Gross Anatomy - Female Reproductive
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
81 Terms
b. Pudendal Nerve
Which of the following innervates the female urethra?
a. Vaginal Nerve
b. Pudendal Nerve
c. Uterine Nerve
d. Deep perineal nerve
c. Uterine artery
Which of the following does NOT supply the female urethra?
a. Internal pudendal artery
b. Vaginal artery
c. Uterine artery
d. Inferior vesical branch of vaginal artery
b. Internal iliac vein
The internal pudendal vein, one of the main venous drainage of the female urethra, drains into?
a. Internal and external iliac veins
b. Internal iliac vein
c. Inferior vena cava
d. Left inferior suprarenal vein
a. Urinary Tract Infection
Which of the following is the disease that is more common in females due to females having a shorter urethral length?
a. Urinary Tract Infection
b. Bartholin’s Cyst
c. Ectopic Pregnancy
d. Endometritis
b. It belongs exclusively to the urinary system
Which of the following statements is true of the female urethra?
a. It is longer compared to the male urethra
b. It belongs exclusively to the urinary system
c. The paraurethral glands (skene’s glands) is homologue to the bulbourethral glands
d. It is common to both the urinary and reproductive systems
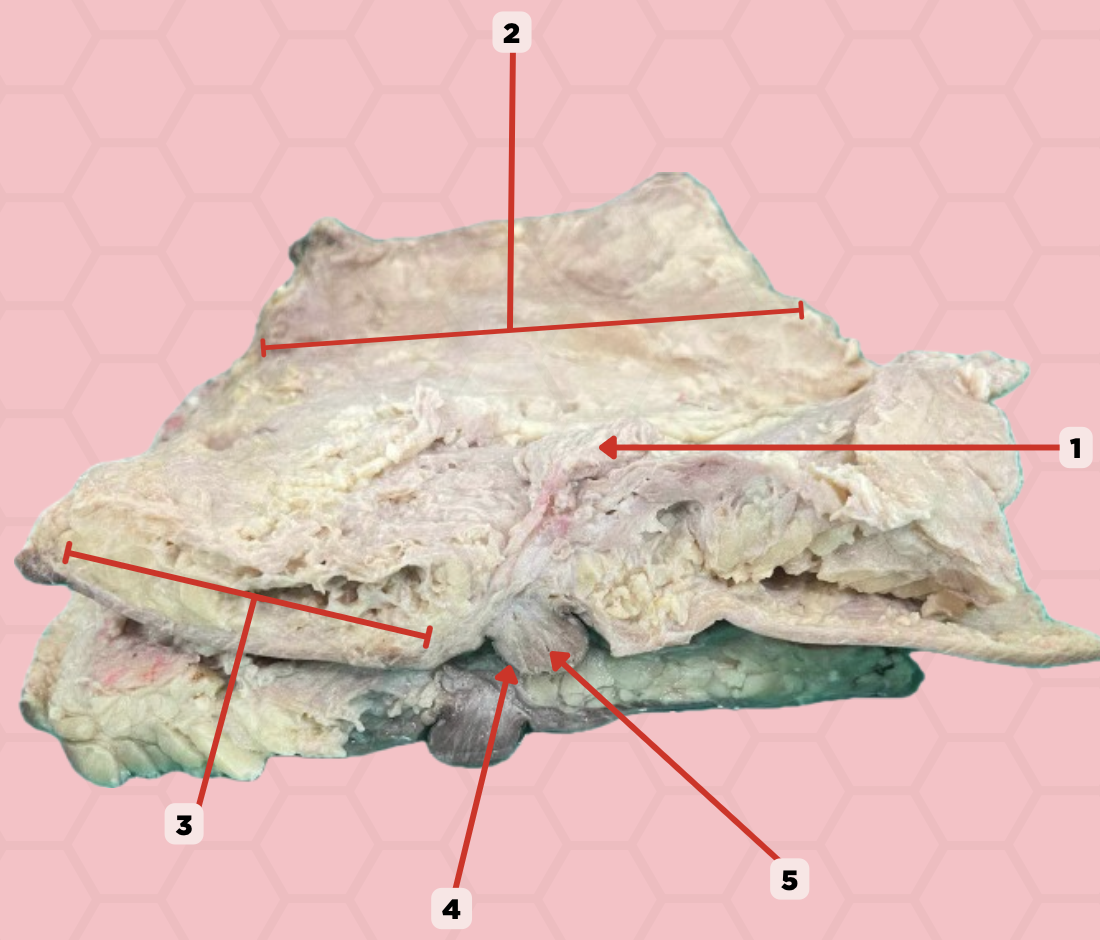
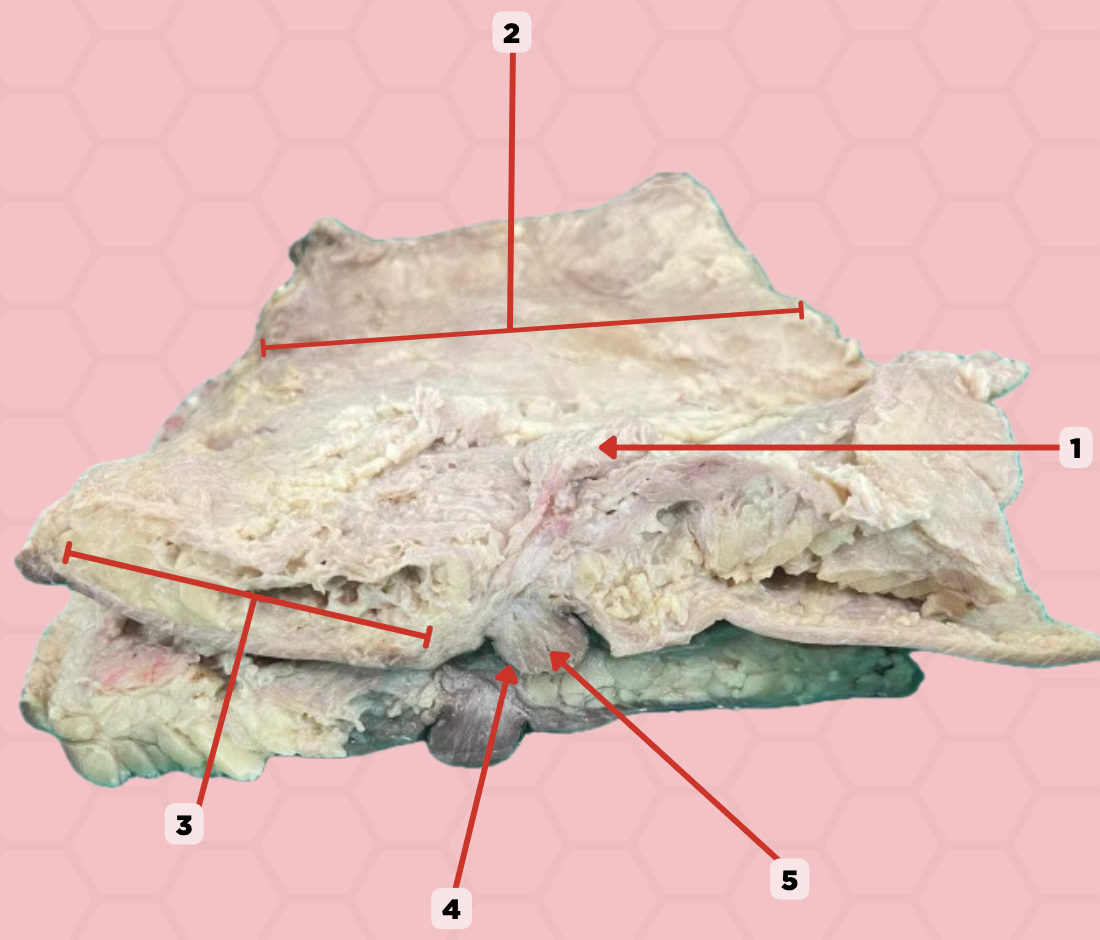
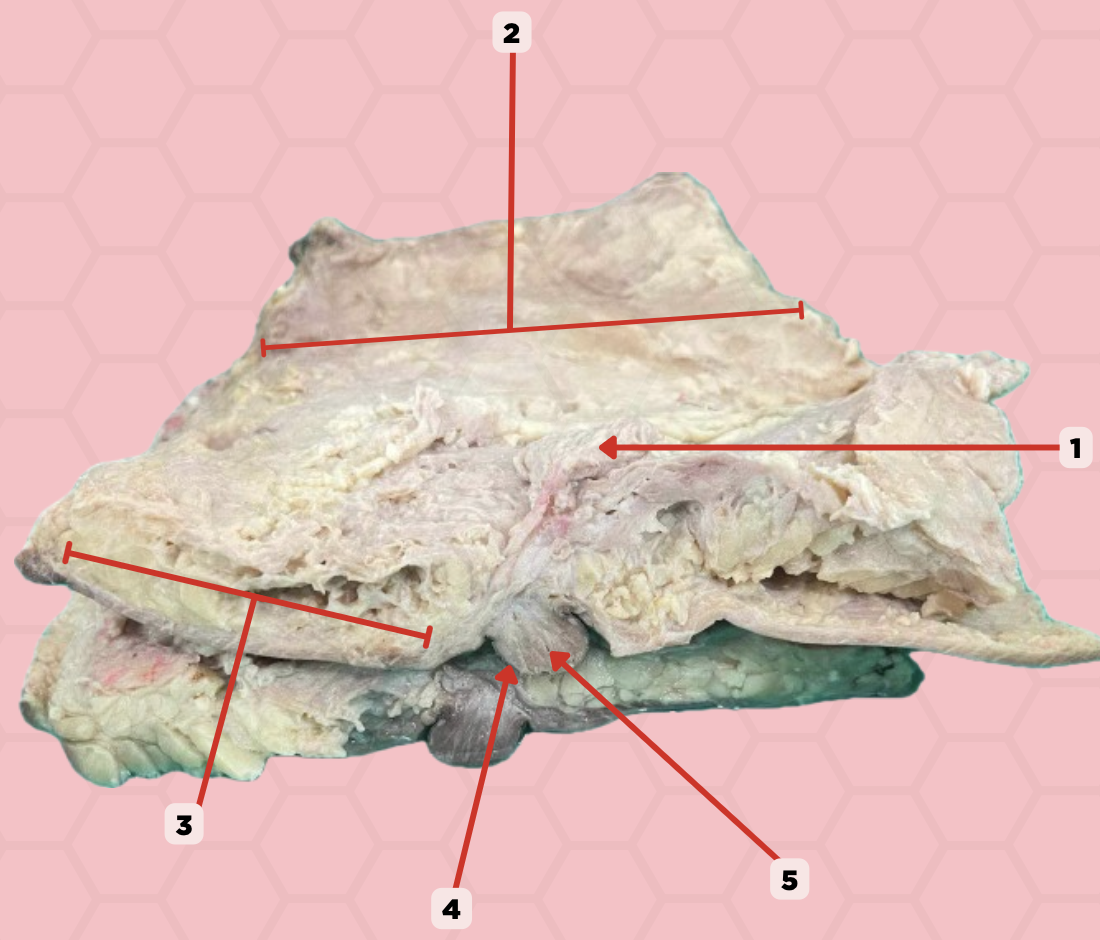
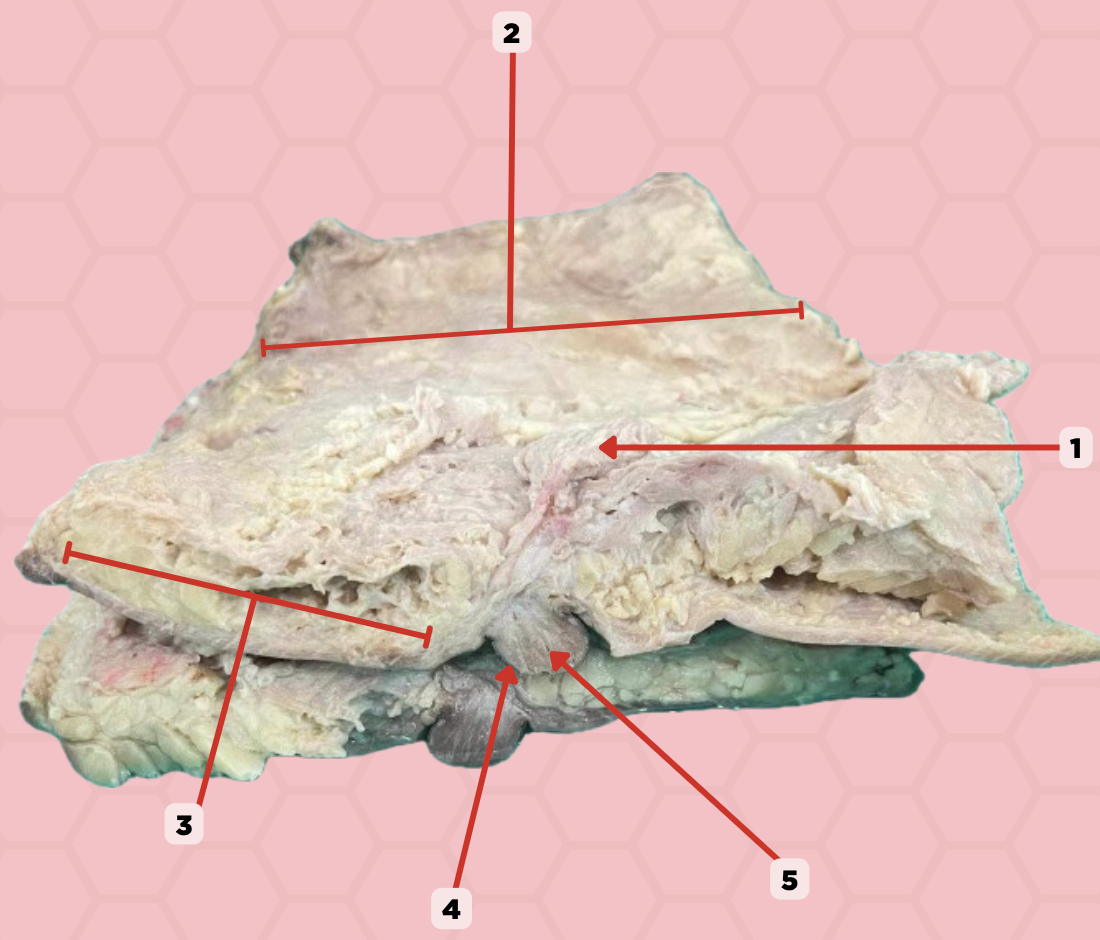
Uterus
Identify the structure labeled as 1.
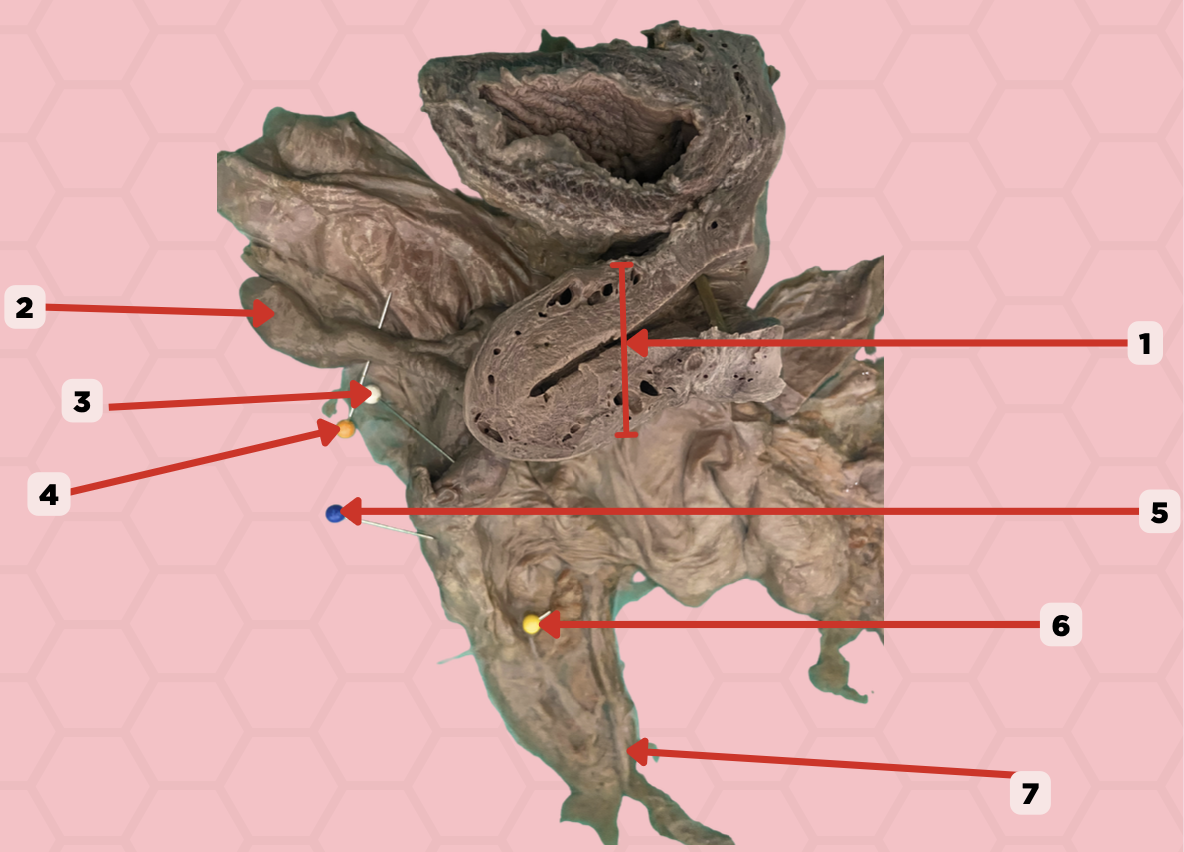
Fallopian tube
Identify the structure labeled as 2.
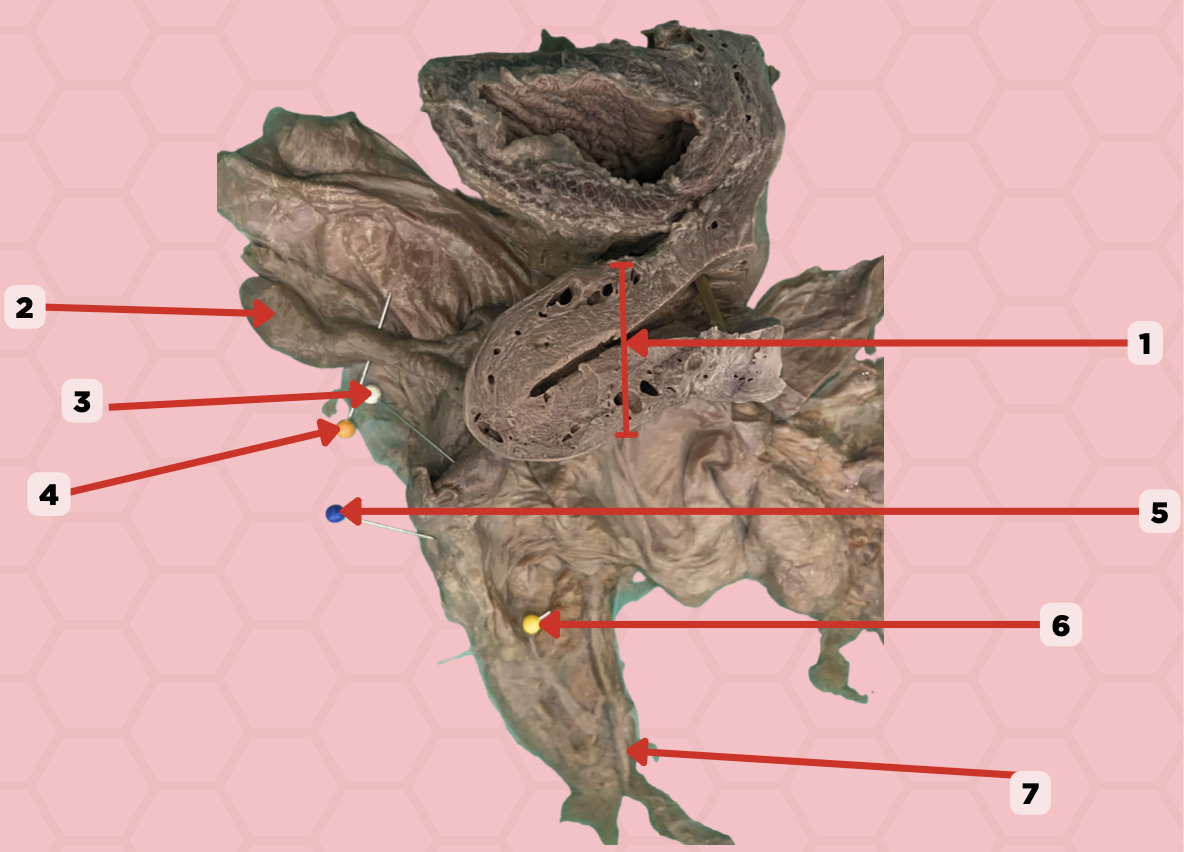
Ovary
Identify the structure labeled as 3.
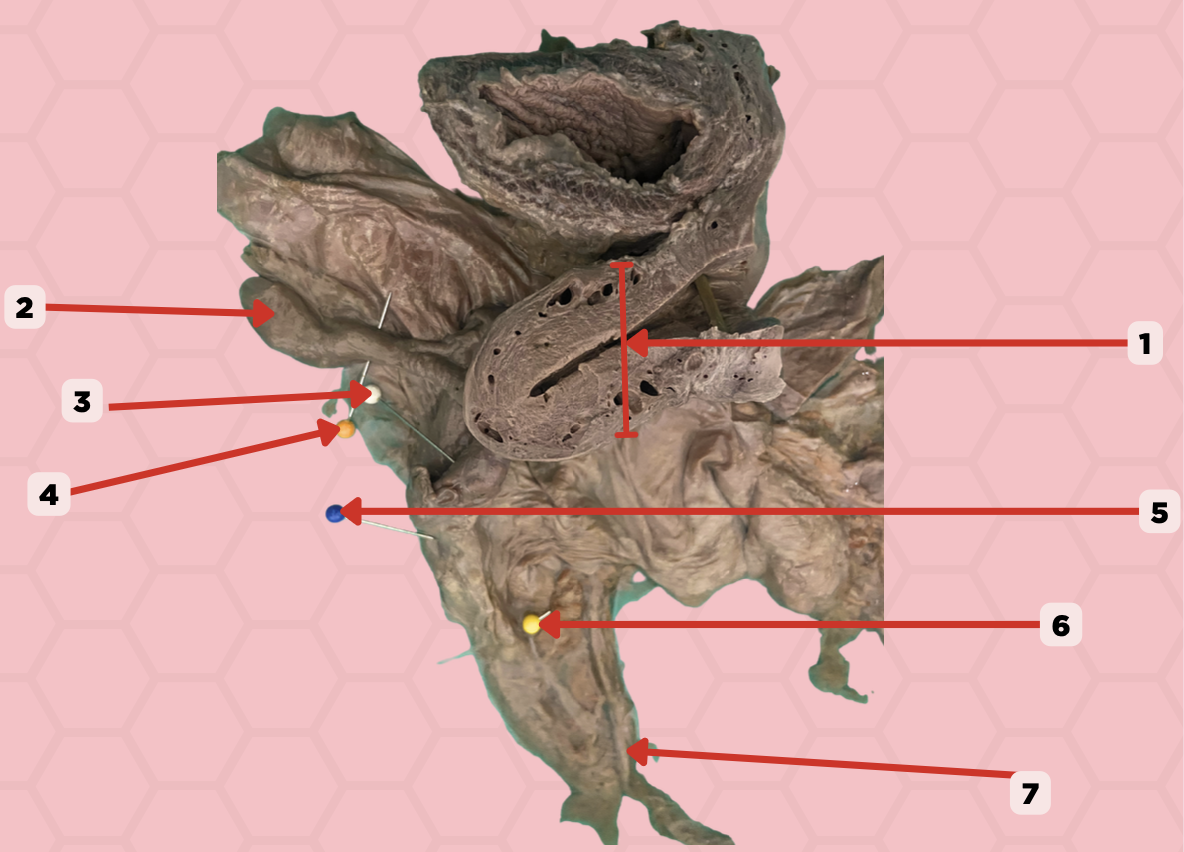
Mesosalpinx
Identify the structure labeled as 4.
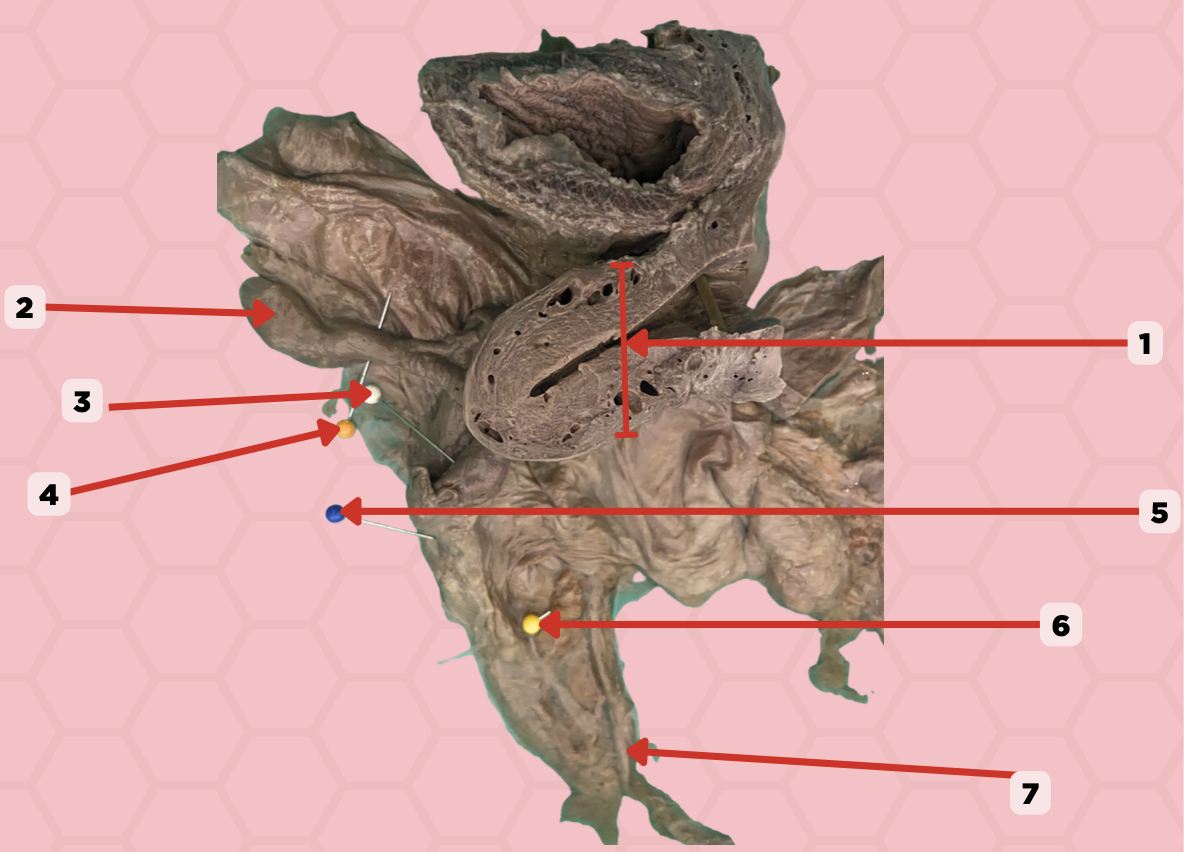
Suspensory Ligament of Ovary
Identify the structure labeled as 5.
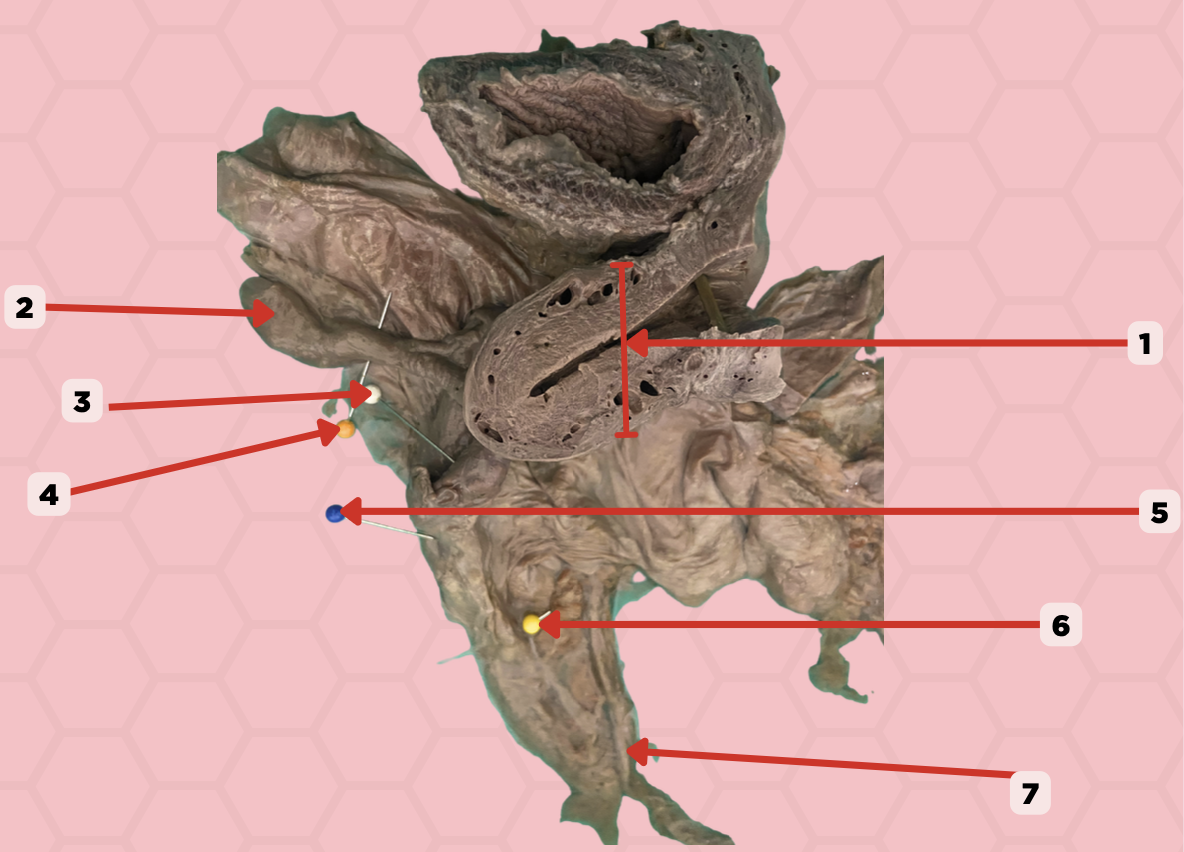
Mesovarium
Identify the structure labeled as 6.
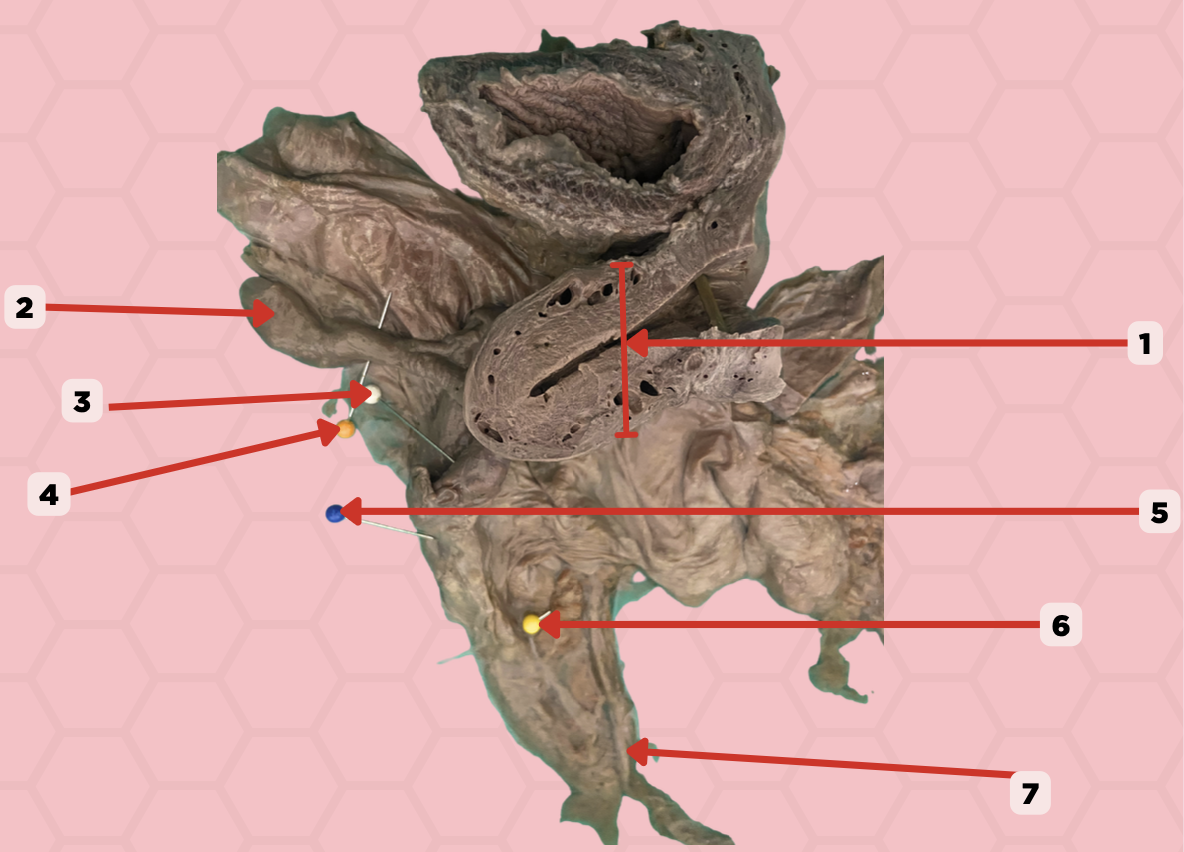
Ureter
Identify the structure labeled as 7.
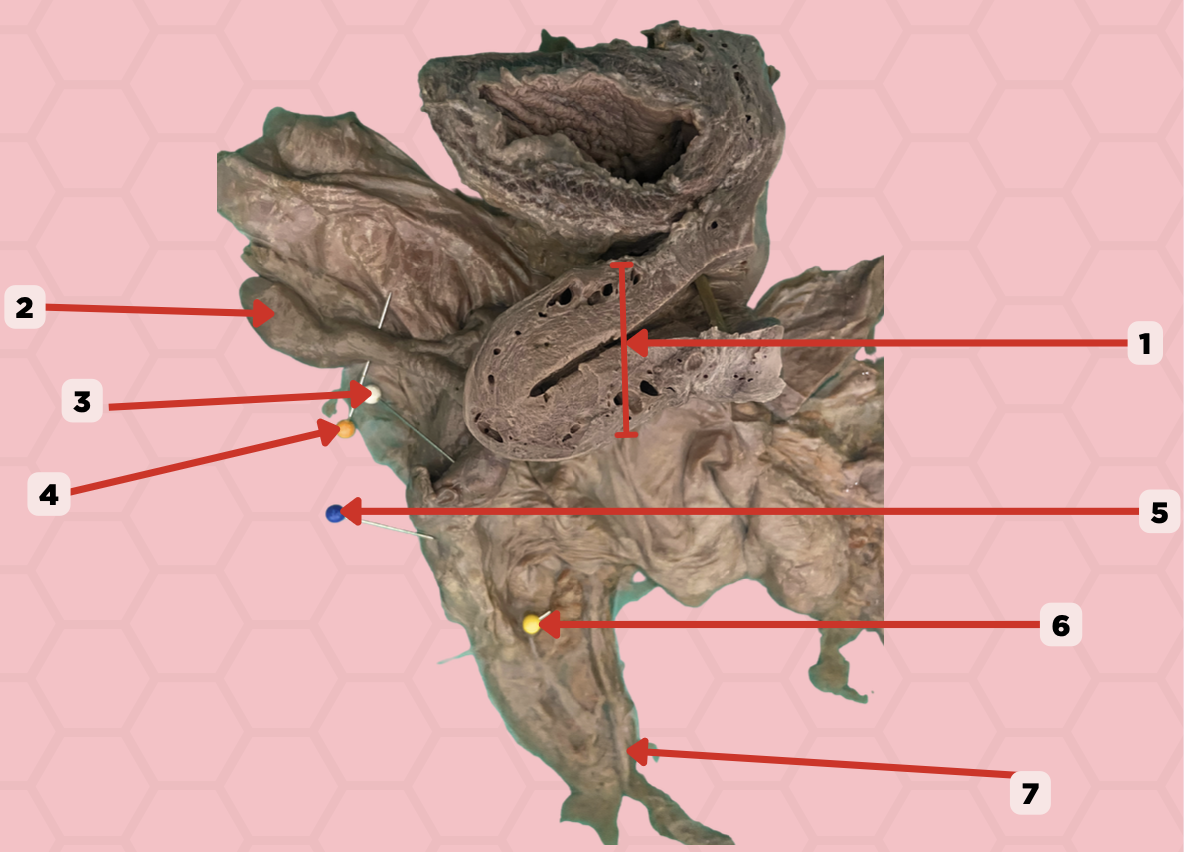
Internal Pudendal and Vaginal Arteries
What are the arterial blood supply of the female urethra?
Internal Pudendal and Vaginal Veins
What are the venous drainage of the female urethra?
Vesical Nerve Plexus and Pudendal Nerve
What are the innervation of the female urethra?
Urinary Tract Infection
More common in women than in men. Attributed to the shorter length of the female urethra as compared to the male urethra.
a. Pouch of douglas
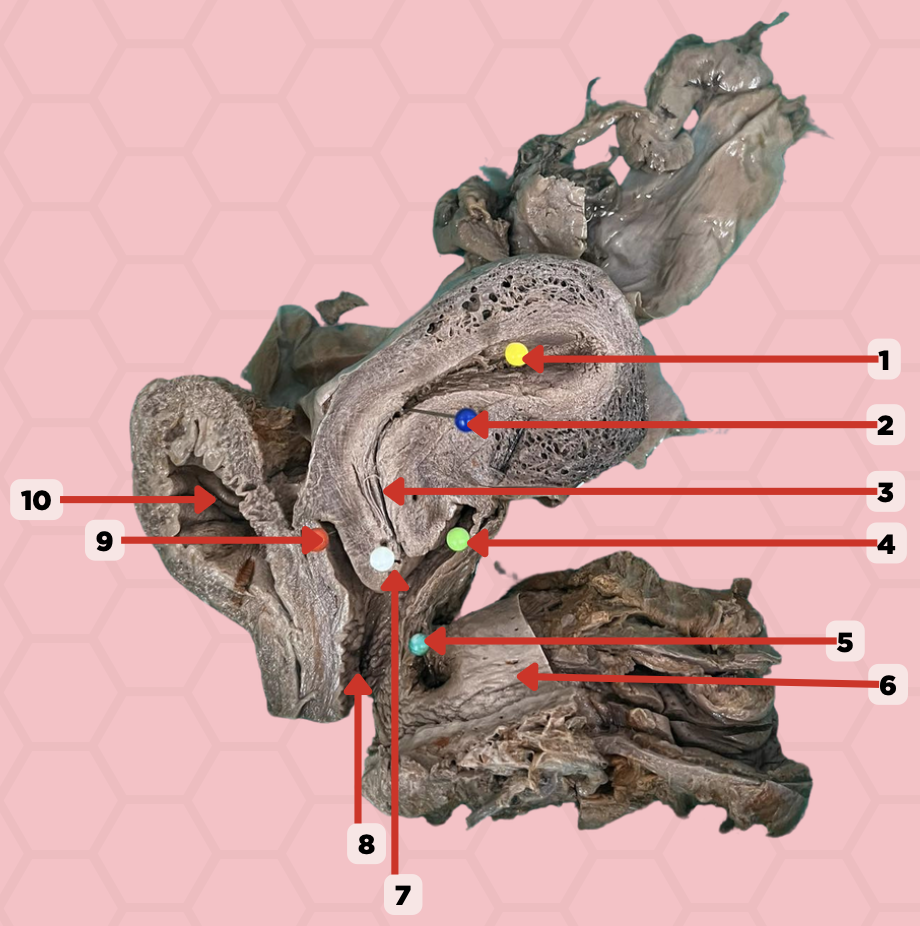
Aspiration of non-clotting blood can be accessed in this specific area when confirming a ruptured ectopic pregnancy. Where does the blood accumulate specifically indicated in Pin #4?
a. Pouch of douglas
b. Deep perineal pouch
c. Superficial Perineal Space
d. Anterior Fornix
b. Anomalous communication between the rectum and vagina
In the pinned structure marked as #5, what anatomical condition is often indicative of an infection?
a. Abnormal partition within the vagina
b. Anomalous communication between the rectum and vagina
c. Protrusion of the rectum through the anus
d. Unusual connection between the urethra and vagina
d. Anteflexed Uterus
If the pinned structure marked as #1 managed to abnormally, bend forwards and position itself atop of structure marked as #10, this anatomical condition would be indicative of what condition?
a. Retroverted Uterus
b. Anteverted Uterus
c. Retroflexed Uterus
d. Anteflexed Uterus
b. Myometrium
The pinned structure indicated by pointed by pin # 1 is composed of four layers, which of the following histological layers of this structure would contain the smooth muscles responsible for muscular contractions
a. Endometrium
b. Myometrium
c. Perimetrium
d. Verometrium
c. Feces
If pinned structure #6 was filled with the respective material it is supposed to contain under normal circumstances, what would you most likely find in its cavity.
a. Vitrelline Fluid
b. Urine
c. Feces
d. Intrauterine Fluid
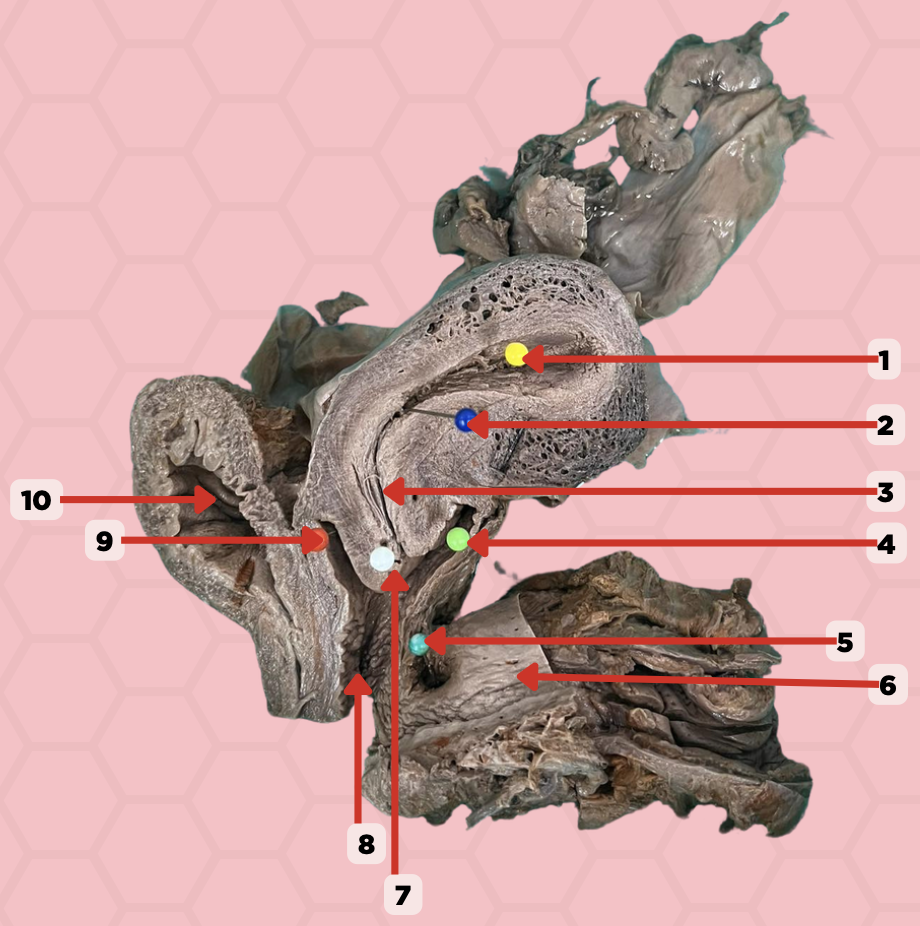
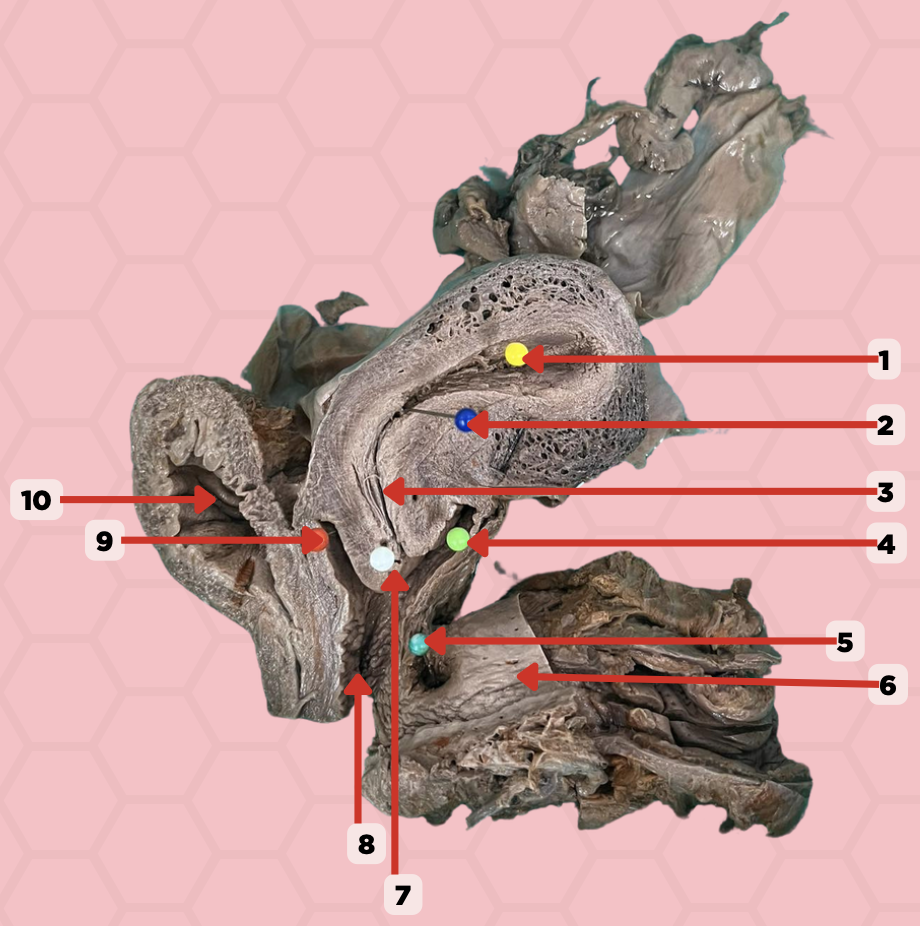
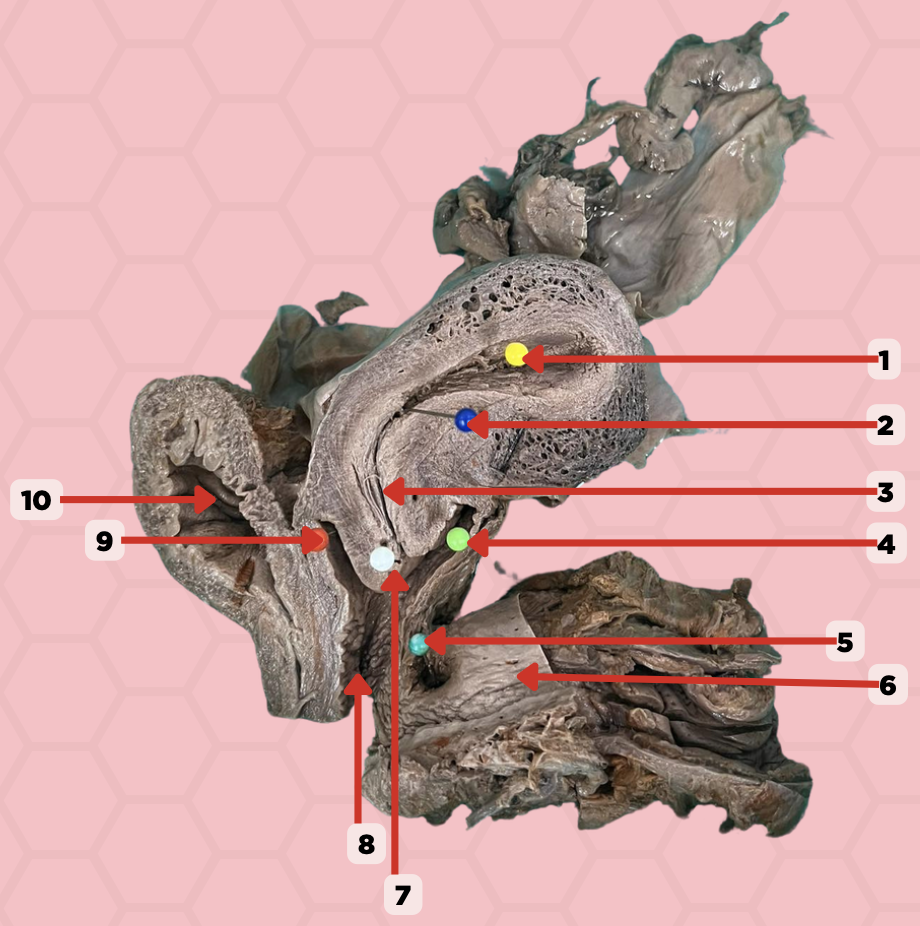
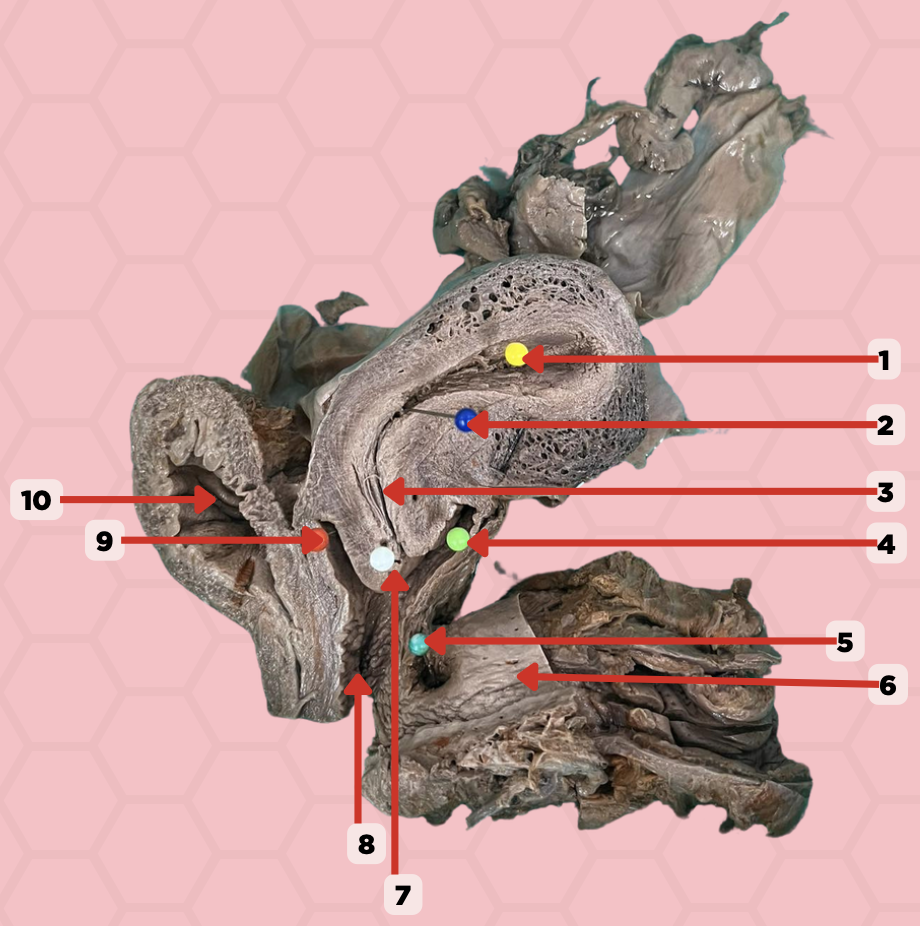
Uterine Cavity
Identify the structure labeled as 1.
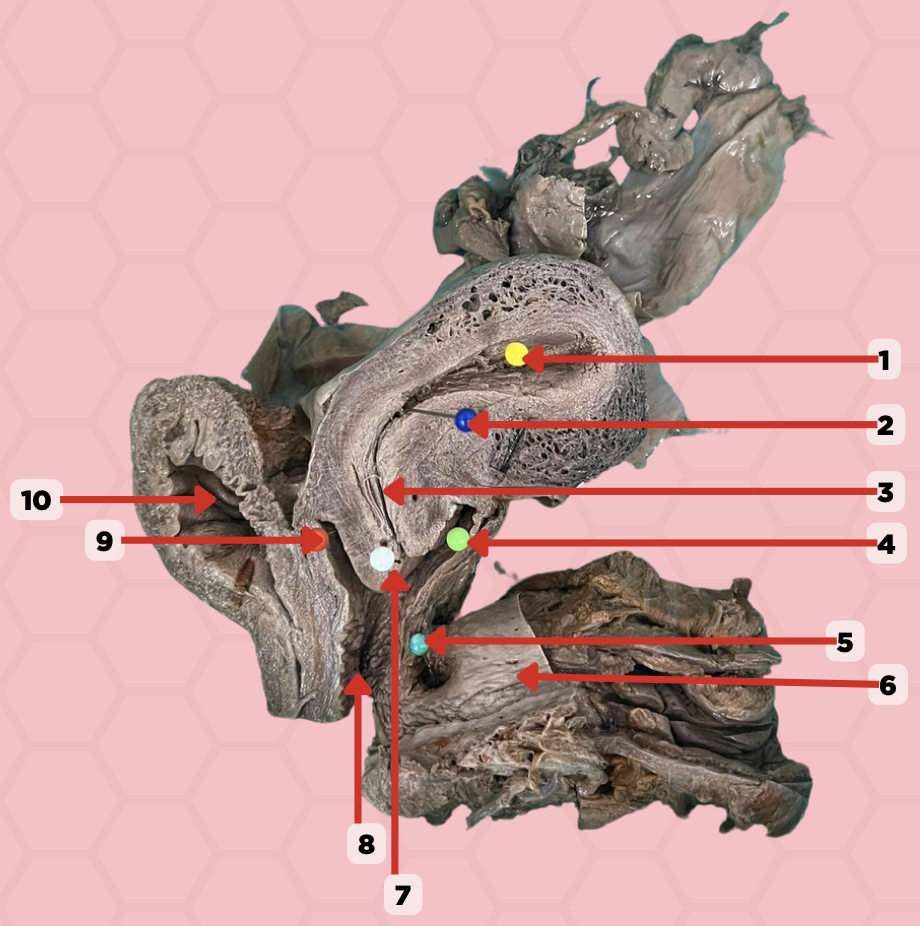
Internal OS
Identify the structure labeled as 2.
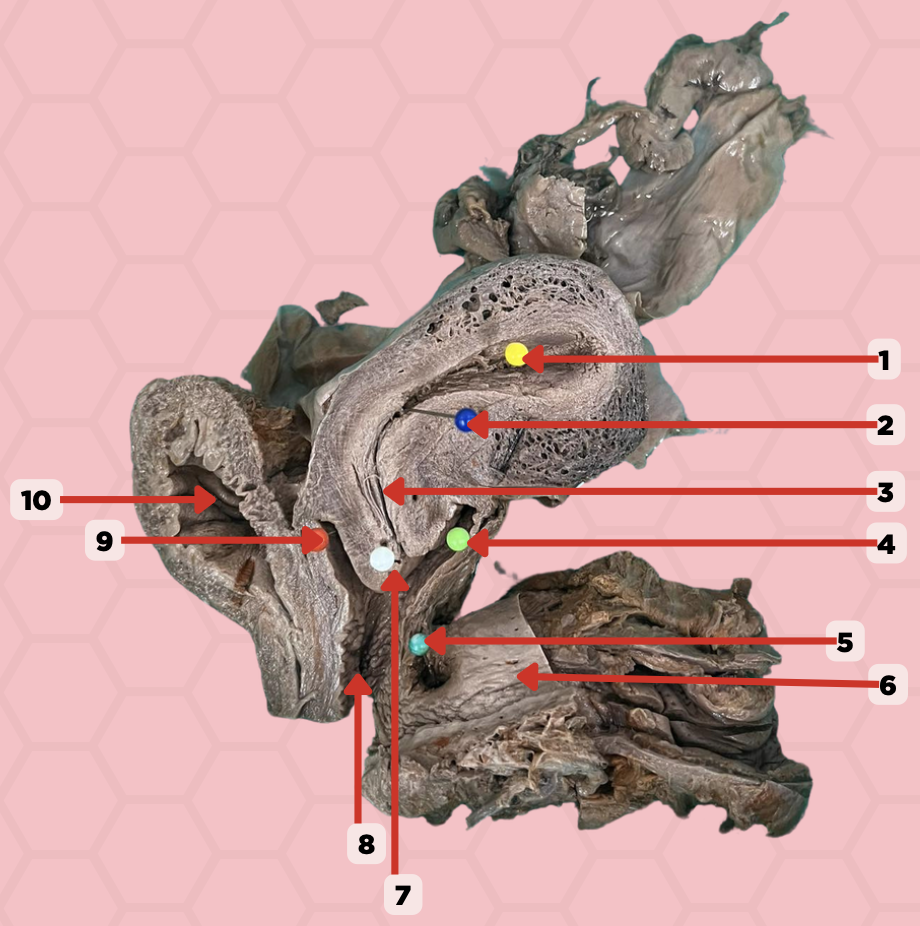
Isthmus
Identify the structure labeled as 3.
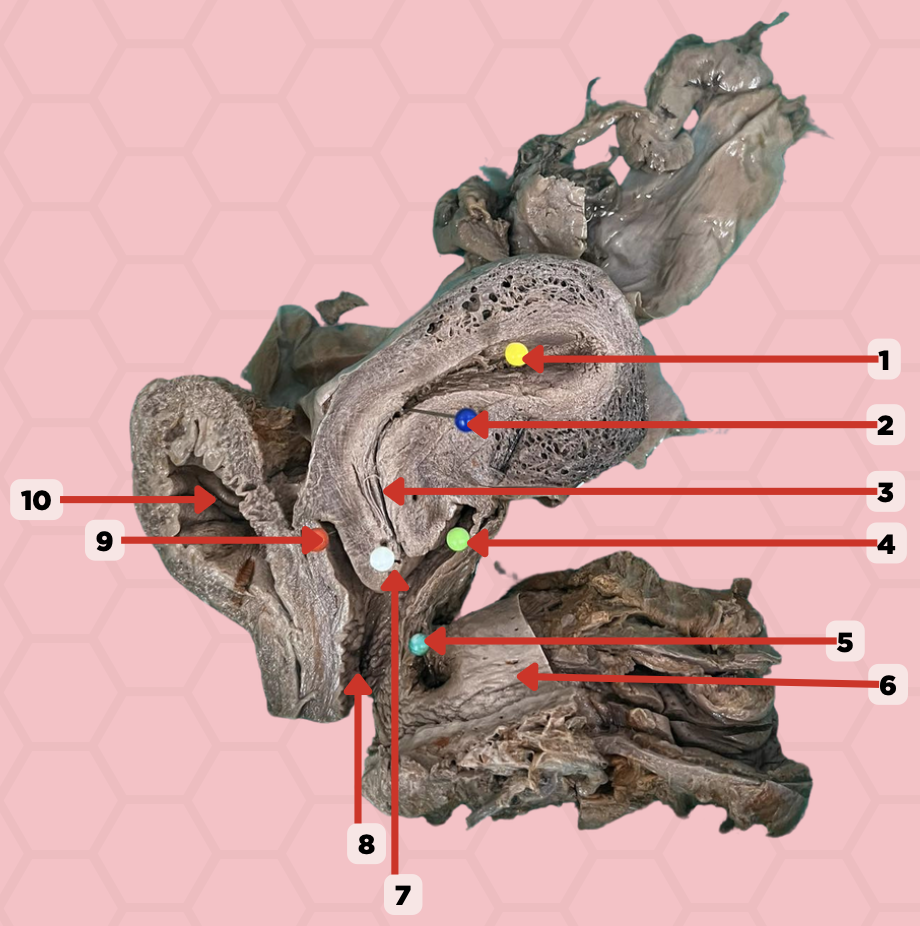
Posterior fornix
Identify the structure labeled as 4.
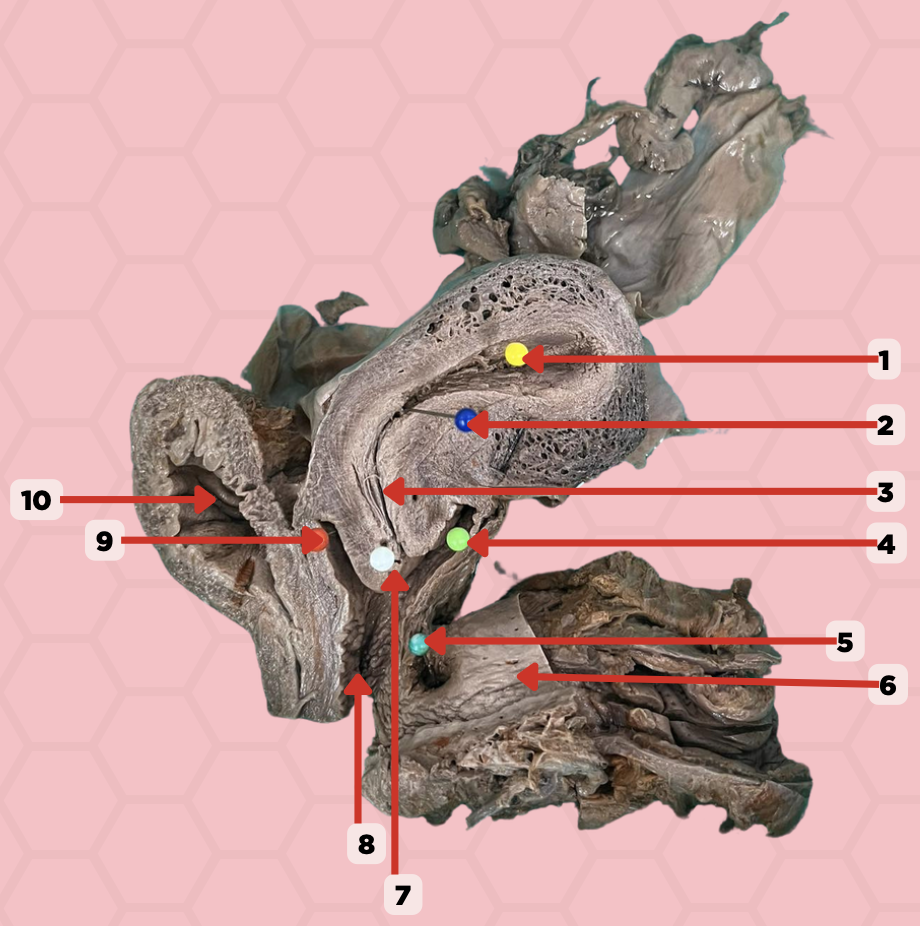
Recto-vaginal fistula
Identify the structure labeled as 5.
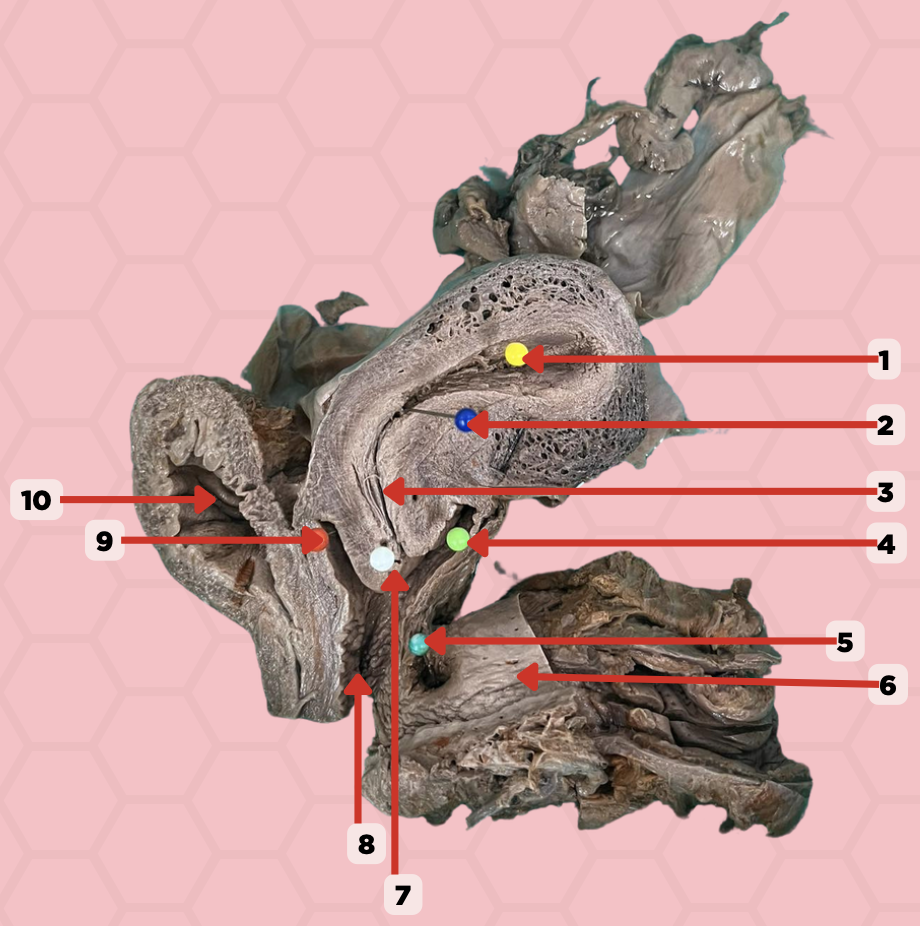
Rectum
Identify the structure labeled as 6.
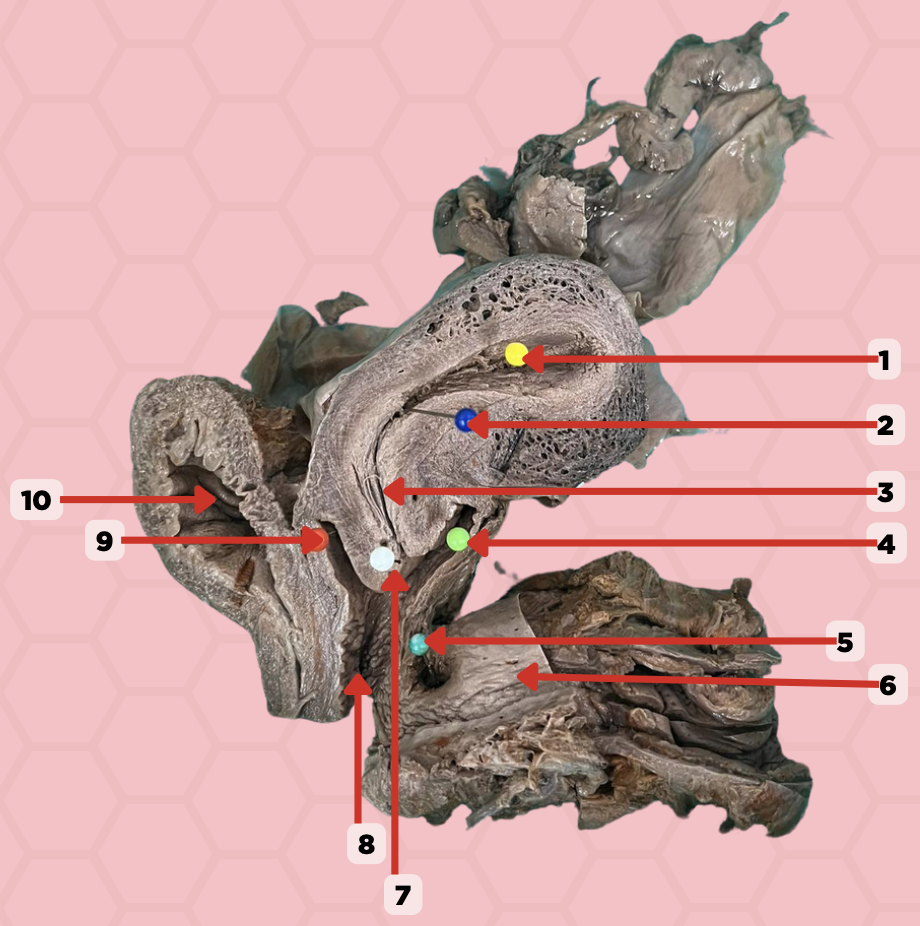
External OS
Identify the structure labeled as 7.
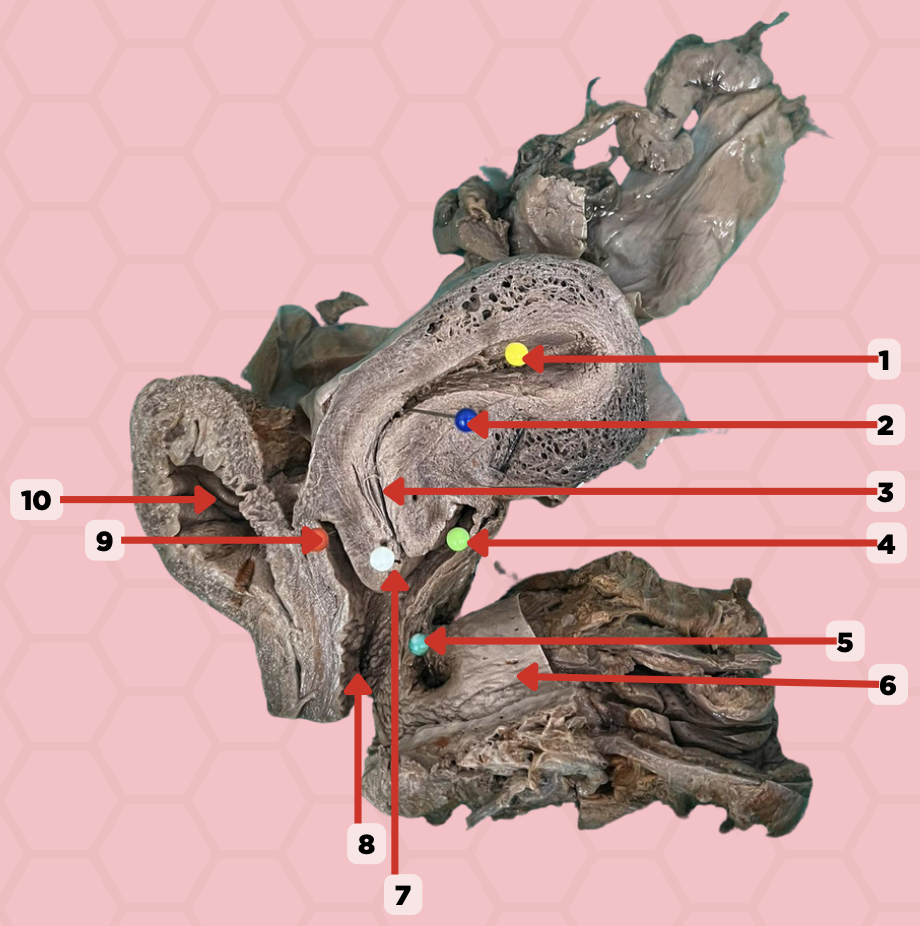
Vaginal canal
Identify the structure labeled as 8.
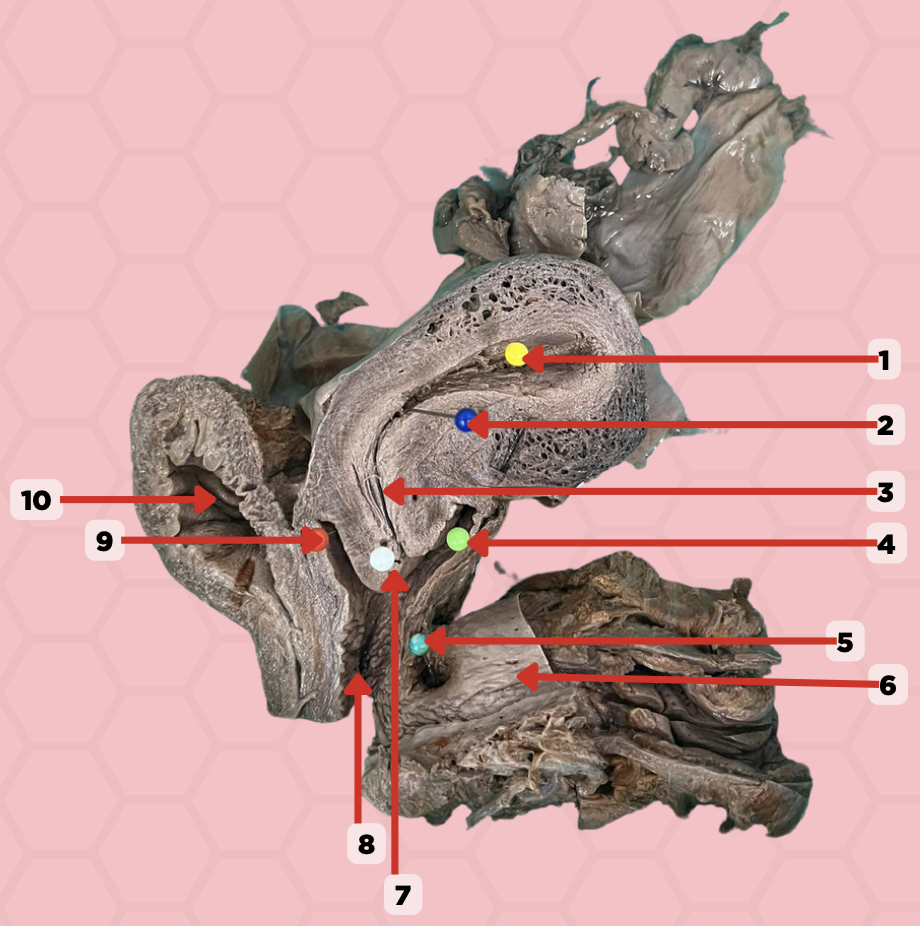
Anterior fornix
Identify the structure labeled as 9.
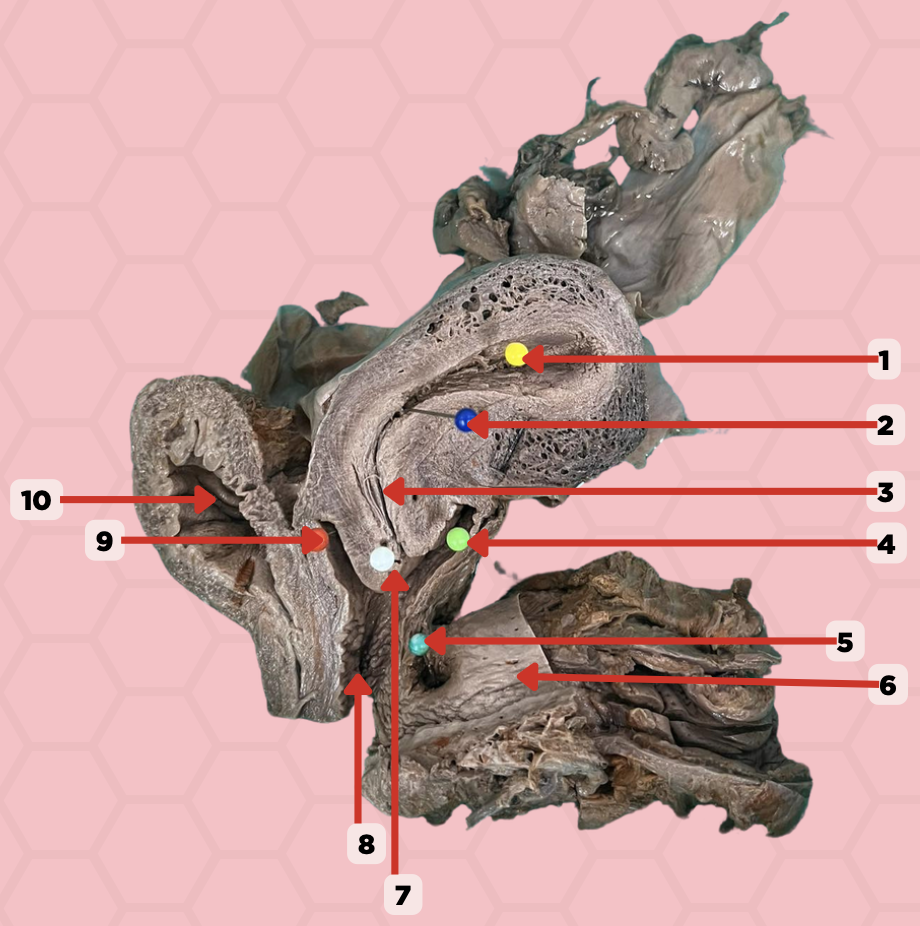
Urinary bladder
Identify the structure labeled as 10.
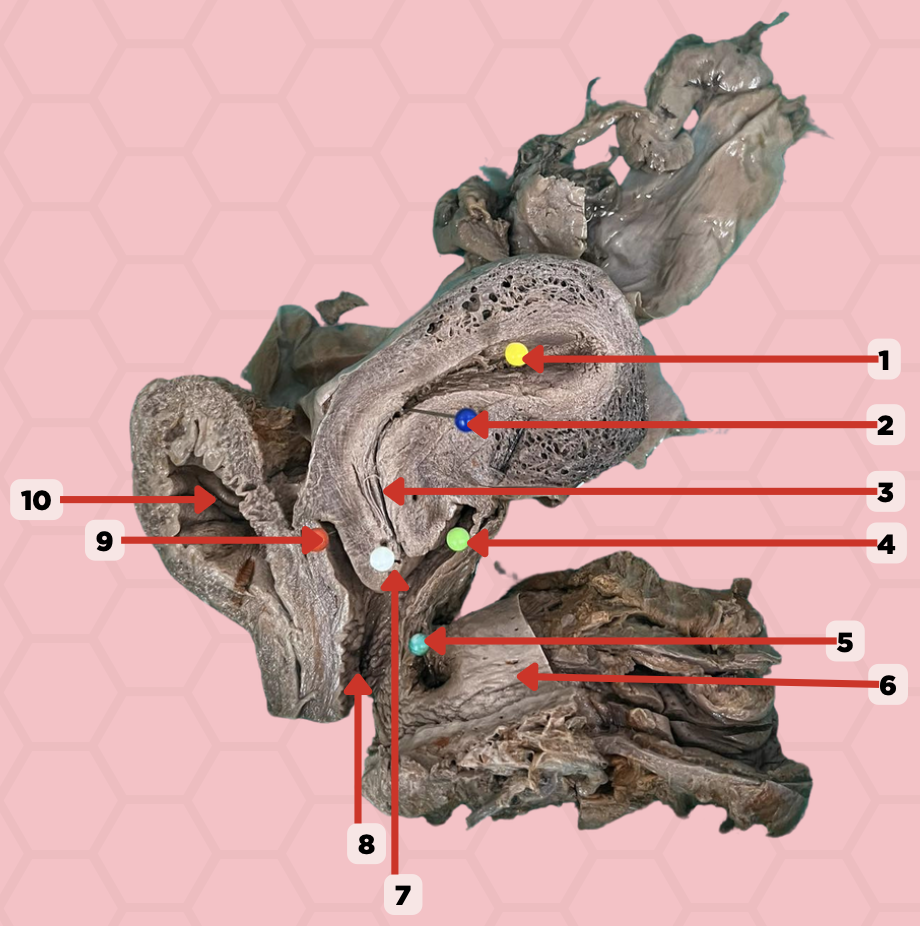
Tubal Branch of Ovarian Artery and Ascending Branch of Uterine Artery
What is the arterial blood supply of the uterine tube and ovary?
Uterine Artery
What is the arterial blood supply of the uterus?
Pampiniform plexus → IVC and Left Renal Vein
What is the venous drainage of the ovary?
Tubal Veins → Ovarian Veins and Uterine Venous Plexus
What is the venous drainage of the uterine tube?
Uterine Veins → Uterine Venous Plexus → Internal Iliac Vein
What is the venous drainage of the uterus?
Anteverted and anteflexed
What is the normal anatomical position of uterus?
Retroverted and retroflexed uterus
This anatomical position of the uterus is more prone to uterine prolapse
Valsava maneuver
An increase in abdominal pressure may push the uterus into the vaginal canal.
1st Degree
Degree of uterine prolapse where the uterus occupies the upper half of the vaginal canal.
2nd degree
Degree of uterine prolapse where the uterus is within the vaginal canal, occupying more than half.
3rd degree
Degree of uterine prolapse where the uterus or part of the uterus is outside of the introitus.
4th degree
Degree of uterine prolapse where the the uterus is completely prolapsed.
Total Abdominal Hysterectomy and Bilateral Salpingo-Oophorectomy (TAH-BSO)
Removal of the uterus, uterine tube, and ovaries. The uterine artery is one of the important vessels that will have to be ligated
Ectopic Pregnancy
A common condition wherein the embryo is implanted in the fallopian tube instead of implanting into the uterine wall
d. Modified apocrine sweat glands
What type of gland is #1?
a. Modified apocrine serous glands
b. Merocrine glands
c. Eccrine sweat glands
d. Modified apocrine sweat glands
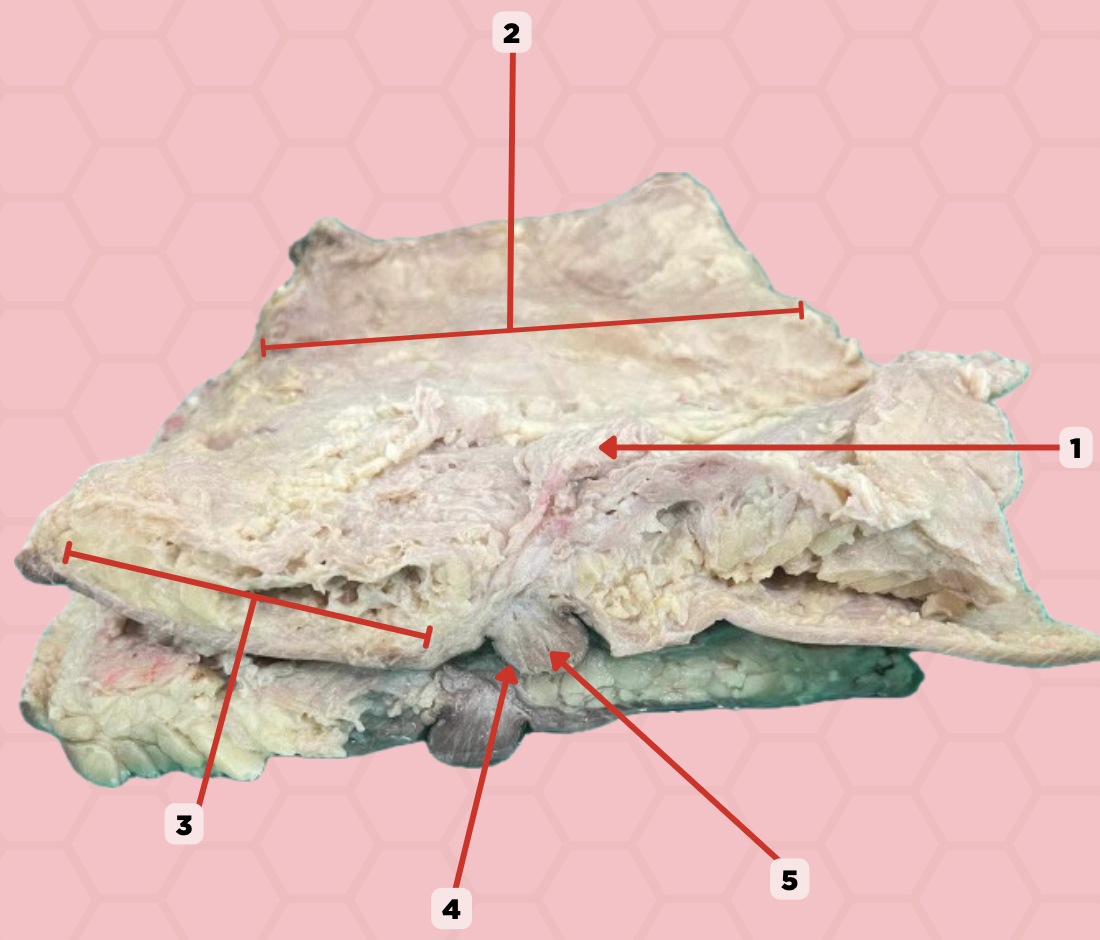
b. It is a space located behind the mammary gland and anterior to pectoralis muscle, allowing for movement of the breast within the thoracic wall.
What is the anatomical significance of the structure on #2 in relation to the mammary gland?
a. It is the primary location for milk storage within the breast.
b. It is a space located behind the mammary gland and anterior to pectoralis muscle, allowing for movement of the breast within the thoracic wall.
c. It contains the major blood vessels supplying the mammary gland.
d. It is the area where the mammary glands are attached to the skin.
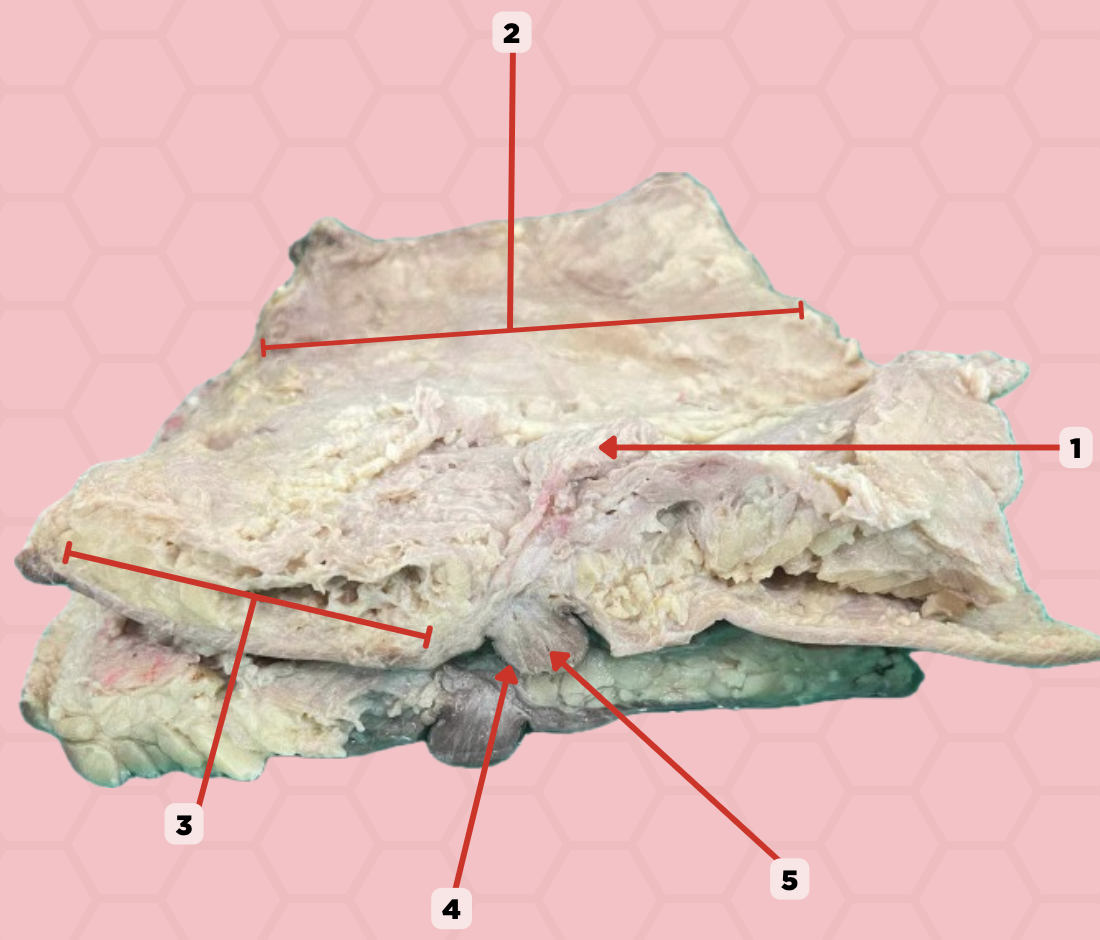
c. Breast carcinoma
In the indicated region #2, what clinical manifestation could be seen that diminishes the mobility of the breast?
a. Peau d’orange
b. Pregnancy
c. Breast carcinoma
d. Polythelia
b. It is a thickened reticula cutis, providing structural support and contributing to the contour and shape of the breast by anchoring the skin to the underlying fascia.
What is the function of the structure on #3?
a. It facilitates the movement of lymph through the breast's lymphatic system
b. It is a thickened reticula cutis, providing structural support and contributing to the contour and shape of the breast by anchoring the skin to the underlying fascia.
c. It primarily functions as a conduit for the neurovascular supply to the mammary glands.
d. It is a muscle that contracts to assist in milk ejection during lactation.
b. Loose subcutaneous tissue
In the pointed region #2, what is the most likely type of tissue may be observed when a histological sample collected from this region is viewed under a microscope
a. Loose areolar tissue
b. Loose subcutaneous tissue
c. Dense subcutaneous tissue
d. Dense areolar tissue
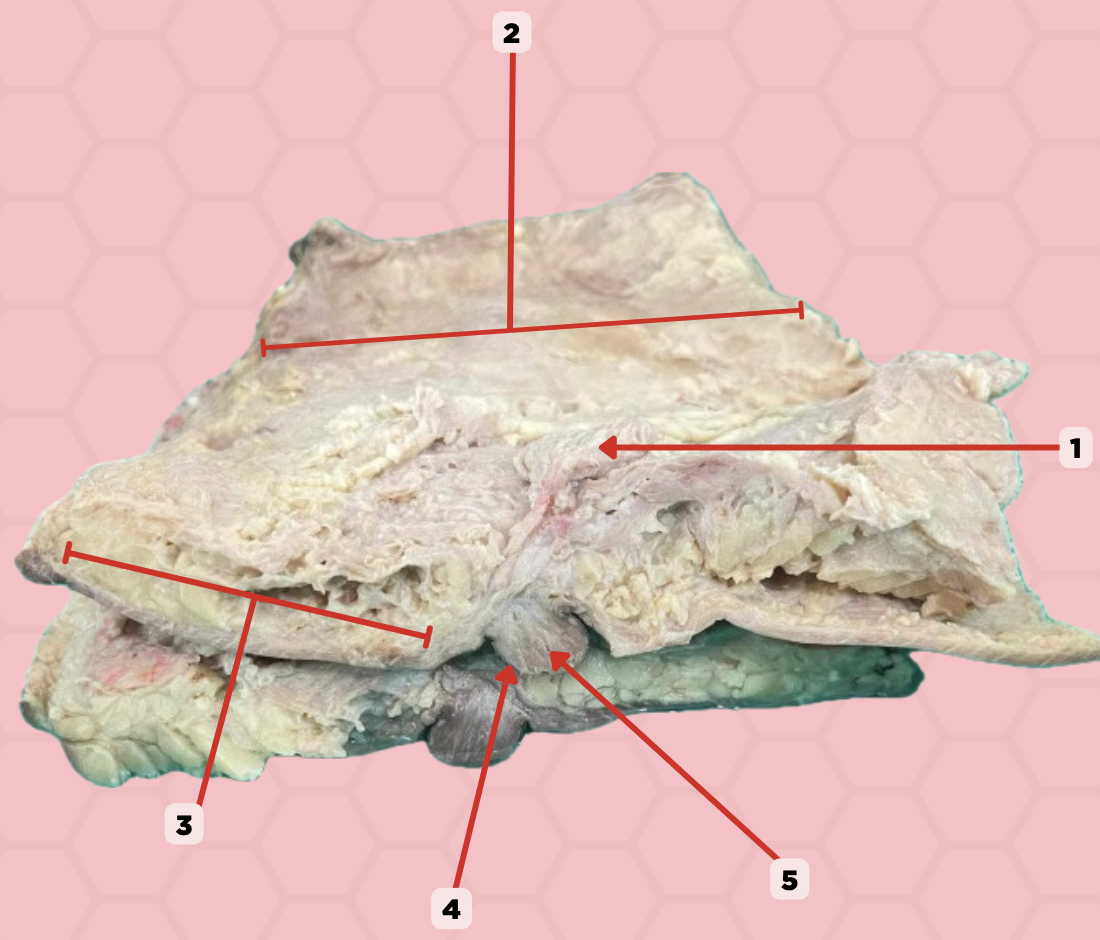
Mammary gland
Identify the structure labeled as 1.
Retromammary space
Identify the structure labeled as 2.
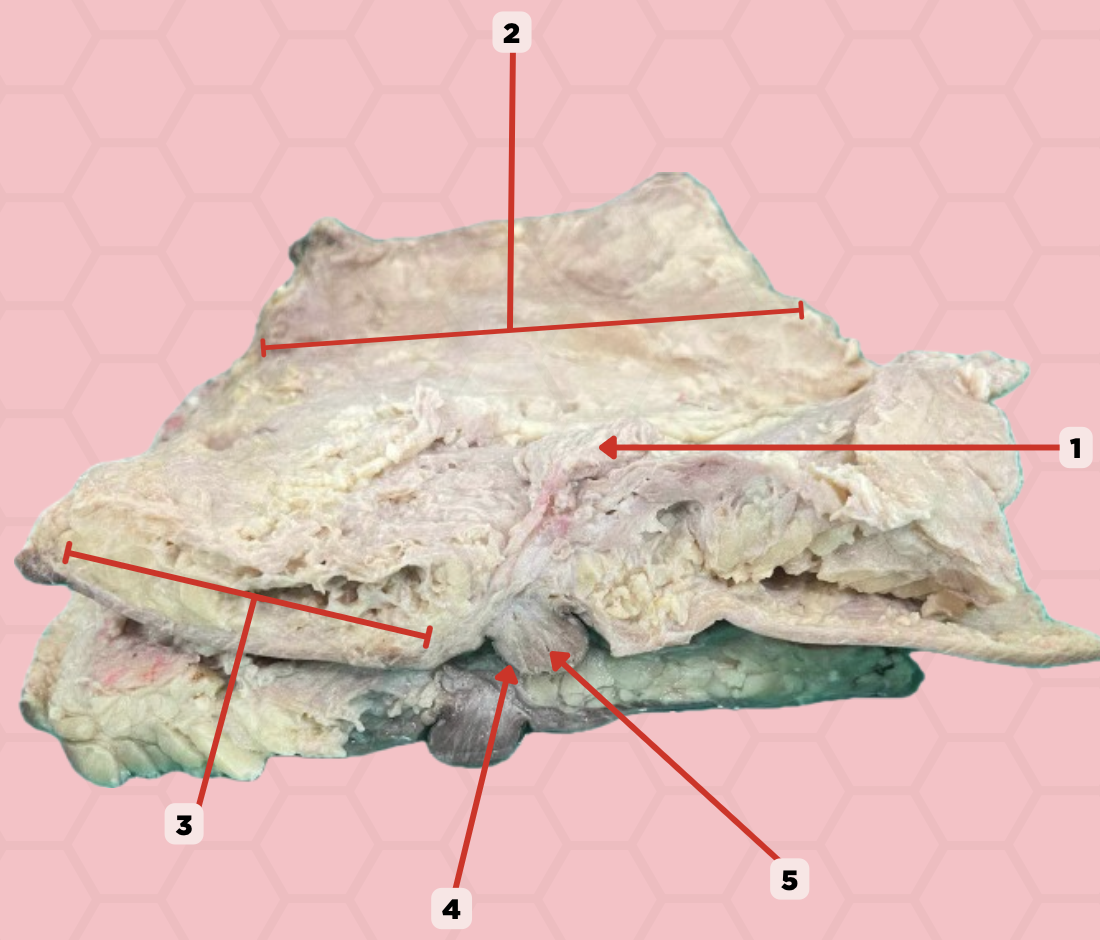
Suspensory ligament of Cooper
Identify the structure labeled as 3.
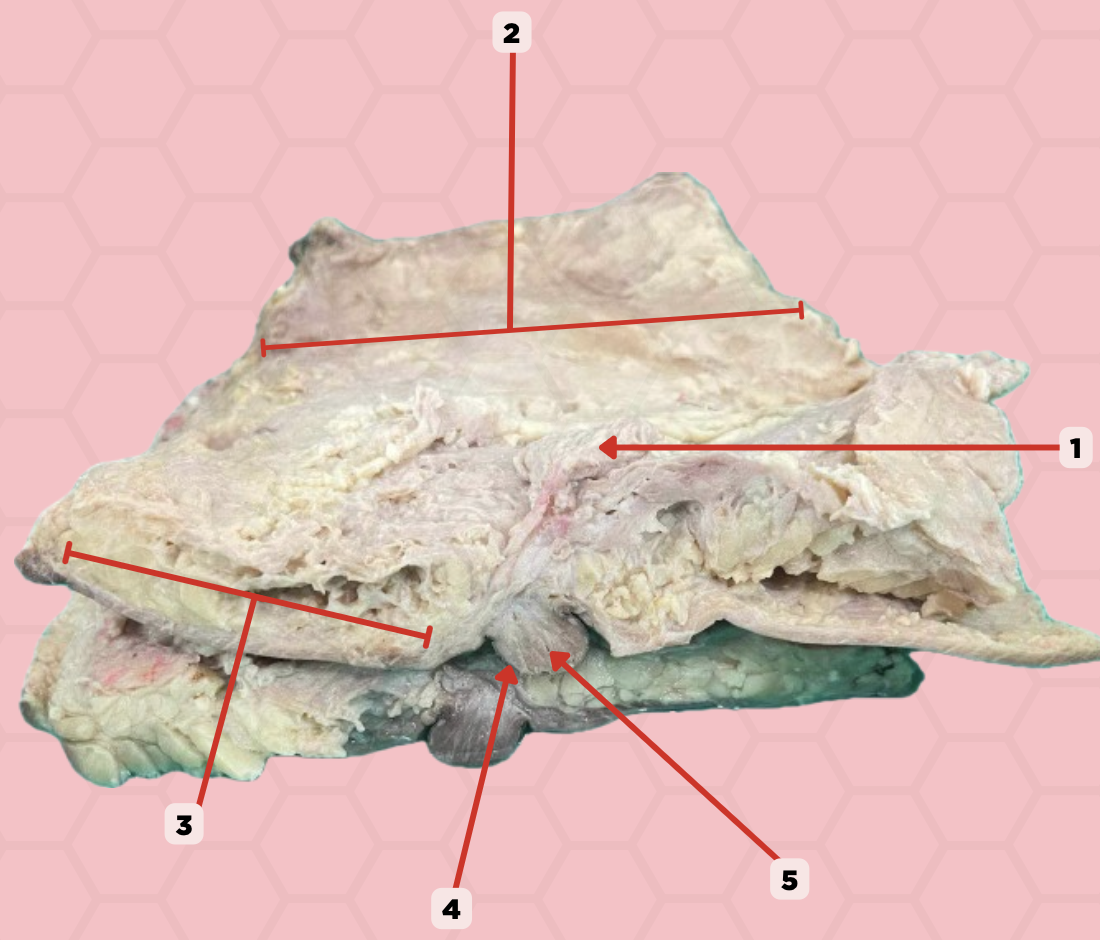
Nipple
Identify the structure labeled as 4.
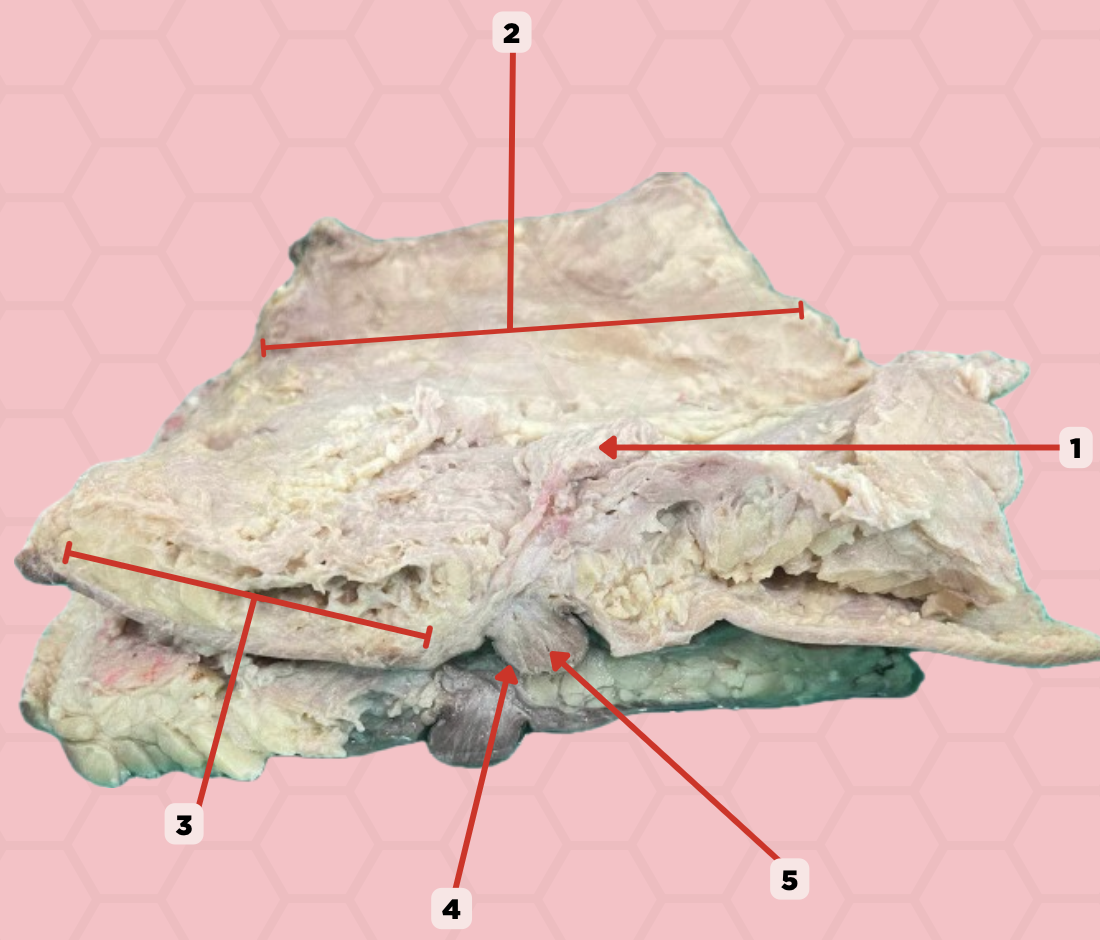
Lactiferous duct
Identify the structure labeled as 5.
Medial Thoracic Artery and Medial Mammary Branches
What is the arterial blood supply of the medial breast?
Lateral Thoracic and Thoracoacromial Artery
What is the arterial blood supply of the lateral breast?
Parasternal Lymph Nodes
What is the lymph node drainage of the medial breast?
Axillary Lymph Nodes
What is the lymph node drainage of the lateral breast?
Axillary Vein and Internal Thoracic Vein
What is the venous drainage of the breast?
Breast Cancer
Abnormal cells that arise either from the ducts or lobes of the mammary glands. Metastatic cancer cells that enter the lymphatic vessel will usually pass through 2 or 3 groups of lymph nodes before entering the venous system in the first few lymph nodes in which the tumor will drain are called sentinel lymph nodes.
Lymph Node Biopsy
Surgeons inject a radioactive solution or dye near the tumor. The stained nodes are then removed and examined by a pathologist for cancer cells.
Lymphedema
Interference with the lymphatic drainage due to the cancer of the breast can cause nipple deviation, thickened skin, and an orange peel appearance (Peau D'Orange sign). Larger dimples, abnormal breast contour, and nipple retraction result from cancerous invasion shortening the suspensory ligaments.
Gynecomastia
Breast hypertrophy in males after puberty. Drug-related is due to the hormonal therapy with diethylstilbestrol (DES). Some patients with liver problems may also present with breast enlargement due to the imbalance in the metabolism of sex hormones by the liver.
Polymastia
Also known as supernumerary breast. Involves a rudimentary nipple and areola, often mistaken for a mole until pigmentation changes
Polythelia
Also known as accessory nipples. Involves extra nipples occurring above or below the normal breasts, often along the milk line from the axilla to the groin, including the axillary fossa or anterior abdominal wall.
Symmastia
Rare condition where the breasts are joined in the middle due to abnormal mammary tissue development or as a complication of breast augmentation. Normally, a gap called the intermammary cleft separates the breasts.
b. Anteverted and anteflexed
What is the normal anatomical position of the uterus?
a. Retroverted and retroflexed
b. Anteverted and anteflexed
c. Anteverted and retroflexed
d. Retroverted and anteflexed
c. Dorsal Nerve
What innervates this portion of the external vagina?
a. Posterior Labial Nerve
b. Anterior Labial Nerve
c. Dorsal Nerve
d. Pudendal Nerve
a. Internal pudendal artery
What ultimately supplies structure #1?
a. Internal pudendal artery
b. Ovarian artery
c. Uterine artery
b. Pudendal veins
Which will correctly drain structure #3 in the venous system?
a. Vaginal vein -> internal iliac vein
b. Pudendal veins
c. Vaginal vein -> vaginal venous plexus -> internal iliac vein
d. Vaginal vein -> external pudendal vein
d. Fatty tissue decreases after menopause in this structure
Which is the correct physiological change of structure #3?
a. Fatty subcutaneous tissue will decrease during puberty
b. Fatty tissue will increase after menopause
c. The structure becomes more develop as age increases
d. Fatty tissue decreases after menopause in this structure
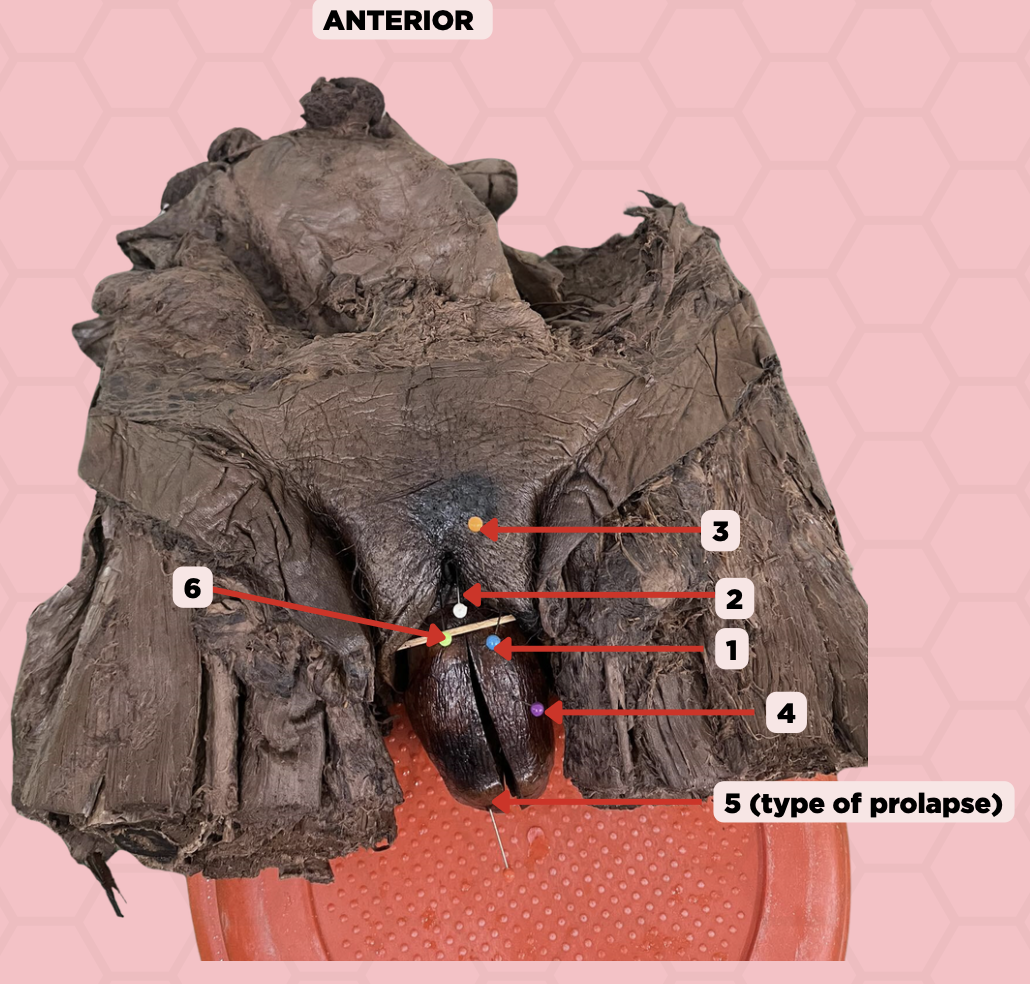
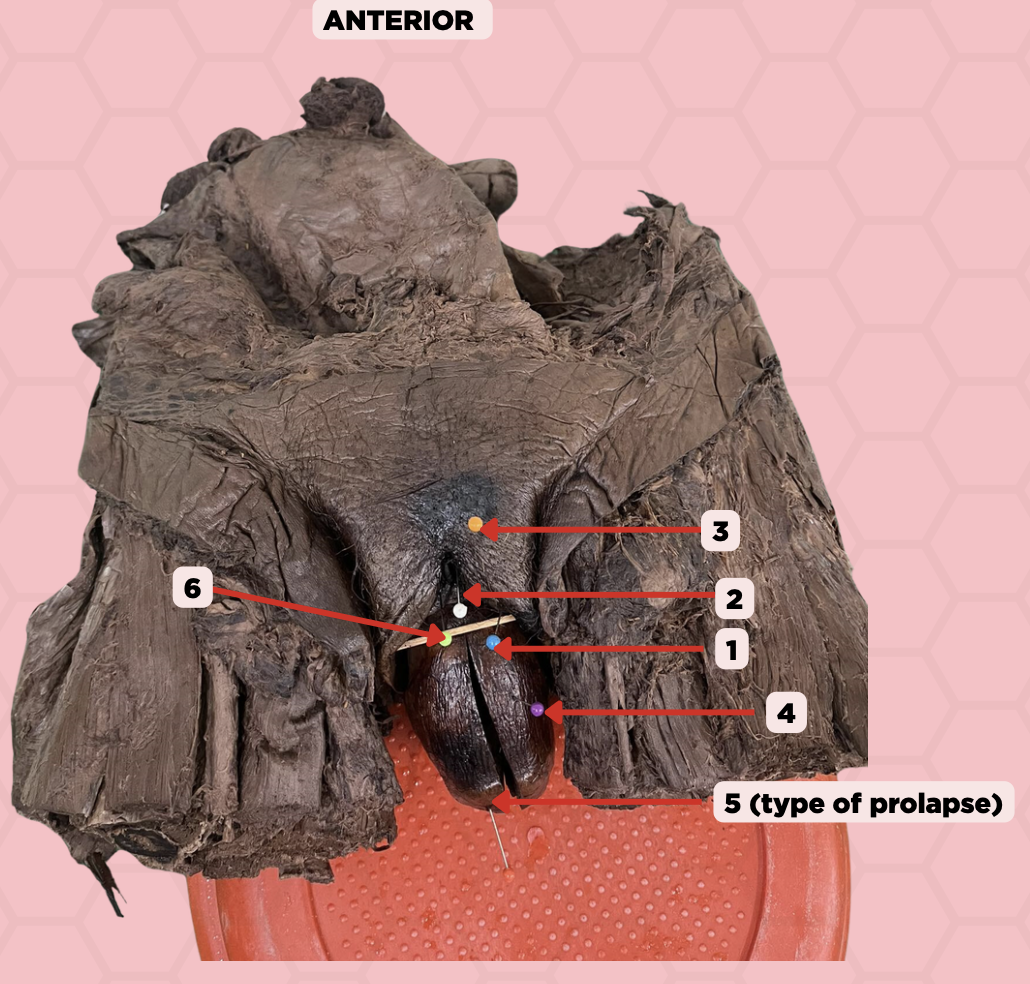
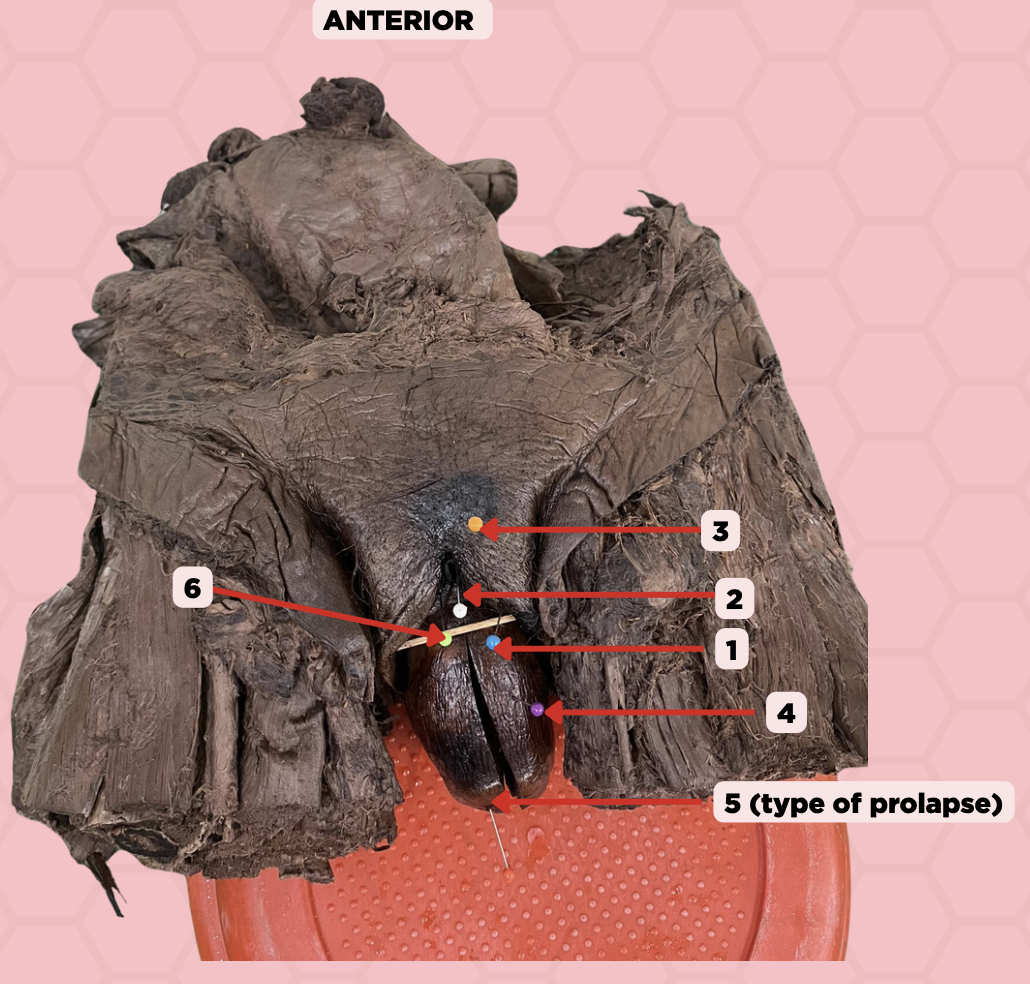
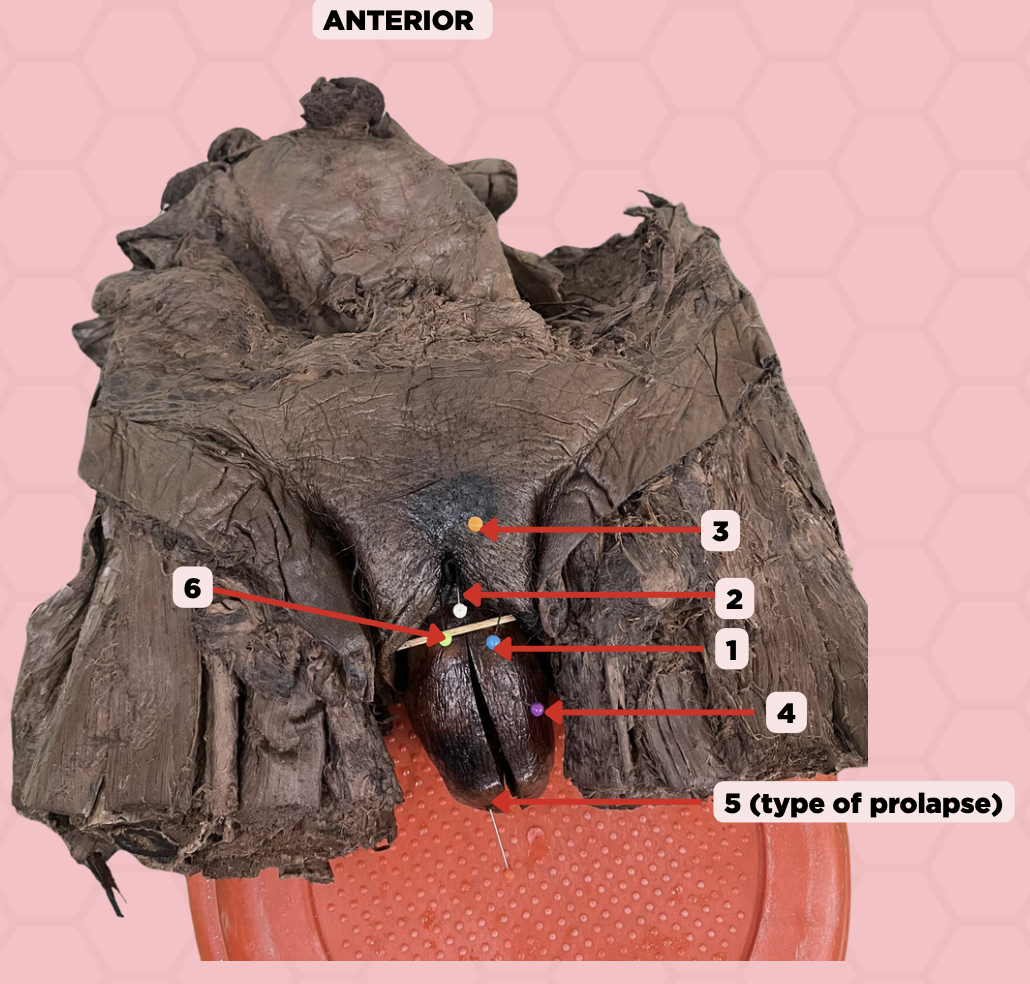
Labia majora
Identify the structure labeled as 1.
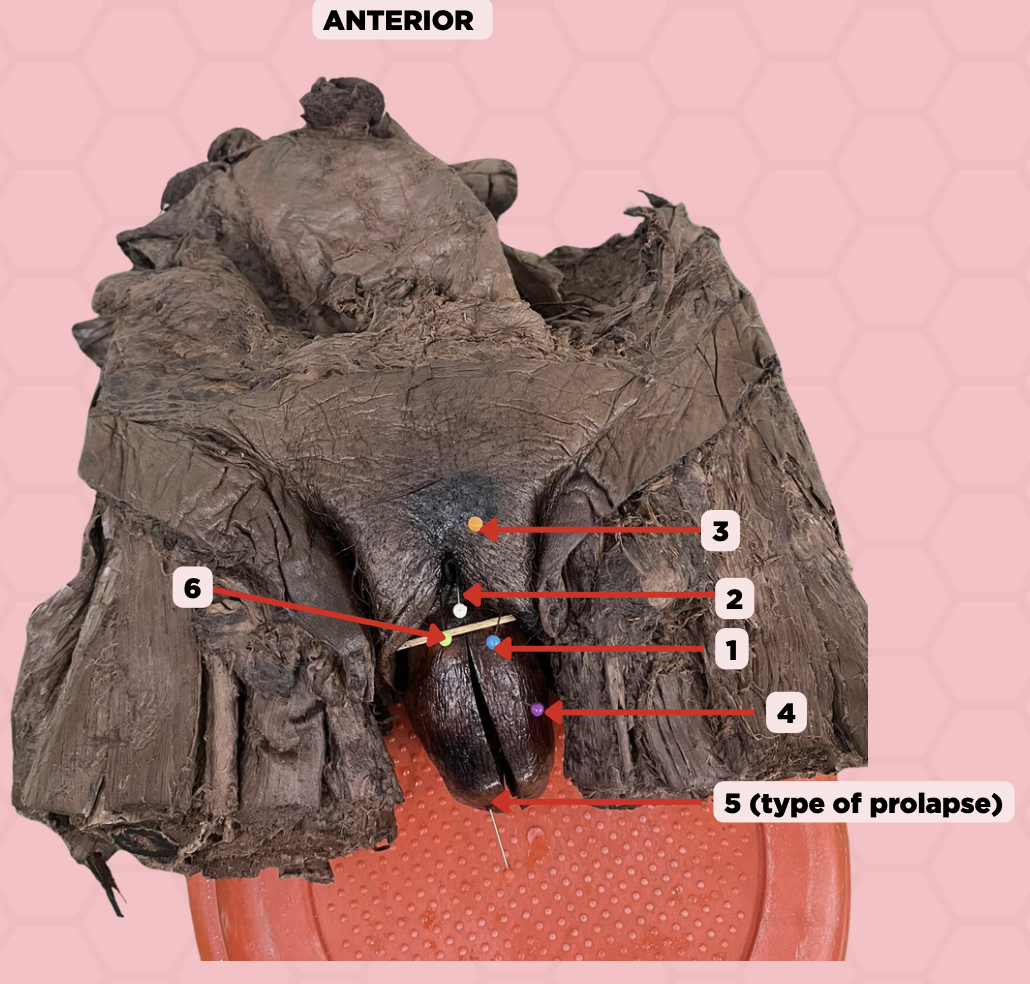
Clitoris
Identify the structure labeled as 2.
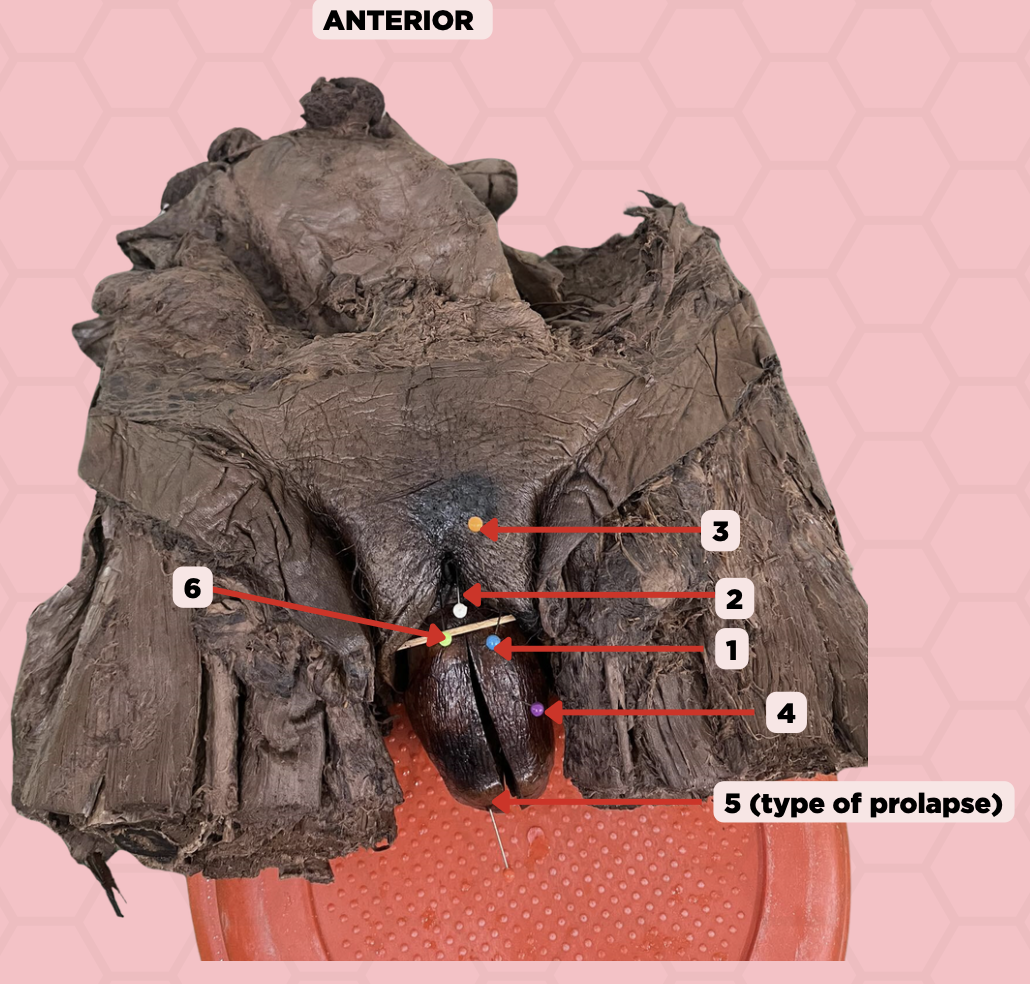
Mons pubis
Identify the structure labeled as 3.
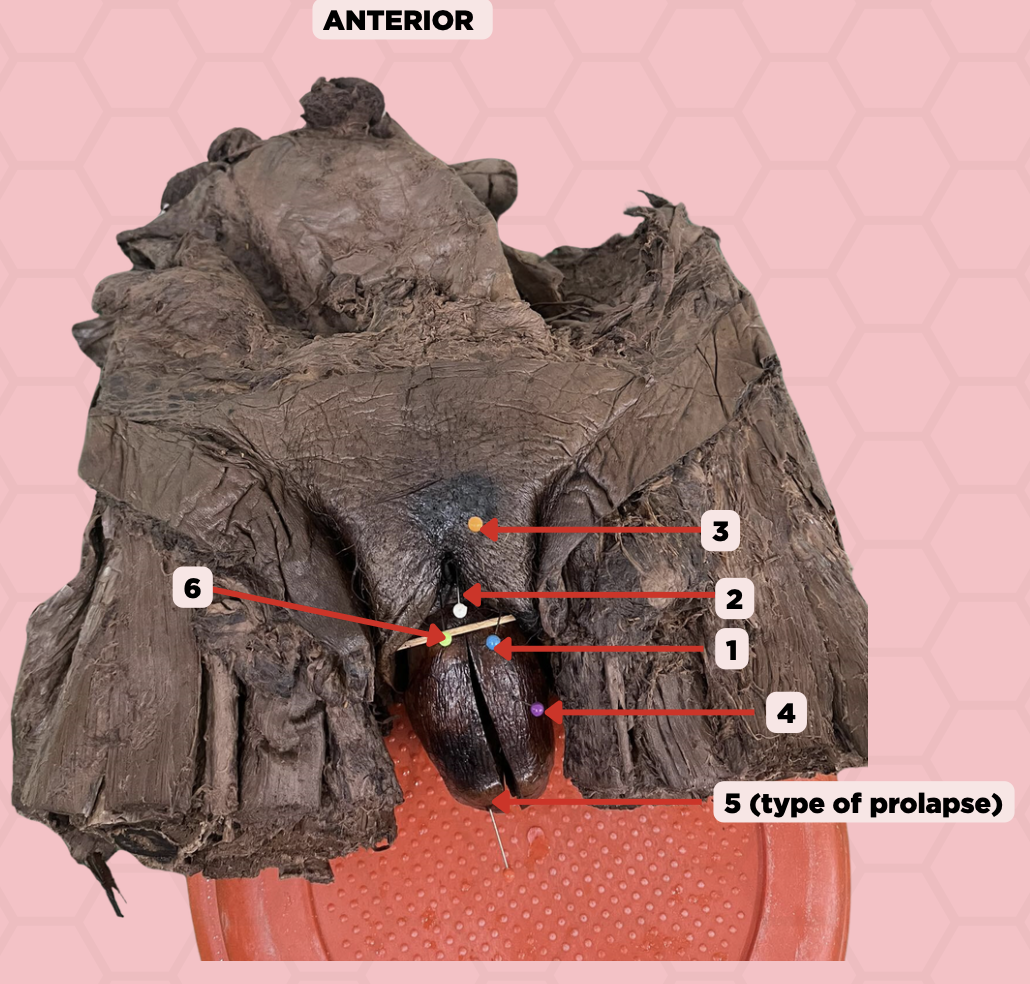
Uterus
Identify the structure labeled as 4.
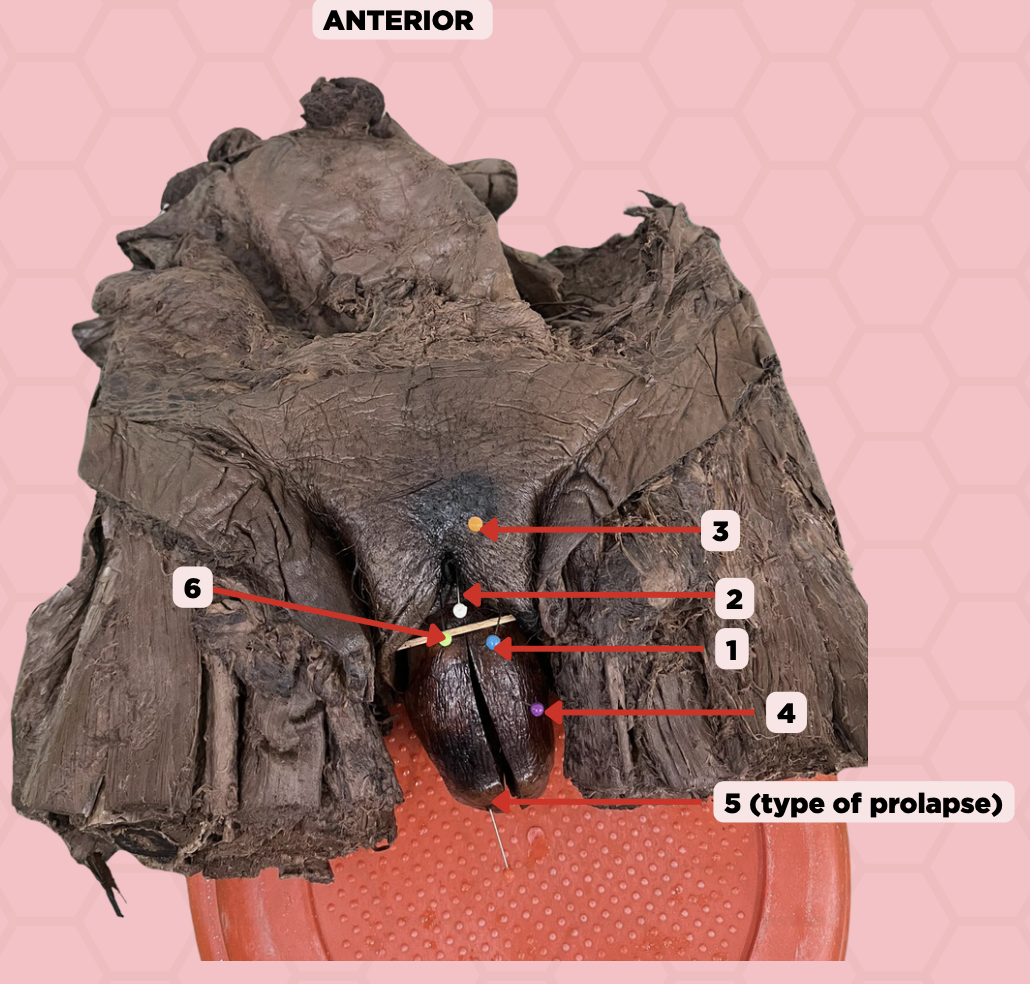
4th degree, complete uterine prolapse
Identify the structure labeled as 5.
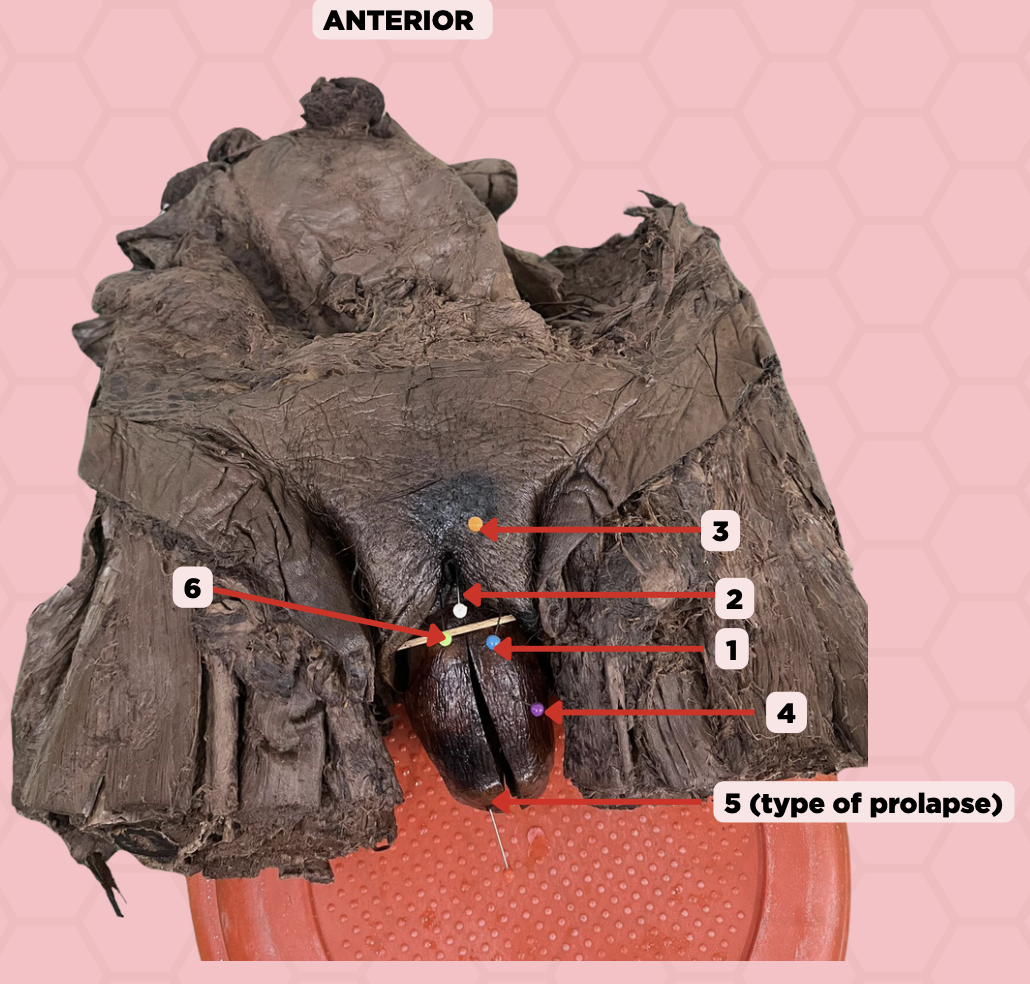
Labia majora
Identify the structure labeled as 6.
Internal Pudendal Artery and Vein, External Pudendal Artery and Vein
What are the neurovascular structures supplying the vulva?
Uterine Arteries
What is the arterial blood supply of the superior portion of the vagina?
Vaginal and Internal Pudendal Arteries
What is the arterial blood supply of the middle and inferior portion of the vagina?