achieve 1-5 midterm practice
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Organic chem
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
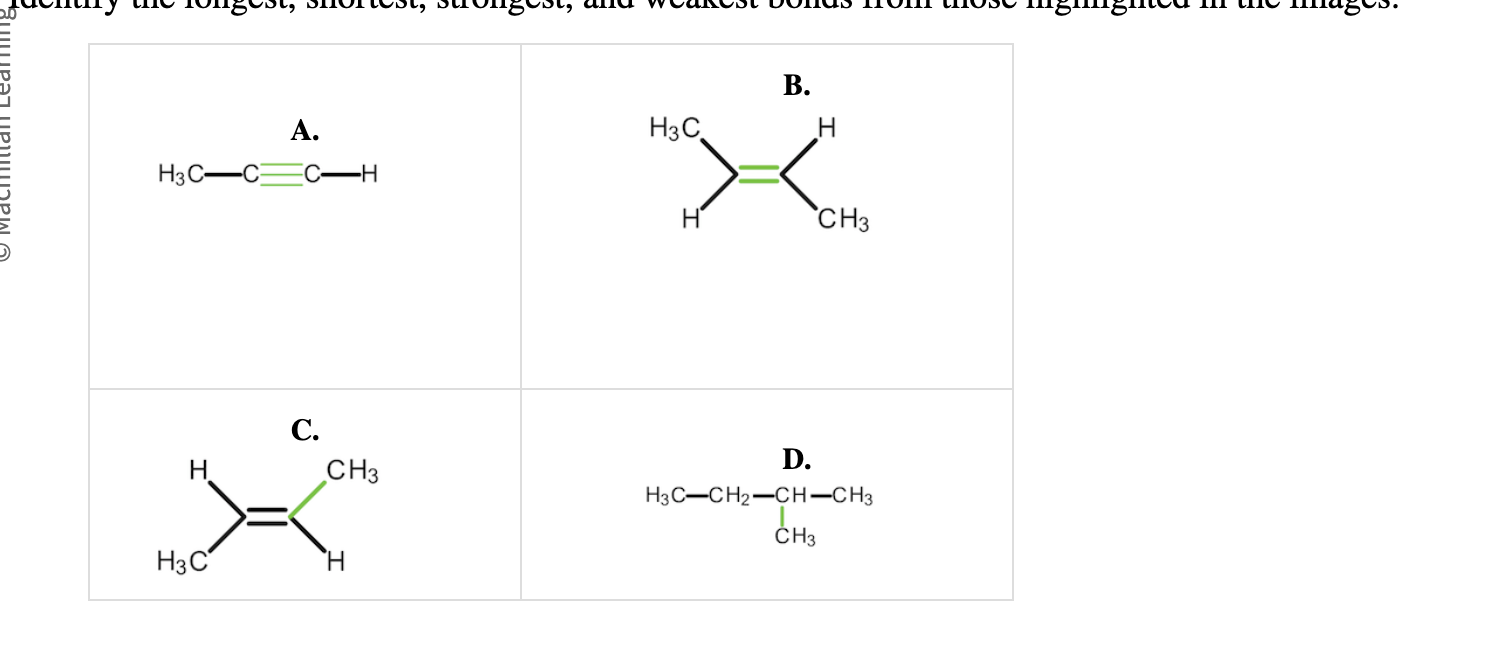
1- longest bond?
2- shortest bond?
3-strongest?
4-weakest?
1-D
2-A
3-A
4-D
The greater the number of electrons involved in bond formation (the greater the bond order), the stronger the bond.
A triple bond (bond order equals 3, with six bonding electrons) has more bonding electrons than a double bond (bond order equals 2, with four bonding electrons), which has more bonding electrons than a single bond (bond order equals 1, with two bonding electrons).
Recall that bond strength increases as bond length decreases.
Bond A, a triple bond, is the strongest and shortest bond. This bond has more bonding electrons (six) than Bond B, a double bond, and Bonds C and D, which are both single bonds.
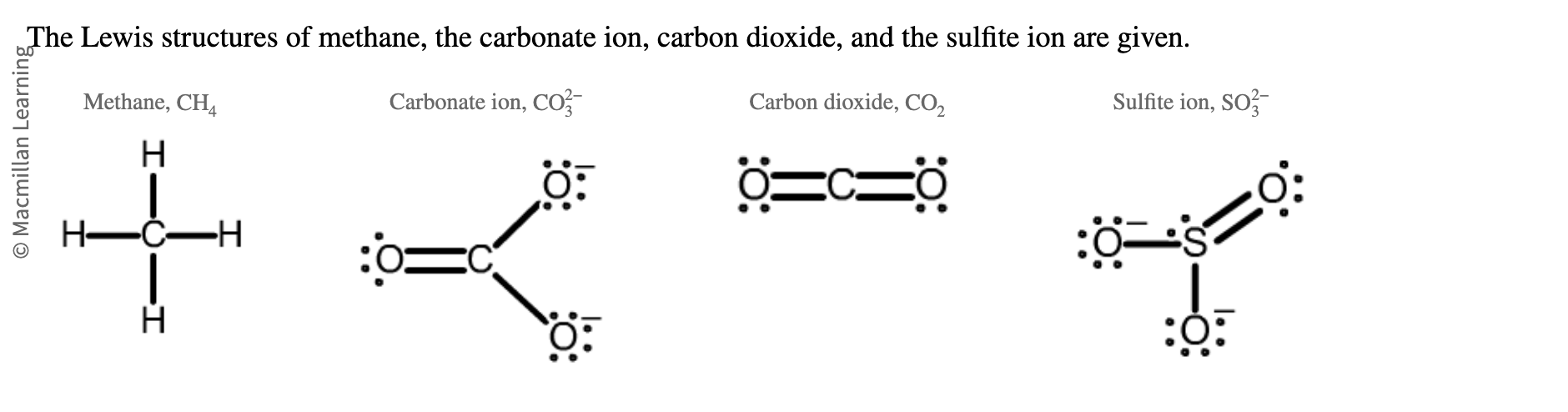
predict molecular shape of
methane?
carbonate ion?
carbon dioxide
sulfite ion
tetrahedral
trigional planar
linear
trigional pyramidal
tetrahedral
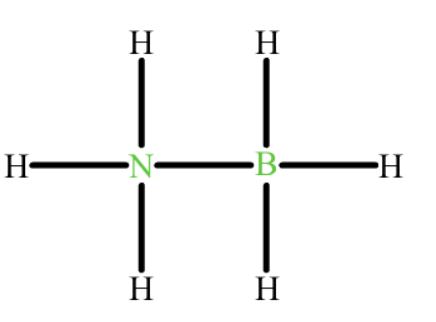
formal charge of N?
formal charge of B?
N- +1
B- -1
formal charge= valence electrons-(bonds +dots)
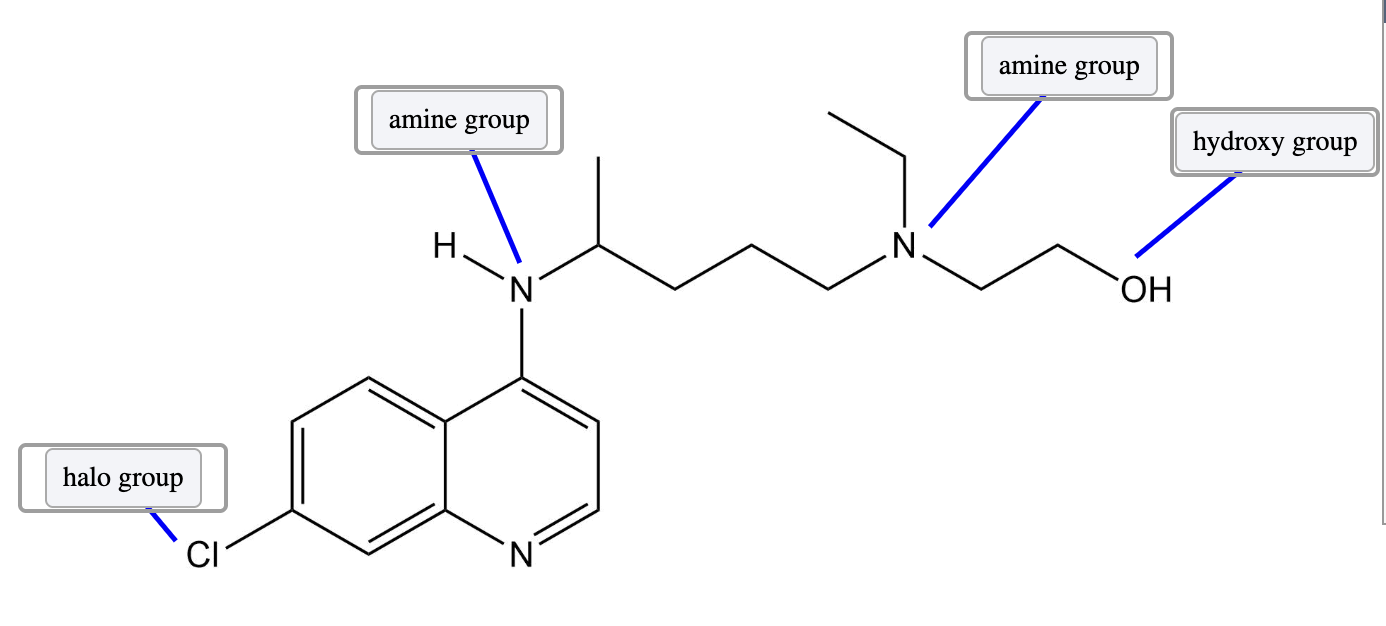
Both an −NR3 and −NHR2 groups are amine groups. If the nitrogen was bonded to a carbonyl group (C=O), then it would be an amide functional group.
An −OH group is a hydroxy or hydroxyl group and is found in alcohols. An ether group consists of an oxygen bonded to two alkyl carbons.
A chlorine is a halo group. Other halides include fluorine (F), bromine (Br), and iodine (I).
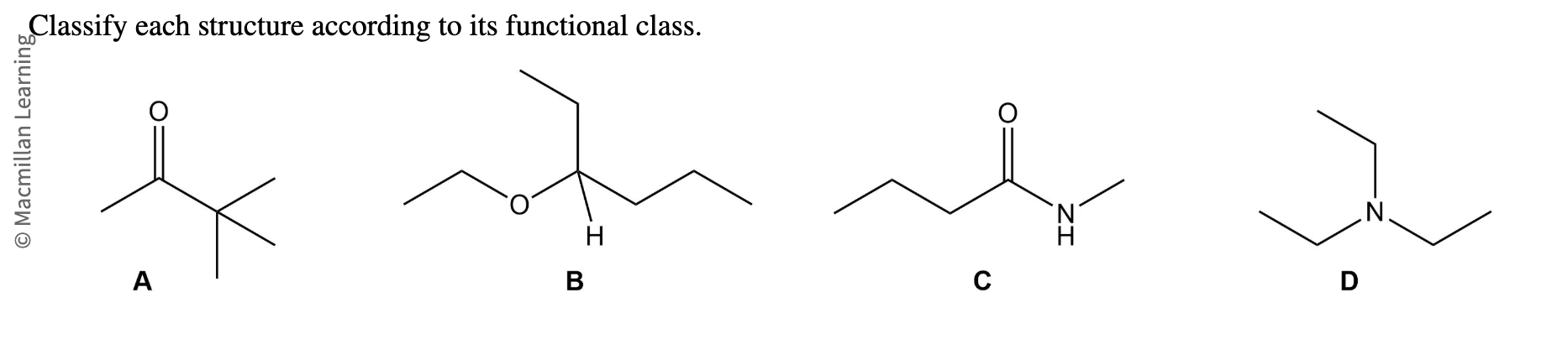
a,b,c,d?
a- ketone
b-ether
c-amide
d- amine
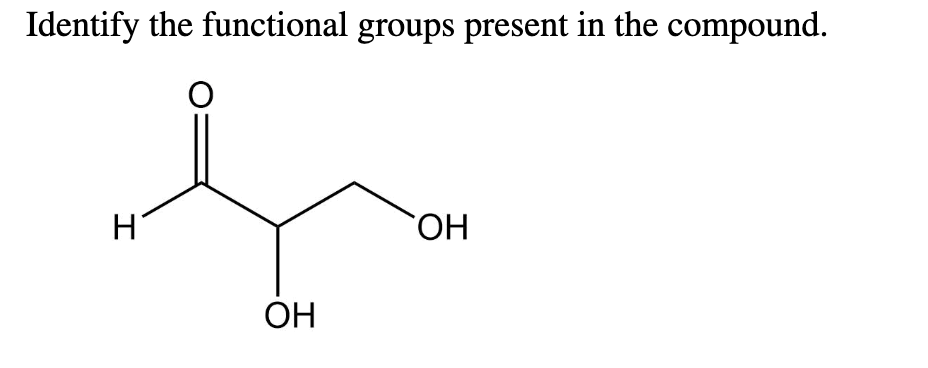
aldehyde
alcohol
aldehyde( c=o with at least 1 hydrogen atom attached)
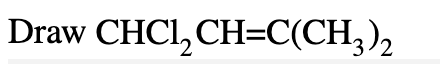
The highest mass in a mass spectrum is generally the molecular ion peak. The molecular ion and the molecule differ by an electron only, so they have the same mass. Thus, this compound has a molecular mass of 86 amu.
The mass of C2H3O is 43 amu (half the molecular mass), so the subscripts in the empirical formula should be multiplied by 2. The molecular formula of the compound is C4H6O2.
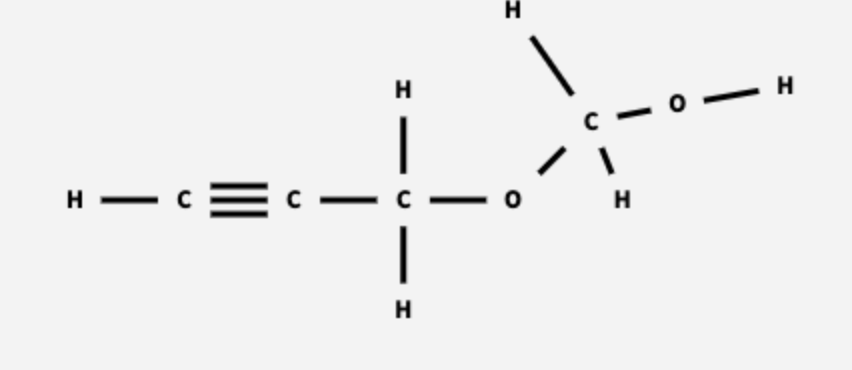
There are several plausible structures for this compound. The first structure should contain some combination of the functional groups alcohol (−OH), ether (C−O−C), and alkyne (C≡C). The second structure will contain two C=O groups, one on a terminal carbon atom (aldehyde) and one on a non‑terminal carbon atom (ketone).
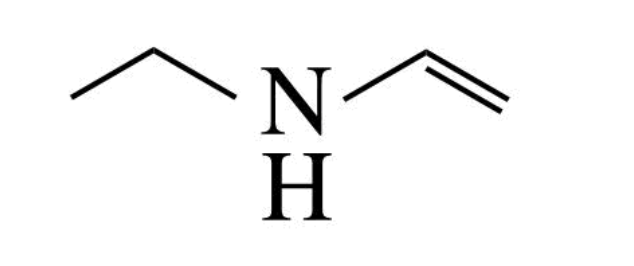
CH3CH2NHCHCH2
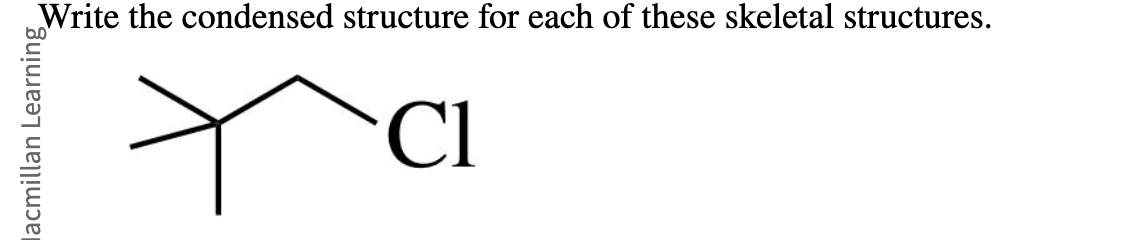
(CH3)3CCH2Cl
what is the difference between 2 resonance structures?
same molecular formula, arrangements of atoms, different arrangements of electrons
Compounds with different molecular formulas are not related.
Compounds with the same molecular formula, but a different arrangement of atoms are constitutional isomers.
Compounds that have the same molecular formula, same arrangement of atoms, but differ only in rotation are conformational isomers.

curved arrow can start from?
a pie bond or electron pair
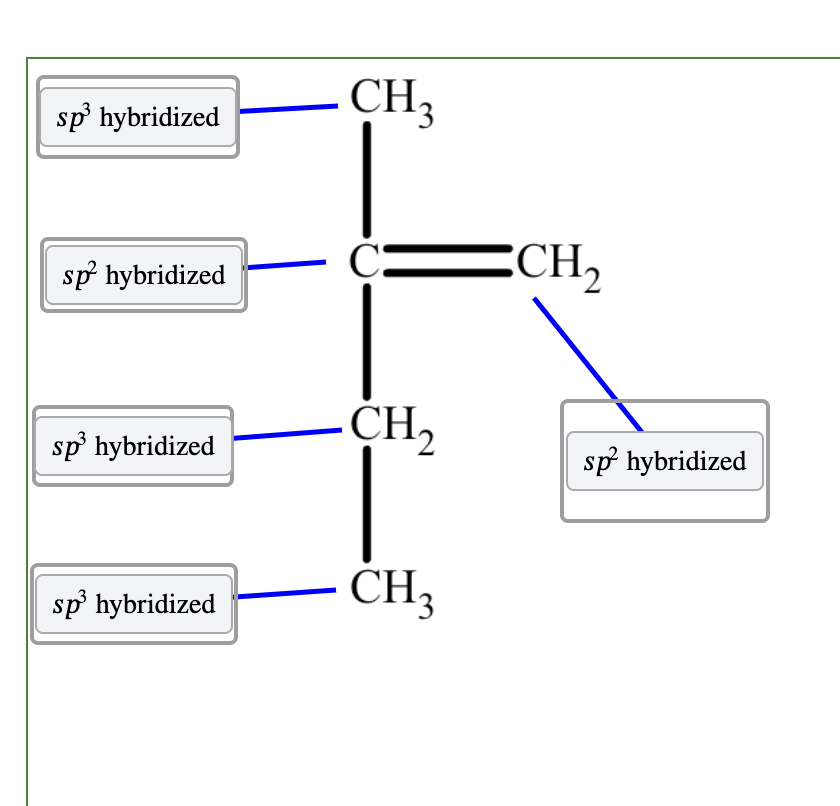
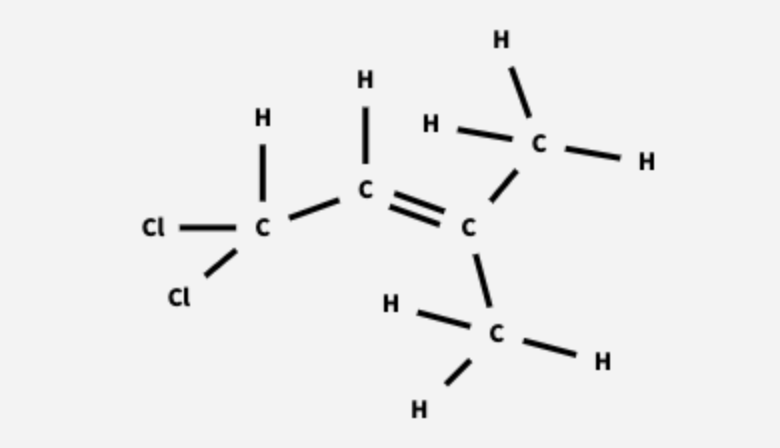
The top carbon atom has four groups bonded to it, three H atoms and one C atom, and it has 𝑠𝑝3 hybridization.
The two carbon atoms that share the double bond each have three groups bonded to them. They each have 𝑠𝑝2 hybridization.
The second carbon atom from the bottom has four groups bonded to it, two H atoms and two C atoms. It has 𝑠𝑝3 hybridization.
The bottom carbon atom has four groups bonded to it, three H atoms and one C atom, and it has 𝑠𝑝3 hybridization.
lewis base requires
a lone pair of electrons
base= donor
lewis acid requires
empty orbital
acid=accept
bronsted theory of acid
proton donor
bronsted theory of bases
proton acceptor
most soluable in water?
O OH, non polar
alkanes are not soluble
the __ projection is the most stable
staggered
local energy min
molecule is most stable point compared to surroundings (ex: in gauche)
global energy min
lowest energy among all conformations ex: anit conformation
gauche conformation
two big groups next to each other, max separated
antistag
two big groups opposite sides
lowest stability conformation
eclipsed
trans
Keep in mind that trans groups are on opposite faces of the ring.
angle strain
3 & 4 membranes rings
steric strain
close proximity of electrons of bulky groups
torsional strain
single bond that rotates from staggered to eclipse
cis
same side of the ring
more stable conformation cis/trans
cis-more stable conformation is the one in which the larger group is in the equatorial position.