cerebellum and lymbic system
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
lesson 3 unit 2 week 5
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
pons function
to act as a relay station for transferring info between the cerebellum and cerbral cortex
along with center in medulla, pons also coordinates and controls breathing
cerebellums location and function
located at posterior region, under occipital lobe, above brain stem
responsible for coordinated movement
processes sensory info
coordinates execution of movement in body
structure w/ largest number of neurons in brain, recieves input from somatic receptors, receptors for equilibrium, balance + motor neurons from higher centers of brain
what specific movement does the cerebellum coordinate
contributes to accurate limb movement
corrects ongoing movements
modifies strength of some reflexes
involved in learning new muscle movements
as well as vestibular ocular reflex (vision stability during head movement)
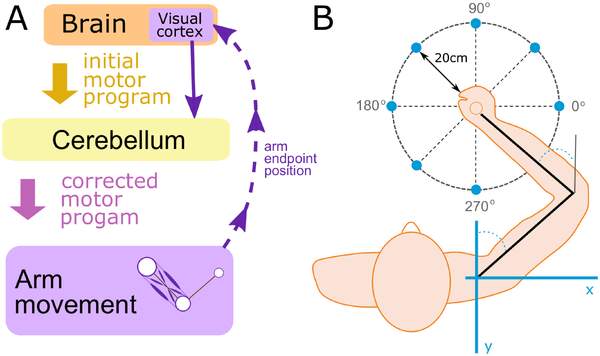
in order for cerebellum to assist in making accurate limb movements and in correcting ongoing movements, it must receive…
info from two diff sources: motor cortex (must recieve same info thats traveling out to the muscles being activated) and the proprioceptors (provides info on position of the limbs in space)
what does the cerebellum compare
the actual signal from motor cortex to that received from the proprioceptors
ensures muscle is doing what its supposed to be doing
if movement is not what if should be, cerebellum will modify the signals from the primary motor cortex and make adjustments
how cerebellum corrects movement
motor cortex send motor info that 1st gets thru cerebellum before reaching muscles
cerebellum intergrates that info
by comparing it to info it gets from proprioceptors
adjustments are needed in this case
thus cerebellum makes + sends the info to the muscles to move arm (purple arrow shifted left)
feedback recieved from sensory input, such as the visual system
gives cerebellum additional info for making those adjustments to the command initially set by motor cortex
limbic system is the..
emotional center within brain
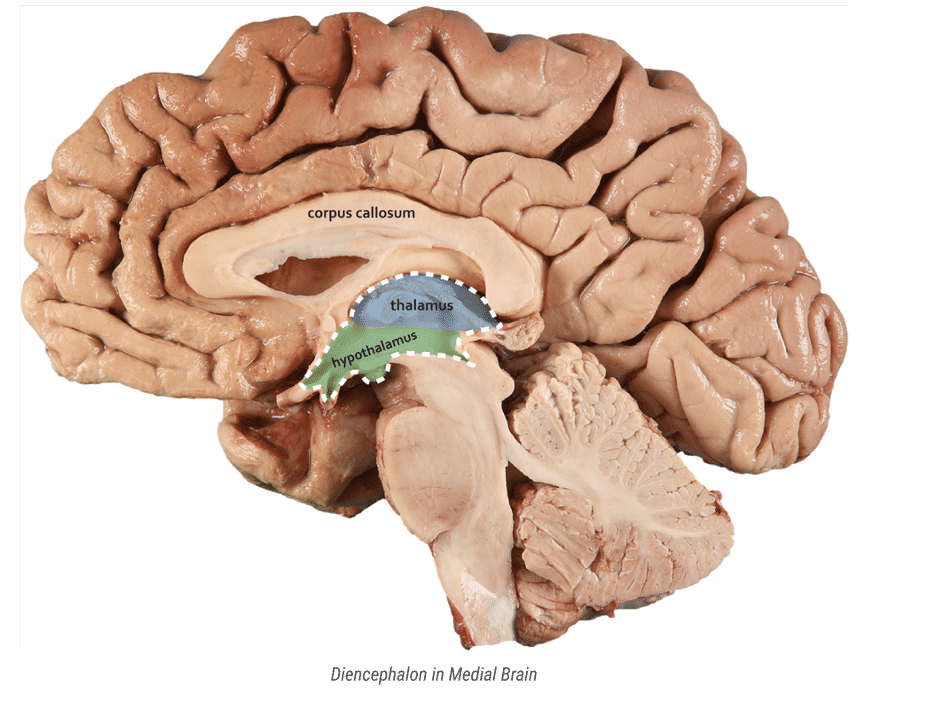
hypothalamus role and relation to limbic system
one of limbic systems components
plays role in homeostasis and hormone release
stimulation of the hypothalamus and limbic system..
may elicit normal behaviours such as:
eating
drinking
locomotion (ability to move from one place to another)
changes in heart rate and blood pressure
sexual behaviours
memory
the limbic system and hypothalamus coordinate…
a variety autonomic, hormonal and motor effects that are associated with constant maintance of internal environment and coordinating emotional behaviours
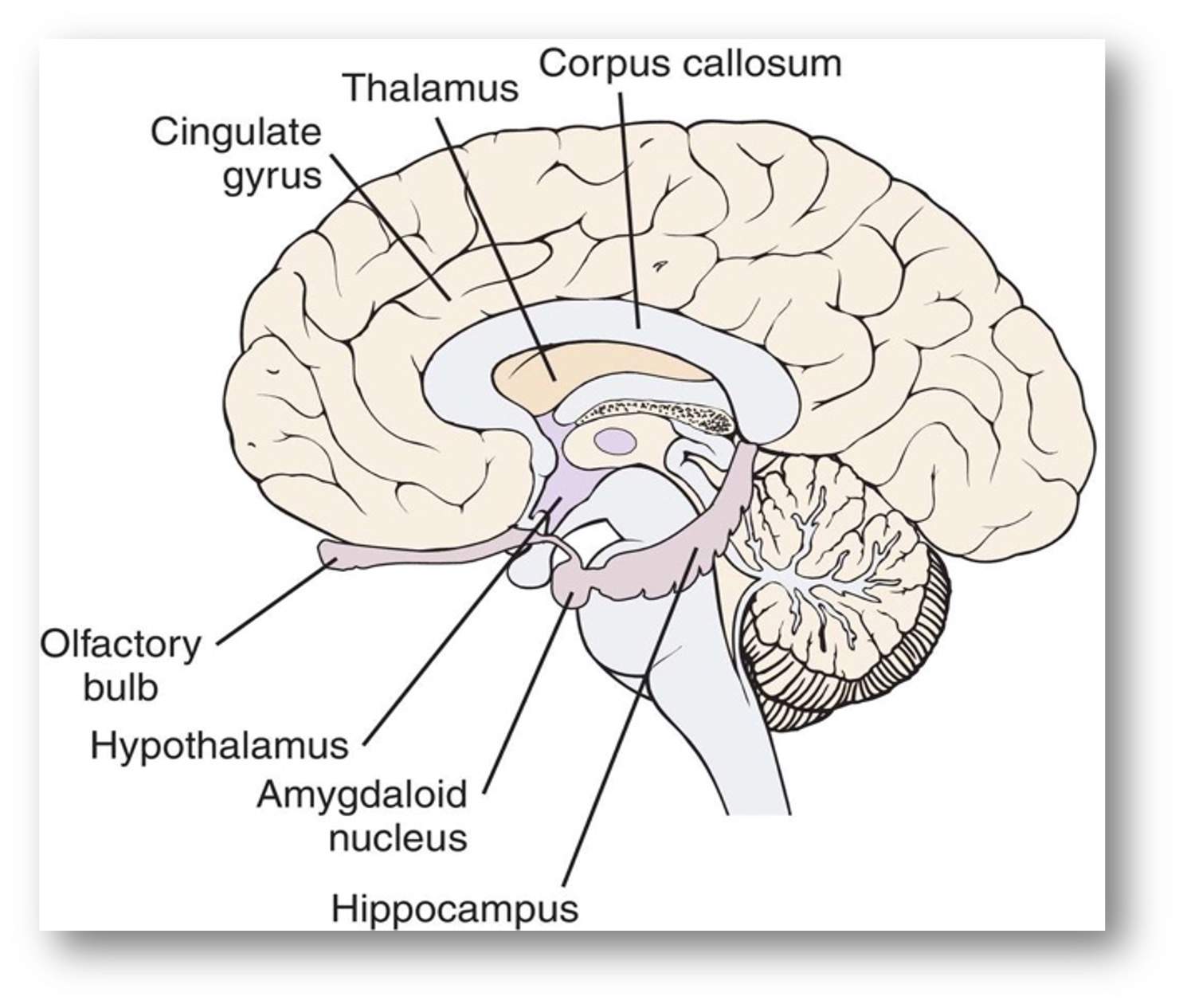
these are components of the…
limbic system
to honnold
to stand in some high, precarious place with ur back to the wall, looking straight into the abyss; to face fear

the amygdaloid body (amygdala) is part of what system and whats its role
part of the limbic system
plays a role in emotion response to situations: fear, anger, anxiety, pleasure
determines how strongly memories are stored, particularly those attached to strong response like fear or anxiety
describe the corpus callosum and its function
this structure is a dense bundle of nerve fibers that serve as pathway and connection btwn the two cerebral hemispheres
this connection allows the brain to integrate sensory and motor info from both sides of the body
and to coordinate whole body movements and function
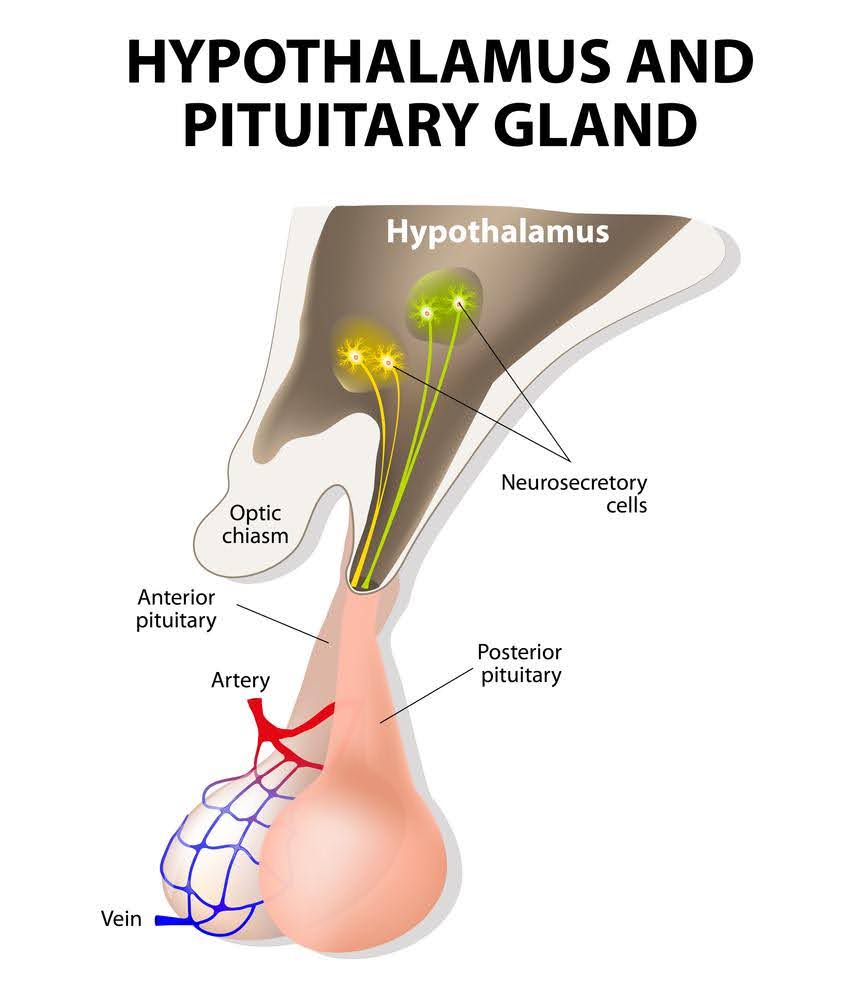
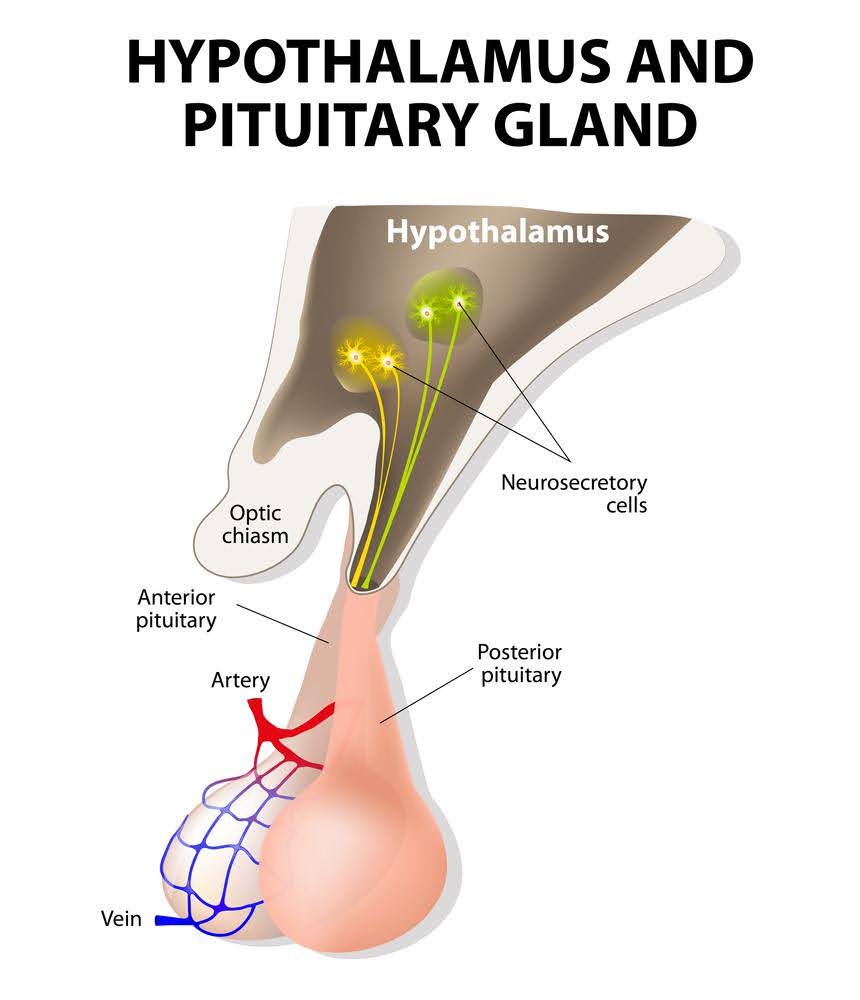
pituitary gland (hypophyse) - the two sections
primarily regulates other endocrine organs
anterior pituitary is derived from epithelial tissue of the pharynx
posterior pituitary derives from neural tissue of the hypothalamus
the two sections secrete diff hormones and have distinct anatomical differences
what are hormones
chemicals that cells use to communicate with each other “long distance” thru blood stream
they send info related to growth, stress, development and homeostasis regulation from higher integration centers to effector organs (skin, muscle, etc)
hormones secreted by pituitary are involved in
stress response
lactation
growth
development
reproduction
function of pituitary is regulated by
hypothalamus
hypothalamus location and function
located at base of brain, anterior to brain stem,
responsible for temp control, body water regulation, regulation of food intake, cardiovascular and circadian clock regulation and coordination of emotional behaviours and control of hormones released from pituitary
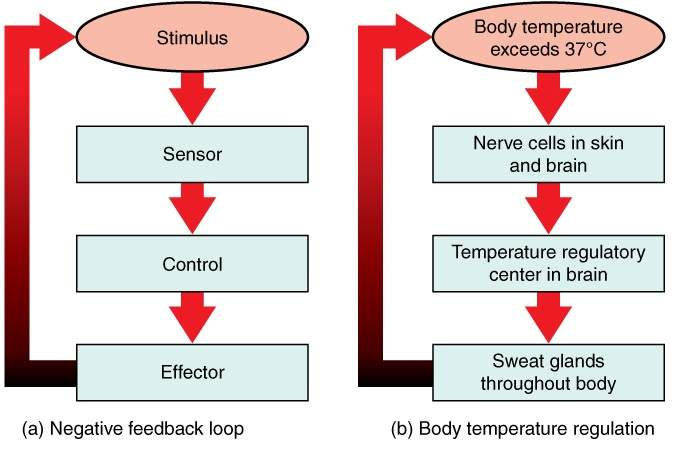
performs these functions thru neg feedback
temp control in the body and hypothalamus role
body has set point for temp (~37c) thats tightly controlled thru sensory info received from peripheral tissues
when temp rises due to exercise for ex,
regions in hypothalamus detects this change and initiates mechanisms to return temp to set point
mechanisms incluse sweating and vasodilation in blood vessels closer to skin to promote heat loss
which return temp to normal
what happens when we spike a fever? why does the hypothalamus not try to reduce the body temp back down to 37
fever is diff from a workout
during a fever, theres presence of markers of infection (bacteria and viruses)
hypothalamus tries to maintain temp around a set point
when we spike a fever, set point changes to a higher temp in attempt to protect the body from invading microorganisms
ex set point goes from 37 to 39, hypothalamus induce mechanisms to generate and retain heat like shivering of skeletal muscles (generates heat)
increased vasoconstriction in periphery (reduce heat loss) thats why hands and feet are cold during fever
bc hypothalamus is trying to conserve heat
now hypothalamus will maintain new set point until infection is no longer detected
thats why u sweat during a fever: hypothalamus induces heat loss mechanisms like sweating and vasodilation to increase heat loss