macules and maculopapules
-starts at neck and trunk
-spreads to face and extremities
-1-5mm in diameter, may last 2 days
Treatment
-no effective pharmaceutical
-supportive w acetominophen
Complications
-febrile seizures
-encephalitis
What is Rubeola? symptoms, complications, treatment
-measles
-paramyxovirus
-incubation 8-13 days
-communicable via 4 day pre and post rash
Symptoms
-morbilliform rash = starts at hairline or mucous membranes (white spots on cheeks) and spreads down to face/neck/trunk
-no palm or sole involvement with rash
-rash preceded by Cough, Coryza, Conjunctivitis (3 C's)
-enanthem = Koplik spots = grey/white papules on buccal mucosa
Complications
-d/t suppression of immune system for 6 weeks
-otitis media
-pneumonia
-encephalitis
-SJS
-glomerular nephritis
-myocarditis/pericarditis
Treatment
-vitamin A
-immunoglobulin
-MMR vaccine for others in the house/people at risk
What is the difference between an enanthem and an exanthem?
Enanthem
-or enanthema
-rash inside the body
-ex. Koplik's spots (measles) inside the mouth that look like tiny grains of white sand surrounded by a red ring
Exanthem
-rash on the outside of the body
-ex. rubella, roseola rash