ART APP (TRINAL EXAM)
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
97 Terms
elements of art
- are sort of like atoms in that both serve as building blocks for creating something. You know that atoms combine and form other things.
- are the basic components of art-marking. It is impossible to create a work of art without using at least one of the seven elements of art.
Line
- is an element of art. It is a mark made upon a surface.
- the mark's length must be longer than its width.
- There are many different types of lines, including horizontal, vertical, wavy, diagonal, and more.
- may be two or three-dimensional, descriptive, implied, or abstract.
Shapes
- These are areas of enclosed space that are two-dimensional.
- are flat, and can only have height and width.
Geometric Shapes
shapes that are mathematical, like circles and squares.
Organic shapes
- come from nature, like clouds and leaves.
- Henri Matisse uses a collection of organic shapes.
Space
- It deals with the illusion of depth on a flat surface.
- The element of space can be used in three-dimensional art as well.
Value
- This refers to the lightness and darkness of areas in an art work.
- White is the lightest value, while black is the darkest.
- halfway between these extremes is called middle gray.
Color
- is the most prominent element of design and is one of the most powerful and yet subjective elements in art.
- is an element of art made up of three properties: hue, value, and intensity.
Texture
- An element of art that refers to the way things feel, or look as if they might feel if touched.
- describes the surface quality of an artwork.
- is an important element of design because it engages the sense of touch as well as vision.
Actual texture
is primarily- though not exclusively - sculptural.
implied texture
is primarily used in two-dimensional works of art. (kind of texture)
Form
- An element of art that is three-dimensional and encloses volume; includes height, width and depth (as in a cube, a sphere, a pyramid, or a cylinder).
- may also be free flowing.
Design
- differs from art in that it has to have a purpose. Visually, this functionality is interpreted by making sure an image has a center of attention, a point of focus.
Balance
- is the distribution of the visual weight of objects, colors, texture, and space.
- If the design was a scale, these elements should be balanced to make a design feel stable.
symmetrical balance
The elements used on one side of the design are similar to those on the other side
asymmetrical balance
the sides are different but still look balanced.
radial balance
the elements are arranged around a central point and may be similar.
Emphasis
is the part of the design that catches the viewer attention.
(Usually the artist will make one area stand out by contrasting it with other areas. The area could be different in size, color, texture, shape, etc.)
Pattern
is the repeating of an object or symbol all over the work of art.
Repetition
- works with pattern to make the work of art seem active. -- - creates unity within the work of art.
Proportion
- is the feeling of unity created when all parts (sizes, amounts, or number) relate well with each other.
- When drawing the human figure, refer to the size of the head compared to the rest of the body.
Rhythm
- is created when one or more elements of design are used repeatedly to create a feeling of organized movement.
- creates a mood like music or dancing.
Variety
- is the use of several elements of design to hold the viewer's attention and to guide the viewer's eye through and around the work of art.
Unity
is the feeling of harmony between all parts of the work of art, which creates a sense of completeness.
artist
- often restricted to a person working in the fine arts (such as paintings, sculptures, or printmaking) and not the handicraft, craft, or applied art media.
art school
made a distinction between the fine arts and the crafts.
Art as representation (Aristotle)
- aristotle
- was not against literature as such; he stated that human beings are mimetic beings, feeling an urge to create texts art that reflect and represent reality.
- is not only imitation but also the use of mathematical ideas and symmetry in the search for the perfect, the timeless, and contrasting being with becoming.
Example: Imagine a sculpture that's perfectly shaped, or a building with beautiful, even columns. That's not just copying—it's using math and design to make something feel just right and peaceful.
art for art sake
- Emmanuel Kant
- the beauty possessed by the object is necessary, and that agreement as to the beauty would be universal.
- the status of aesthetic judgment is not empirical but logical, based upon the powers of human reason and rationality.
Example: Think of a beautiful sunset. You might say, "Wow!" and so might your mom, your friend, and even a stranger. Kant believed that true beauty makes most people feel the same way inside—even if no one says it out loud.
Art as Mimesis
- Plato
- all artistic creation is a form of imitation; that which really exists, in the 'world of ideas.'
- The concrete things man perceives in his existence are supernatural representations of this ideal type. Therefore, the painter, the tragedian, and the musician are imitators of an imitations, twice removed from the truth.
Imagine:
You draw a picture of a tree. The tree is real, but your drawing is just a copy of it.
Mimesis
- mimos (greek word) meaning to imitate
- The term carries a wide range of meanings, which include imitation, representation, mimicry, imitation, receptivity, the act of resembling, the act of expression, and the representation of the self.
decorative arts and crafts
- ceramic and studio pottery, mosaic art, mobiles, tapestry, glass arts, and others.
Example: A beautifully designed plate you can eat from, or a colorful basket that holds fruit.
fine arts
- refers to an art form practiced mainly for its aesthetic value and its beauty rather than its functional value.
Example: A painting of a sunset on your wall. You don't use it for anything—it's just there to look nice and make you happy.
Contemporary Arts
- The visual arts also include a number of modern art forms, such as assemblage, collage, mixed-media, conceptual art installation, happenings, and performance arts, along with the film based disciplines such as photography, video art, and animation, or any combination thereof.
Example:A painting made last year that shows how people feel about using phones all the time.
Emmanuel Kant
- "Beauty is that which, without any concept, is recognized as the object of necessary satisfaction."
the subject of art
- To a majority of people, the appeal of most works of art lies in the representation of familiar subjects.
- the satisfaction they get out of recognizing the subject or understanding the narrative content.
- refers to any person, object, scene or event described or represented in a work.
Example:
Let's say two people look at a painting:
One painting is just random colors splashed everywhere.
The other painting shows a mother holding a baby.
(Most people would probably say they like the second one more because they understand the subject: it's something real and emotional.)
still life
These are groups of inanimate objects arranged in an indoor setting

Landscapes, Seascapes, and Cityscapes
Artists have always been fascinated with their physical environment.

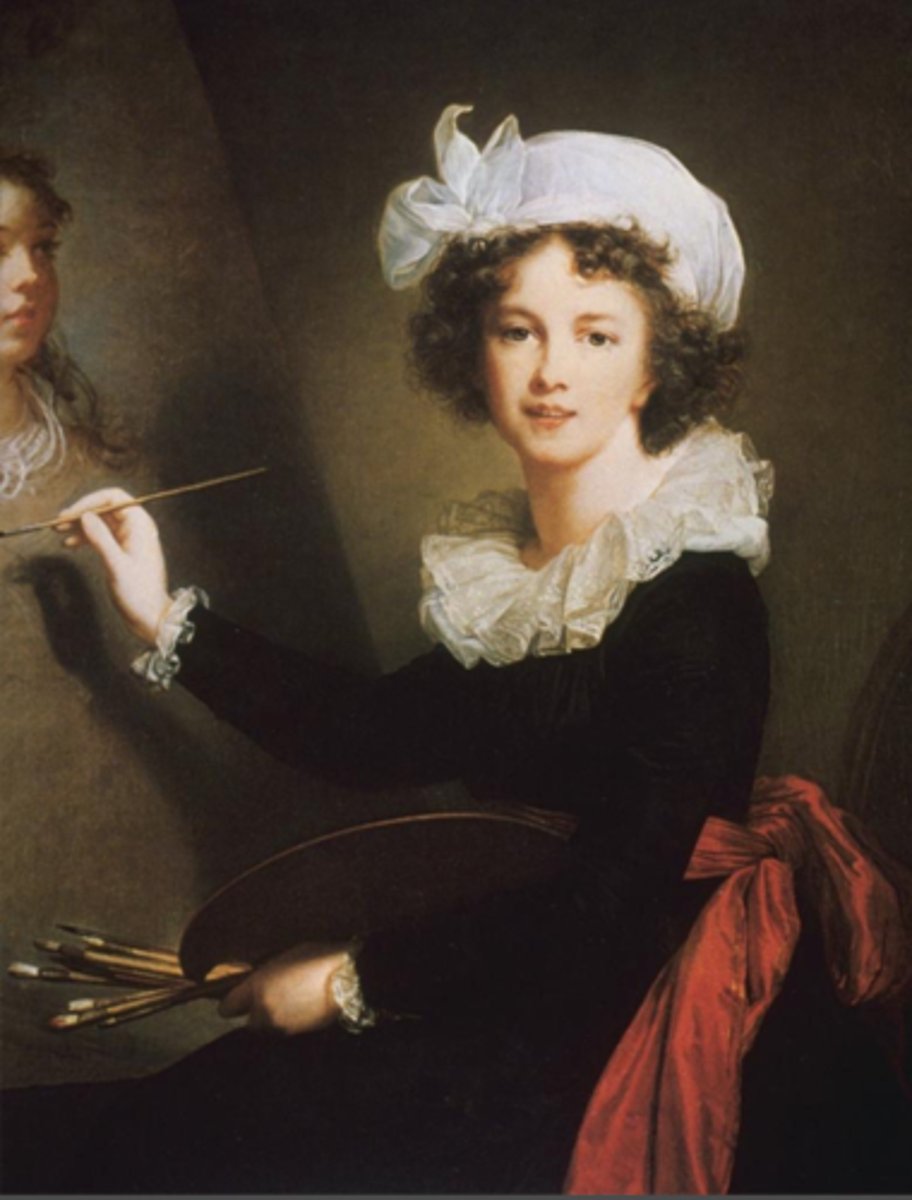
portraits
- these are realistic likeness of a person in sculpture paintings drawing or print

figures
- The sculpture's chief subject has traditionally been the human body, nude or clothed.
- The body's form, structure, and flexibility offer the artist a big challenge to depict in variety of ways.

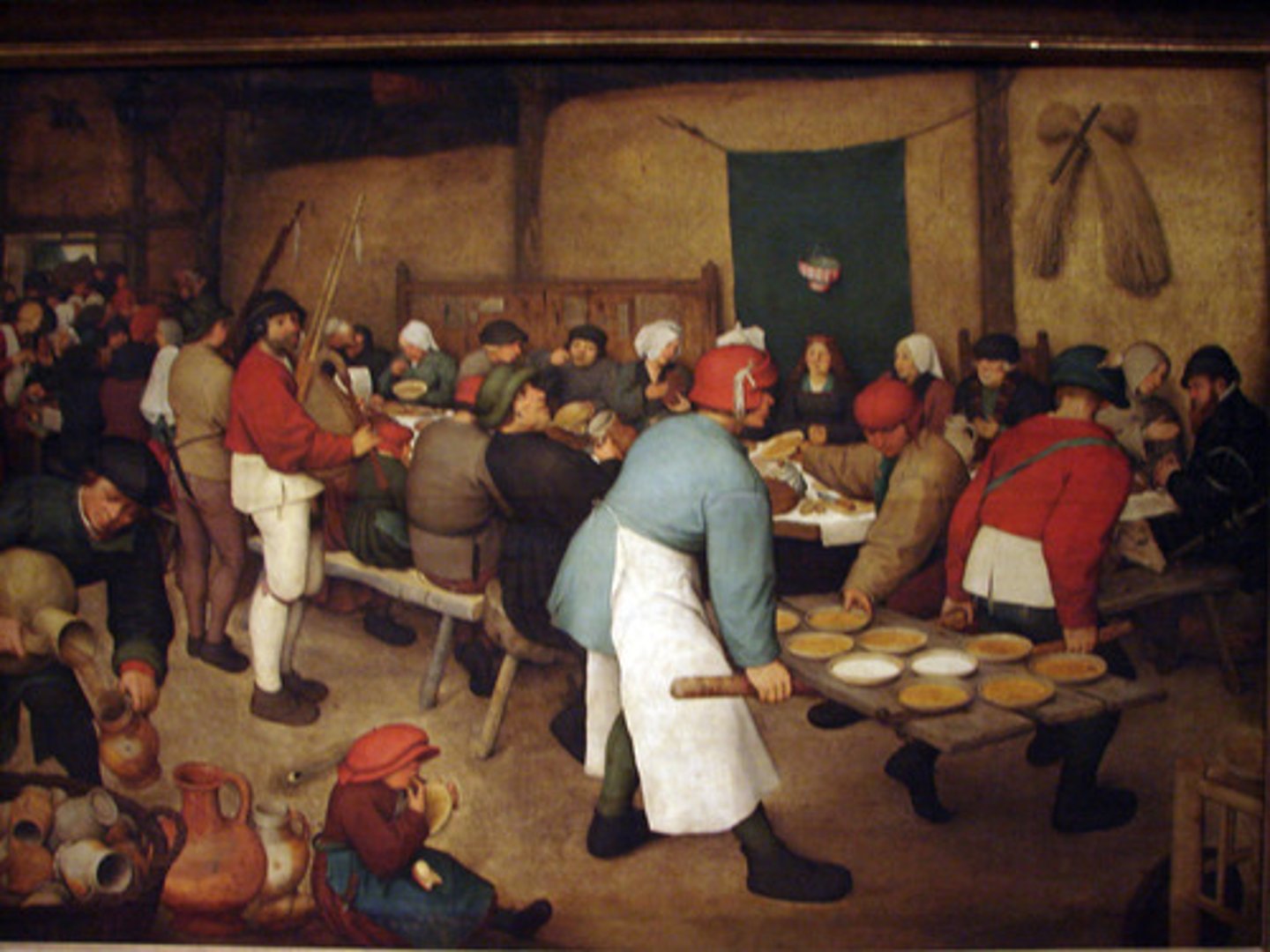
everyday life
observation of people going about their usual ways and performing their usual tasks.

Religion and Mythology
Most of the world's religions use the arts to aid and worship, to instruct, to inspire feelings of devotion, and to impress.

factual meaning
- the literal meaning or the narrative content, or the work.
- Objects presented are easily recognized.
ex: Stones, rivers, house, histories, recorded later
Conventional Meaning
refers to the special meaning that a certain object or color has in a particular culture or group of people.
ex: flag symbols of a nation, religious symbols
Subjective Meaning
- any personal meaning consciously or unconsciously conveyed by the artist using a private symbolism which stems from his own association of certain objects, actions or colors with past experiences.
ex: An artist paints a small, blue bird sitting alone on a tree branch.
To most people, it just looks like a pretty bird.
But to the artist, that blue bird represents their childhood loneliness, because when they were little, they used to watch birds alone at the park when they felt sad.
non-representational or non-objective
- These are those arts without reference to anything outside themselves.
- It has no recognizable object.
- it is abstract; it does not represent real objects
- It is content and concerned with how the artwork is depicted
representation arts or figurative arts (objective)
- represents objects or events in the real world, usually looking easily recognizable.
- it uses form and is concerned with what is to be depicted in the artwork.
Visual Arts
- are art forms that create works that are primarily visual in nature, such as ceramics, drawing, paintings, sculptures, printmaking, designs, crafts, photography, video, film making and architecture.
ars
- latin word which means a craft or specialized form of skill, like carperntrt or surgery.
art
is primarily visual that expresses ideals about our human experience and the world around us.
humanities
- It refers to academic disciplines that study aspects of human culture and society.
- encompass a broad range of fields, including art, literature, philosophy, history, and music, among others.
Philosophy
Love of wisdom; uses logic and reason to understand life and existence.
Example: Debating “What is the meaning of happiness?” in class.
Builds critical thinking, clear writing, logical analysis, and reasoning—useful in any career and life.
Example: Using philosophical reasoning to resolve workplace conflict.
Art History
Study of art objects in historical and stylistic context.
Example: Researching how Gothic architecture developed in medieval Europe.
Aesthetics
- Branch of philosophy studying beauty and the sublime.
Example: Discussing why sunsets are considered beautiful.
Imagination
Thinking of something not present or real. Example: Imagining flying cars.
Creativity
Doing something meaningful with imagination.
Example: Designing a prototype for a flying car.
Physical function
Created to perform service
Form and Function
The function of an object is generally essential in the basic form that it takes.
(A chair is so designed as to allow the seated body to rest comfortably on it. The shapes, sizes, and different parts are harmoniously related to one another and integrated into an object that fulfills and tells about their particular purpose.)
Architecture
The design of the building is determined primarily by its operational function.
(What is the building for? Who are going to use it? How many are they? The design that a building takes is also adapted to the climate of the region.)
Community Planning
involves the efficient organization of buildings, roads, and spaces so that they meet the physical and aesthetic needs of the community.
Artists
- are individuals with the talent and skills to conceptualize and create works primarily for aesthetic enjoyment.
Artisan
- are manual workers who produce functional items with beauty and craftsmanship.
- They may create decorative or utilitarian art such as quilts, baskets, jewelry, ironwork, and glass objects.

Medium
- is the material an artist uses to express thoughts or feelings.
- Artists choose based on ease of handling, suitability to the plan, and ability to convey their intended qualities.
- uses to express ideas; chosen for suitability and expressive potential.
Examples: include visual arts, auditory arts, and combinations of both.
Techniques
- refer to how artists control their mediums to achieve specific effects.
- differ even within the same medium, producing unique styles and expressions.
- The way an artist handles the medium to achieve desired effects; personal
style affects results.
Encaustic
Uses hot wax and pigments on wood surfaces.

Fresco Secco
Painting on dry plaster.

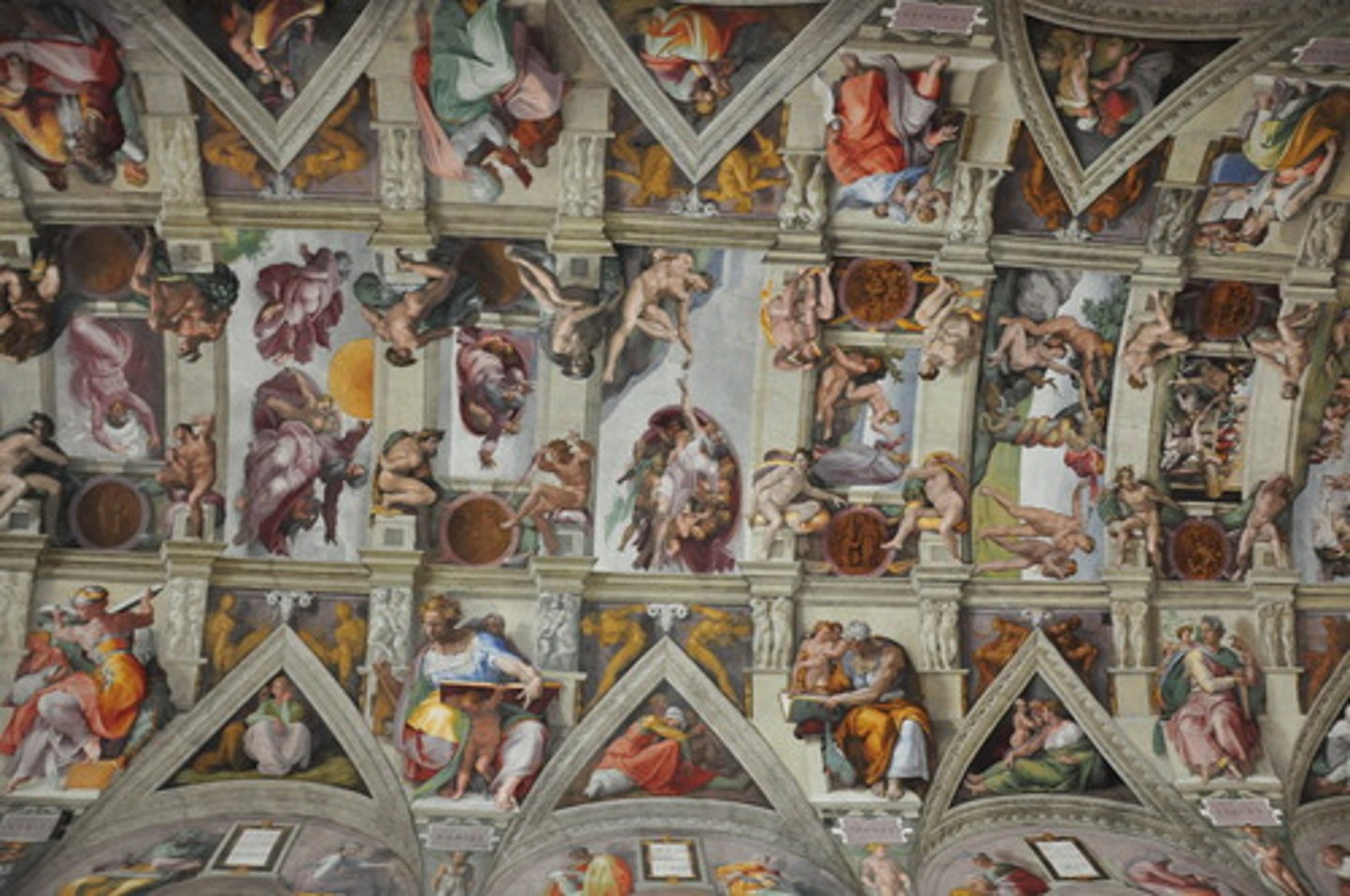
True Fresco
Painting on wet plaster, as in Michelangelo's Sistine Chapel.

egg tempera
Pigment mixed with egg yolk, producing bright, opaque colors.

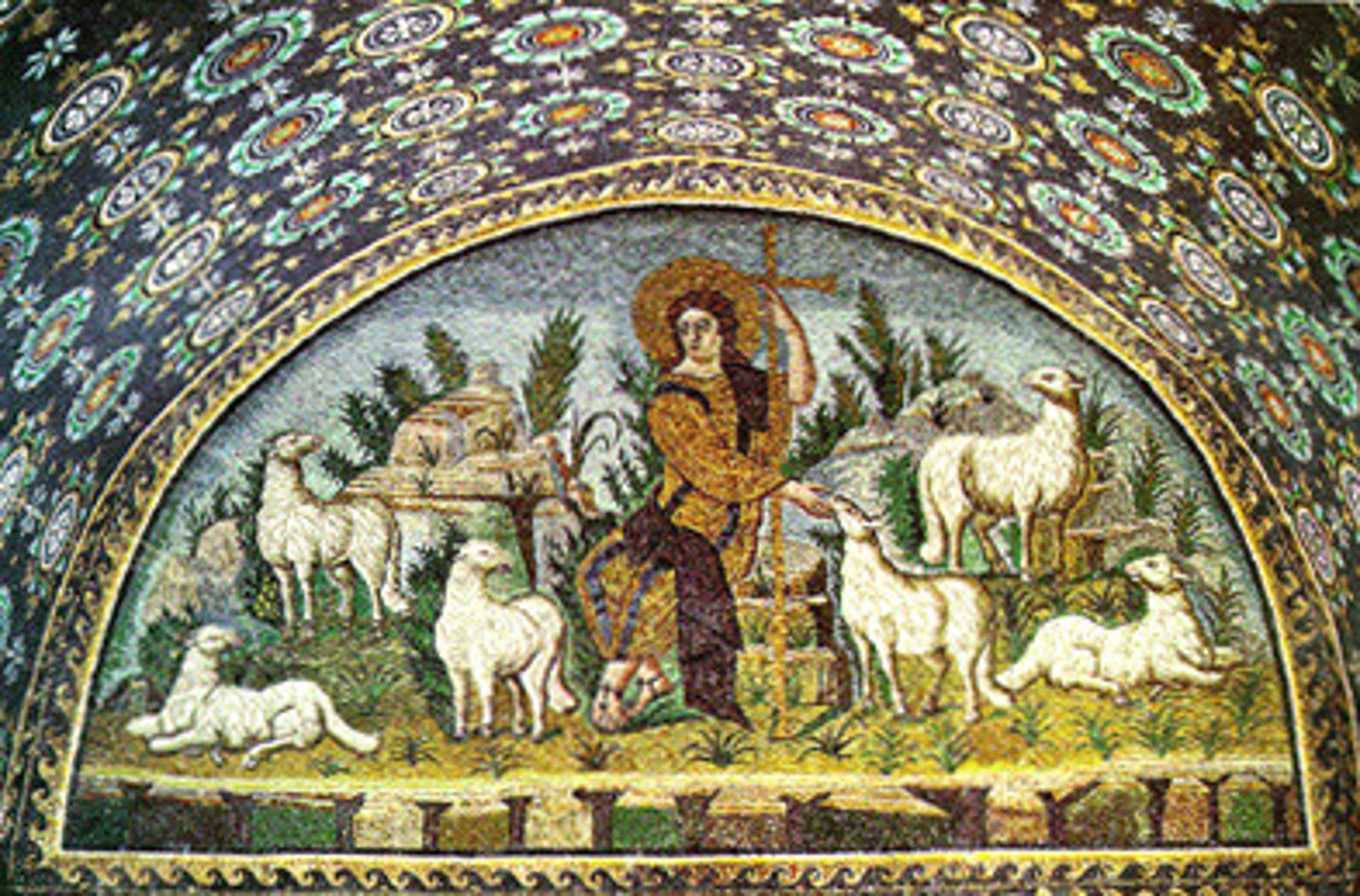
Mosaic
Designs created with small pieces of glass, stone, or ceramics.

Oil Paint
Pigments mixed with oil; slow drying allows blending.

Watercolor
Transparent washes of pigment in water.

Acrylic
Fast-drying synthetic paints.

Collage
Combining pasted materials and painted areas.

Drawing
The most basic and portable artistic method.

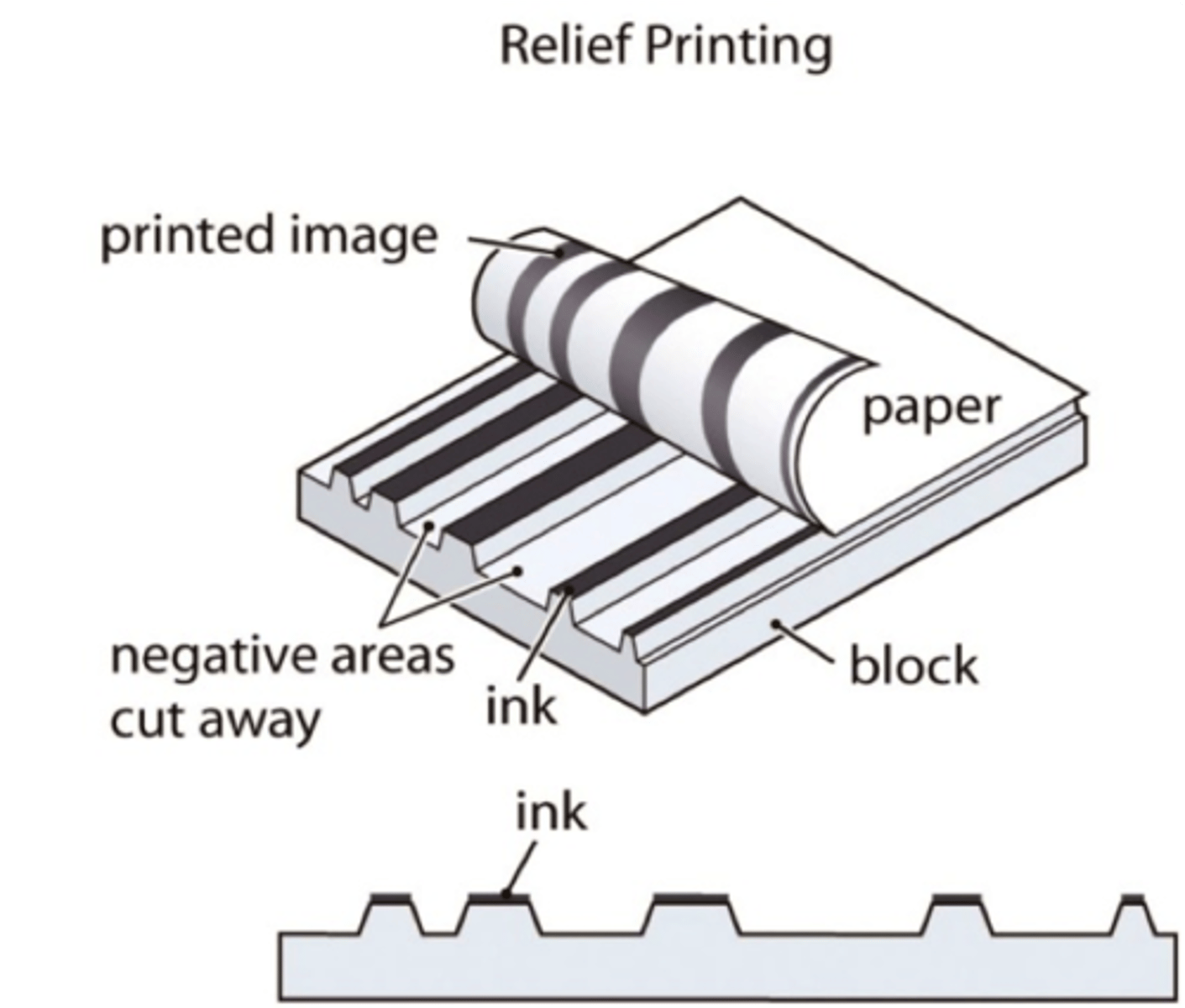
Relief
Carved surface areas hold ink.
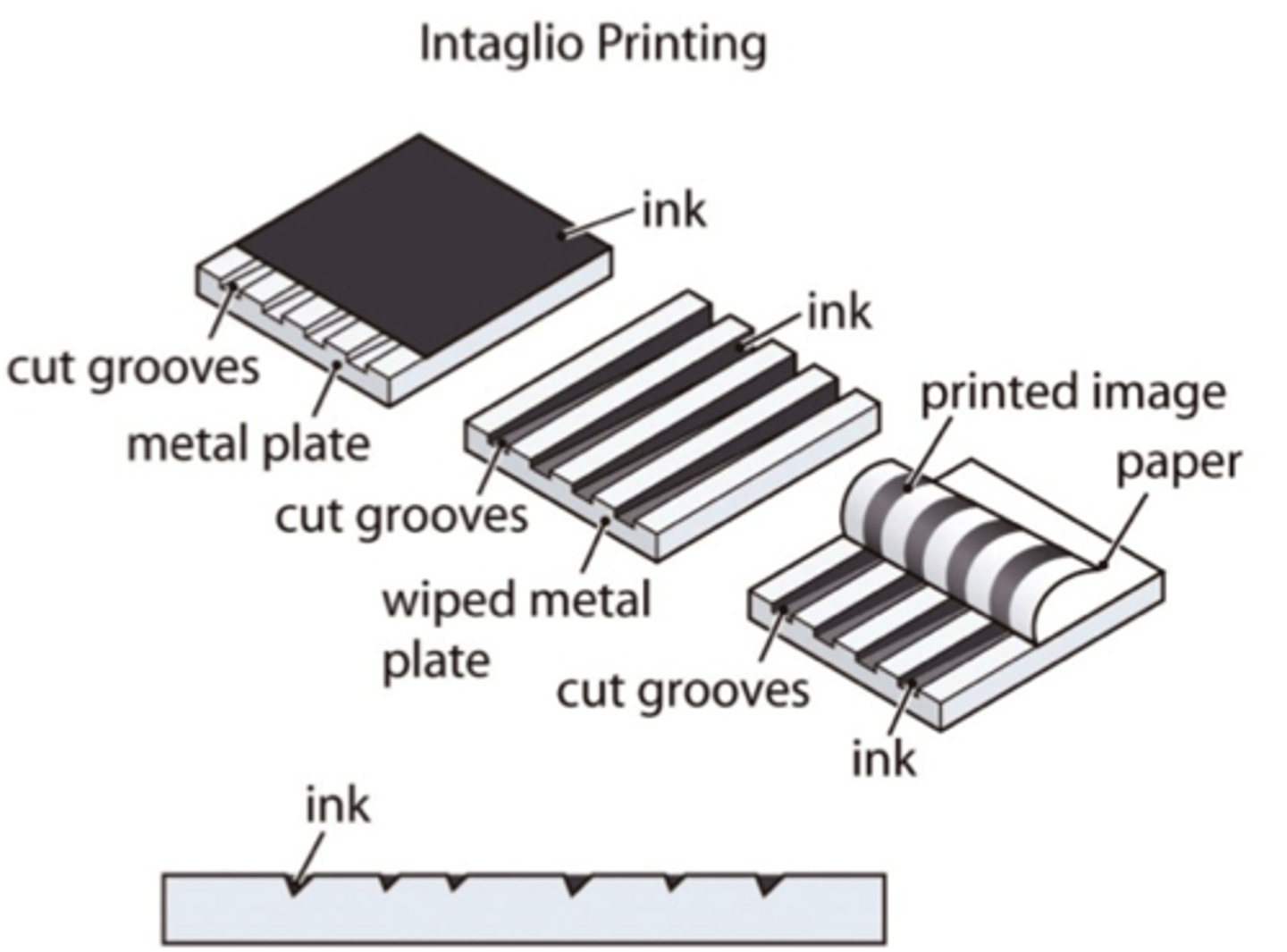
Intaglio
Ink collects in scratches or grooves.
Stencil
Ink passes through a mesh.

Woodcut
Images carved on wood blocks

Engraving
Designs cut into metal plates with a burin
GAMBA
honors Filipino folk and indigenous artists preserving traditional culture.
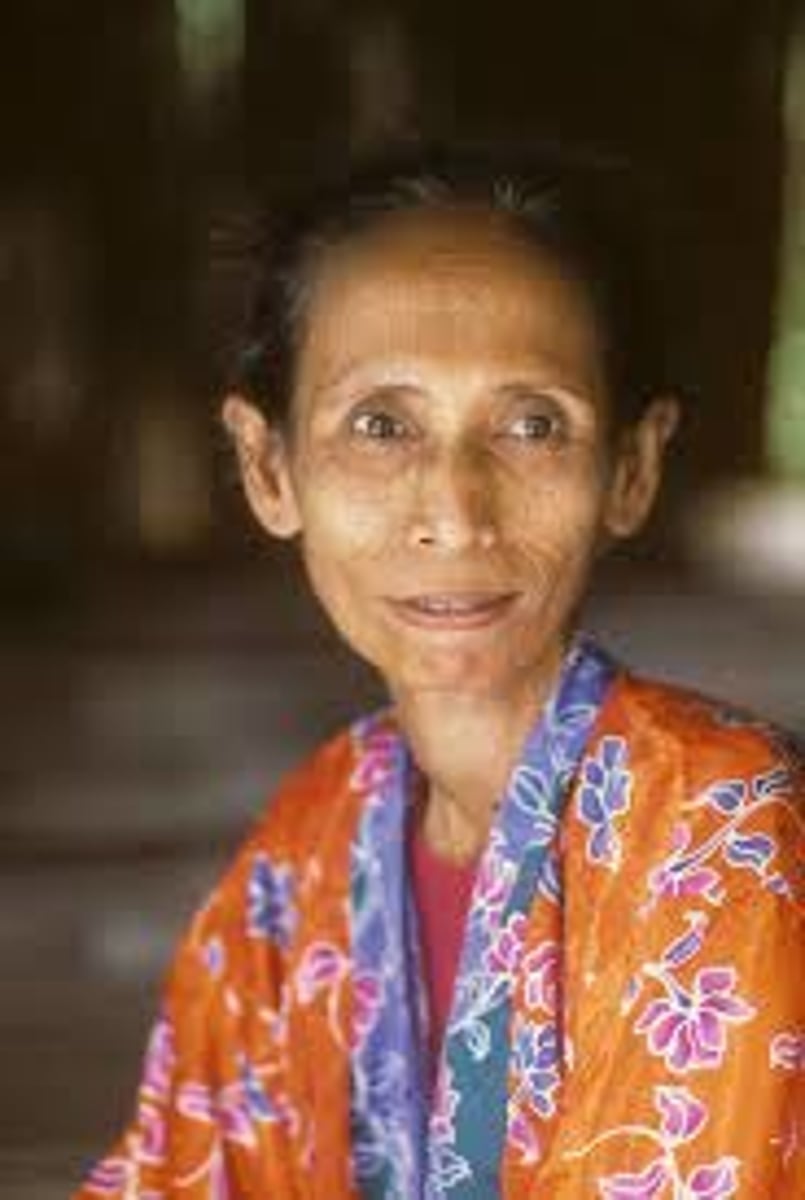
Darhata Sawabi
(Tausug weaving)

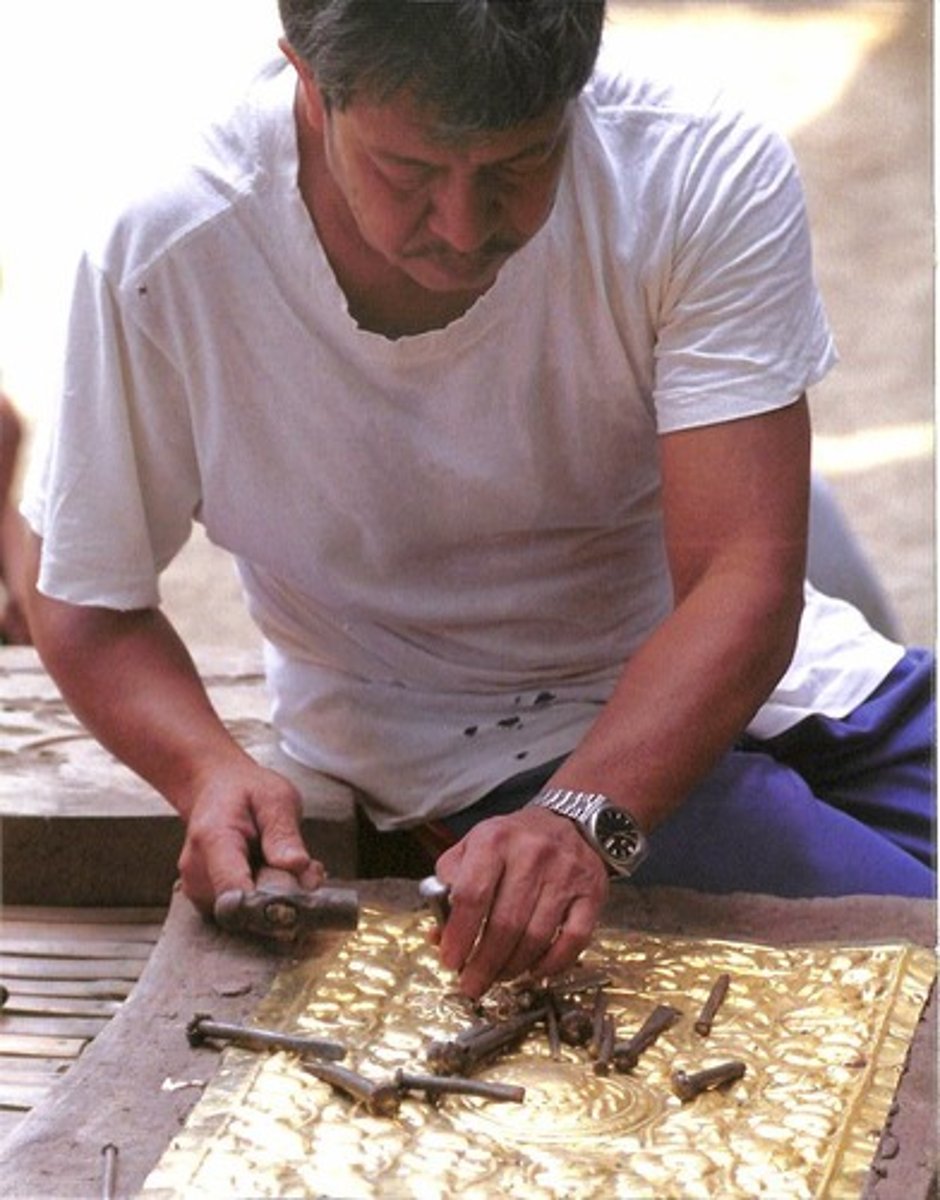
Eduardo Mutuc
(religious and secular art in metal and wood)

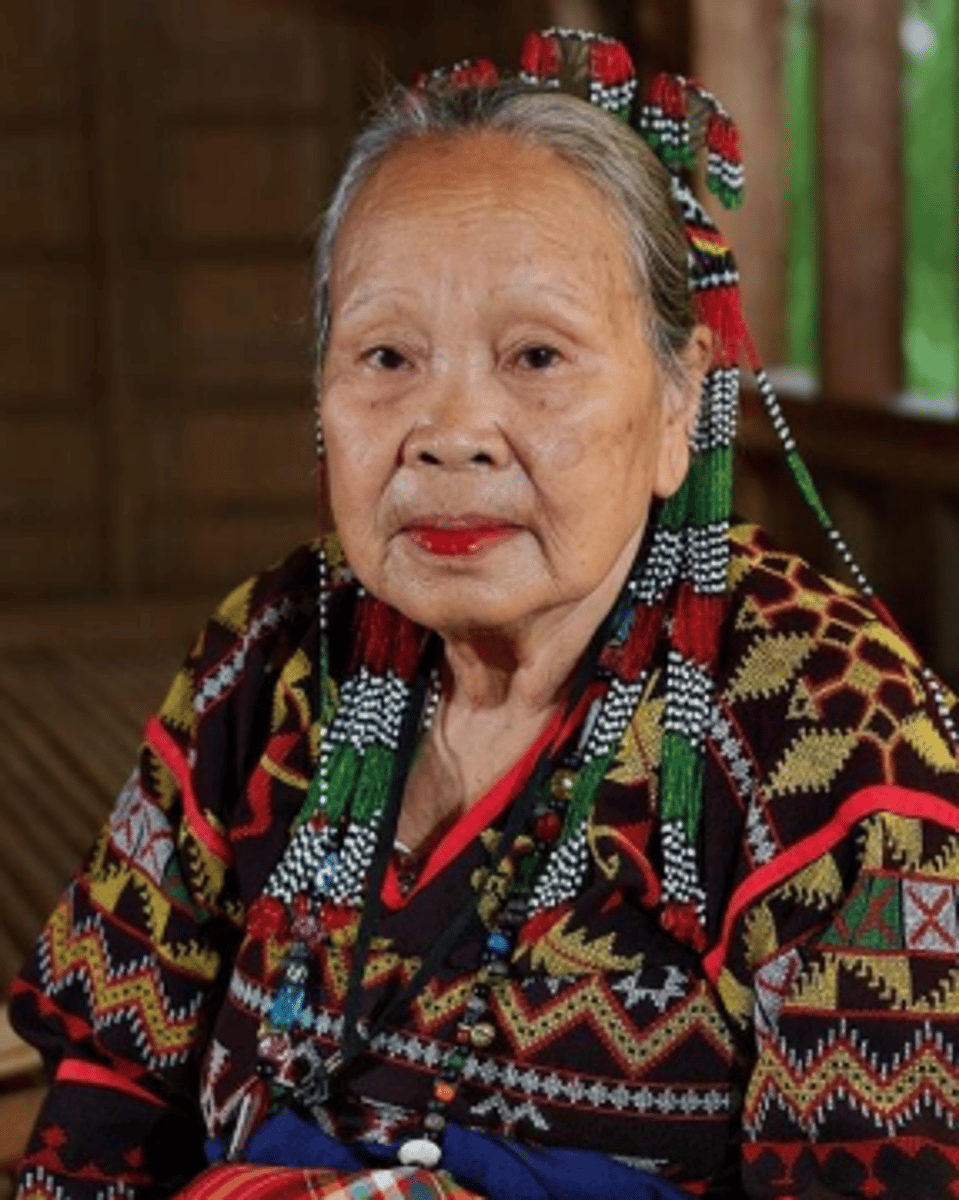
Lang Dulay
(T'boli weaving of T'nalak)

Performance art
integrates time, space, the performer's presence, and audience interaction.
Interdisciplinary art using time, space, the performer’s body/presence, and audience interaction.
Transcreation
- is adapting messages from one language to another while keeping intent, tone, and cultural context.
- It is widely used in advertising, marketing, and media to resonate with target audiences.

Lang Dulay
– T’nalak weaving
Federico Caballero
– Epic chanting
Salinta Monon
– Inabal weaving
Ginaw Bilog
– Ambahan poetry
Masino Intaray
– Palawan music and storytelling
Opera
– Music, drama, and theatre combined, often in opera houses.
Music
– Organized sound with elements like rhythm, pitch, timbre.
Dance
– Rhythmic movement for expression, ritual, or entertainment.
Drama
– Fictional stories enacted by actors.
Spoken Word
– Performed poetry, storytelling, speeches.
Two-dimensional (2D)
– Painting, drawing, printmaking, photography.
Three-dimensional (3D)
– Sculpture, architecture, crafts.
Auditory Arts
– Music and sound-based time arts.