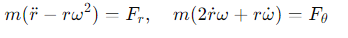4- Motion in plane using Cartesian and Polar coordinates
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
How can any vector A be represented in the Cartesian coordinate system?
Ax and Ay = the projections of the vector A onto the x- and y-axes.
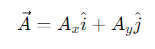
What are i^ and j^ in the Cartesian coordinate system?
Unit vectors along the x- and y-axes, respectively.
How is the velocity vector v expressed in Cartesian coordinates?
x˙ and y˙ = the time derivatives of the position components along the x- and y-axes.
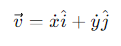
How are the components of velocity expressed in Cartesian coordinates?
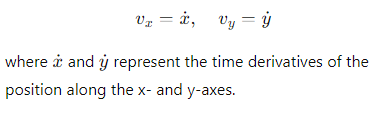
How are the components of acceleration expressed in Cartesian coordinates?

How is Newton's second law written in Cartesian coordinates?
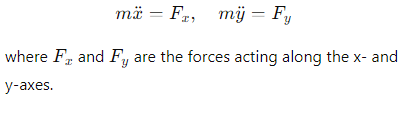
How is the position of a point defined in polar coordinates?
Its defined by a distance r from a fixed origin and an angle θ from a fixed reference line.
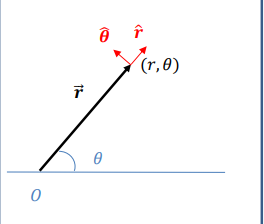
What are the unit vectors in the polar coordinate system?
r^ pointing in the direction of increasing r
θ^ pointing in the direction of increasing θ
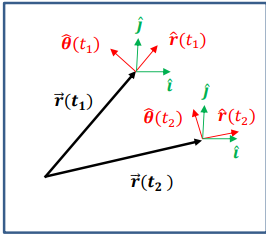
How do the unit vectors in polar coordinates differ from those in Cartesian coordinates?
In Cartesian coordinates, i^ and j^ are constant
In polar coordinates, unit vectors r^ and θ^ change with the position of the object
What is the expression for the position vector in polar coordinates?
r is the distance
r^ is the unit vector pointing in the direction of increasing r.
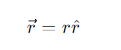
How is the velocity vector expressed in polar coordinates?
r˙=the radial velocity
ω = the angular velocity.
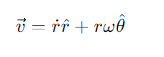
What are the time derivatives of the unit vectors r^ and θ^ in polar coordinates?
θ˙= the angular velocity.
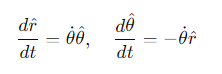
What is the angular velocity in polar coordinates?
Its the rate of change of the angle θ
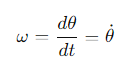
How is the acceleration vector derived in polar coordinates?
r¨ = the radial acceleration
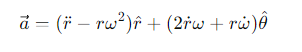
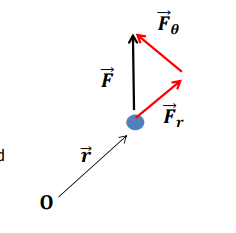
How is the force vector expressed in polar coordinates?
Fr and Fθ are the radial and tangential components of the force.
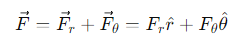
What is the form of Newton's second law in polar coordinates?
Fr and Fθ are the radial and tangential components of the force.