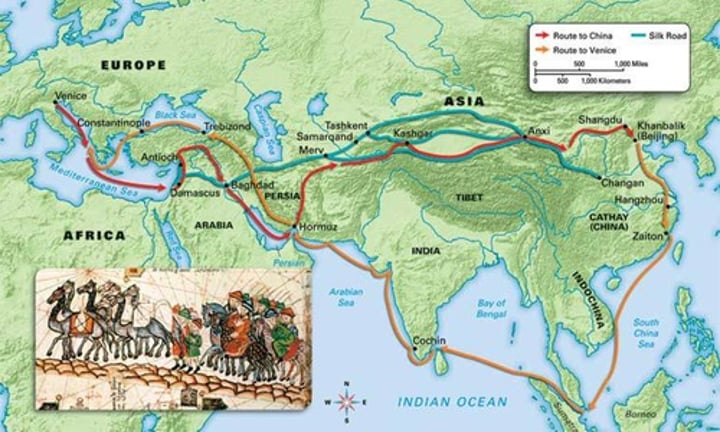
2.1 The Silk Roads
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Sea trade
traveling by water to trade with other countries.
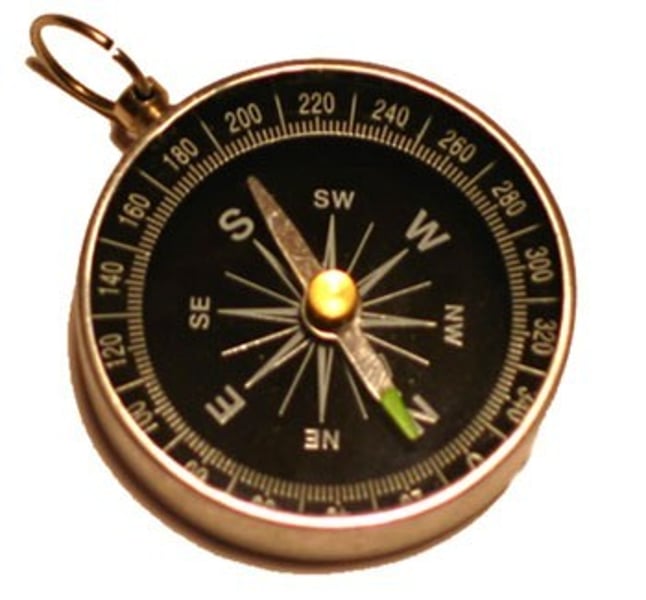
Magnetic compass
Chinese invention that aided navigation by showing which direction was north with a magnetic needle.

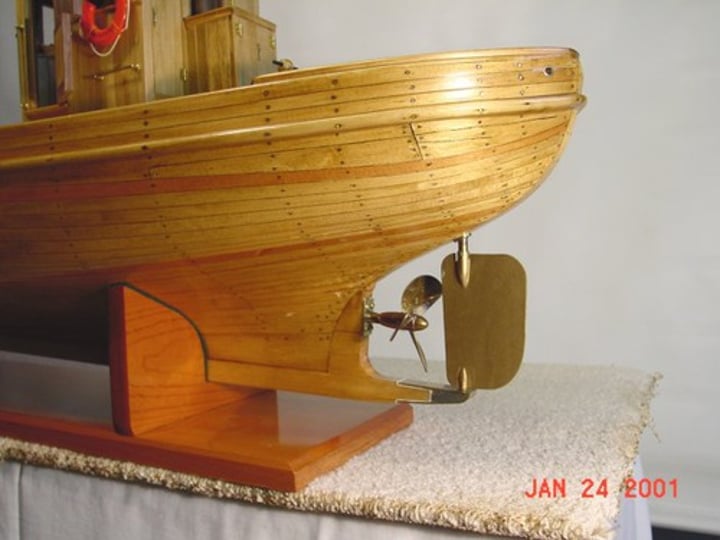
Rudder
Steering device, usually a vertical blade attached to a post at, or near, the stern of the boat.

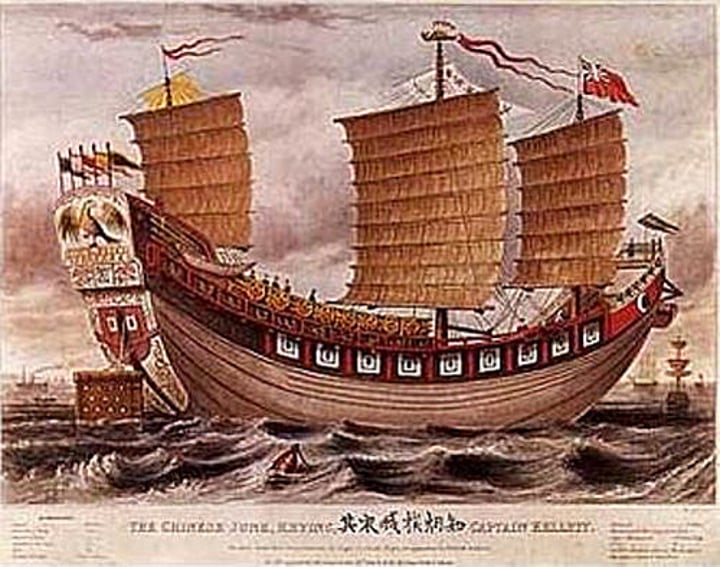
Junk (boat)
A very large flatbottom sailing ship produced in the Tang and Song Empires, specially designed for long-distance commercial travel.

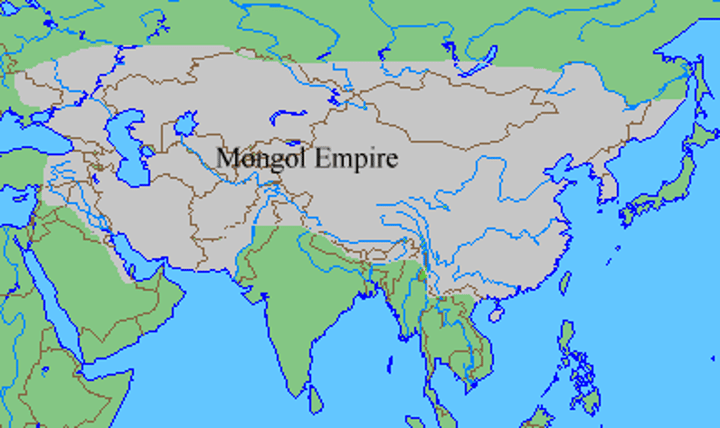
Mongol Empire
Largest land empire in the history of the world, spanning from Eastern Europe across Asia. Founded in the 12th century by Genghis Khan, which reached its greatest territorial extent in the 13th century, encompassing the larger part of Asia and extending westward to the Dnieper River in eastern Europe.
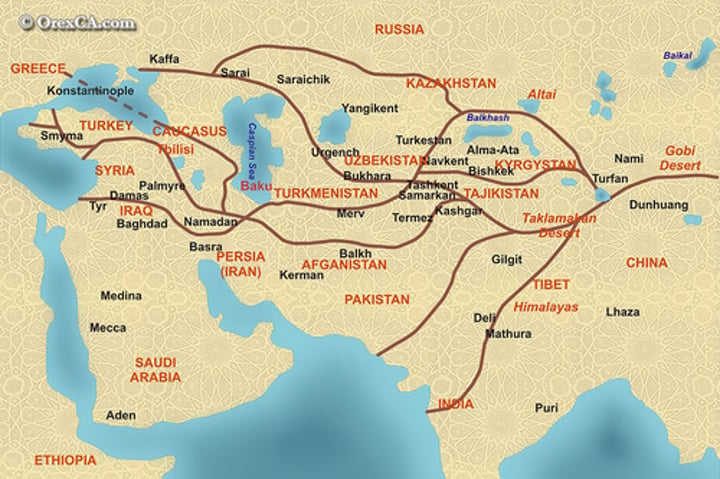
Kashgar(trade city)
A central trading point at which the western and the eastern Silk Road met.
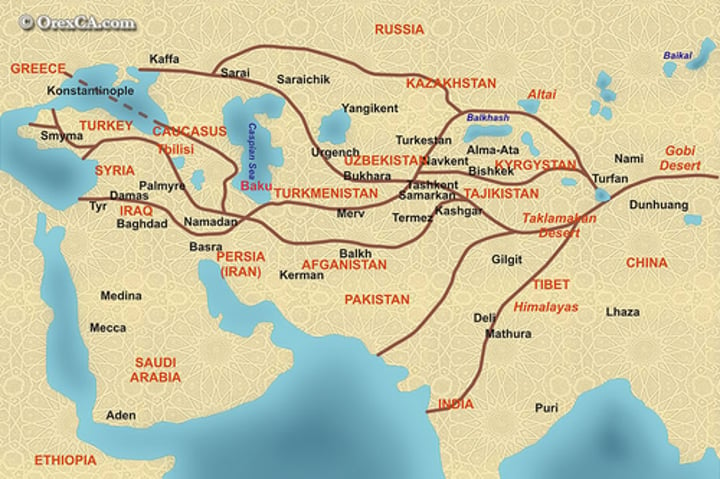
Samarkand(trade city)
During the rule of Timur Lane was the most influential capital city, a wealthy trading center known for decorated mosques and tombs.
Caravanserai
an inn in some Eastern countries with a large courtyard that provides accommodation for caravans inn for travelers in the desert regions of Asia or North Africa.

Money economy
a system or stage of economic life in which money replaces barter in the exchange of goods.

Flying cash
a paper currency of the Tang dynasty in China; can be considered the first banknote.

Paper money
legal currency issued on paper; it developed in China as a convenient alternative to metal coins

Banking Houses
European banks developed during the Middle Ages to aid trade. Along with innovations such as bills of exchange, or bank drafts, and credit, the rise of banking houses supported the development of interregional trade in luxury goods; handled the financial transactions of a variety of merchants as well as of ecclesiastical and secular officials. Specialized in money changing, loans, and investments. Banking was introduced to encourage the exchange of money and goods over a large distance. The largest trading and banking operations in Italy, Southern Germany, the Low Countries, France, and Britain were capitalistic, meaning they were controlled by private owners for profit, rather than by the state.

Bill of exchange
issued by a banker in one city to a merchant who could exchange it for cash in a distant city, thus freeing him from traveling with gold, which was easily stolen.

Hanseatic League
an organization of north German and Scandinavian cities for the purpose of establishing a commercial alliance.