AP Microeconomics Exam Study Guide
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards for key concepts in AP Microeconomics.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
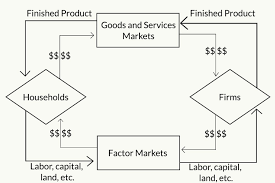
Circular Flow Diagram
Law of Supply
States that there is a direct relationship between the price of a good and the quantity supplied.
Law of Demand
States that there is an indirect relationship between the price of a good and the quantity demanded.
Income Effect
The change in quantity demanded of a good resulting from a change in real income due to a change in the price of that good.
Substitution Effect
The change in quantity demanded caused by a change in the relative price of a good, which leads consumers to substitute one good for another.
Normal Goods
Goods for which demand increases as consumer income increases.
Inferior Goods
Goods for which demand decreases as consumer income increases.
Determinants of Demand
Factors that cause the demand curve to shift, including consumer preferences, prices of related goods, future expectations, income, the number of consumers, and special circumstances.
Elasticity
A measure of how much one variable responds to changes in another variable.
Price Elasticity of Demand
A measure of the responsiveness of quantity demanded to a change in price.
% △ Qd
% △ P
Total Revenue Test


Utility Maximization Rule
Consumers should allocate their resources such that the marginal utility per dollar spent is equal across all products.
MU of product A
P of A
=
MU of product B
P of B
Marginal Cost (MC)
The additional cost of producing one more unit of a good.
Marginal Revenue Product (MRP)
The revenue generated by employing one more unit of a resource.
MRP = MPP x P
Monopoly
A market structure characterized by a single seller, selling a unique product with no close substitutes.
Natural Monopoly
A monopoly that exists when a single firm can supply the entire market at a lower cost than multiple firms.
Market Failure
A situation in which the allocation of goods and services is not efficient, often due to externalities or public goods.
Coase Theorem
The theory that if property rights are well-defined and transaction costs are low, parties will negotiate to correct externalities.
Economic Rent
The payment to a factor of production in excess of the minimum necessary to keep that factor in its current use.
Rent-seeking Behavior
Expenditures made by a firm to achieve or maintain monopoly power.
Monopsony
A market situation where there is only one buyer for many sellers.
Positive Externality
A benefit that is enjoyed by a third-party as a result of an economic transaction.
Negative Externality
A cost that is suffered by a third-party as a result of an economic transaction.
Direct government regulation
Government intervention to control the supply of goods and services.
Subsidies
Financial support extended by the government to economic sectors, intended to promote economic and social policy.
Price elasticity of Supply
% △ Qs
% △ P
Cross price elasticity
%△ Qd of good x
% △ P of good y
implicit costs
oppurtunity cost of employing self-owned resources toward one activity rather than another (INCLUDES NORMAL PROFIT)
explicit costs
the money costs of employing resources owned by others, in the form of wages, rent, and interest
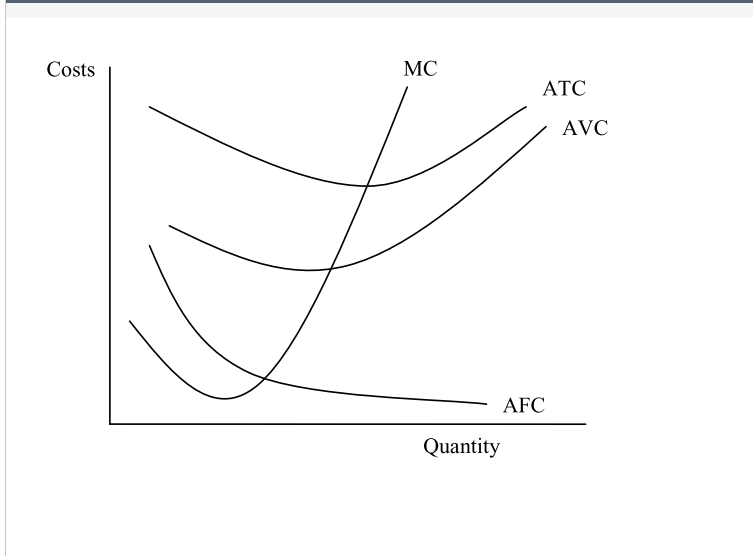
TC = FC + VC
ATC = AFC + AVC
the distancve between ATC and AVC is AFC
AVC is significant for firms cuz if price ever falls below AVC = shut down
MC intersects both ATC and AVC at their lowest points
cost shifters
any variable costs (work wages, rent on land, interest on loans, technology or productivity) will shift MC, AVC, and ATC
dominant strategy
a strategy that is optimal regardless of what an opponent does, in one column
nash equilibrium
set of strategies in which each firm does the best it can given its competitors actions, NO INCENTIVE TO CHANGE STRATEGY