Key Concepts in Biochemistry and Water Properties
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering essential vocabulary and definitions related to biochemistry and the properties of water.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Biochemistry
The study of the chemical processes and substances that occur within living organisms.
Universal Solvent
Water's ability to dissolve and interact with a wide variety of substances.
Polarity
The property of a molecule that results from the unequal sharing of electrons, causing a positive and negative end.
Hydrogen Bonding
Weak interactions that occur between a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to an electronegative atom and another electronegative atom.
Hydrophilic
Describes compounds that dissolve easily in water; generally charged or polar.
Hydrophobic
Nonpolar molecules that do not dissolve in water; also known as water-fearing.
Amphipathic
Compounds containing both polar (or charged) regions and nonpolar regions.
Bond Energy
The average amount of energy required to break a bond; energy is absorbed when bonds break and released when they form.
Micelles
Thermodynamically stable structures formed by amphipathic compounds in water, where nonpolar regions cluster together.
Noncovalent Interactions
Weaker interactions than covalent bonds, important for the stability of macromolecular structures.
Polar covalent bonds
Unequal sharing of electrons between O and H and Creates a charge across the bond (dipole)
Formation
When a bond forms, energy is released.
Breakage
When a bond breaks, energy is absorbed
Hydrogen Bonds req.
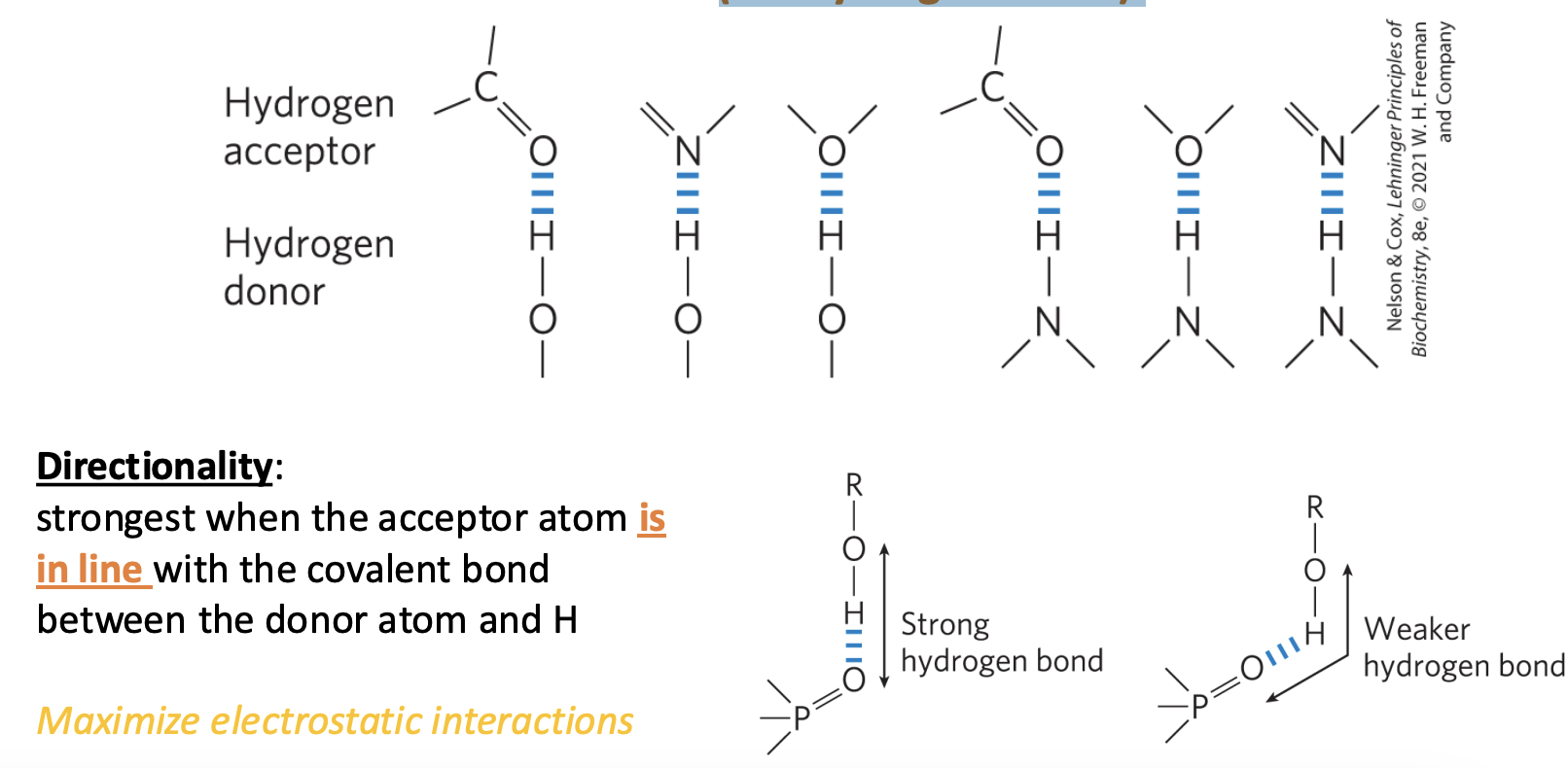
Hydrogen must be attached to a very electronegative atom • N, O, or F
hydrogen bonds readily form between an electronegative atom (the hydrogen acceptor) and a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to another electronegative atom (the hydrogen donor)
hydrophobic effect
nonpolar regions cluster together
polar regions arrange to maximize interactions with each other and with the solvent
van der Waals interactions (London dispersion forces)
Distance-dependent weak attractions and repulsions between transient dipoles
van der Waals radius:
measure of how close an atom will allow another to approach
cytochrome f
has a chain of five bound H2O molecules
may provide a path for protons to move through the membrane