Solute and Water Handling Part 2
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
The liver generates urea from …?
NH4+ (ammonium)
Labs report plasma urea levels as
blood urea nitrogen (BUN)
what are normal blood urea nitrogen (BUN) levels aka plasma urea levels?
7-18 mg/dL
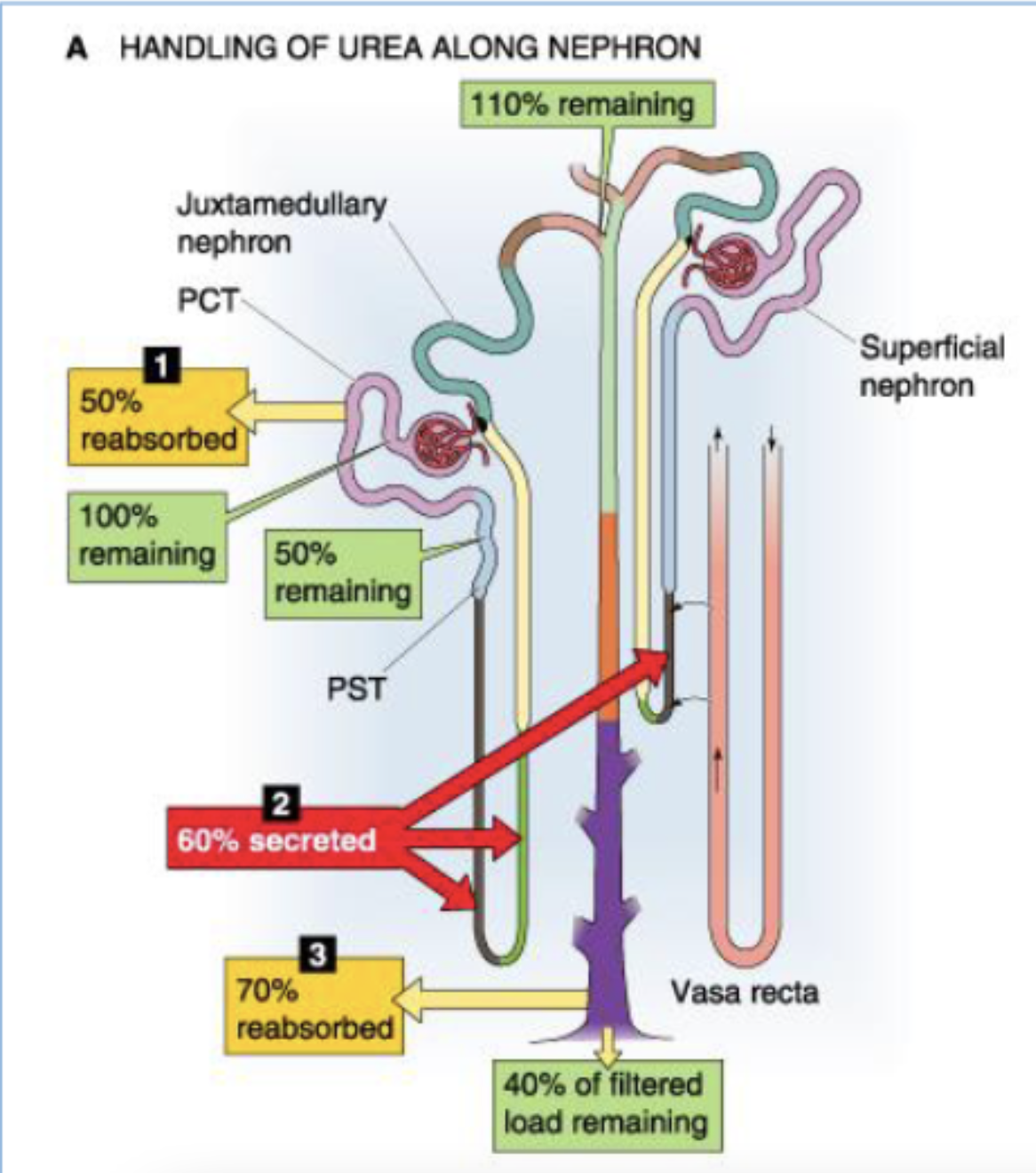
what happens to urea in the PCT?
50% reabsorbed (start at 100% → 50% remaining)
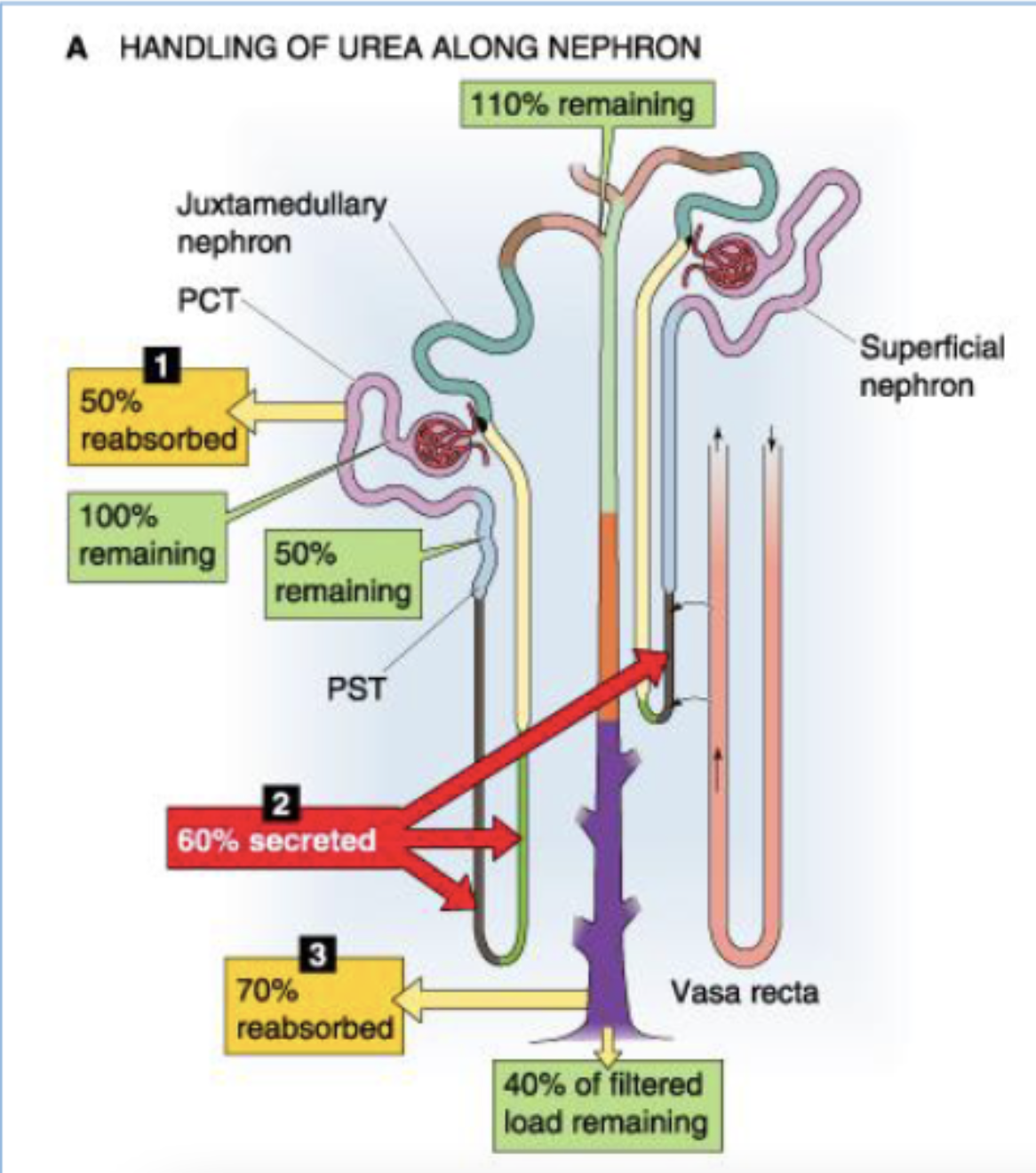
what happens to urea in the think loop of Henle?
60% secreted (start at 50% → 110% remaining)
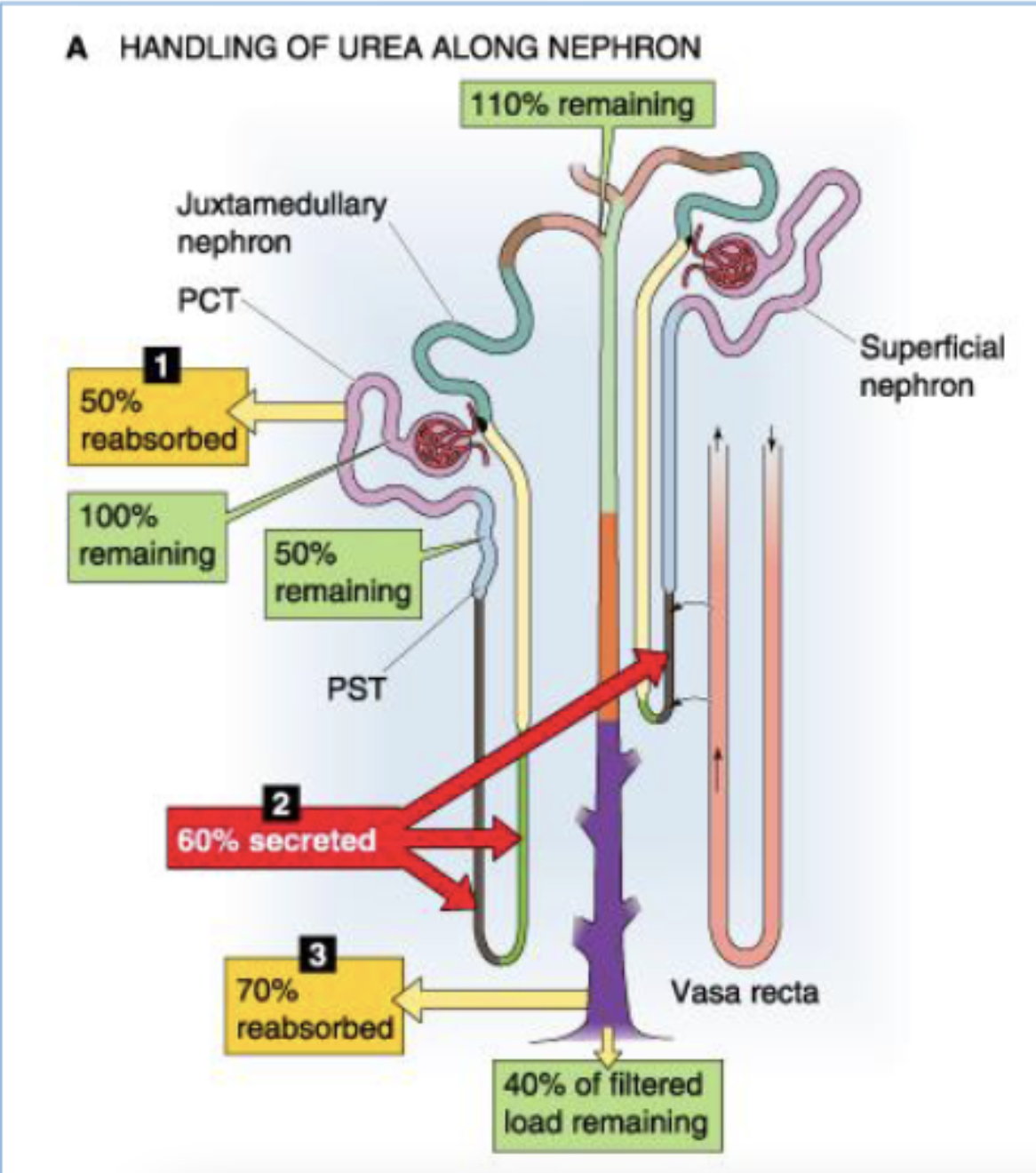
what happens to urea in the collecting duct?
70% reabsorbed (start 110% → 40% of filtered load reamining)
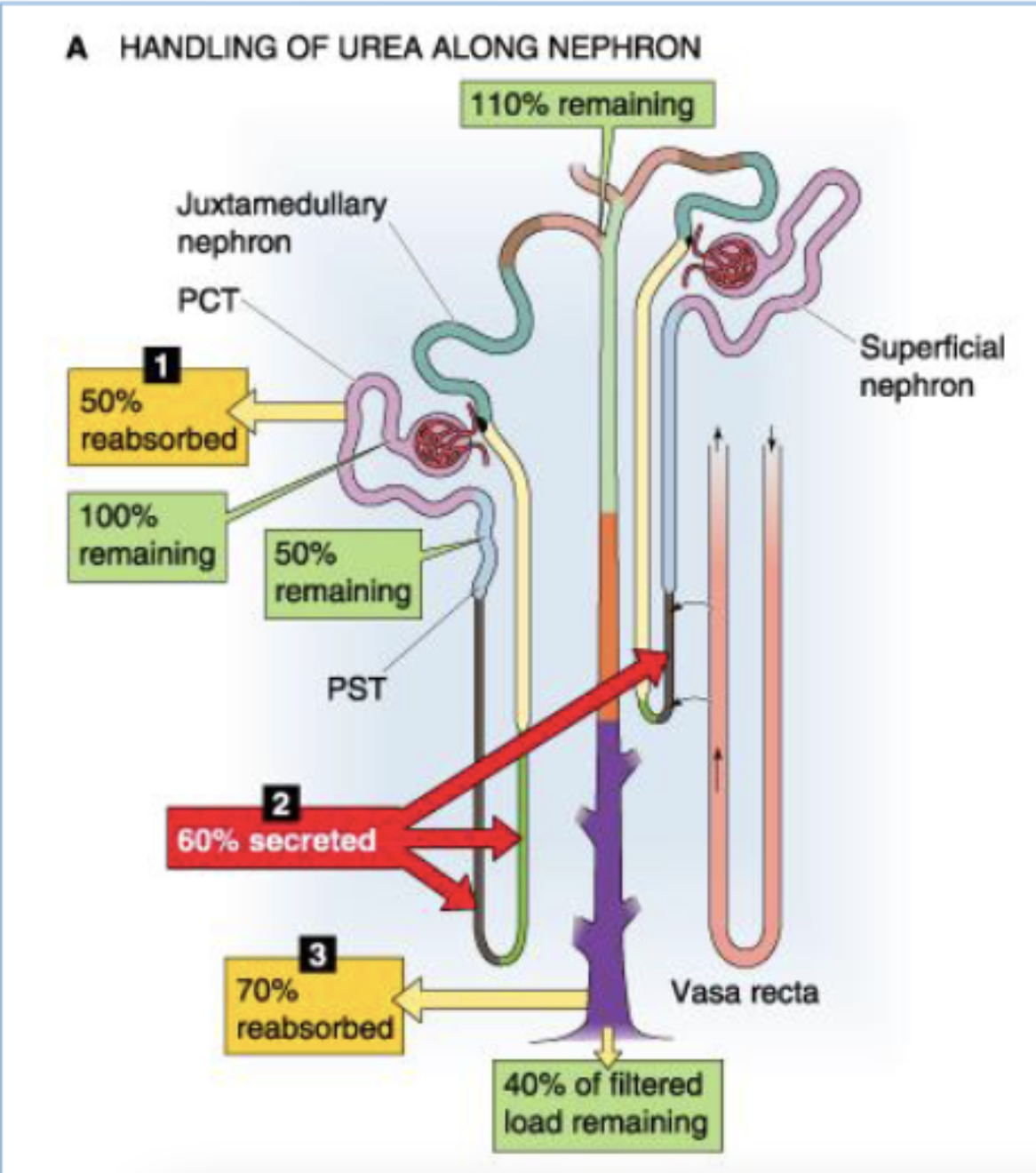
describe the contribution of the tubules to the reabsorption of filtered load of urea.
(start at 100% urea)
PCT reasborbs 50%
50% remaining
thin loop of Henle secretes 60%
110% remaining
collecting duct reabsorbs 70%
40% of filtered load remaining
why is it important for NH4+ levels to be regulated via urea secretion?
NH4+ messes with cognitive function
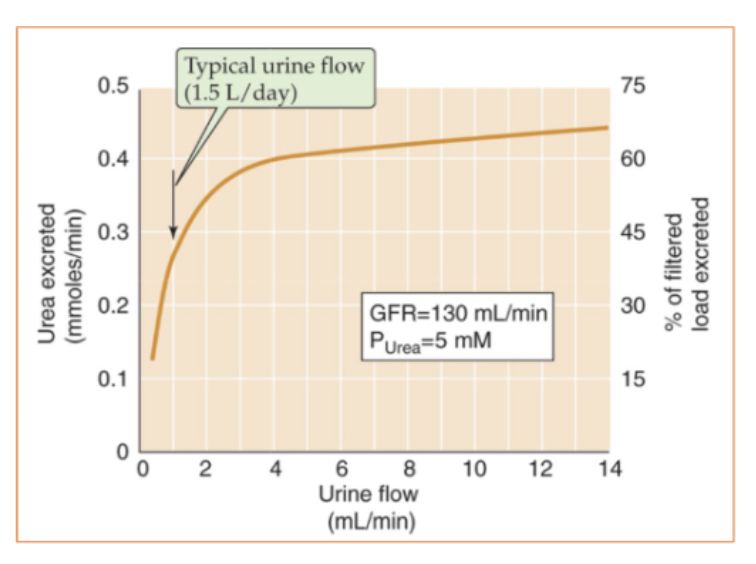
At low urine flow, when the tubule reabsorbs considerable water and urea, the kidneys excrete only % of filtered urea
∼15%
At high urine flow, kidneys may excrete as much as % of filtered urea when the tubules reabsorb relatively less water and urea
70&
During the progression of renal disease, the decline of the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) leads to a low urine flow and urea retention, and thus an increase in
BUN
what clinical condition has urine flow declines sharply, urea excretion decreases out of proportion to the fall in GFR?
volume depletion
The resulting high BUN can thus serve as laboratory confirmation of dehydration
what is the relationship between urea excretion and urinary flow?
Urea excretion rises with increasing urinary flow
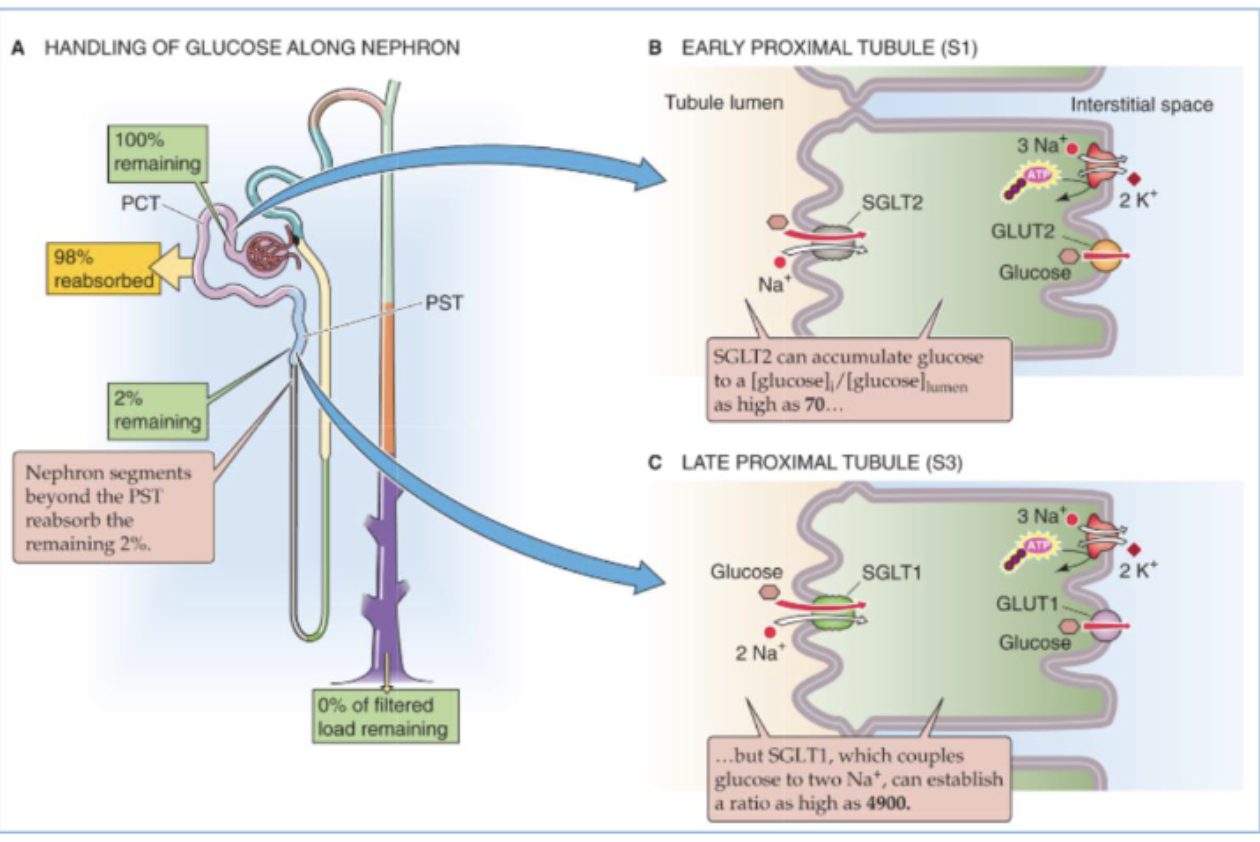
The kidneys freely filter glucose at the glomerulus and then which segment reabsorbs nearly all the filtered load?
the proximal tubule (through SGLT)
Glucose moves from the lumen to the proximal tubule cell through …?
a Na/glucose cotransporter (SGLT)
describe the contribution of the tubules to the reabsorption of filtered load of glucose.
starting at 100% remaining
PCT reabsorbs 98%
2% remaining
segments beyong PSY reabsorb remaining 2%
0% of filtered load remaining by collecting duct
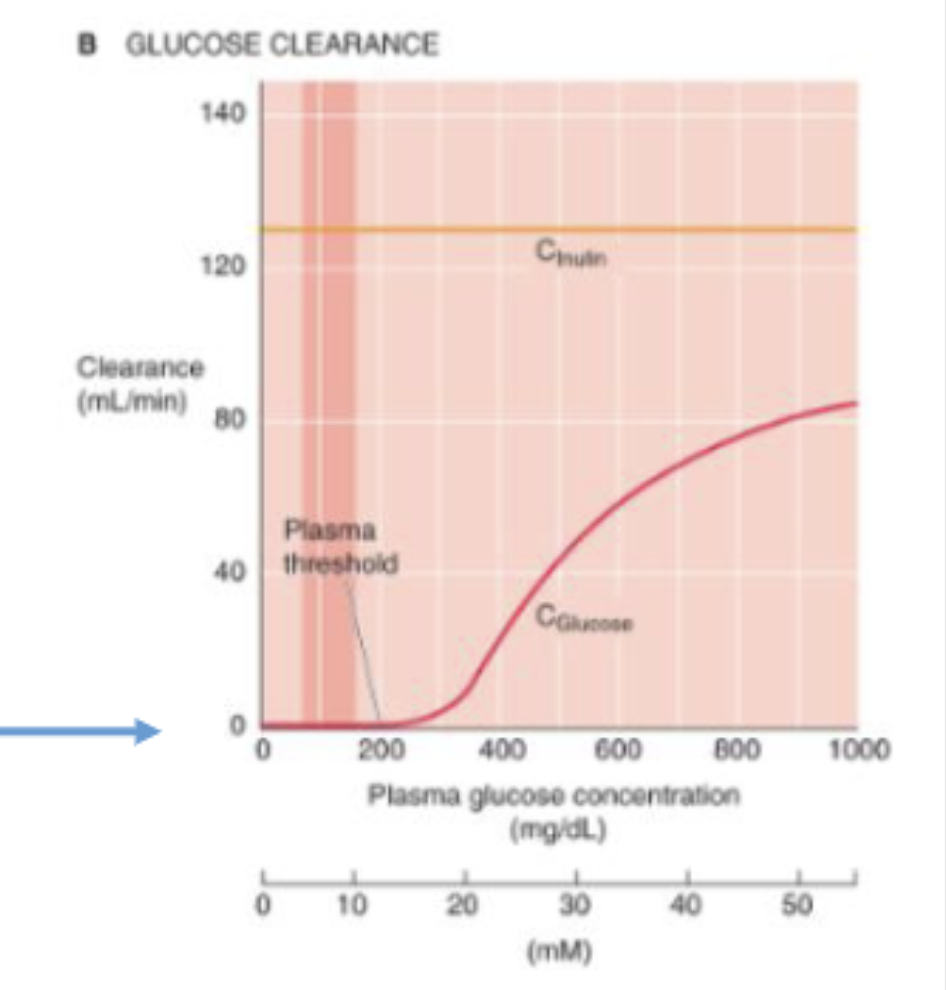
As plasma [glucose] rises from control levels to ∼__ mg/dL (threshold), glucose excretion remains zero
180
what is the relationship between glucose excretion and plasma glucose concentration?
Glucose excretion rises linearly as plasma [glucose] increases further
![<p>Glucose excretion rises <strong>linearly</strong> as plasma [glucose] increases further</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/798ec11b-b175-4df2-8afe-e86f2329643b.png)
At normal blood glucose levels, how much glucose appears in the urine? what is the clearance of glucose?
no glucose appears in the urine, the clearance of glucose is zero
The rate of glucose reabsorption reaches a plateau (Tm) at ∼___ mg/min. The reason for the Tm value is …?
400
that the SGLT1 and SGLT2 cotransporters become fully saturated
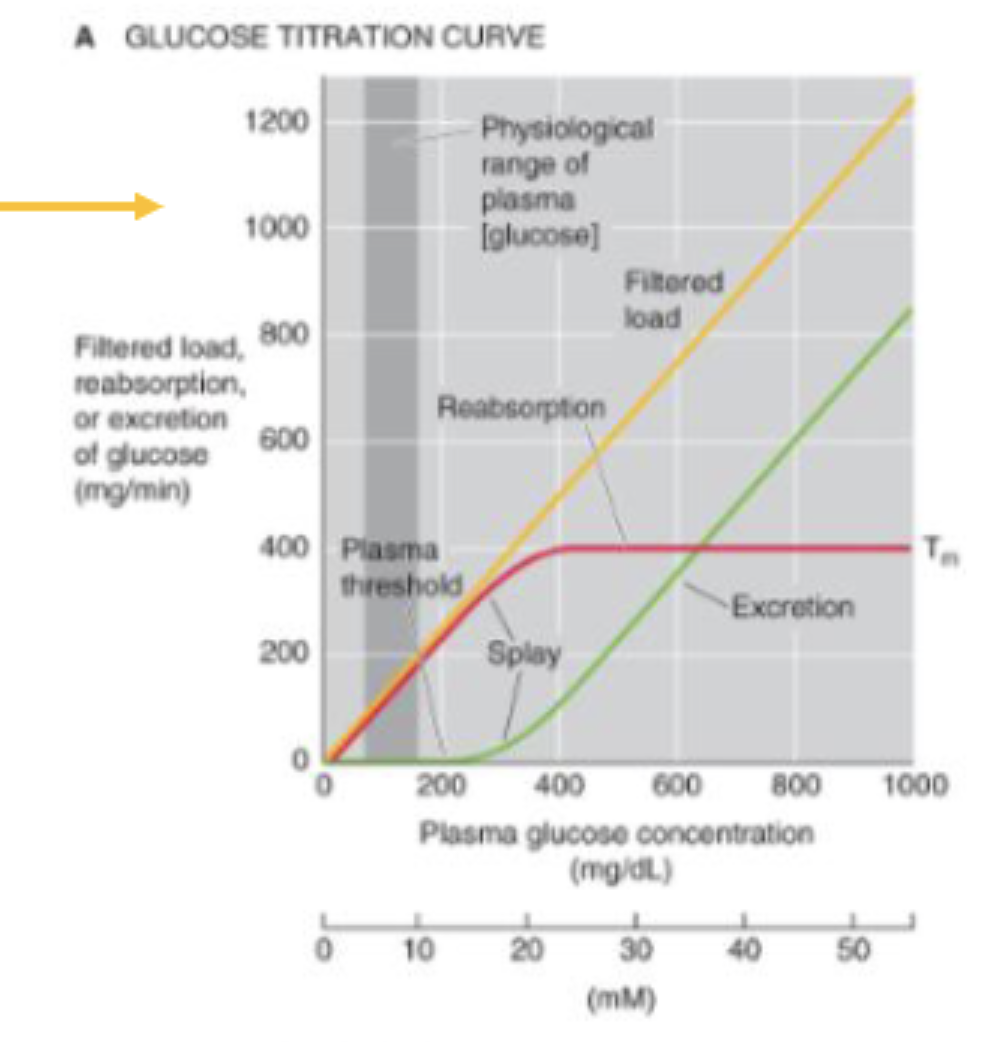
why do healthy people not excrete any glucose in the urine, even after a high sugar meal?
Because the threshold is higher than the normal plasma [glucose] of ∼100 mg/dL,
![<p>Because the threshold is higher than the normal plasma [glucose] of ∼100 mg/dL, </p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/7c4dd21a-905a-4a91-be77-98cf6df68b7a.png)
t/f: patients with diabetes mellitus do not experience glucosuria until the blood sugar level exceeds a threshold value of 180 mg/dL
true
describe the contribution of the tubules to the reabsorption of filtered load of amino acids.
glomeruli freely filter AAs
PCT reabsorbs 99% of AAs
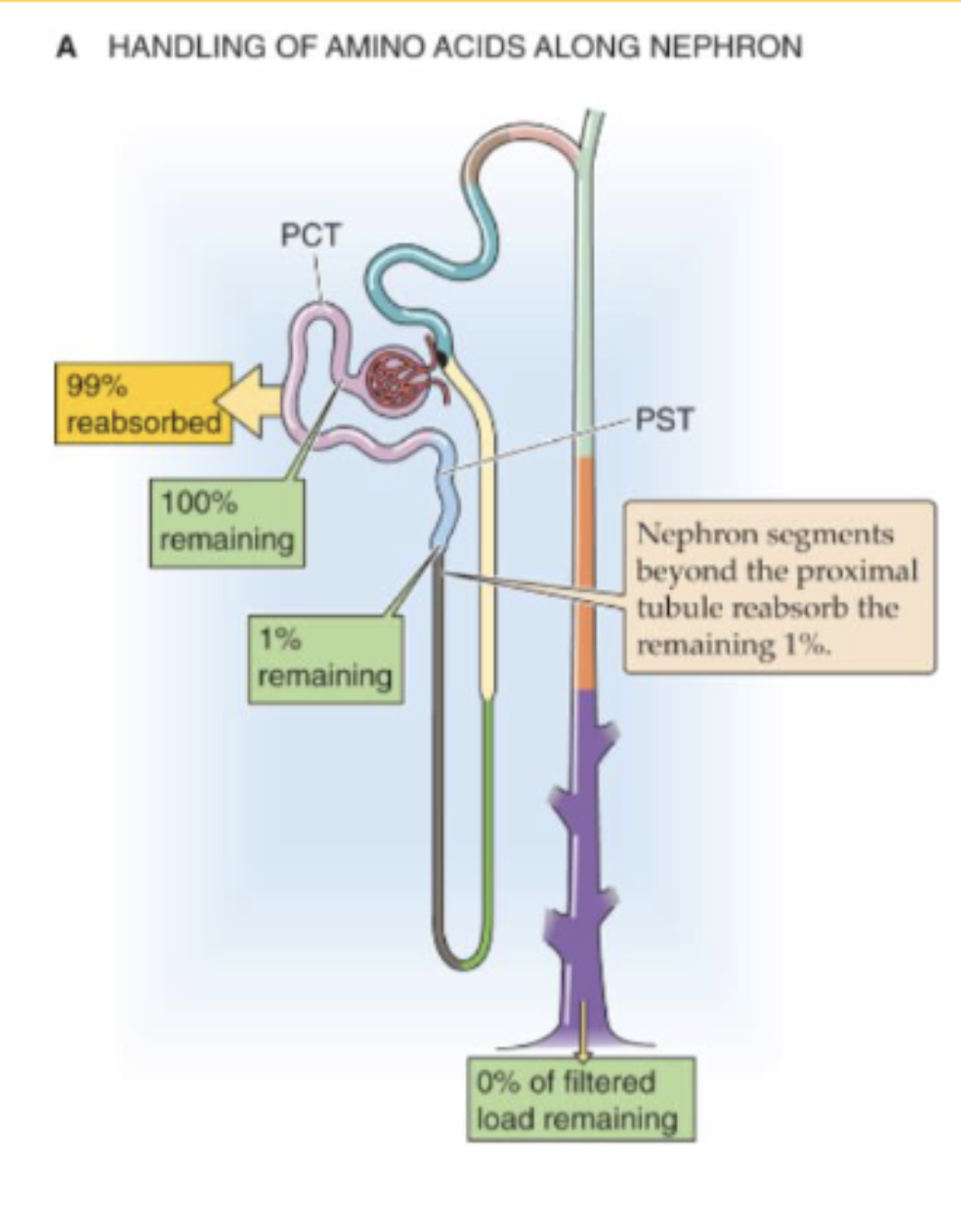
t/f: amino acids are almost 100% reabsrobed from the filtrate because they are important nutrients. it is advantageous
true
why is it important not to use diuretics to target the PCT Na+ reabsorption, specifically regarding amino acid renal handling?
many amino acid cotransporters use Na+ concentration gradient to reabsrob them back into circulation
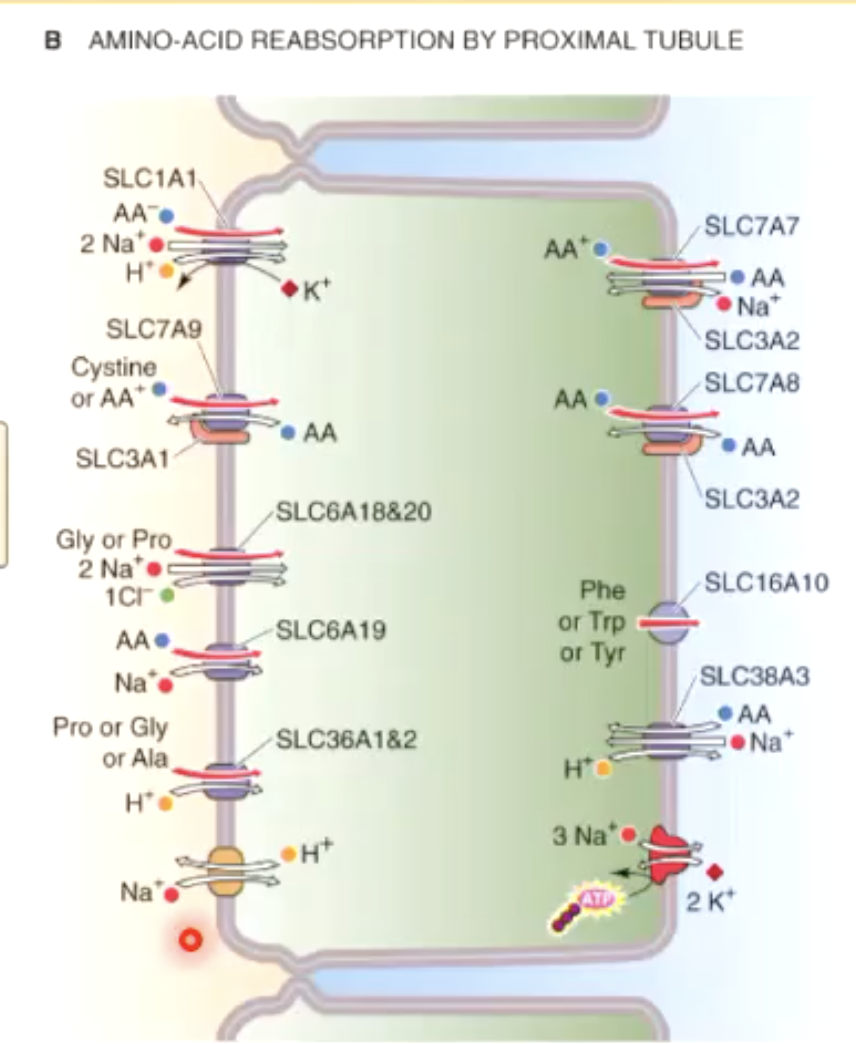
what is Fanconi syndrome?
all amino acids lost to urine (panaminoaciduria)
caused by metabolic, immune, or toxic conditions that impair PCT function
what is Hartnup disease?
all neutral and ring-structured AAs like phenylalanine lost to urine (neutral aminoaciduria)
caused by defective SLC6A19 (autosomal recessive)
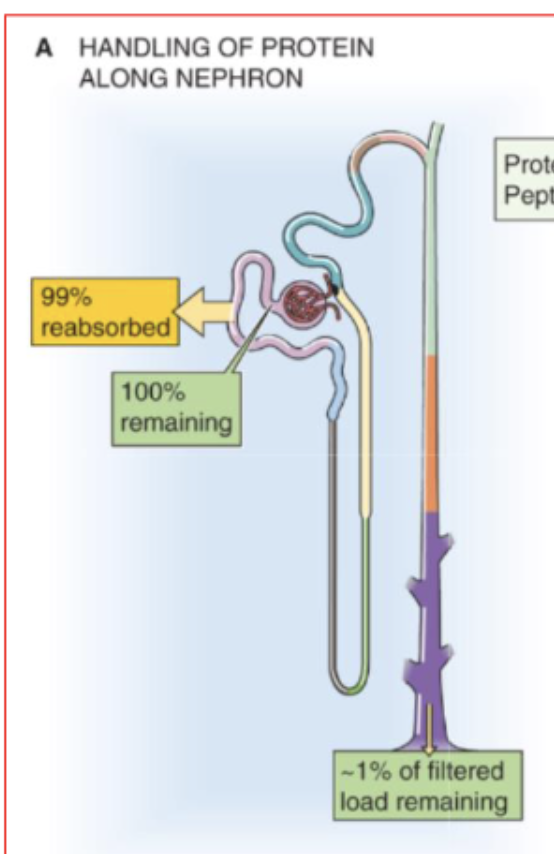
describe the contribution of the tubules to the reabsorption of filtered load of proteins.
Although the glomerular filtration barrier generally prevents the filtration of large amounts of protein, this restriction is incomplete.
tubules reabsorb 99% of filtered albumin
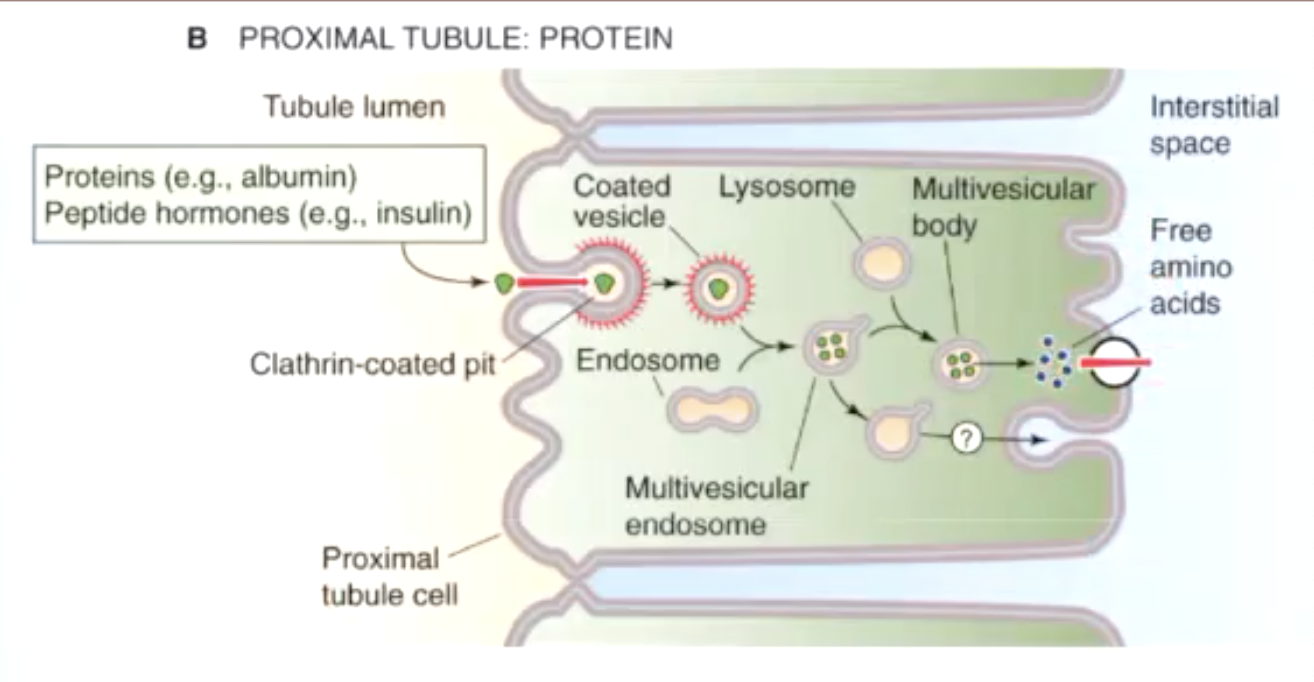
how are proteins reabsorbed in proximal tubules?
proteins (albumin) / peptide hormones (insulin) are taken in by endosomes and broken down into free amino acids by lysosomes
describe the contribution of the tubules to the reabsorption of filtered load of urate.
start with 100% reamining
PCT reasborbs 99% AND secretes 49%
PST reabsrobs 40%
10% remaining
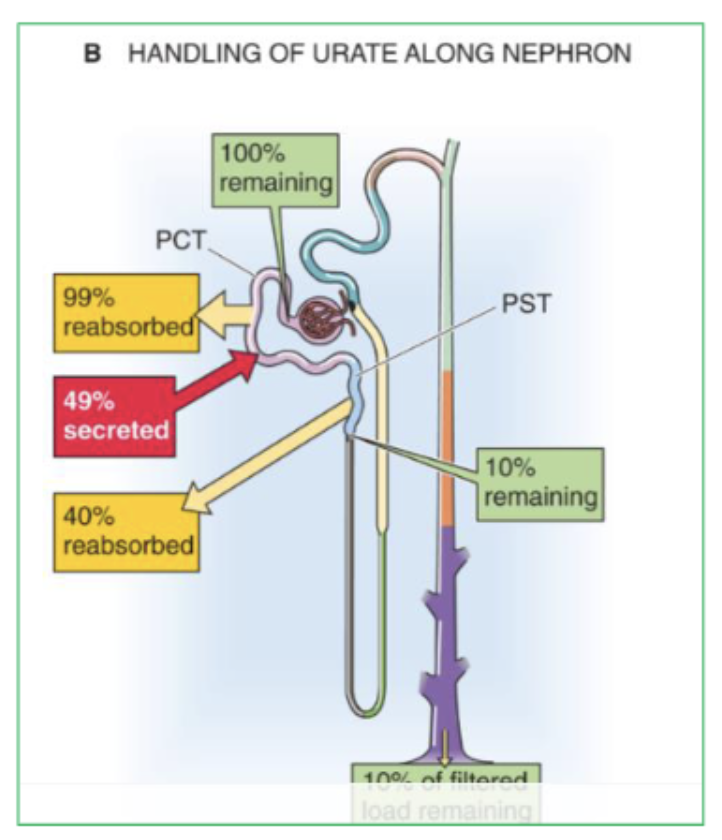
urate is the end product of…?
purine catabolism
what is normal plasma urate concentration? elevated urate concentration causes what condition?
3-7 mg/dL
gout
what drug is useful in the treatment of gout?
Probenecid
how is urate reabsrobed in proximal tubule?
via URAT1 transporters
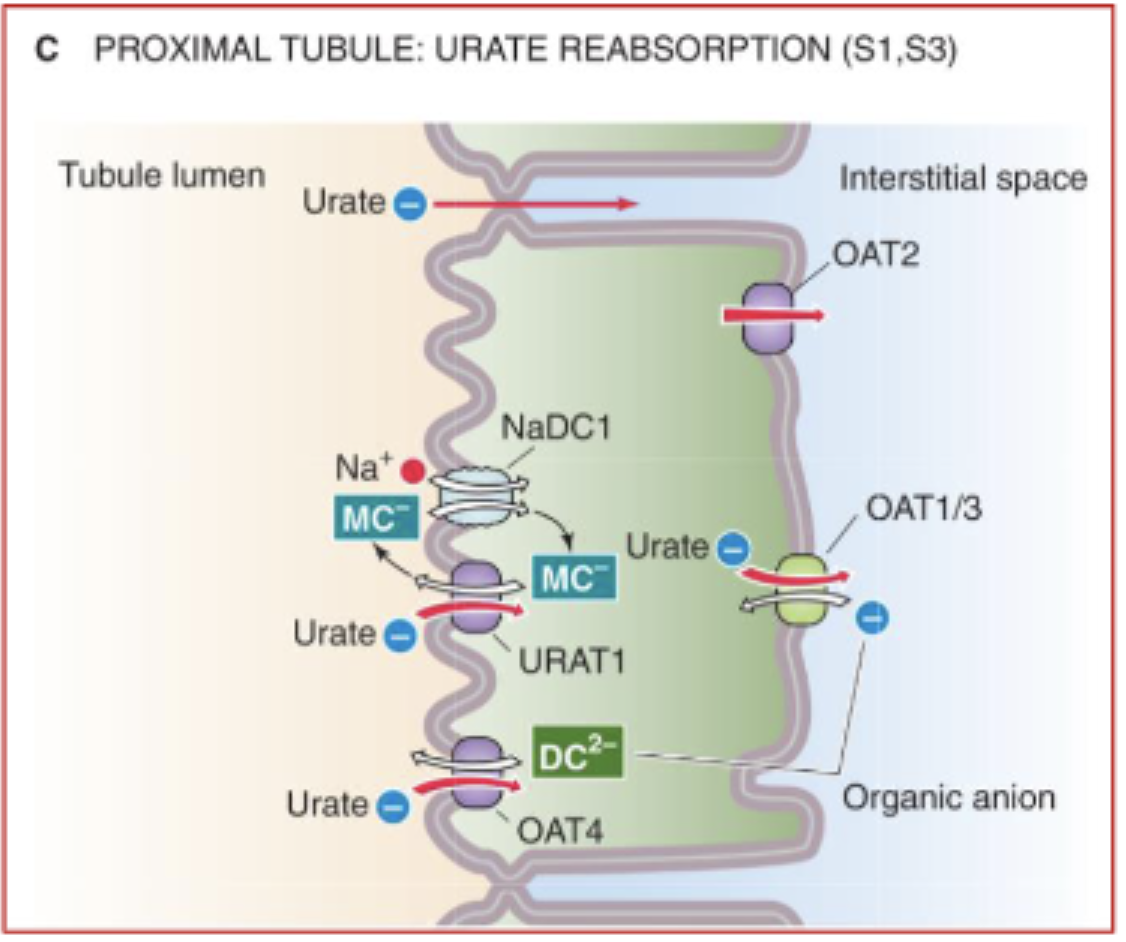
Uricosuric agents such as probenecid, salicylate, and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs have what effect?
inhibit URAT1 (useful for treating gout)