thermodynamics quiz
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
open systems
like an open water bottle - allow transfer of matter and energy
closed systems
like a closed water bottle - do not allow transfer of matter, but do allow transfer of energy
Isolated systems
do not allow transfer of matter nor energy. Bomb calorimeters are isolated systems due to being insulated.
state functions
are variables that define how a system starts from howit ends. We calculate final-initial with state functions
path functions
follow the mechanism, or the path, for a given process
extensive property
a property that depends on the extent or size of a system. eg: volume, mass, moles, energy
intensive properties
a property that defines a system. This is not additive. If you ratio two extensive properties, you get out an intensive property. eg: temp, density, prssure
generally if something leaves the system the sign is
(-)
generally if something enters the system, the sign is
(+)
q & w r negative when
energu leaves the system
q & w r positive when energy
enters the system
∆G is negative =
spontaneous
∆G is positive =
non-spontaneous
∆S is positive =
increasing disorder
∆S is negative
increasing order
∆H is negative =
exothermic
∆H is positive=
endothermic
Heat is
chaotic energy, whereas work is a concerted flow of energy that can be easily controlled/guided
Both heat & work r PATH functions, meaning
the methods you take to heat something, change its volume, etc affect the outcome
1st law, ΔUuniv=
0, so energy is conserved
ΔU =
q + w
U is all the sources of
potential and kinetic energy in a system
calorimetry allows ΔUsys=
- ΔUsurrondings
ΔH =
ΔU + PΔV
in a closed system, v is constant so
ΔU = qv because no PΔV work
In an open system, P is constant so
ΔH = qp
W =
-PΔV = -ΔngRT
For a chemical reaction in which there is a change in # ofgas molecules, it is easy
to determine PΔV work
general equation for enthalpy
H=U+PV
change in enthalpy
ΔH=ΔU+PΔV
q
heat
w
work (energy transfer due to forces like expansion or compression)
ΔG
change in Gibbs free energy (determines spontaneity)
ΔS
change in entropy (disorder or randomness)
ΔH
change in enthalpy (heat at constant pressure)
If products are greater than reactants, energy enters or exits & is ΔU positive/negative
enters, positive
if products are less than reactants, energy enters/exits & is ΔU positive/negative
exits, negative
parts of a bomb calorimeter
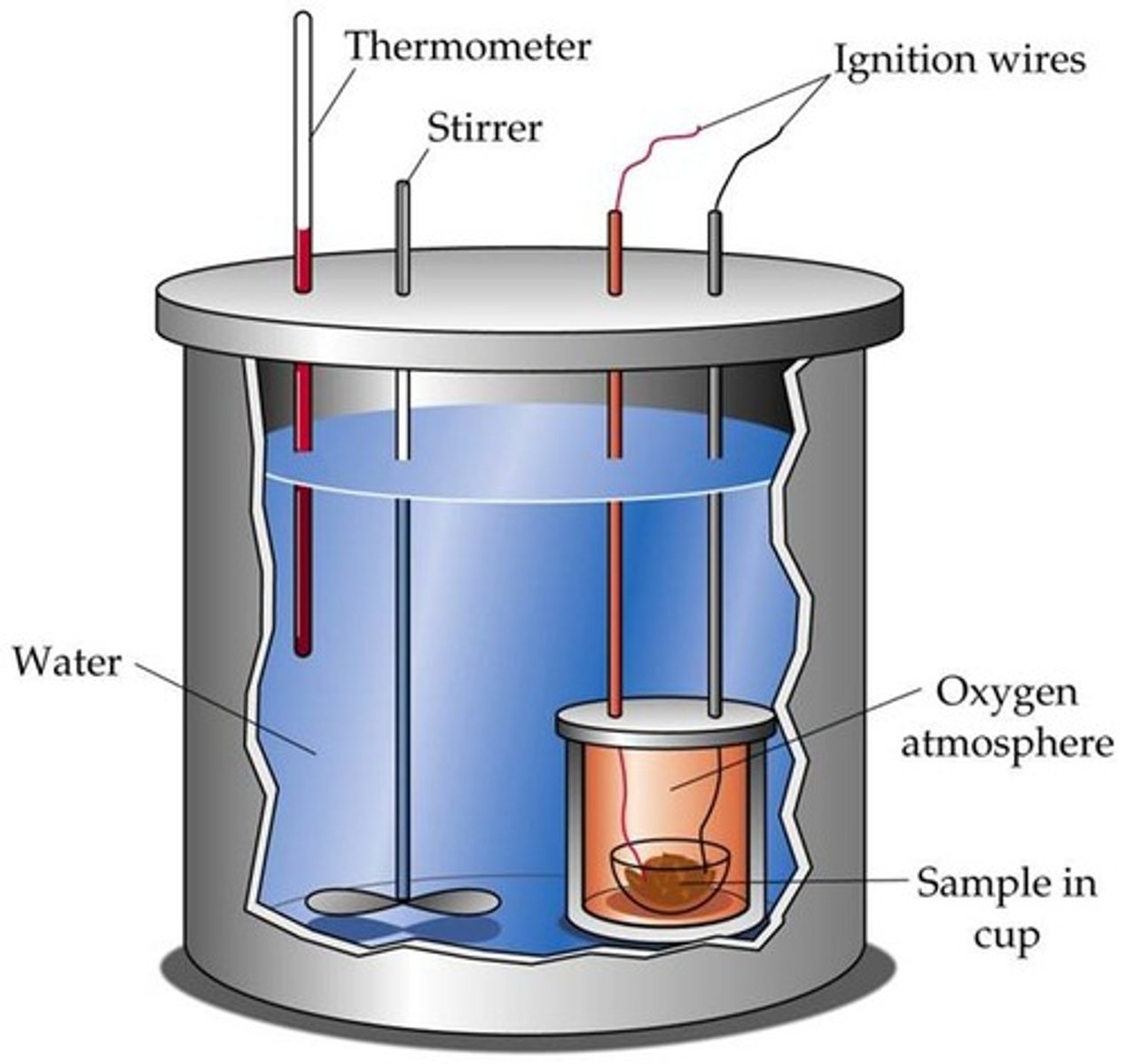
whats does igniting the bomb calo0rimeter do
starts the reaction of the sample
the water serves as a ______ _____ in order to measure the temp change
heat sink
the setup needs constant stirring to ensure accurate
ΔT
Bomb calorimeters measure ____ ____ at _____ ______ (ΔU = qV)
heat change, constant volume
bomb calorimeters arent isolated so they arent sufficiently isolated for heat change from ΔT is
completely accurate, they arent completely isolated bc only universe can truly be isolated completely
q=
mC∆T+CΔT. mC∆T is water, C∆T is calorimeter
qsys=
-qsurr
f given multiples (moles or #
items), then convert to PER
____ or PER ____
mole, item
specific heat capacity is ____ proportional to temp
inversely