Enzymes Clinical Chemistry
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
what are some non-protein components of enzymes
holoenzyme (completely functional enzyme)
apoenzyme (protein portion of an enzyme)
co-factor (non-protein portion of an enzyme)
cofactors
metallic elements that help activate enzyme
ex) iron, zinc, and magnesium
coenzyme
vitamin-derived molecules who participate directly in the reaction
NAD and FAD
prosthetic groups
a tightly-bound non-protein portion of the enzyme
heme
how does temperature affect the rate of a reaction?
if too low → less enzyme-substrate binding = slower rate
falsely LOWERED results
if too high → more enzyme-substrate binding = faster rate
falsely ELEVATED results
what are the different kinds of inhibitors
reversible
competitive
non-competitive
uncompetitive
irreversible
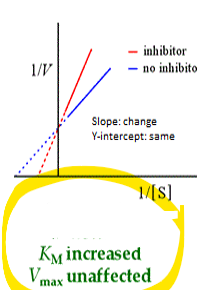
what kind of enzyme inhibition is this
•Increased Km, no change in Vmax
Competitive
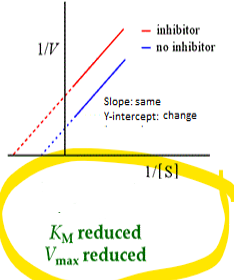
what kind of enzyme inhibition is this
•Reduced Km, Reduced Vmax
uncompetitive inhibition
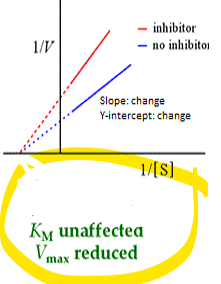
what kind of enzyme inhibition is this
•No change Km, Reduced Vmax
Noncompetitive (mixed) inhibition
what is the equation for calculating international units (IU)
(absorbance/minute) x 106/(a)(b) x total volume/sample volume
creatine kinase (CK)
associated with regeneration and storage of ATP
what are the 3 CKs
CK-1 : CK-BB
CK-2 : CK-MB
CK-3 : CK-MM
•CK-BB
•Brain type
•CK 1
what can CK-BB indicate
CVA (cerebrovascular accident)
seizure
nerve degeneration
•CK-MB
•Mostly found in Cardiac Muscle (Heart)
•hybrid type
•CK 2
what can CK-MB indicate
myocardial infarction (MI)
CK-MM
•Striated Muscle type
•Skeletal Muscle (rhabdomylosis)
•CK 3
what can CK-MM indicate
skeletal muscle disorders such as muscular dystrophy or crushing injury
What Kinetic method belongs to CK
Measures the NADH or NADPH at 340nm
hexokinase & G6PDH coupling enzyme
hemolysis will cause false increase
cannot use EDTA, oxalate, citrate
need non-hemolyzed serum or heparinized plasma
What Kinetic method belongs to lactate dehydrogenase (LDH/LD)
Measures the NADH or NADPH at 340nm
pyruvate & LD coupled
what is elevated LDH associated with
heart problems
liver disease
hematologic and neoplastic disorders
what are the 2 types of transaminases
Aspartate transaminase (AST)
Alanine transaminase (ALT)
aspartate aminotransferase (AST)
•Measure NADH or NADPH at 340nm. Produces oxalacetate and L-glutamate.
•Glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase is the other name.
alanine transaminase (ALT)
•Measure NADH or NADPH at 340nm. Produces oxalacetate and L-glutamate.
•Glutamic pyruvic transaminase is the other name.
alkaline phosphatase (ALP)
•Measures release of a chromogenic para-nitrophenol and inorganic phosphate at 405nm in the presence of ALP.
acid phosphatase (ACP)
•Y-glutamyl-p-nitroanilide (substrate) is used in the indicator reaction. Produces a para-nitrophenol and inorganic phosphate at 405nm in the presence of ACP.
what conditions are associates with ACP
Monitors bone disease, forensic ID of seminal body fluid, monitors prostate cancer
gamma-glutamyltransferase (GGT)
“gotta get tequila”
Y-glutamyl-p-nitroanilide (substrate) is used in the indicator reaction. It produces a p-nitroaniline at 405nm
amylase
•Measures an increase in iodine concentration from starch catabolism. Measures the disappearance or appearance of the starch or by product
lipase
•Contains a triglyceride substrate and has a choline group in it.
•Cholinesterase hydrolyzes and breaks acetylcholine into its acetate and choline components…..Acetylcholinesterase
Acetylcholinesterase or cholinesterase enzyme = Decreased levels are clinically significant in pesticide exposure
what condition is associated with ALP and LD increase?
bone disease or breakdown
what condition is associated with CK and LD increase?
•Think heart, MI
what condition is associated with •ALP, ALT, AST, LD increase?
hepatitis, think liver issues
what condition is associated with amylase increase?
acute pancreatitis or salivary gland lesions (mumps)
what condition is associated with lipase increase?
acute pancreatitis (lasts longer & more specific than amylase)
what condition is associated with an ALP increase?
typically due to bone cancer and bone disease in general
what condition is associated with AST, ALT, ALP, LDH, ALK increase?
•hepatitis (liver associated issues)
what condition is associated with increase in lipase?
acute pancreatitis (more specific and lasts longer)
what condition is associated with an increase in amylase?
acute pancreatitis
what condition is associated with increase in CK?
•myocardial infarction, heart muscle issue