Edexcel IGCSE Physics: 2 Electricity
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
What is insulation in domestic appliances ?
1. insulation in a plug is when the live, neutral and earth wires are covered with a plastic layer
2. plastic is a good insulator
3. this prevents contact with the live wire when handling the plug and prevents the person receiving a large current
What is double insulation in domestic appliances?
1. double insulation is when the casing of the plug is made of plastic and wires are covered in plastic casing
2. this means that even if the live wire breaks and touches the outer casing a charge cannot go through
3. as plastic is a good insulator
4. preventing any risk of electric shock as well as reducing the need for an earth wire
What is earthing in domestic appliances?
1. earth connected to (metal) casing;
2. If casing becomes live/ live wire touches case;
2b. absorbs electrons
3. Provides low resistance path (to earth);
4. (So) large/surge current in earth wire;
5. (hence) fuse breaks/melts/blows;
6. (so) circuit switches off
What are fuses ?
1. a thin piece of metal with a low melting point
2. if there is a current which is too large, the fuse heats up and becomes very hot and melts/breaks
3. breaking the circuit and preventing the large current from flowing
4. preventing the risk of electrical fire and severe electrical shock
What are circuit breakers?
1. A circuit breaker has a coil or a metallic strip which detects the amount of current lowing through a circuit
2. When the current goes above the acceptable range the current sensing system detects it and causes the circuit breaker contacts to open
3.Breaking the circuit preventing the large current from flowing , preventing electrical fires and risk of electrical shock
4.After the fault is checked the circuit breaker can be reset and some do this on their own, meaning a circuit breaker can be re-used
5.This makes it better to use than a fuse, however they are more expensive than fuses
How do resistors heat up and how can this be used in domestic appliances?
1. when resistors are applied current is reduced and the rate of flow of electrons slows down
2. this means that there is more collision of electrons and ions in the resistor
3. this means there are more transfers of electrical energy into heat energy in the resistor
P= I x I x R so higher R is more power dissipated as heat
State the relationship between power , current and voltage
Power[W] = current [A] x voltage [v]
P = I x V
State the relationship between energy transferred, current, voltage and time
Energy Transferred [J] = Current [A] x Voltage [v] x Time [s]
E = I x V x t
What is the difference between alternating current and direct current ?
1. Alternating current is supplied by mains electricity
Direct current is supplied by a cell or battery
2. Alternating current changes direction , Direct current travels in one direction
3. Alternating current can vary in size , Direct current remains at one size
Which is better suited for domestic lighting series or parallel circuits , and why ?
1. A parallel circuit is better suited
2. because if there is a fault in one of the branches it will not effect the others
3. whereas in a series circuit if there is a fault in any part the whole circuit stops working
What factors affect current in a series circuit ?
Voltage:
the higher the voltage the higher the current (I=V/R)
Number of components :
The higher the number of components the lower the current as the overall resistance increases and voltage has to be split up further resulting in a lower current
Nature of components:
components with a higher resistance will reduce current as I=V/R
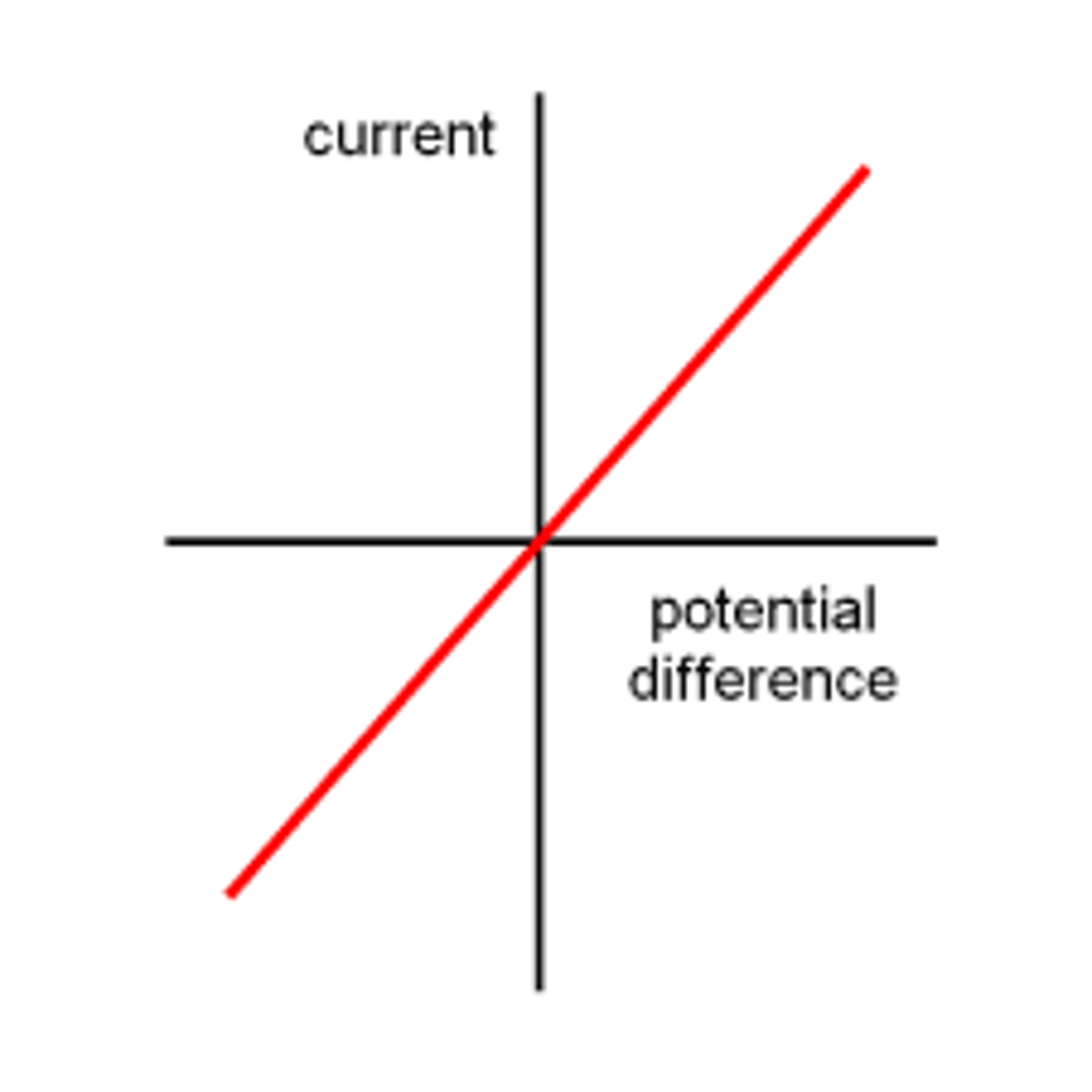
Describe the IV characteristics of a. wire
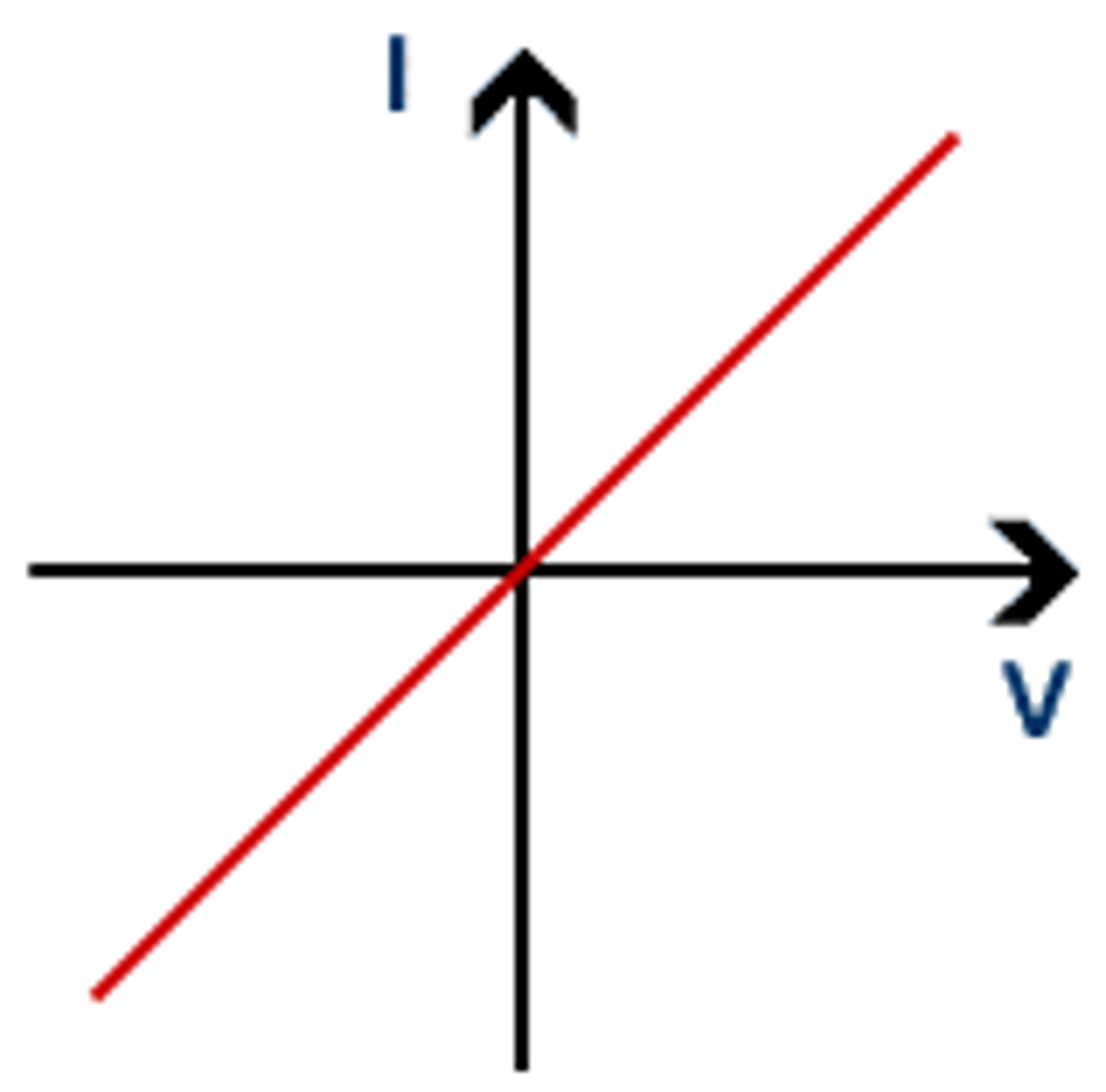
Describe the IV characteristics of a resistor
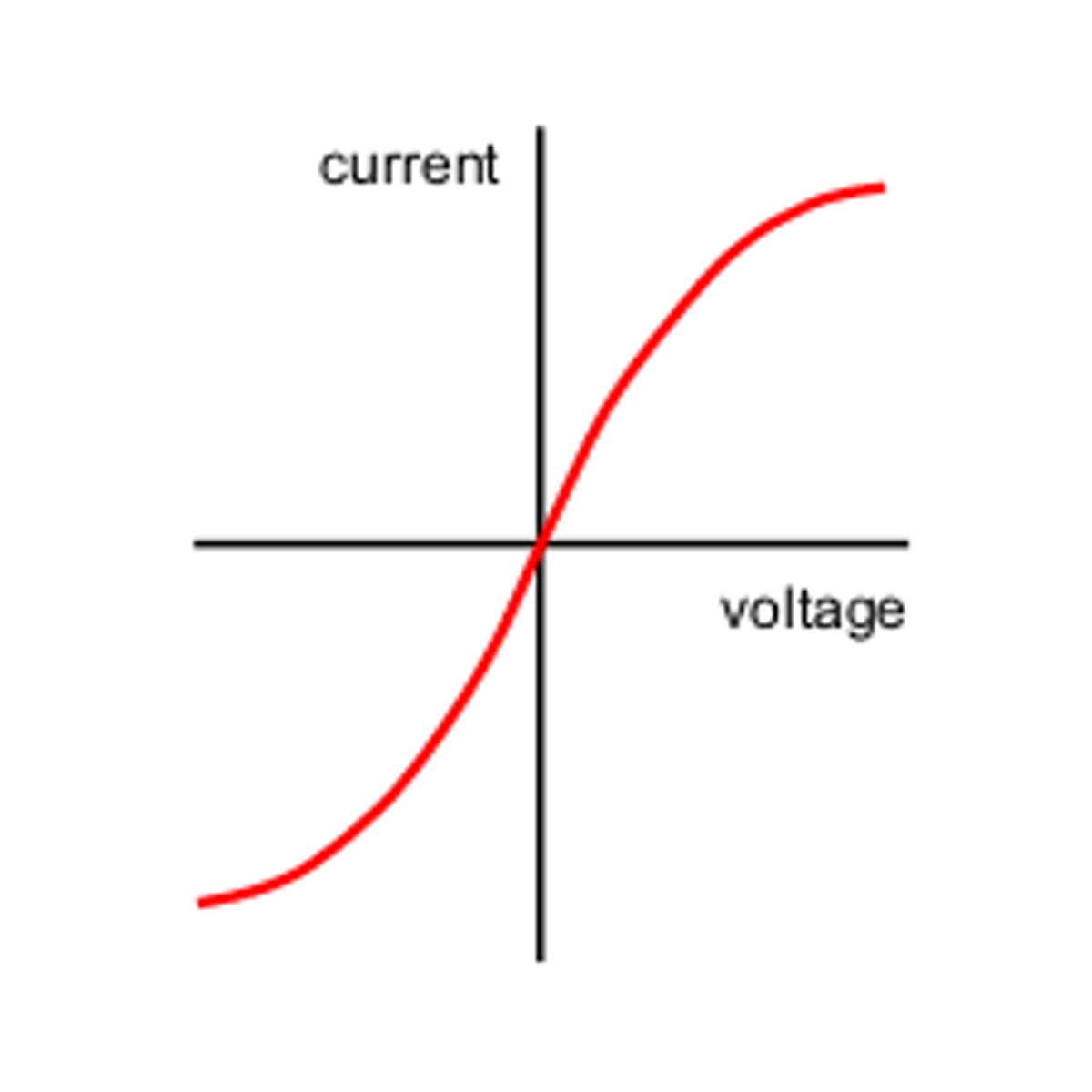
Describe the IV characteristics of a filament lamp
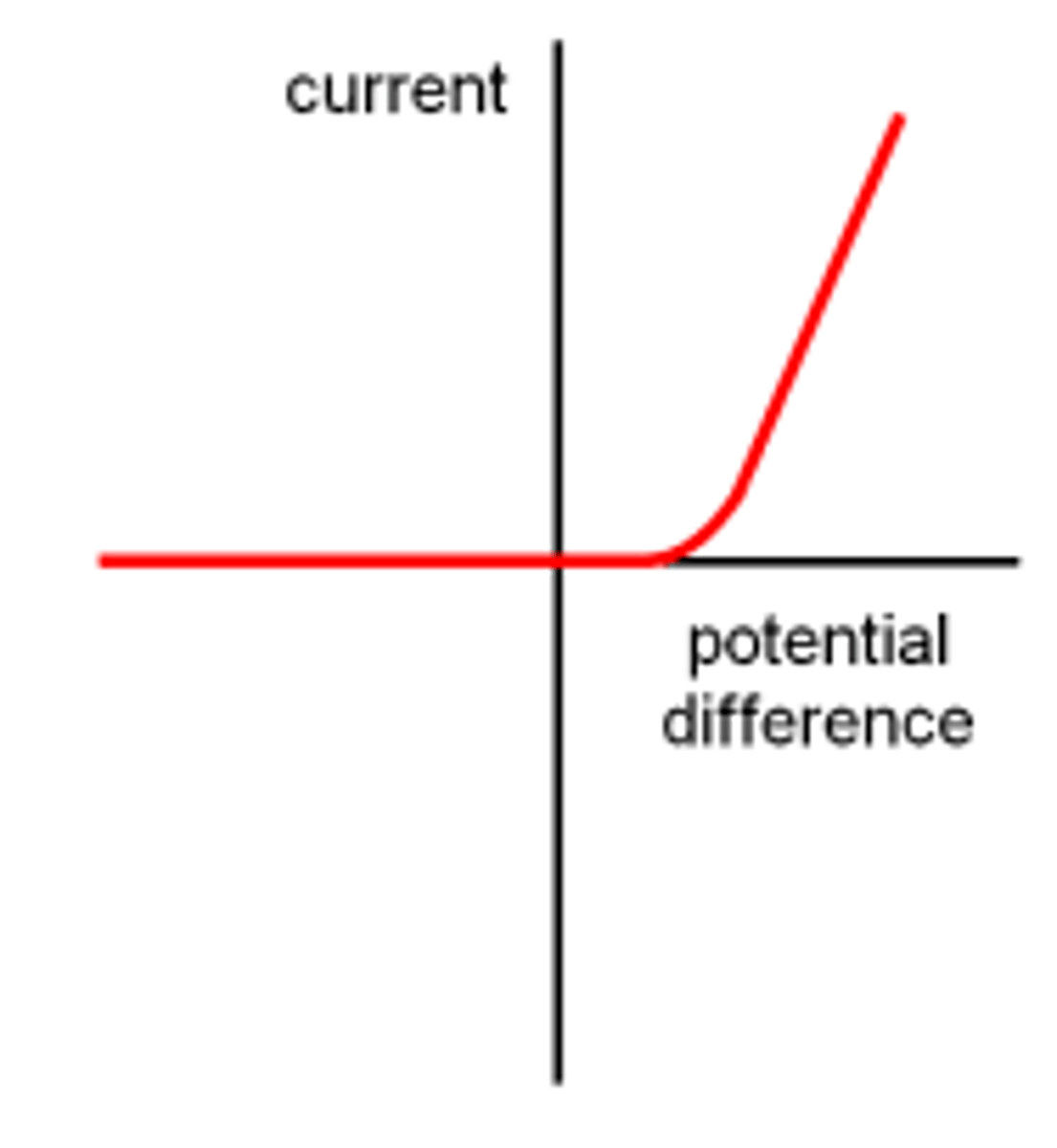
Describe the IV characteristics of a diode
How do you test the IV characteristics of a component?
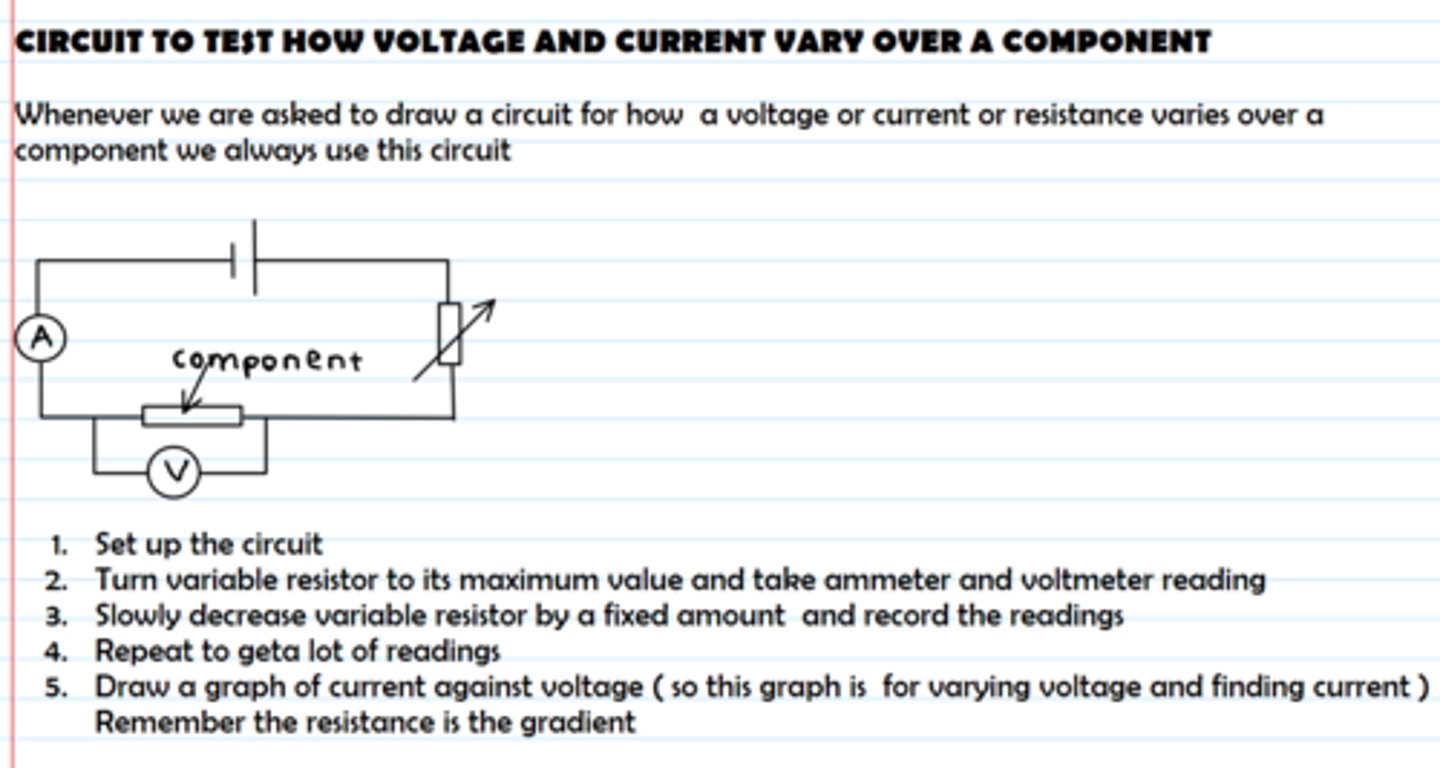
What is the effect of changing resistance on the current in a circuit?
increasing the resistance in a circuit reduces the amount of current which flows through the circuit
(so we use resistors to limit current, e.g. before lamps)
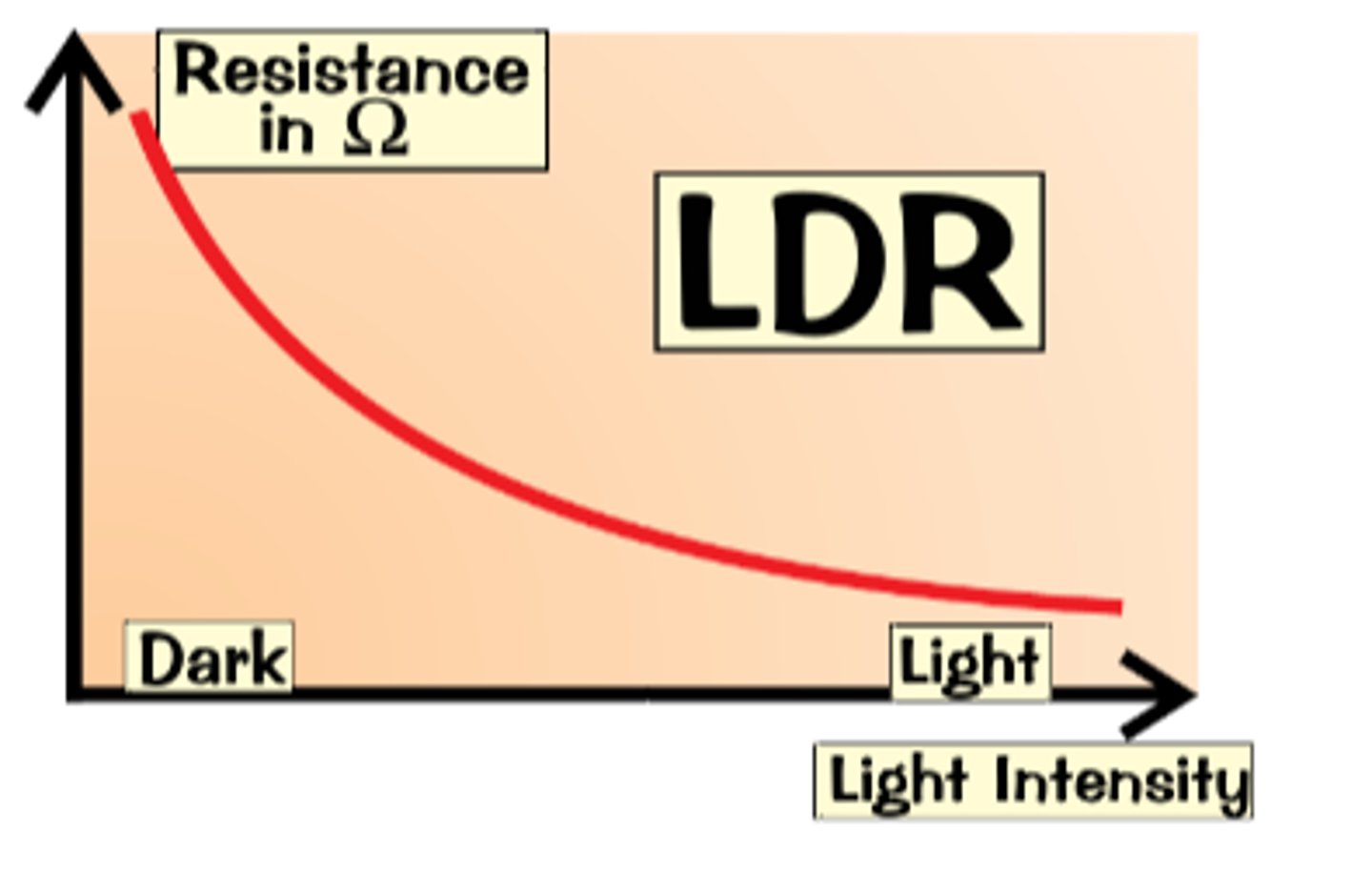
How does a LDR work ?
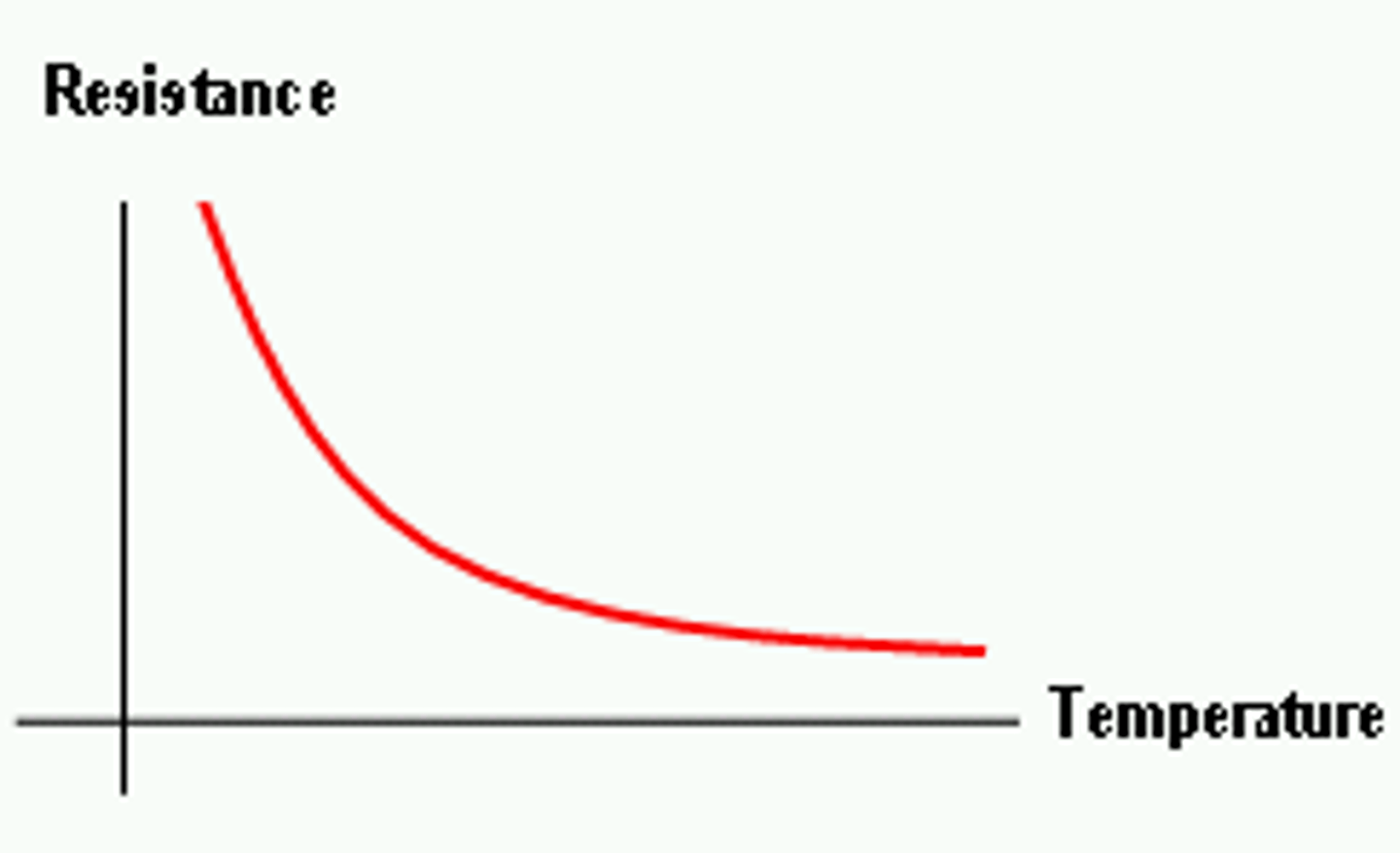
How does a thermistor work ?
State the formula for voltage , current and resistance
Voltage [V] = Current [A] x Resistance [Ohms]
V=I x R
Define the term current
current is the rate of flow of charge(/electrons)
State the formula for charge, current and time
Charge [C] = Current [A] x time [s]
Q = I x t
Define the term electric current
electric current in solid metallic conductors is the flow of negatively charged electrons
Why is current conserved at a junction in a circuit ?
this is because the current entering a junction = the current exiting a junction
Describe the voltage in a parallel circuit ?
The voltage across two components connected in parallel is the same
How do you calculate the current, voltage and resistance of two components connected in series ?
the current through both components is the same
To calculate voltage :
1. use V=IR to find voltage over one component
2. subtract voltage from power supply to find voltage over other component
To calculate resistance:
1. use V=IR to find voltage over one component
2. subtract voltage from power supply to find voltage over other component
3. Use R = V/I to find resistance of second component
Define the term voltage
voltage is energy transferred per unit charge passed
What is a volt
a volt is a measure of joule transferred per coulomb
State the relationship between energy transferred, charge and voltage
Energy transferred [J] = Charge [C] x Voltage [V]
E = Q x V
Which common materials are electrical insulators ?
a material that doesn't allow electricity to flow through easily
examples :
plastic
rubber
glass
wood
Which common materials are electrical conductors?
A conductor is a material that allows electricity to flow through it easily
Examples:
Graphite
Copper
Tin
Gold
Practical: Investigate how insulating materials can be charged by friction
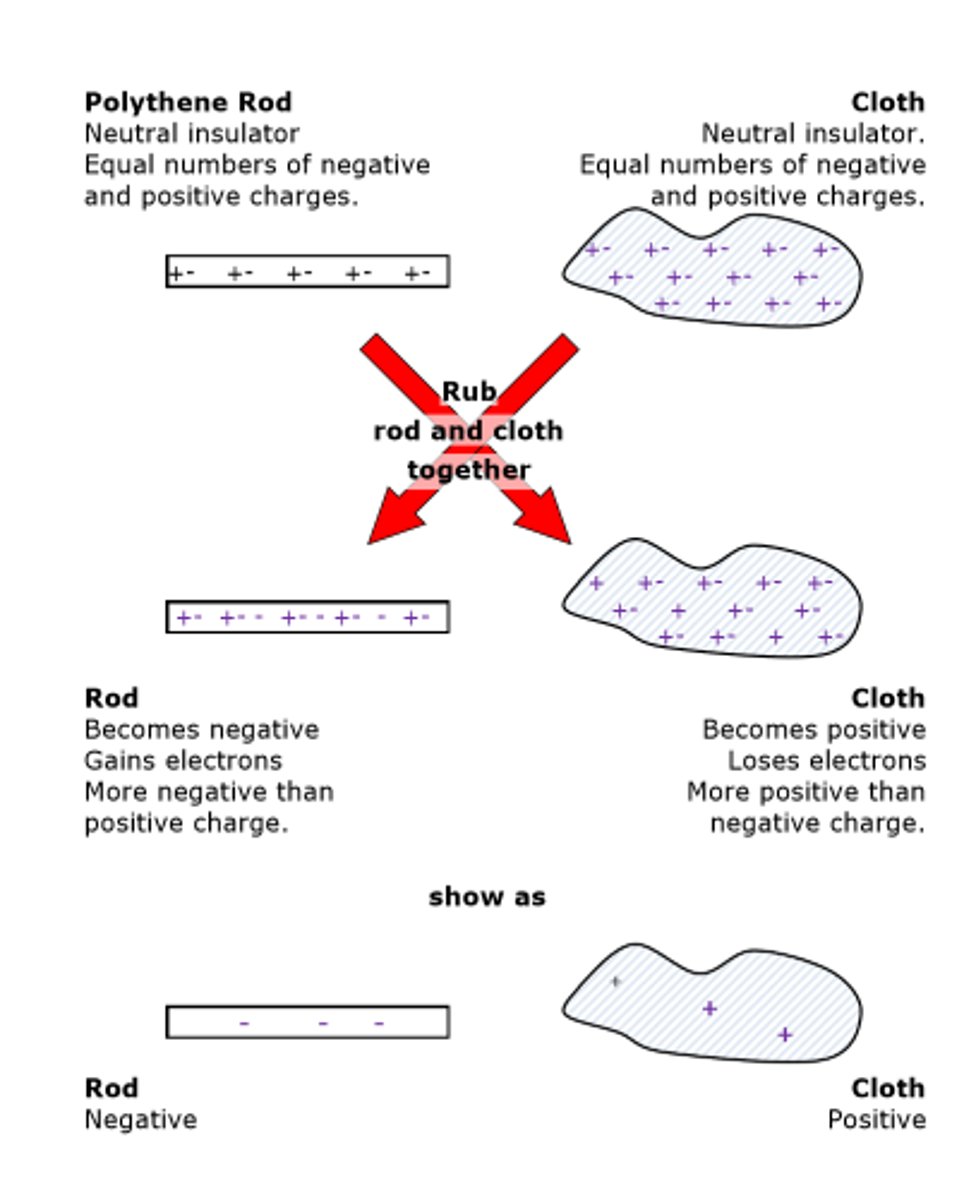
How are positive and negative electrostatic charges produced on materials ?
1. when you rub two neutral insulators together
2. the friction causes one of the materials to take electrons from the other
3. the material which loses electrons becomes positively charged
4. the material that gains electrons becomes negatively charged
State the law of electrostatics
Like charges repel and unlike charges attract
Explain an electrostatic phenomena?
Lightning:
1. rubbing of air and dust particles causes some negatively charged particles at the bottom of clouds
2. these negative charges repel electrons in the ground leaving a positive charge near the top of the ground
3. the difference in charge becomes too large and a potential difference which drives a current between the cloud and the ground is created
4. current heats the air till it begins to glow as a flash of lightning
5. (due to the quick heating ) the air also expands rapidly creating the sound of thunder
What are the dangers of electrostatic charges when fuelling aircrafts and tankers ?
1. Planes travel through air and clouds
2. friction between the plane, air and dust particles causes the plane to become charged with static electricity
3. when the plane lands the charge could escape to earth as a spark or flash
4. however if someone is trying to refuel the plane during this a spark could occur and cause an explosion
How can electrostatic charges be used in photocopiers ?

How can electrostatic charges be used in inkjet printers?
