Titration curves and indicator theory
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 10:23 AM on 6/9/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
1
New cards
What are the 4 main types of titration curve?
* strong acid and strong base
* weak acid and strong base
* strong acid and weak base
* weak acid and weak base
* weak acid and strong base
* strong acid and weak base
* weak acid and weak base
2
New cards
Define end point
point at which the indicator changes colour (due to pH change)
3
New cards
Define equivalence point
volume at which titrant is chemically equivalent to the analyte
4
New cards
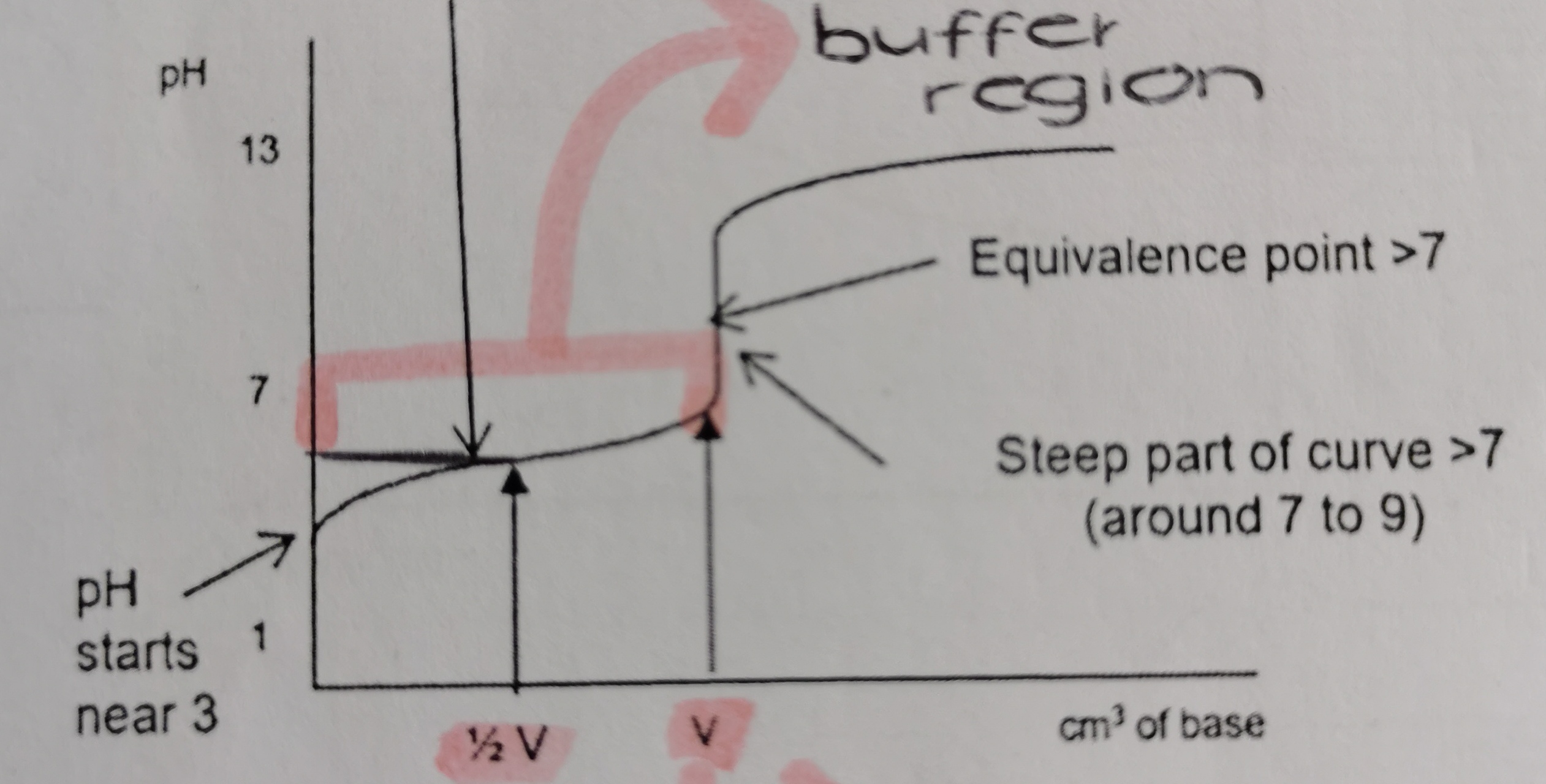
Where does the pH of the equivalence point lie on a titration curve?
the mid-point of the extrapolated vertical position of the curve
5
New cards
Where does neutralisation occur on a titration curve?
the steepest part of the curve
6
New cards
What is the pH of the equivalence point of a strong acid and strong base titration?
7
7
New cards
Between which pHs is the steepest part of a strong acid and strong base titration curve?
3 pH - 9 pH
8
New cards
What is the pH of the equivalence point of a weak acid and strong base titration?
>7 pH
9
New cards
Between which pHs is the steepest part of a weak acid and strong base titration curve?
7pH - 10pH
10
New cards
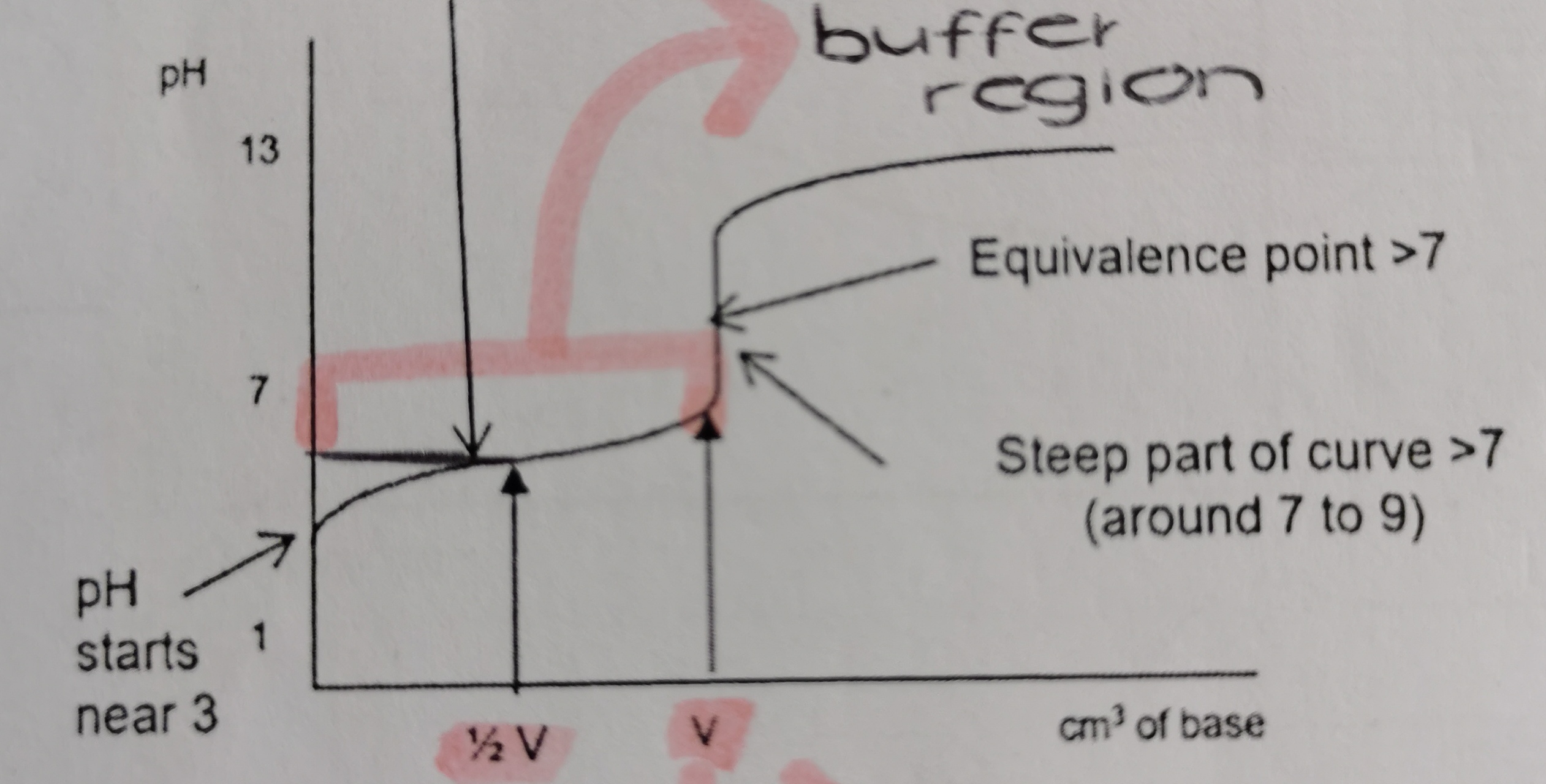
What is unique about the titration curve of a weak acid and strong base titration?
it has a buffer region → pH rises quickly at start and then flattens as buffer is made
11
New cards
What happens at half-neutralisation?
Ka = \[H+\]
pKa = pH
pKa = pH
12
New cards
Between which pHs is the steepest part of a strong acid and weak base titration curve?
4 pH - 7 pH
13
New cards
What is the pH of the equivalence point of a strong acid and weak base titration?
14
New cards
What is the usual end-point of a weak acid and weak base titration and what can affect this?
* around 7 pH
* the relative strengths of the acid and the alkali
* the relative strengths of the acid and the alkali
15
New cards
Why don’t weak acid and weak base titration curves have an equivalence point?
* behave as buffer solutions
* no dramatic pH change at end point → no steep part of curve
* no dramatic pH change at end point → no steep part of curve
16
New cards
What is a polybasic acid?
an acid with more than one proton
17
New cards
How do polybasic acid and strong alkali titration curves differ from strong base and strong acid titration curves?
* reaction proceeds through more than one stage
* reactions don’t occur simultaneously → occur one at a time
* each stage has its own end point → reaction has as many end points as the number of protons in the acid
* reactions don’t occur simultaneously → occur one at a time
* each stage has its own end point → reaction has as many end points as the number of protons in the acid
18
New cards
What are indicators?
acid or bases that can lose or gain protons
19
New cards
What is the equation for the dissociated of a protonated indicator?
HIn ⇌ In- + H+
20
New cards
What is the justification for the selection of a suitable indicator?
pH range of the indicator lies of the steepest part of the titration curve
21
New cards
What are indicators used for in acid-alkali titrations?
to find the end-point of a titration
22
New cards
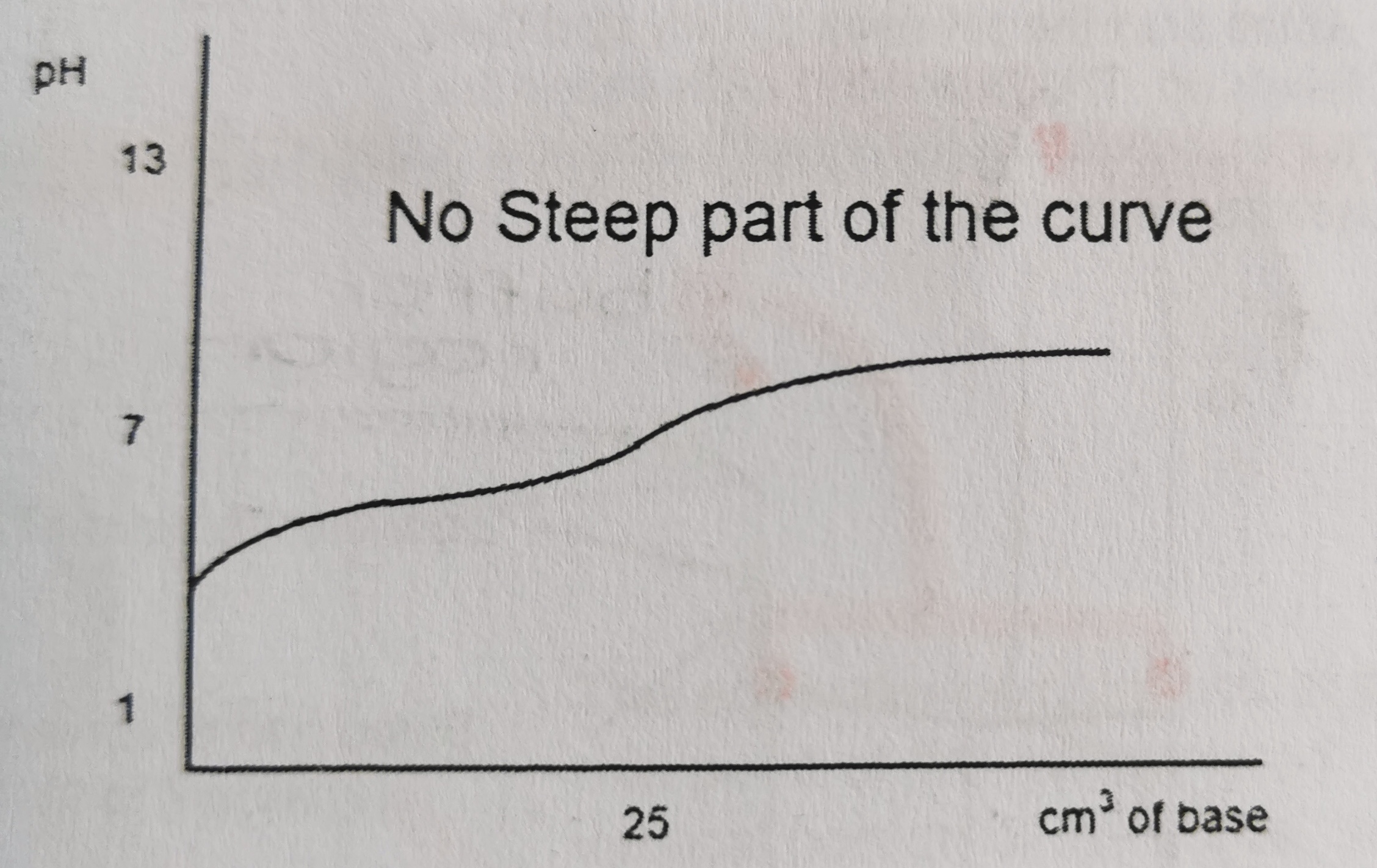
Which titration curve is this?
weak acid and weak base
23
New cards

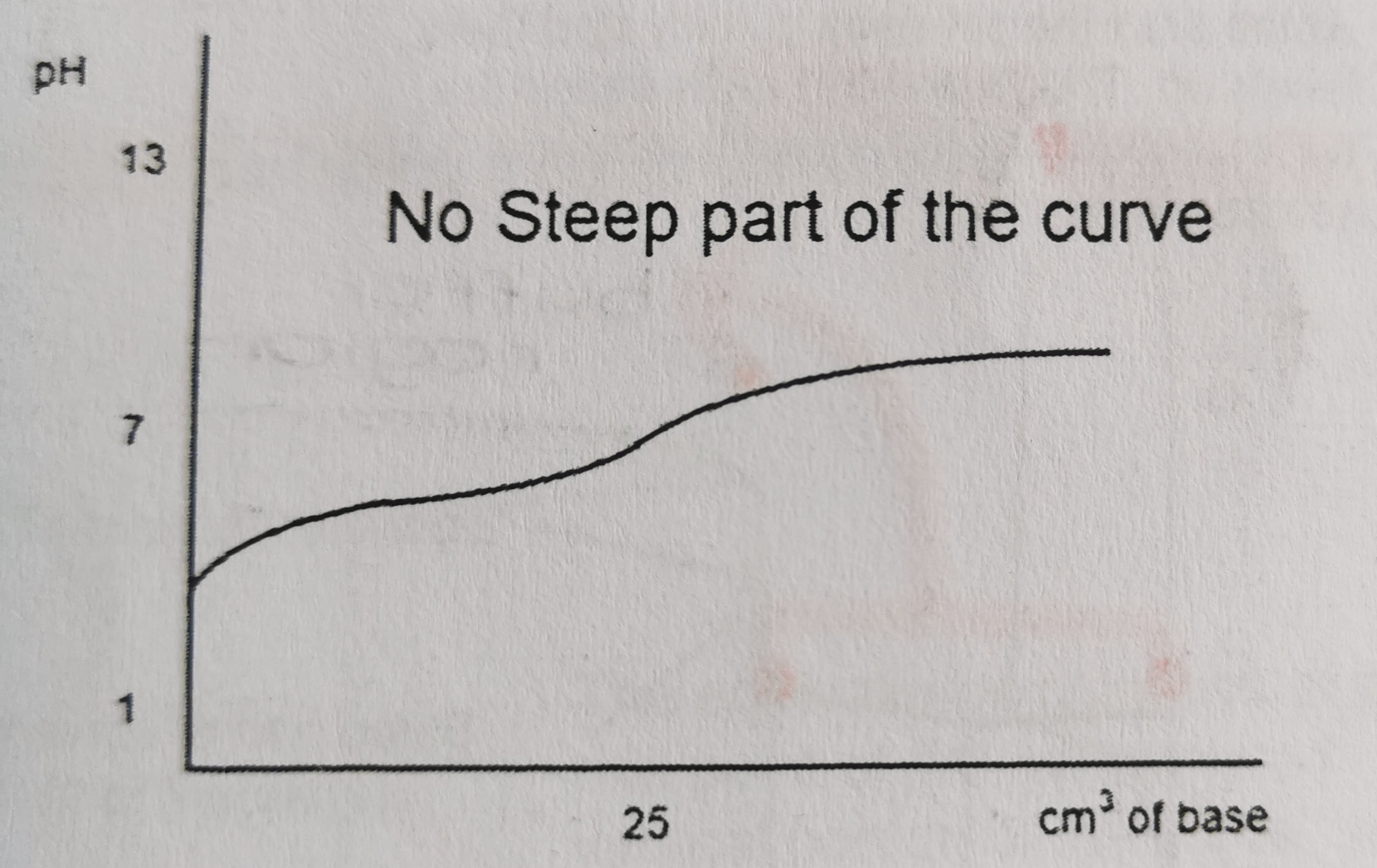
Which titration curve is this?
strong acid and weak base

24
New cards
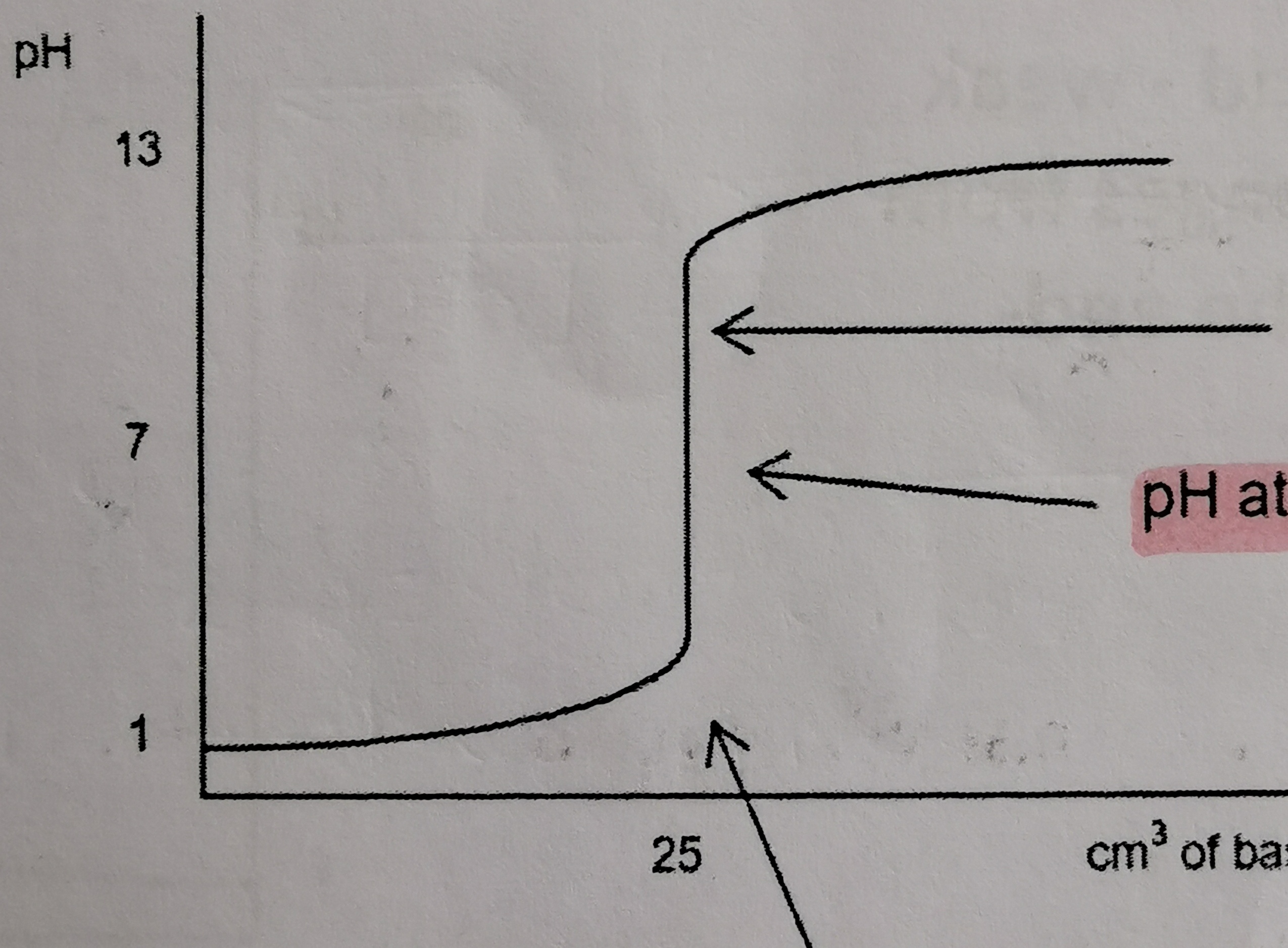
Which titration curve is this?
weak acid and strong base
25
New cards
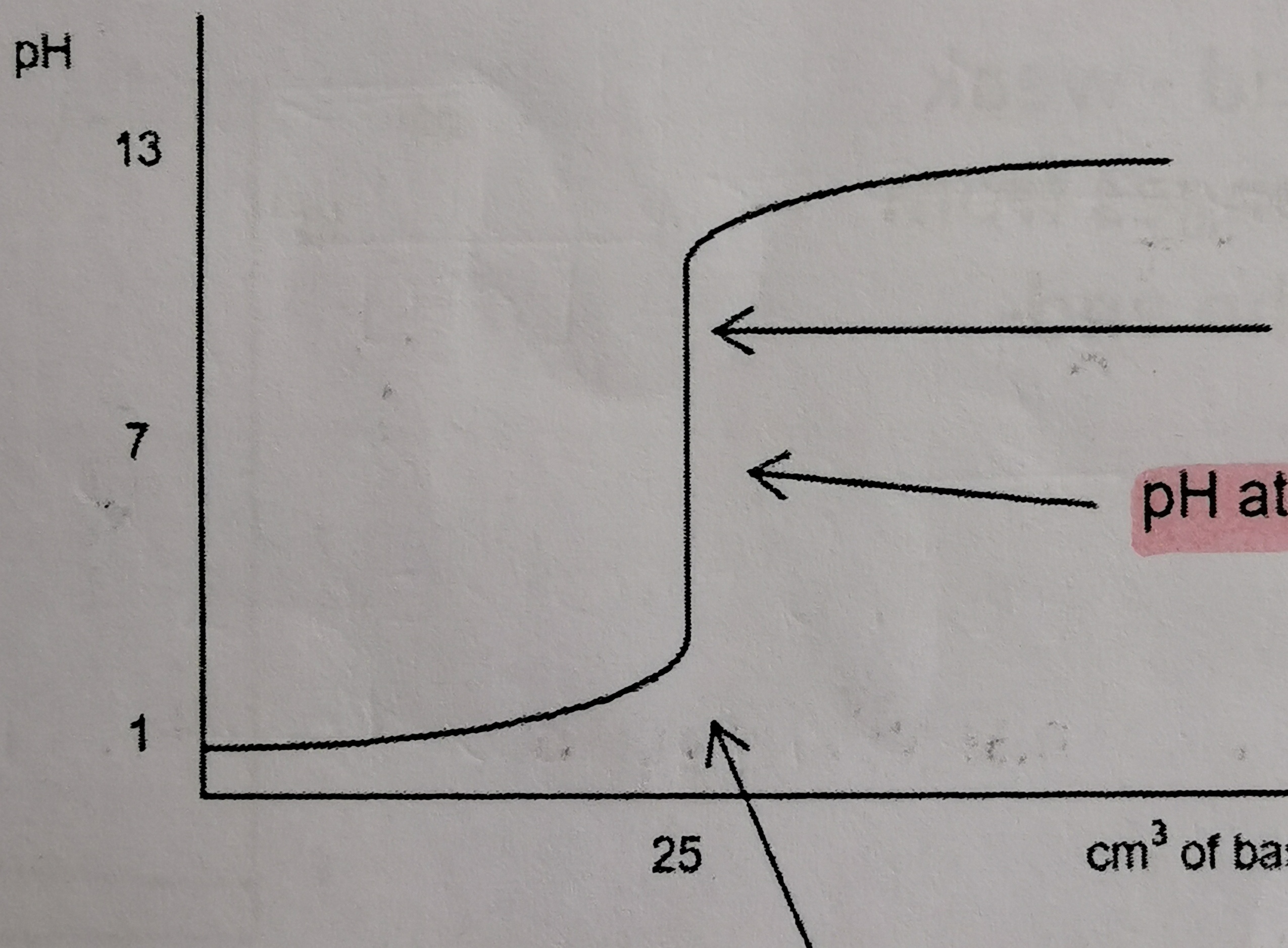
Which titration curve is this?
strong acid and strong base