APES Everything - USA
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
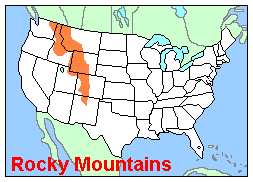
Rocky Mountains
Mountain top removing mountain
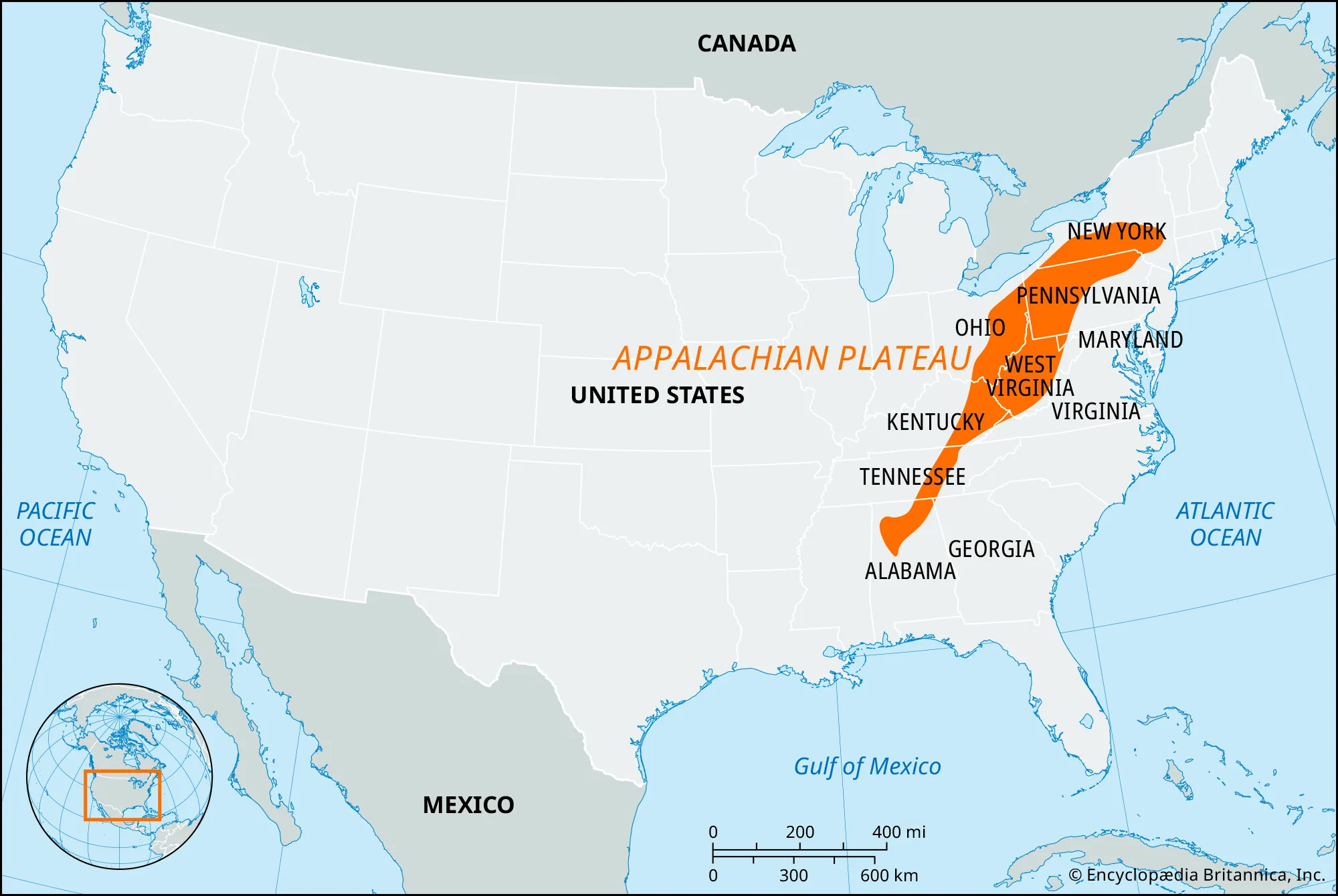
Appalachian Mountains
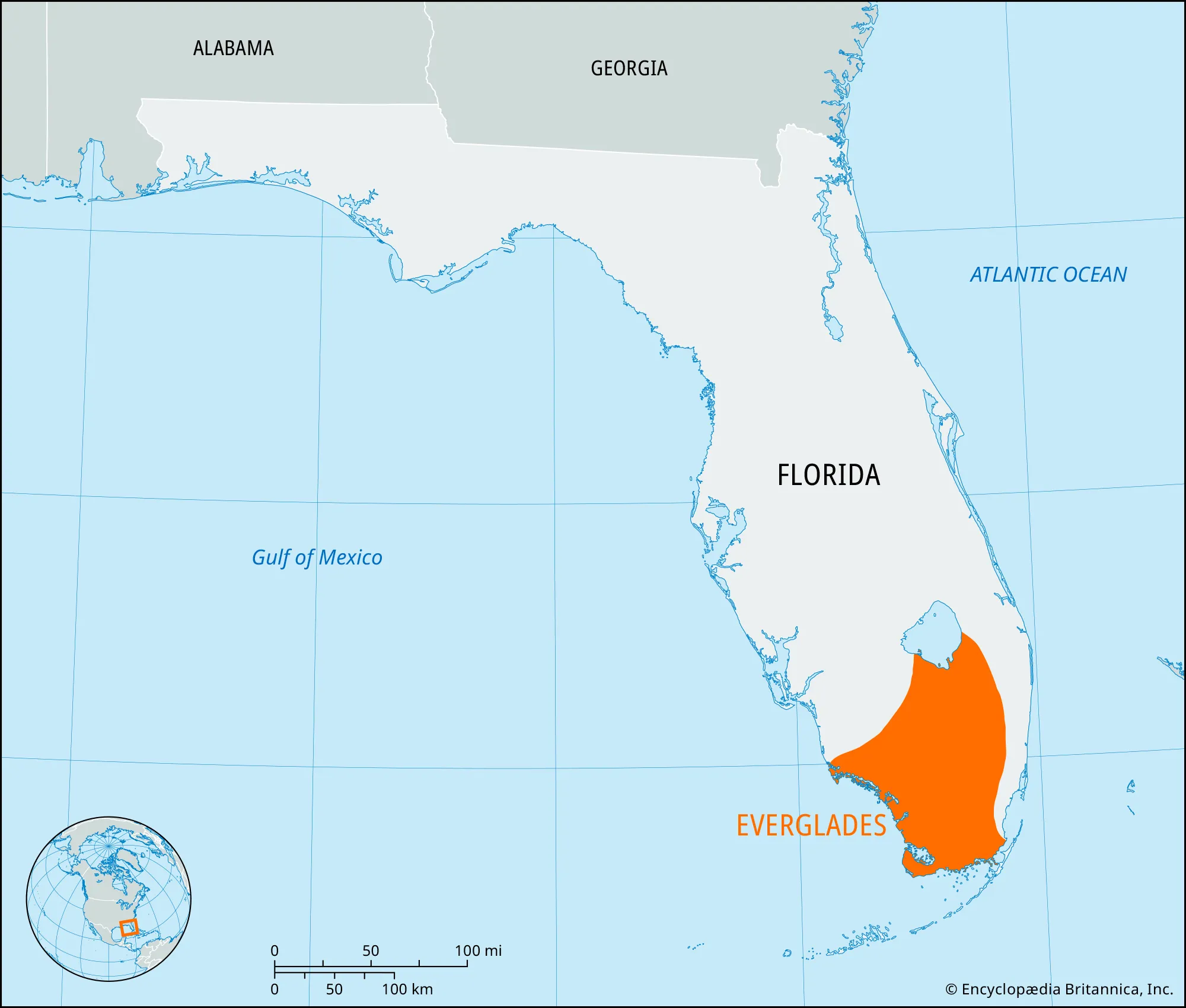
Largest Wetland. Sawgrass marshes, Mangrove forests
Florida Everglades
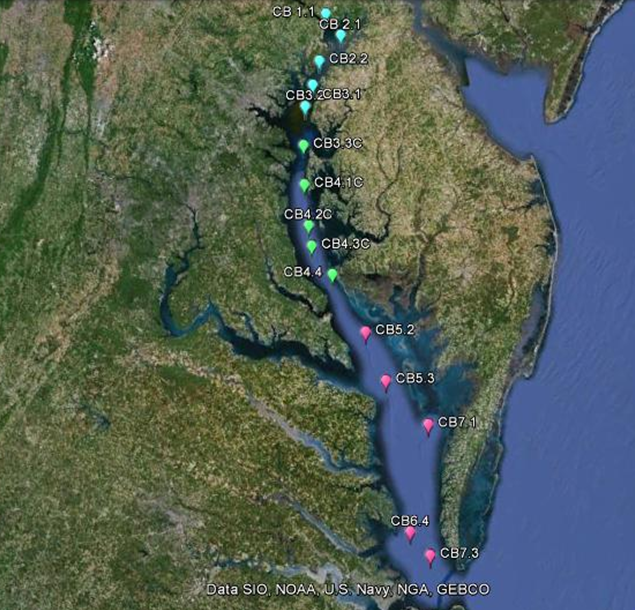
the largest estuary in the United States, has long suffered from eutrophication, a process driven by excessive nutrient pollution, primarily nitrogen and phosphorus. Here's an AP Environmental Science fact about it:
Chesapeake Bay(eutrophication)
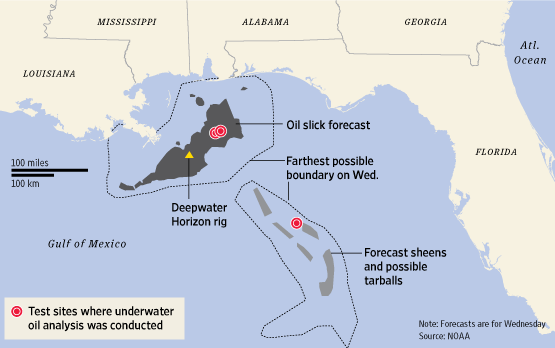
(BP Oil Spill, Dead Zone)
Gulf of Mexico
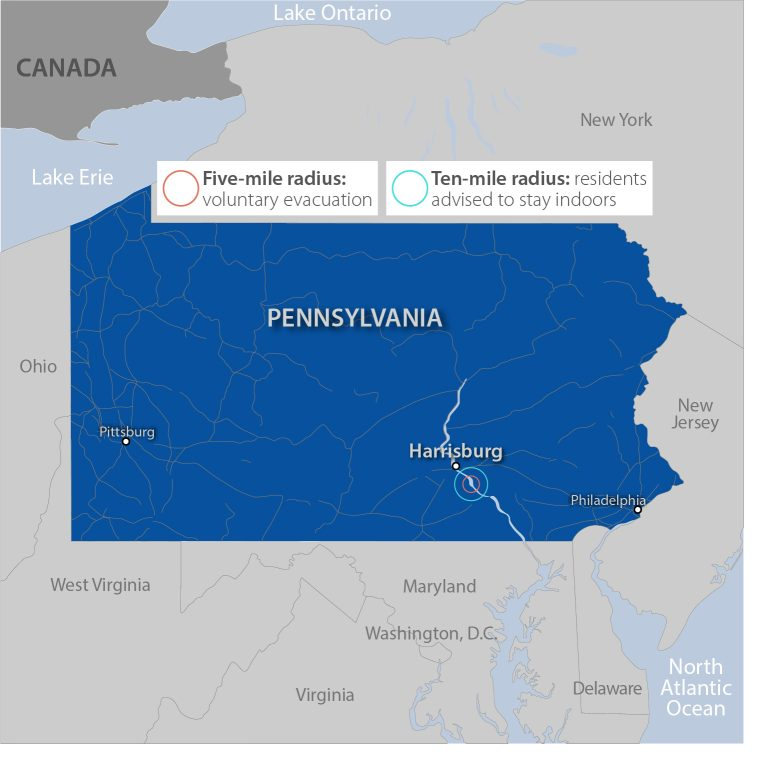
partial reactor meltdown but released minimal radioactive material into the environment, according to extensive studies. These studies concluded that the radiation releases had negligible direct health or environmental consequences for the surrounding area. However, the incident significantly impacted public perception and led to stricter regulations within the U.S. nuclear power industry.
Three Mile Island, Pennsylvania
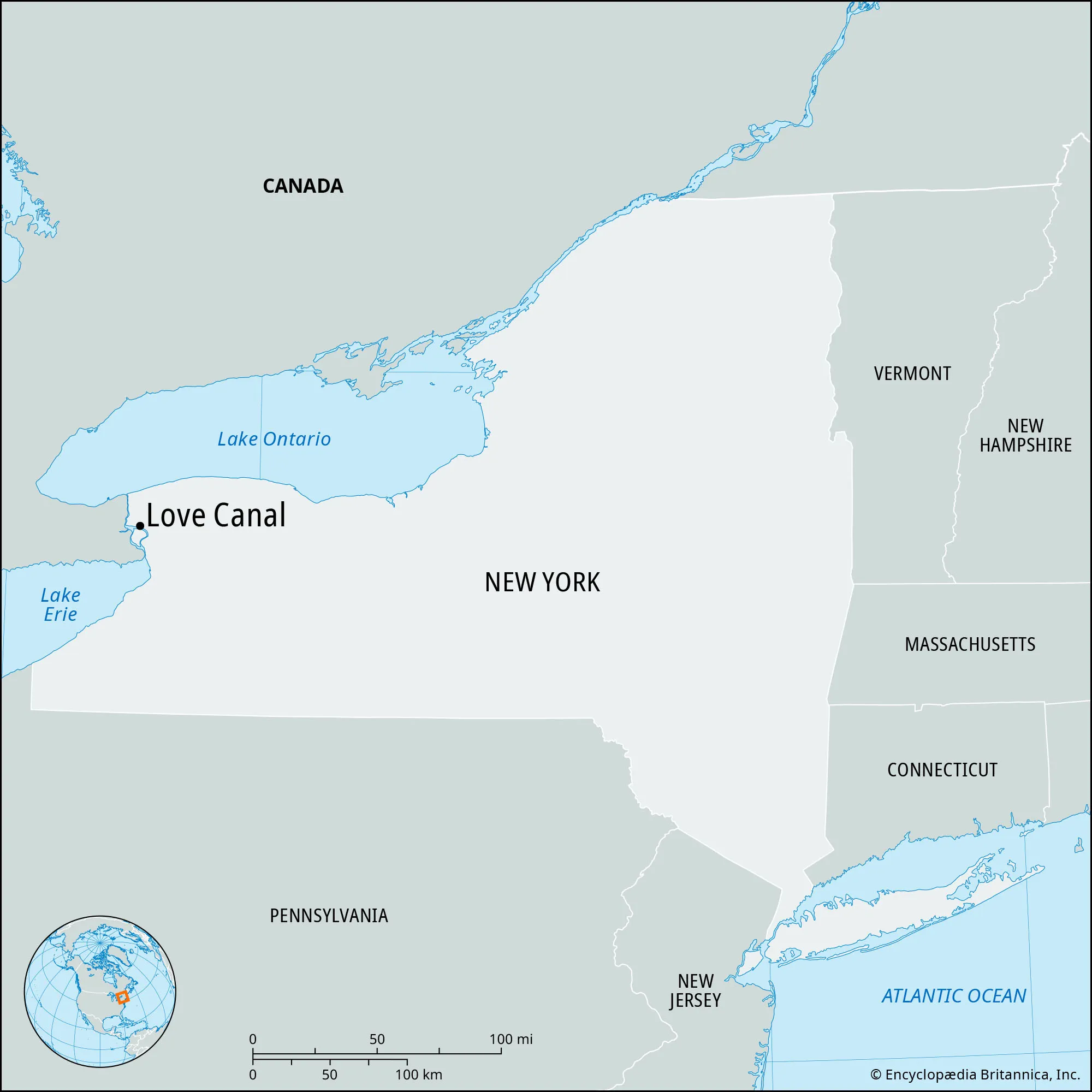
residents discovered their community was built on a former chemical waste landfill where Hooker Chemical had dumped over 21,000 tons of toxic substances. Leaking chemicals caused severe health problems, including birth defects, miscarriages, and cancers, leading to a state of emergency and the evacuation of hundreds of families
Love Canal, NY
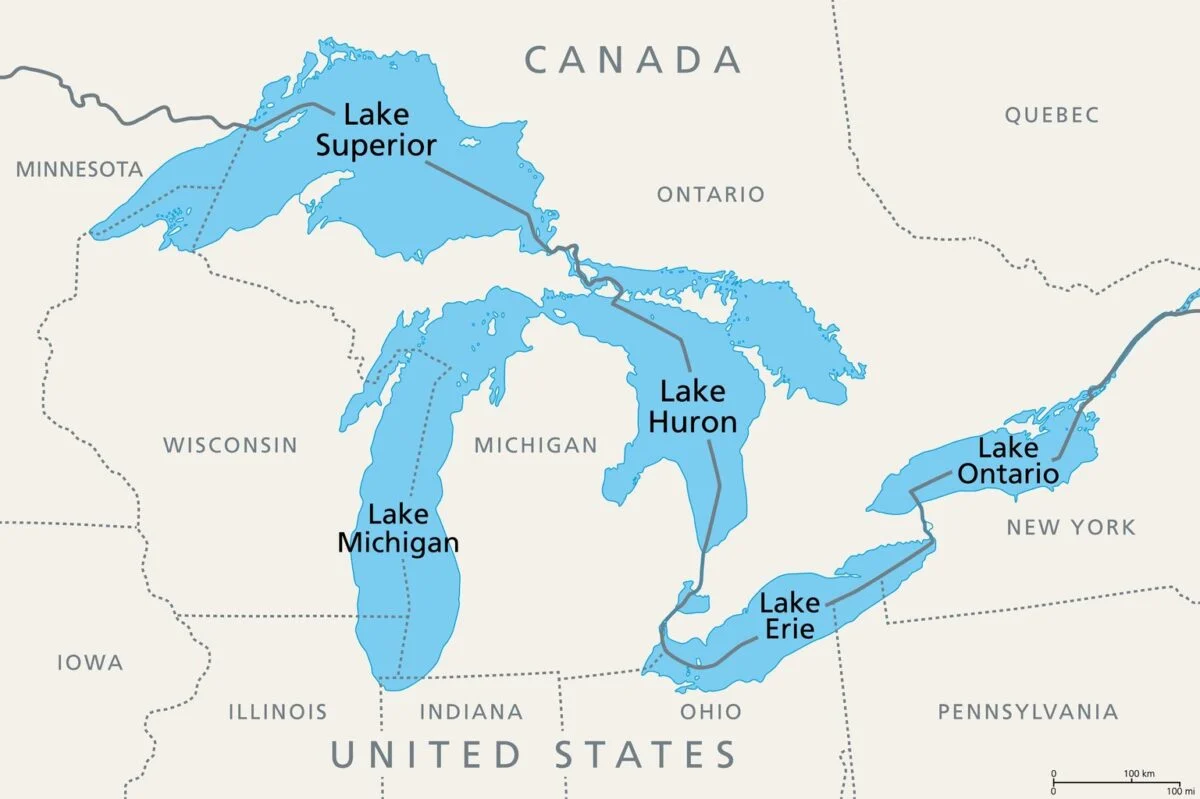
zebra mussels (Dreissena polymorpha) to the Great Lakes in the late 1980s, likely via ballast water from transoceanic ships, has had significant and cascading ecological and economic impacts. As prolific filter feeders, they have dramatically increased water clarity by consuming phytoplankton, which disrupts the base of the aquatic food web and reduces food availability for native species like zooplankton and some fish. Furthermore, zebra mussels attach to nearly any hard surface, including native mussels (often leading to their death), water intake pipes (causing billions of dollars in damage to infrastructure), and fish spawning reefs, altering habitats and impacting fish populations.
Great Lakes(Zebra Mussels)
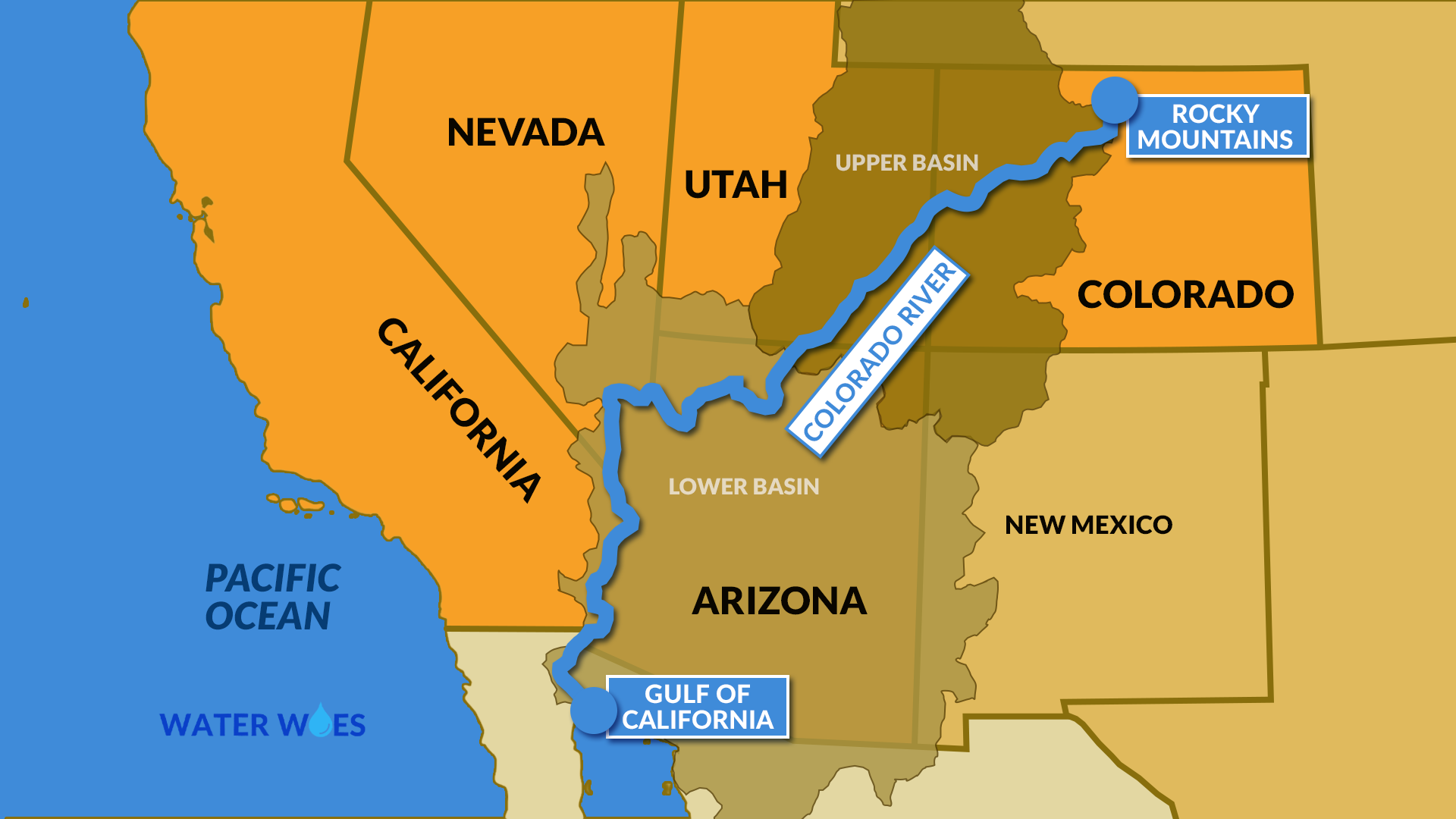
Colorado River
extraordinary geothermal features, including geysers and hot springs, are a direct result of its location above a continental hot spot
Yellowstone Naitonal Park(Hot spot)
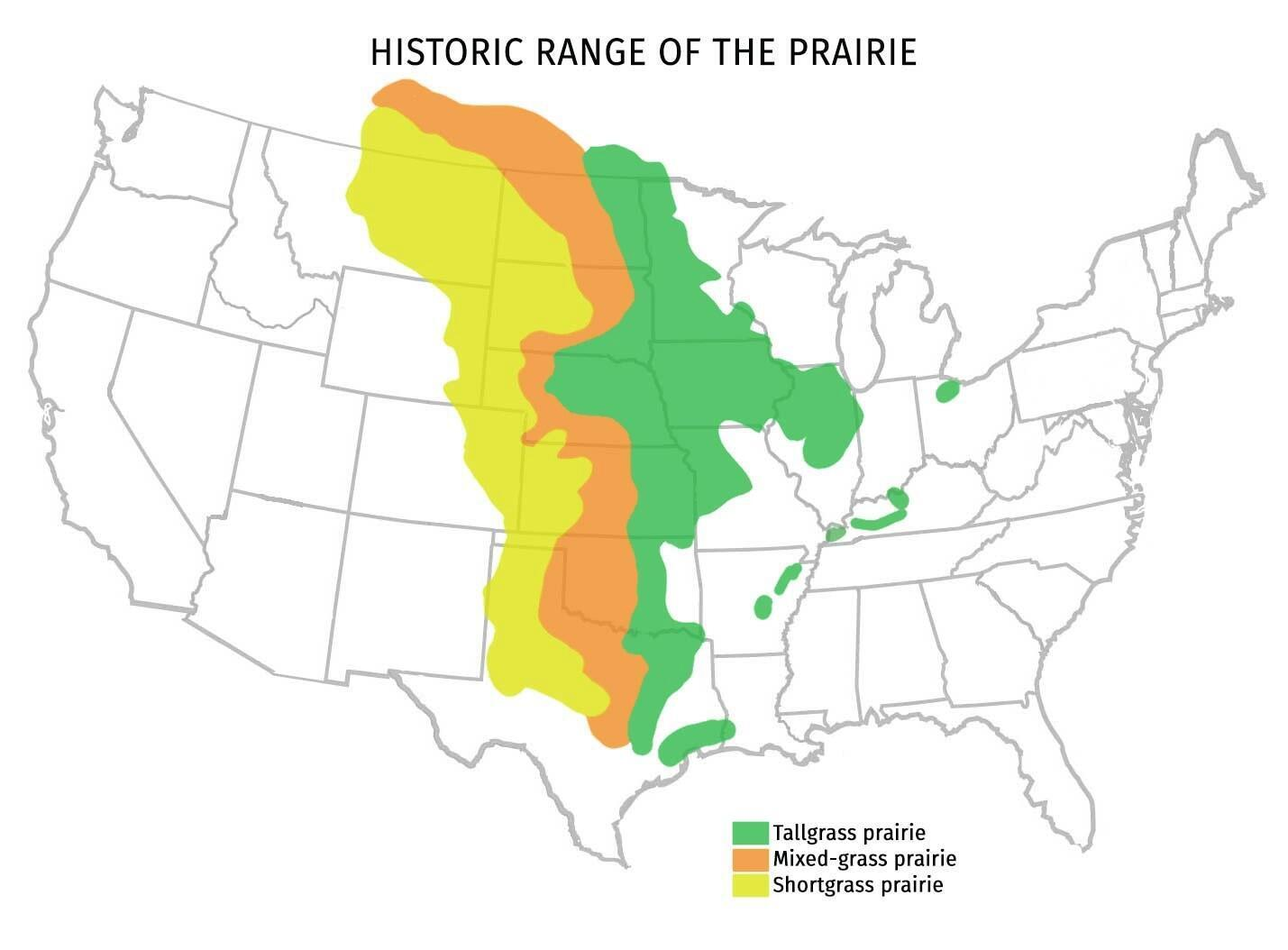
American Great Plains
driest desert in North America, its xerophytic vegetation
Majave Desert
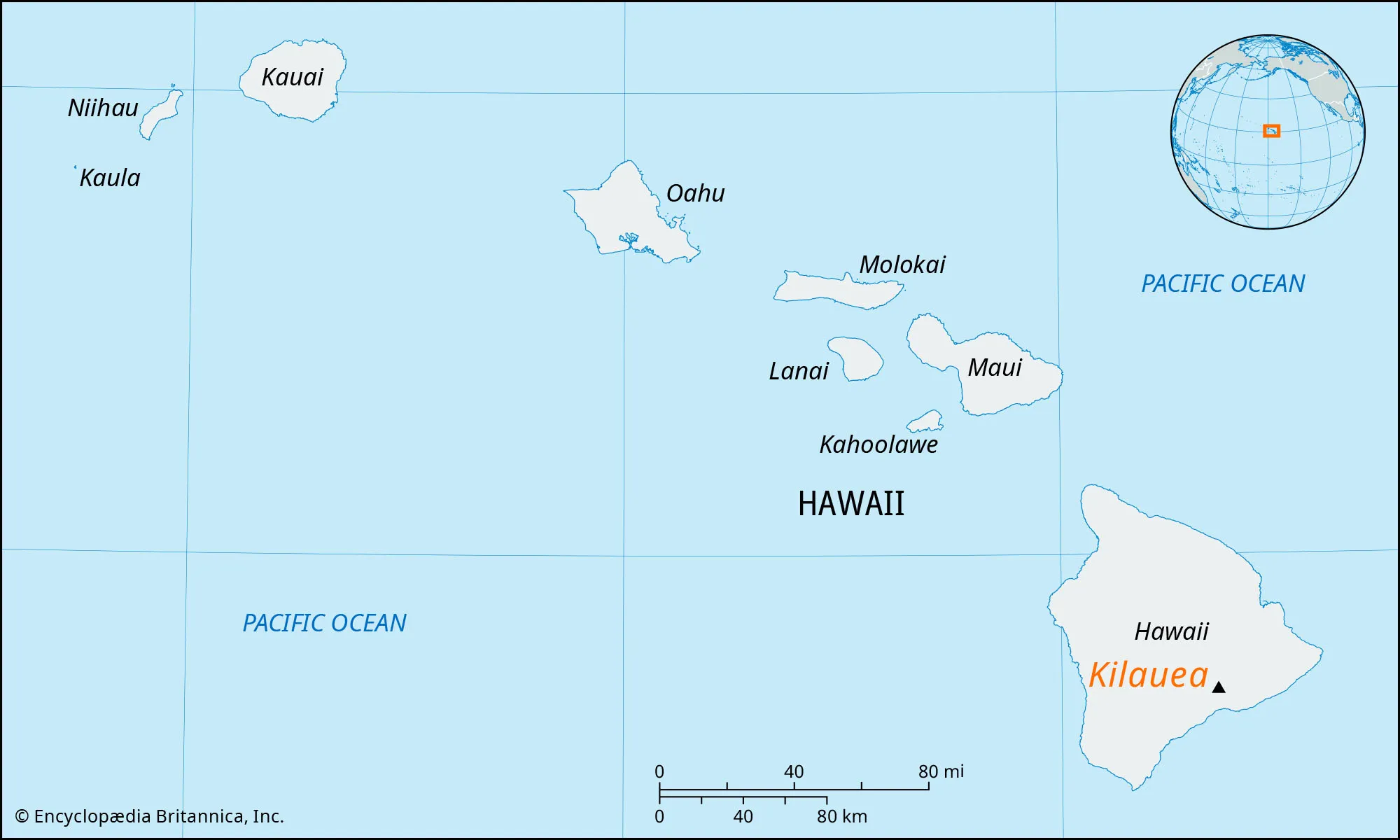
persistent volcanic activity to its location above the Hawaiian hot spot, a plume of upwelling magma from the Earth's mantle.This ongoing geological process makes Kīlauea one of the most active volcanoes on Earth and a prime example of hot spot volcanism.
Kilauuea Volcano(Hot Spot), Hawaii
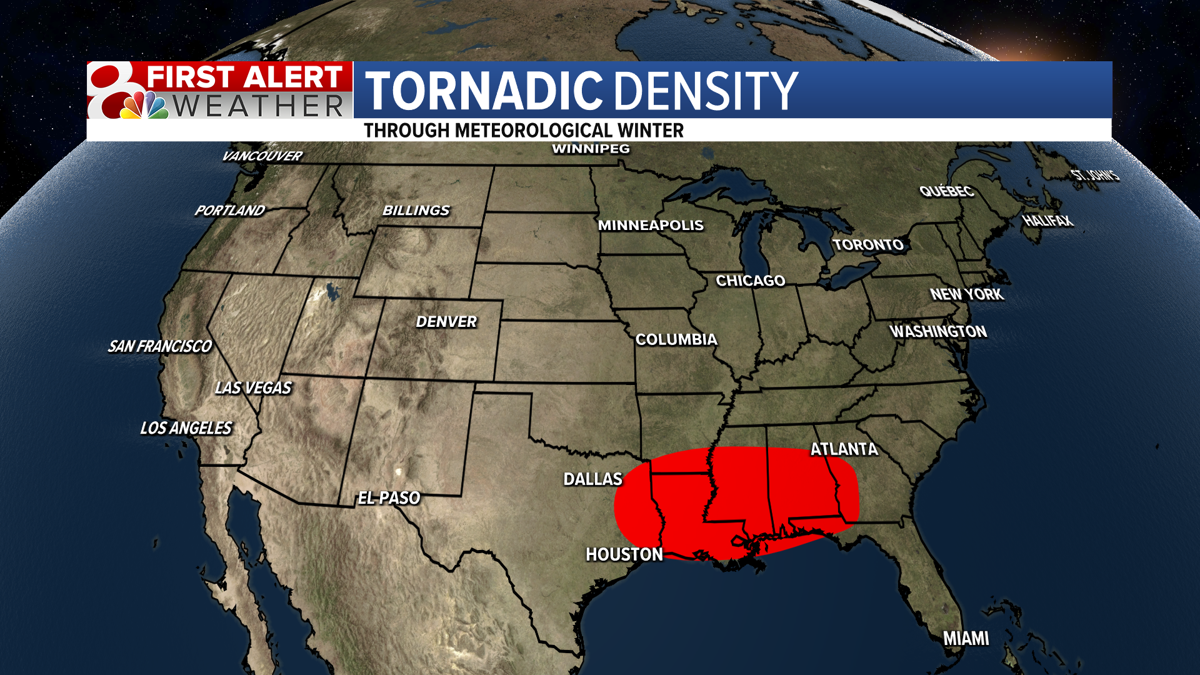
Tornado Alley
a massive dam on the Colorado River, created Lake Mead, the largest reservoir in the United States, to provide hydroelectric power, flood control, and water storage for the arid Southwest. However, this damming of the river has significantly altered the natural flow, preventing the transport of water and sediments downstream, leading to the decline of ecosystems in the Colorado River Delta. Additionally, Lake Mead's water levels have been critically low due to prolonged drought and increased water demand, threatening the dam's ability to generate power and supply water to millions in Nevada, Arizona, and California.
Hoover Dam / Lake Mead