Unit 6: (6.6) Nuclear Energy
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Radioactivity
The spontaneous emission of radiation by an unstable atomic nucleus such as uranium-235.
Uranium-235
A radioactive isotope used to fuel most nuclear fission reactors.
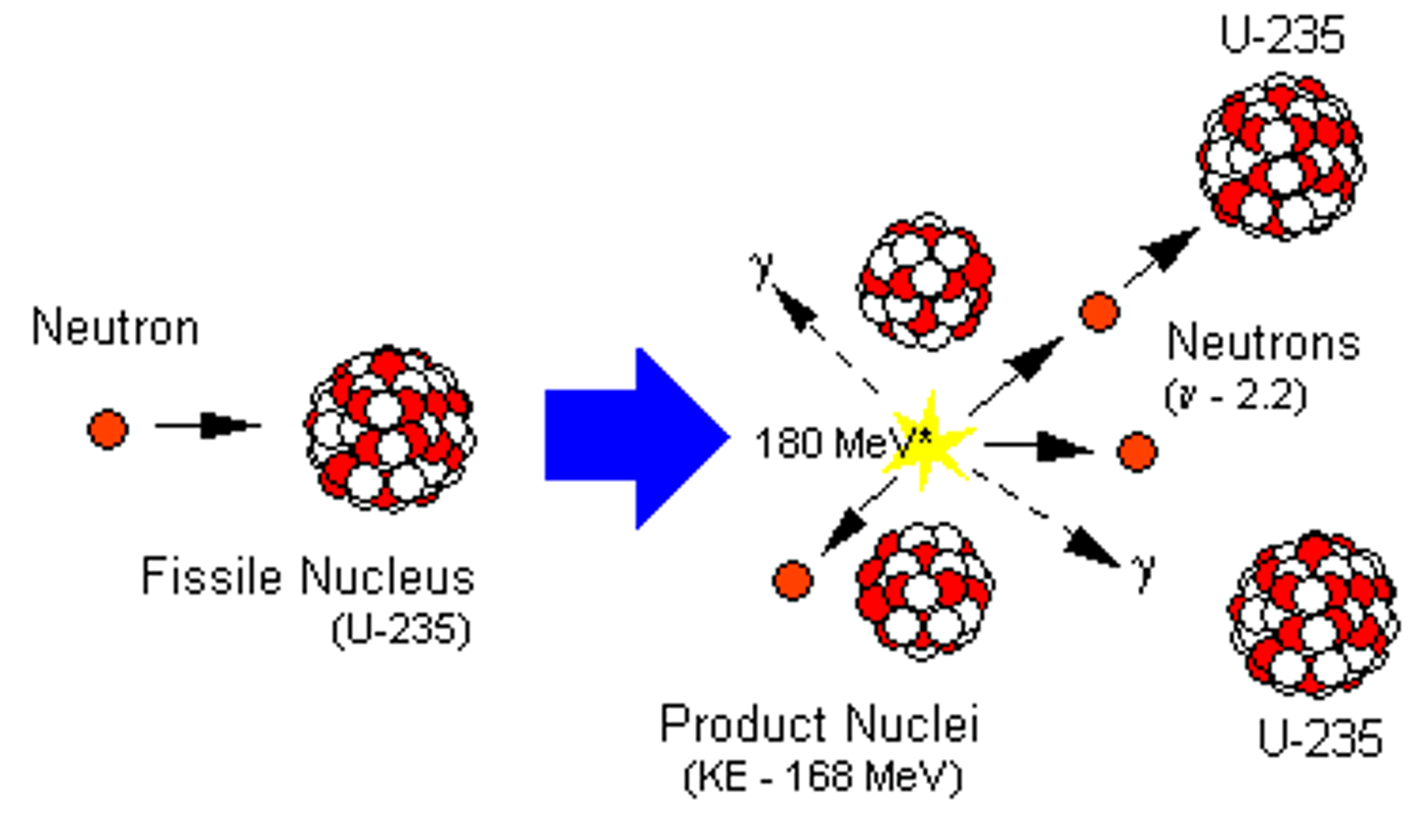
Fission
The splitting of an atomic nucleus with neutrons in order to release energy. The energy given off can be used to heat water into steam, to turn a turbine and power an electric generator.
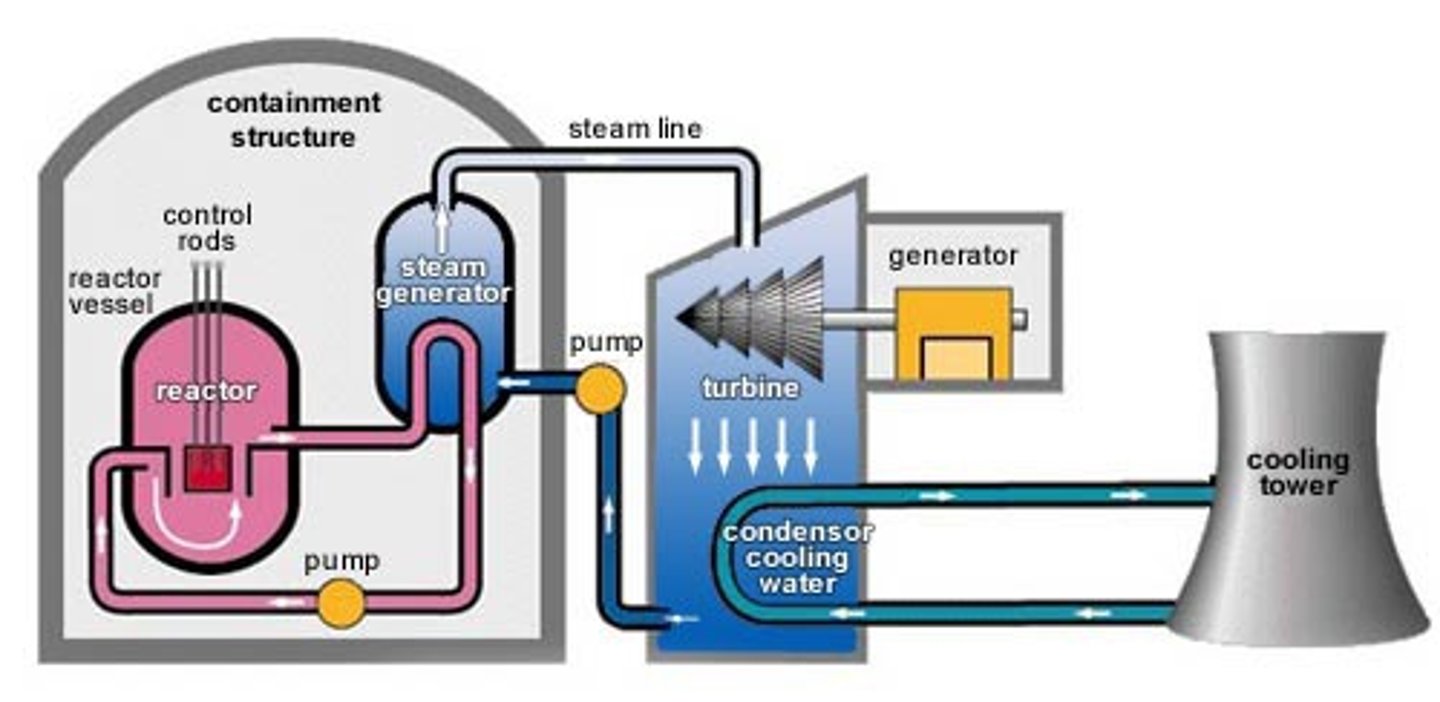
Reactor core
the thick steel vessel used to contain nuclear fuel rods in a nuclear power plant. Fission reaction occurs here to heat water into steam.
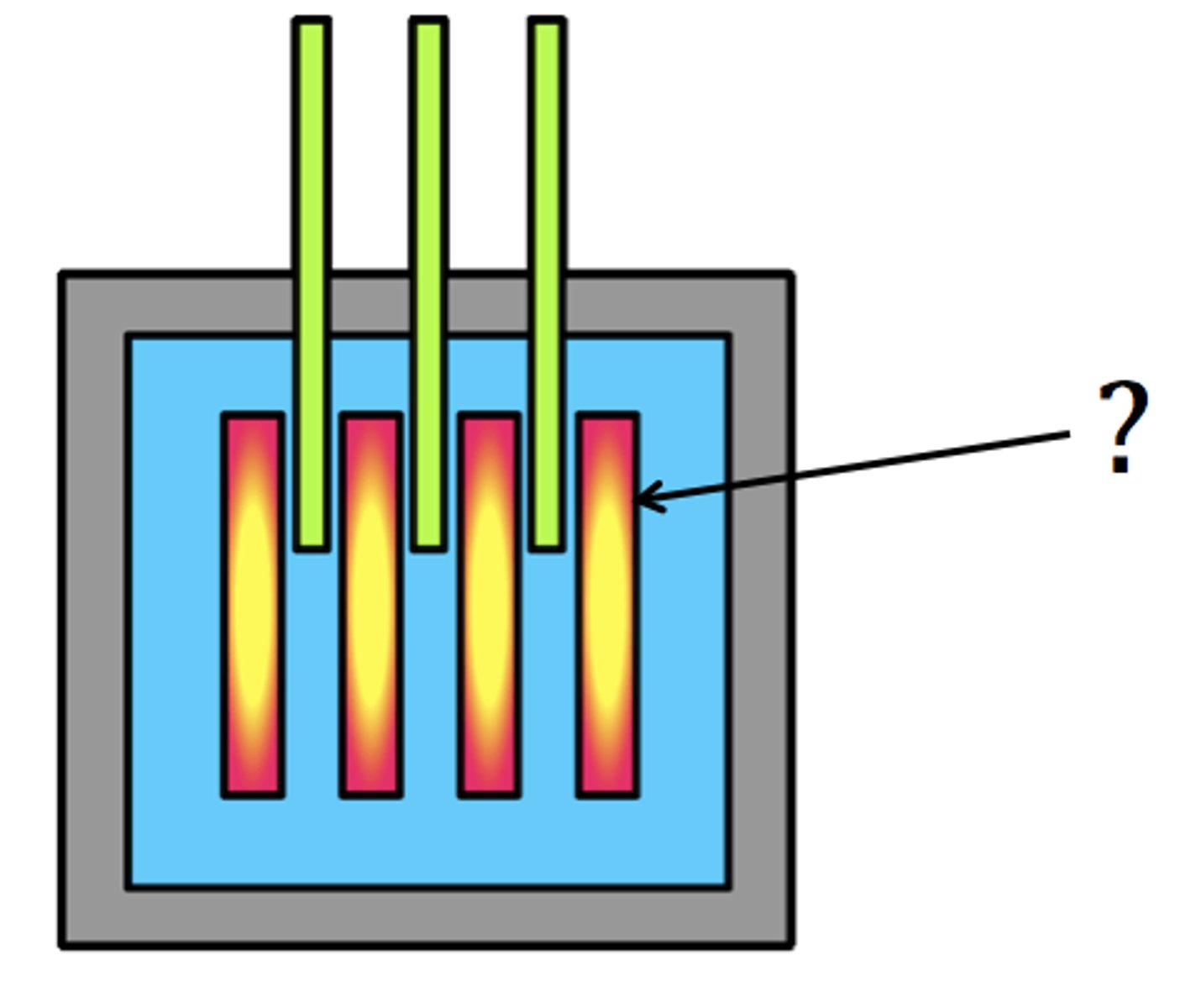
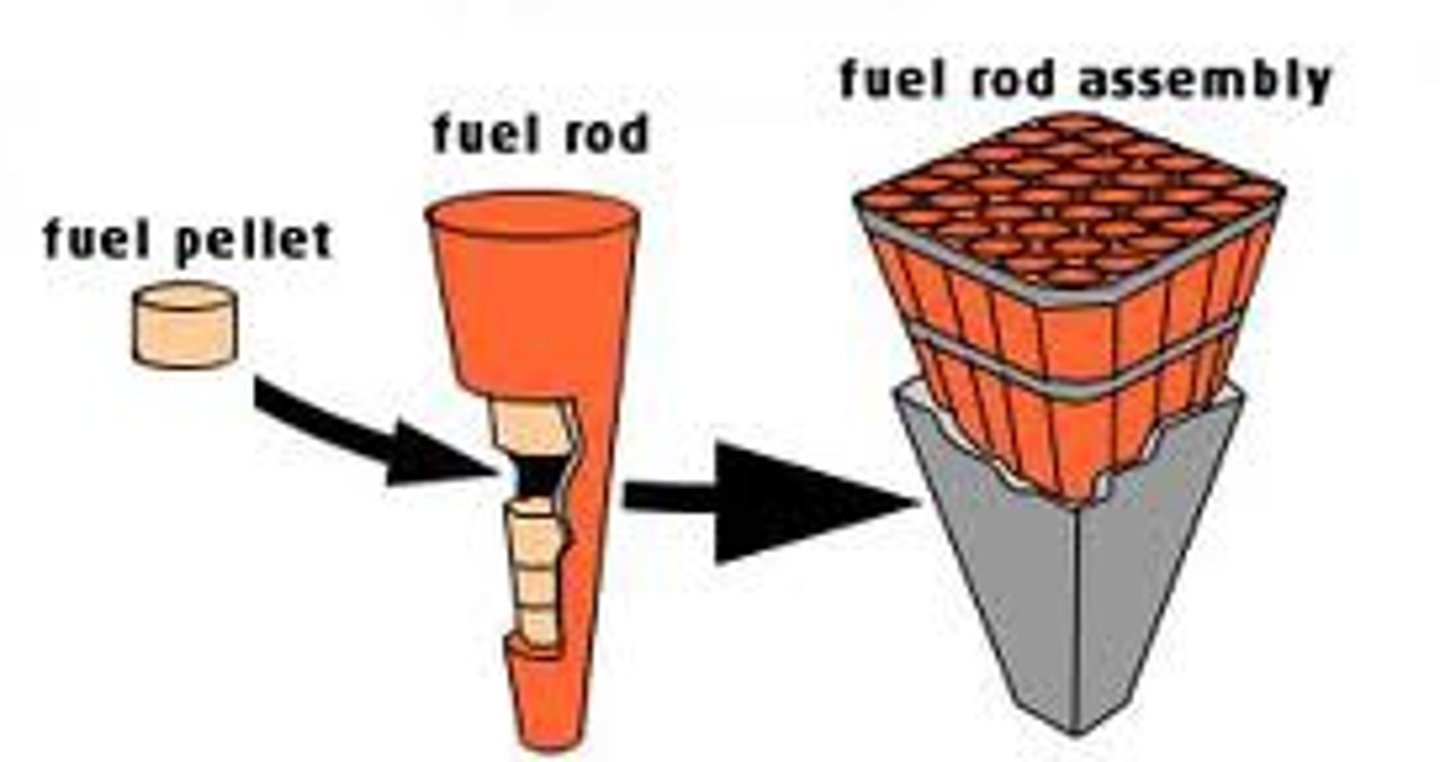
fuel rods
hollow metal cylinders filled with uranium fuel pellets for use in fission reactors. Found in the reactor core.
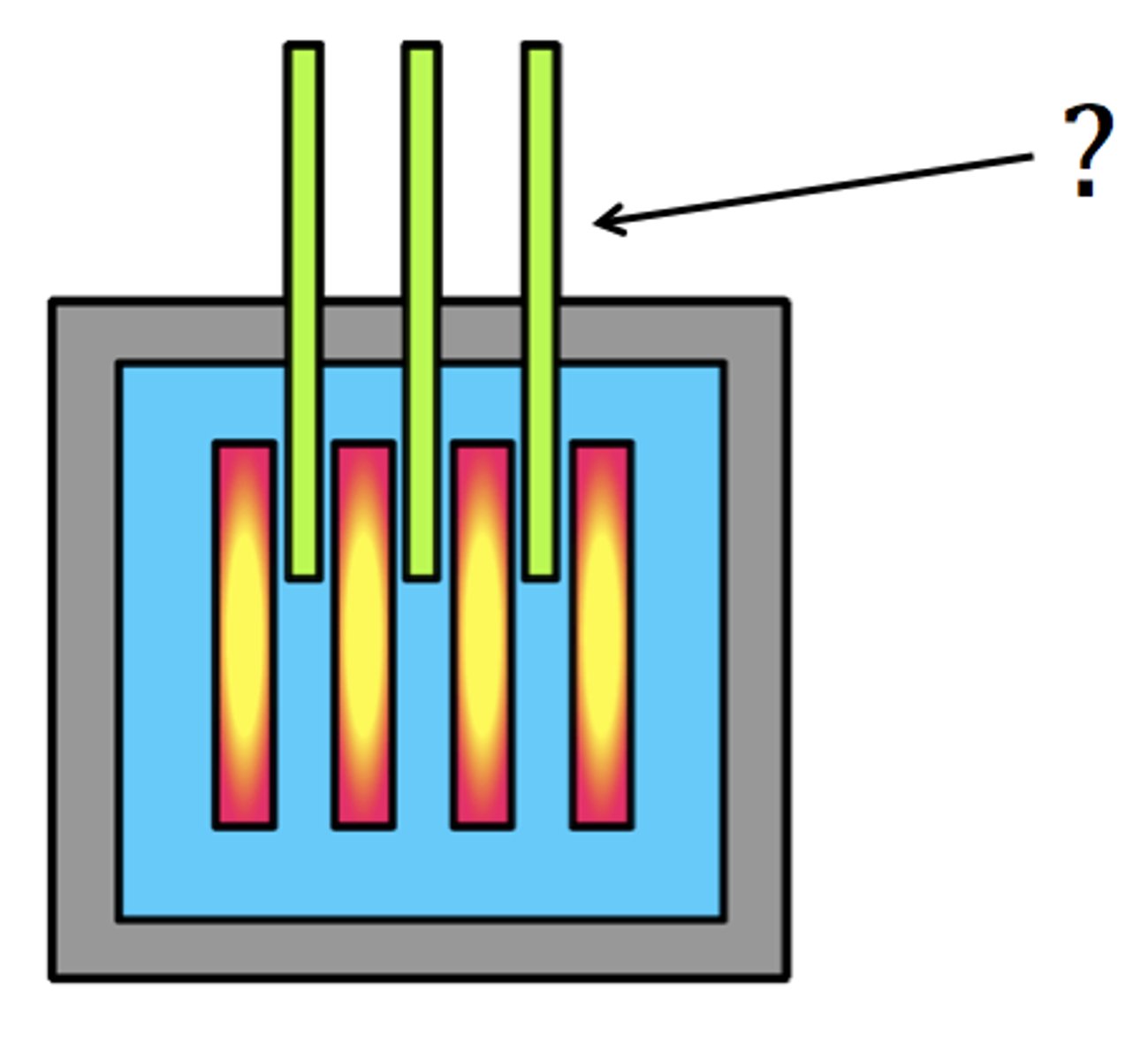
control rods
A cylindrical device inserted between the fuel rods in a nuclear reactor to absorb excess neutrons and slow or stop the fission reaction.
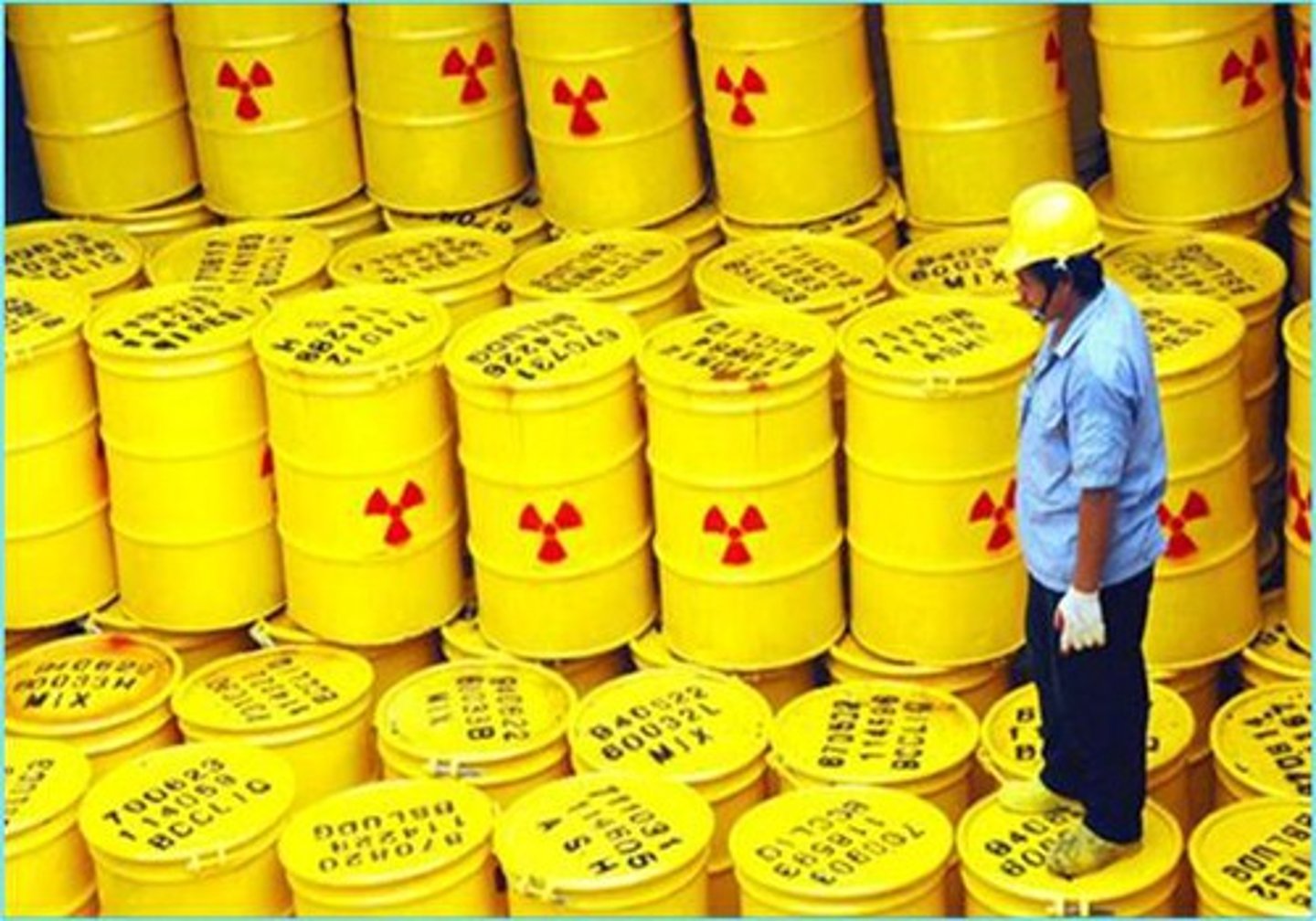
radioactive waste
Materials from a nuclear reaction that emit radiation; therefore, the materials must be safely stored for thousands of years

spent fuel rods
Fuel rods that no longer contain enough uranium 235 to be used in fission, but are still highly radioactive.
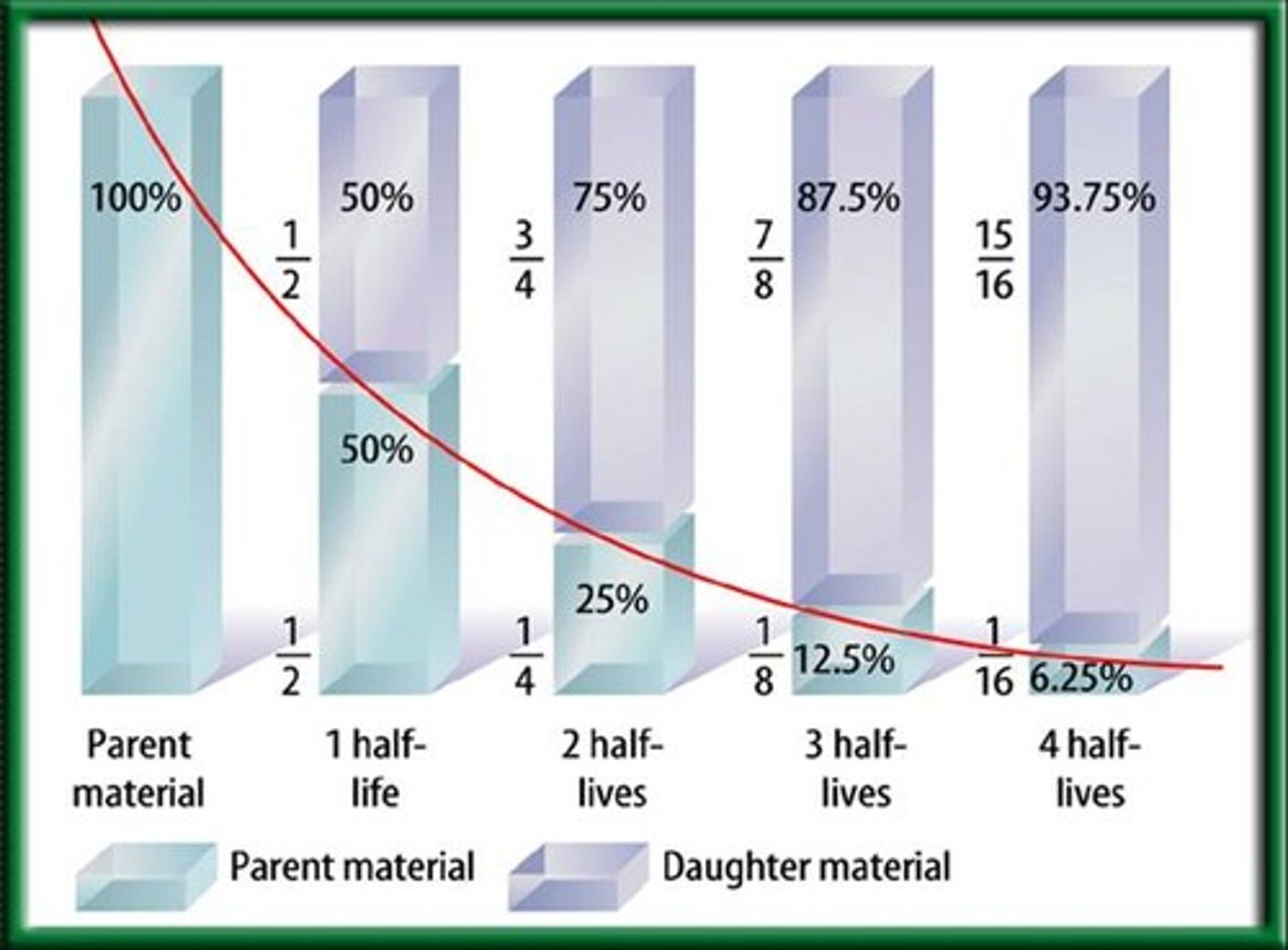
Half-life
length of time required for half of the radioactive atoms in a sample to decay
Three Mile Island
1979 - A mechanical failure (cooling valve stuck shut) and a human error at this power plant in Pennsylvania combined to cause a partial nuclear meltdown and release of radiation over a 16 mile radius.
Chernobyl
The nuclear power plant in the Ukraine that suffered two large explosions which released massive amounts of radioactive materials. It is the worst nuclear accident in history.
Fukushima, Japan
2011; meltdown of three nuclear reactors following a tsunami resulted in the second largest nuclear meltdown in history
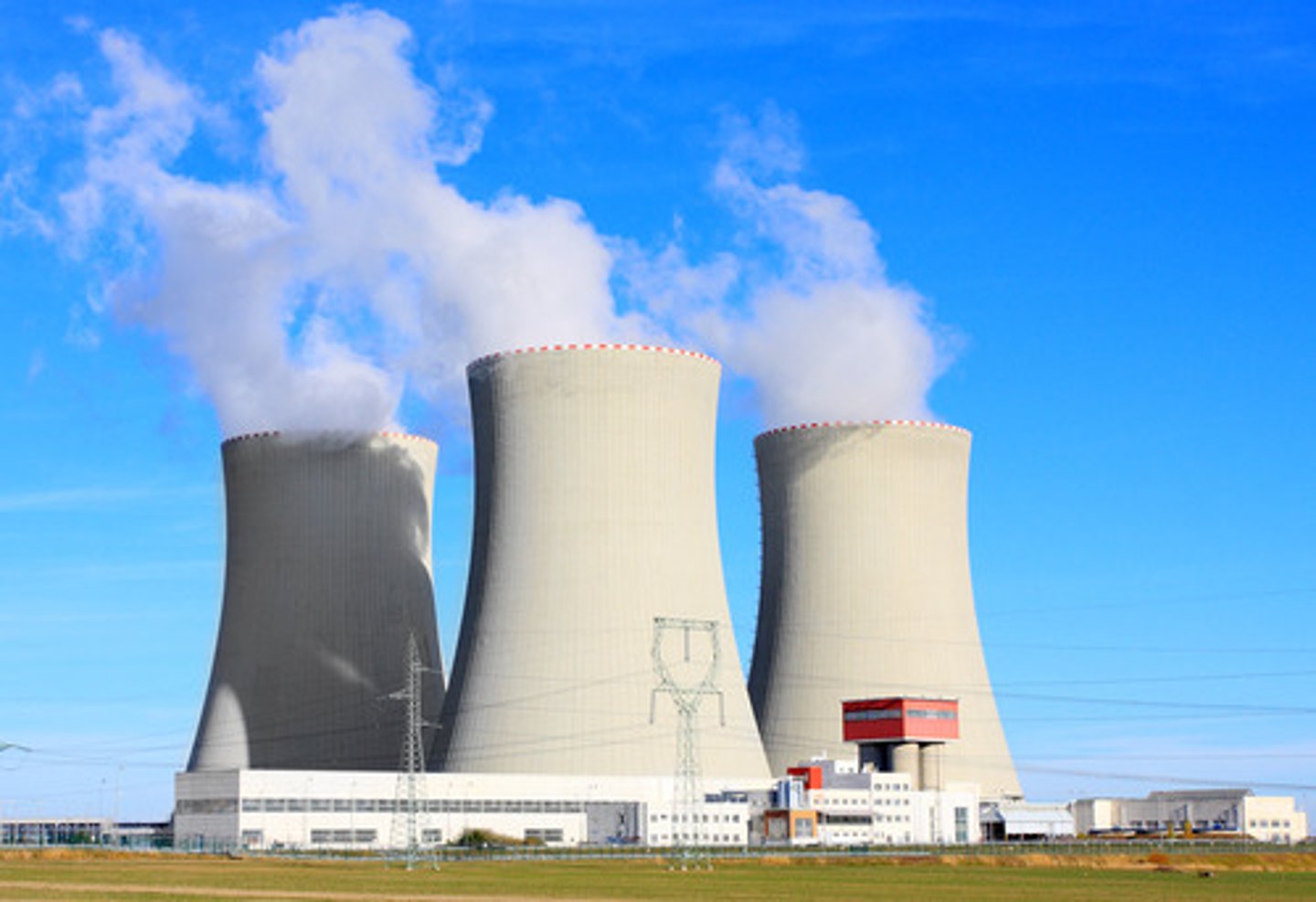
Cooling tower
a tall, open-topped, cylindrical concrete tower, used for cooling water or condensing steam from an industrial process, especially the water used to cool nuclear reactor cores.

thermal pollution
A temperature increase in a body of water (often following discharge of hot water used to cool a nuclear reactor core) that can cause low O2 levels and death in aquatic organisms