Exam 3 BTECH
1/144
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
145 Terms
Potential Advantages of Green roofs and Green walls
Green Roofs:
1.Keep the surface of the roof’s
insulated roof envelope cool
2. Add insulation to the roof
3. Protect the roofing membrane
from the sun
4. Mediate storm runoff
5. Make the roof into a more
usable and attractive space
Green Walls:
1. Act as bio filters cleaning the air
2. Breaks down V.O.C.’s (Volatile
Organic Compounds)
3. Keeps the surface of the wall
envelope cool
4. Absorbs sound
Potential Disadvantages of Green roofs and Green walls
Potential Disadvantages:
Maintenance, harder to repair leaks,
expense, potential water exposure
damage, extra structural demands.
Intensive vs Extensive Green Roofs?
Anything deeper than six inches is Intensive while anything less than six inches is Extensive. Intensive can grow a wider variety while Extensive can pretty much be only surface level.
Containerized Green roof System
Containers holding greenery in them that sit on the roof
Problems that we have to solve with Intensive and Extensive Green Roofing?
Intensive: Roots, Water, Filtration of Water
Extensive: Roots, Water, Holding Water
Root Barrier?
Stops roots from penetrating the building
Growing Medium/Media? Why not just soil? Why use this Engineered Soil?
Soil mix that is used because we cannot use soil due to the weight and drying out. We use Engineered Soil that has a mix of organic and inorganic materials to lighten the load and hold moisture.
How do we do fire control for green roofs?
We usually create barriers around the greenery and leave plenty of room so that the fire cannot spread to important areas.
Passive and Active Irrigation Systems
Passive: Holding the water without any systems in place to keep it there
Active: Holding the water with systems to keep it there
Closed Irrigation Systems vs Open Irrigation systems
Closed systems recycle water, open systems bring in fresh water each time.
Why and When do you need to worry about weight of green roofs?
Why: It affects the loads of the structure
When: When it’s saturated because when the soil is holding water is gets even heavier
Living Walls vs Green Facades?
Living walls have actual plants in them and Green Facades are just walls with climbing plants
Sensory Gardens
Gardens designed to involve the senses and create an experience
Vegetated Mat System
Pockets that have growing medium that you put plants into and cage holds everything up
Monoculture vs Polyculture Wall
Monoculture walls consist of one plant type, Polyculture consists of many. Monoculture is easier to manage however it can have issues with diseases/infections. Polyculture is harder to manage
Sedums?
Hold water better than most plants
How do Vines grow?
Tendrils, Scrambling, Twining, Suction
Greenfield, Brownfield, Infill?
Greenfield is an untouched site, Brownfield is a site that has toxins in the soil, Infill is where you fill in where buildings are missing/destroyed
Heat Islands and Parking lots
We need to create lots of dividers, trees, and water absorption
Paving, what strategies do we use?
Lighter colors in areas where sun will commonly be, greenery woven with the cement
Permeable Paving
Paving that doesn’t absorb water and instead lets it go through, has gravel underneath so it can store the water and trickle it into the soil
Pavers
Enough concrete to support people or cars but also have enough space for soil so grass can grow
Gray Water, Stormwater, Black Water, Potable Water
Gray: laundry water
Storm: rain
Black: feces
Potable: drinkable
Water Efficiency methods
Landscaping decisions, Irrigation systems, capturing rainwater, recycle wastewater
Xeriscaping goal?
Goal is to reduce the amount of water used
Why not just use sprinklers? What other methods could we use?
Water Efficiency, drip irrigation, misters
Zoning? Use groups?
Pieces of property must be in certain zones, use groups are within zones
Why do we care about site decibels?
So that we can control where things will be loud and quiet and thus where we can have people doing certain activities
Septic system?
When you don’t have access to a public waste system, you have your own private disposal system, typically by draining to the groundwater far below
V.O.C’s? (Volatile Organic Compounds?)
Materials that slowly release gas from them, we are trying to reduce V.O.C’s as much as possible
Formaldehyde, Urea and Phenol?
Common in older factory building blocks, highly V.O.C. Urea off-gasses at room temperature and is toxic. Phenol off-gasses at high temperatures
Drywall? Is it fire-rated? Is it water resistant?
It can be both fire-rated and water resistant.
Why use corner bead and other accessories to terminate the drywall
The corner bead is set proud of the surface
so the knife presses against it when placing
the compound
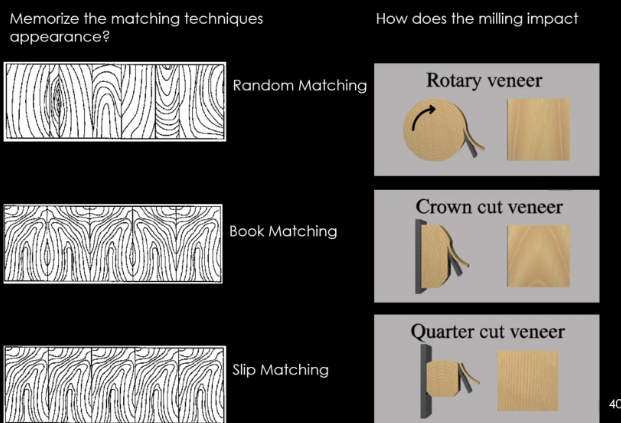
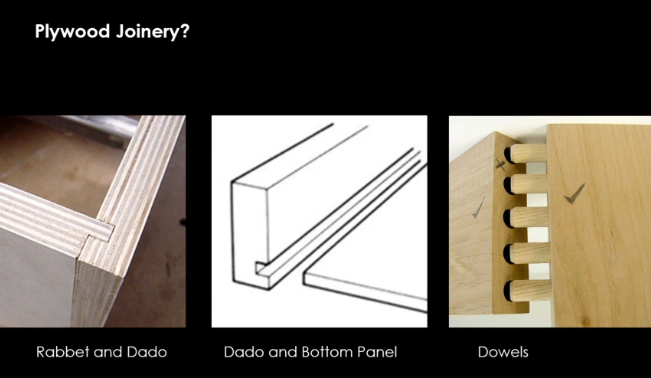
Veneer Plywood, what is a Veneer?
Weaker interior plywood with a stronger outer plywood cover called a veneer
Plywood Grades
A - Sanded Smooth, no repairs or knots
B - Some repairs, tight knots, minor splits
C - Discoloration, knots, knotholes
D - Bigger knots and knotholes, some splits
High Pressure Laminate
Made up of several layers of resin-impregnated kraft paper, decorative paper, and a clear overlay
Cement Fiberboard
Fiber cement siding is made with a mixture of sand, cement, and cellulose fibers


Raised Access Flooring
Good for having mechanical equipment underneath the flooring so that its out of sight and works well.
Raceways
Space in the ground that allows for certain systems to run through while also mostly filling in the area so that its not as hollow underneath the floor
Suspended Ceilings
To hold equipment in the ceiling that is hidden above you
What are the important factors for choosing countertops?
Bacteria, Sealed or not, hardness, weight, etc
Plaster, what are the 3 layers, is it attached to a metal lath? does it need to be metal?
Scratch, Brown, Finish. Yes it has a metal lath. No it doesn’t have to be metal
Veneer coat plaster?
Plaster that is only one coat that goes onto drywall that acts as the finish coat, creates a strong bond.
Plaster Adhesive?
Used when going to apply a veneer coat plaster to a typical drywall.
Tongue and Groove wood flooring, how to keep it from buckling?
Wood flooring that has tongues and grooves to be attached like puzzle pieces.
Spaces at the edge, acclimated to the building
Sanding the floor, why?
Make the floor smooth so that its nicer to walk on and better for staining/coating
Wood Surface Sealer vs Penetrating Sealer
Surface: Creating a layer of resin between user and wood
Penetrating: Soak the wood, so it repels moisture
Issues with Oil-Modified, Moisture Cured, Water based urethanes and epoxy sealer
Oil: yellows, high V.O.C’s
Moisture: expensive, harder to apply, high V.O.C’s
Water based: harder to apply, expensive
Epoxy: more expensive and harder to apply
Slate tile, why grooved back?
To engage thin set of mortar
Quarry Tile, solid clay tiles are often called what?
Terra Cotta
Ceramic and Porcelain tile
Clay tiles with a glaze on them
Mosaic Tile Sheets
Tiles made up of small tiles that create a 12” sheet
Cement Fiber Board:
Thin Set Mortar:
Tile:
Grout:
Cement Fiber Board: Good base for tile system
Thin Set Mortar: Engages the tile and holds it in place
Tile: the Tile
Grout: placed between tiles as filler
Why not just start tile in a corner and go?
So that we don’t have issues with fitting down the line and need to get something recut
Notched Trowel?
Each tile requires a certain notched trowel so that the thin mortar engages properly
Sanded vs Unsanded Grout
Sanded is used for most tile systems, unsanded is used for thinner gaps or smaller tiles
Tile Sealers, Why?
We want sealers so that when we spill something on the tiles it doesn’t get stained forever
Linoleum?
Made of natural fibers and natural oils
Bio based Tiles?
Replacing old high V.O.C tiles
What should we be aware of when choosing adhesives?
That they are V.O.C free
Carpet Tile? Why this over rolling tile?
So that we can replace individual carpet tiles in case of staining
Epoxy floors, why are they nice?
Self leveling, glossy, durable.
Gyp Crete underlayment, why do we use it?
Self leveling so that you can have it underneath your tile so everything is level
Terrazzo colors, How’s it made?
Has a base and then has an aggregate and its mixed
Active vs Passive Ventilation
Active: Mechanical systems
Passive: Uses passive systems
What is R-value? U-value
The material or wall assembly ability to resist the transfer of heat, U-value is the inverse
Energy star insulation zones?
Helpful map that gives you guidelines for insulation for certain climates
Why do we care about Vapor Diffusion
so moisture doesn’t get trapped in walls and leads to damage
Vapor permeability? Permeability is measured in PERMS, when is a material determined to be impermeable?
Allows vapor to pass through things so that it doesn’t get trapped. At 1 PERM or less
Vapor barrier vs Moisture barrier?
Vapor barrier stops water in the air and moisture stops liquid water
Air Barriers, why are they important?
So that we can have controlled air vs letting in wind from outside
What are the important decisions when choosing your barriers?
Location, if you need it or not, which one you’re going to be using
Do you need a vapor barrier? moisture barrier?
Typically not unless for extreme conditions. Moisture barrier is absolutely required
Where does dew point not want to occur? How do we prevent it
On the inside of the wall, continuous insulation
Can moisture and/or vapor barriers be apart of exterior sheathing?
Yes
Why blower door tests?
To test if air is blowing in because we don’t want air to blow in from the outside
Batt Insulations, pros and cons
Easy installable insulation, cheap, hard to not have gaps, doesn’t work perfectly, can be harmful to installers,
Dry blown cellulose insulation
blowing in recycled paper into the walls
Wet sprayed cellulose
Spraying hose of wet cellulose and then flattening it
Open and closed cell insulation
Open cell: thicker, lower r-value
closed cell: thinner, higher r-value
Rigid Board Insulation, it has many types what are some common things that need to be considered when choosing?
Is it touching the ground, cost, r-value, moisture barrier, what thickness makes it a vapor barrier, does it need to be taped?
Tapered roof insulation, why?
Good for insulation and drainage
Positive drainage needs to go from where to where?
Top to bottom
Roof Venting, how and why?
Roof venting requires an exhaust and intake, important for things like attics
How do we prevent ice dams?
Proper ventilation
Forced air HVAC Systems
HVAC systems that use ductwork to push air through the building

Sheet Metal Ductwork
Flexible Ductwork
Exposed Ductwork
Insulated Ductwork
Sheet metal: Easy to do, hidden, straight
Flexible: Convoluted paths
Exposed: Technical but have to make it look good
Insulated: For uninhabited space so that there isn’t any heat loss or gain from the ducts
Chases
Framing that holds the ductwork
Plenums
Bring in air from outside
Geothermal
Putting hot or cold liquids into the earth to heat or cool it for the house
Mini Splits / VRF
Allow for more isolated temperature control, requires outdoor unit, removes ductwork
Electrical: Transformers, Panel boards, circuits
Transformers control amount of energy to house, Panels control circuits, circuits control energy flow to certain rooms
Lumens vs Footcandles
Color Temperature?
Lumens: How bright something is
Footcandles: How much light is hitting a surface
Color Temp: How warm the light is
Cool white light is for what? Warm white light is for what?
Cool white: garages, labs, work areas
Warm white: residential, relaxing
Photovoltaic rays? Thermal solar panels?
Capture the suns energy and converted to useable energy. Heats up liquid that can be used for radiant heating or other liquid heating systems
Net Metering
Ability to get credit from utility systems for excess energy