Global Air Pollution: Ozone Depletion and Climate Change
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Ozone Layer
Stratospheric region with high ozone concentration to protect from UV radiation
A pollutants depends on
location
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)
Chemical compounds (hydrogen, carbon, chlorine, fluorine) that deplete the ozone layer. These are stable but break down in the atmosophere
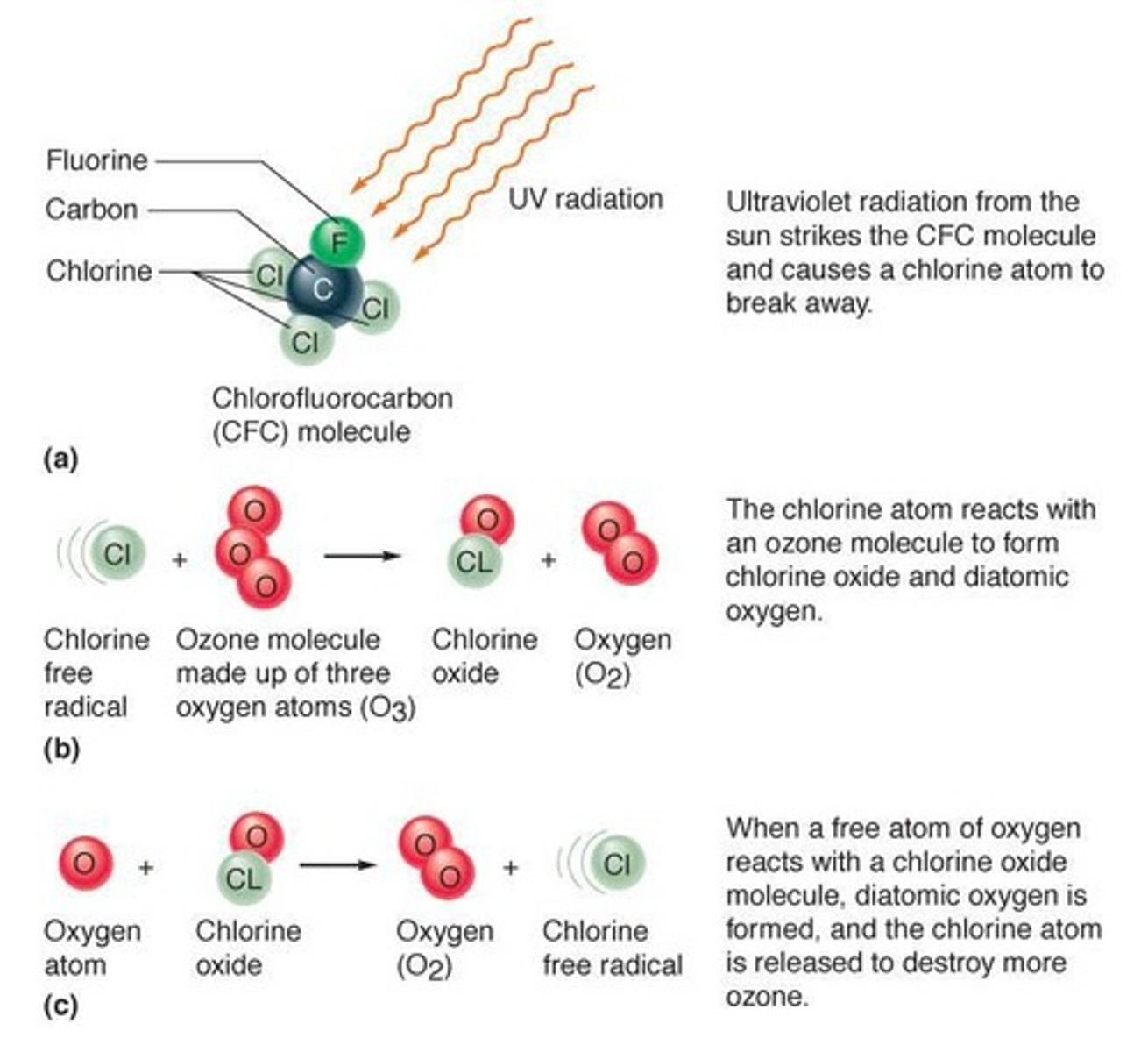
Activities that deplete the ozone layer
CFCs and jet travel (SST) through the stratosphere
Nitric Oxide
Pollutant released by jets affecting ozone.
Where is the most ozone depletion seen?
Southern Hemisphere and Antarctica
What are the health affects of ozone depletion
skin cancer, cataracts, premature aging
Ecosystem Damage as a result of ozone depletion
ecosystems, crops, materials, finishes
How many International Treaties have been signed about ozone
three
HCFCs
Interim substitutes for CFCs, less harmful.
Ozone Recovery
Long process for ozone layer to heal, may take 200 years
Ozone Concentration Decline
Substantial decrease observed globally since 1969.
Atmospheric Pollution
Contamination affecting air quality and health.
What is acid deposition?
rain or snow that has less than 5.7 pH in unpolluted areas
Wet Deposition
Acidic rain or snow reaching the Earth.
Dry Deposition
Acid particles and gases settling on surfaces.
Acid Precursors
Substances that form acids, both natural and anthropogenic.
Where do acids come from anthropogenically
fossil fuel combustion
Natural acid precursor
volcanoes
Transportation of Precursors
Acid precursors can travel hundreds of kilometers.
Industrial Centers acid deposition
Major sources of acid deposition downwind.
Geographic Range of acid deposition
Acid deposition expanding in affected areas.
Acidified Lakes
Lakes with reduced pH, harming aquatic life.
Buffering Capacity
Soil's ability and surface water ability to resist pH changes.
Acidity and heavy metals
acidity leaches heavy metals, toxic to fish, from the soil
Salamanders and birds
Key species affected by acid deposition.
Nitric Acid and Sulfuric Acid
promote plant growth, and their negative affects outweigh benefits from fertilizing soil
Stopgap measures
Smokestack Scrubbers, Low-Sulfur Coal, Liming Lakes
Tradable Permits
Market-based strategy for controlling emissions.
How much sunlight is reflected and absorbed
1/3 reflected, 2/3 absorbed
Greenhouse gases
CO2, CH4, N2O, O3
Global Energy Balance
Equilibrium between incoming solar energy and outgoing heat.
What is responsible for the increase in daily temperatures, rainfall patterns, and the frequency and severity of storms
greenhouse gases
How long does an interglacial period take to complete
200,000 years
Acid Damage Cost
Billions lost due to acid effects on structures.
Major hurricanes
Four major hurricanes hit the U.S. in 2005.
Previous record of major hurricanes
Three major hurricanes in 2004.
Category 5 hurricanes
Three hurricanes exceeded 155 mph in 2005.
Adaptation rate in light of climate change
Rate of change exceeds organisms' adaptation ability.
Ocean currents
Warm tropical water flows northward in Atlantic.
Impact of glacier melting
Could disrupt global ocean currents.
Dwindling resources
Food, water, and energy supplies at risk.
Evidence of climate change
global CO2 levels, sea level, polar ice, global temperatures, glaciers, frequency/severity of storms/droughts
Forest loss
Accelerates carbon dioxide levels increase.
Uncertainty in climate change
Slows progress towards effective solutions.
Cost of greenhouse gas reduction
Believed to be less than climate change costs.
Solving climate change sustainably
reduced population means less fossil fuels and more forests means less CO2