NSC837 Lecture 3 - Sequential imaging, laser light bleed through, confocal scanners, PMT detectors
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
fluorescence crossover
fluorescence from shorter wavelength flurochrome crosses into longer wavelength detection channel (prevent with sequential imaging)
sequential acquistion
illuminate with different lasers separatley to avoid crossover associated with simultaneous acquisition
laser light bleed through
wide band pass filters (ch1 BP 475-525nm would allow 488nm laser light through) (ch2 BP 505-560nm would allow 543nm light through)
confocal laser scanning microscopy
optically reduces the amount of out-of-focus light fromt he image
pinhole apeture blocks out of focus light by
controlling size of pinhole apeture can impact the image
where does term galvo (or scan) mirrors come from
the name of the motor that moves the mirrors
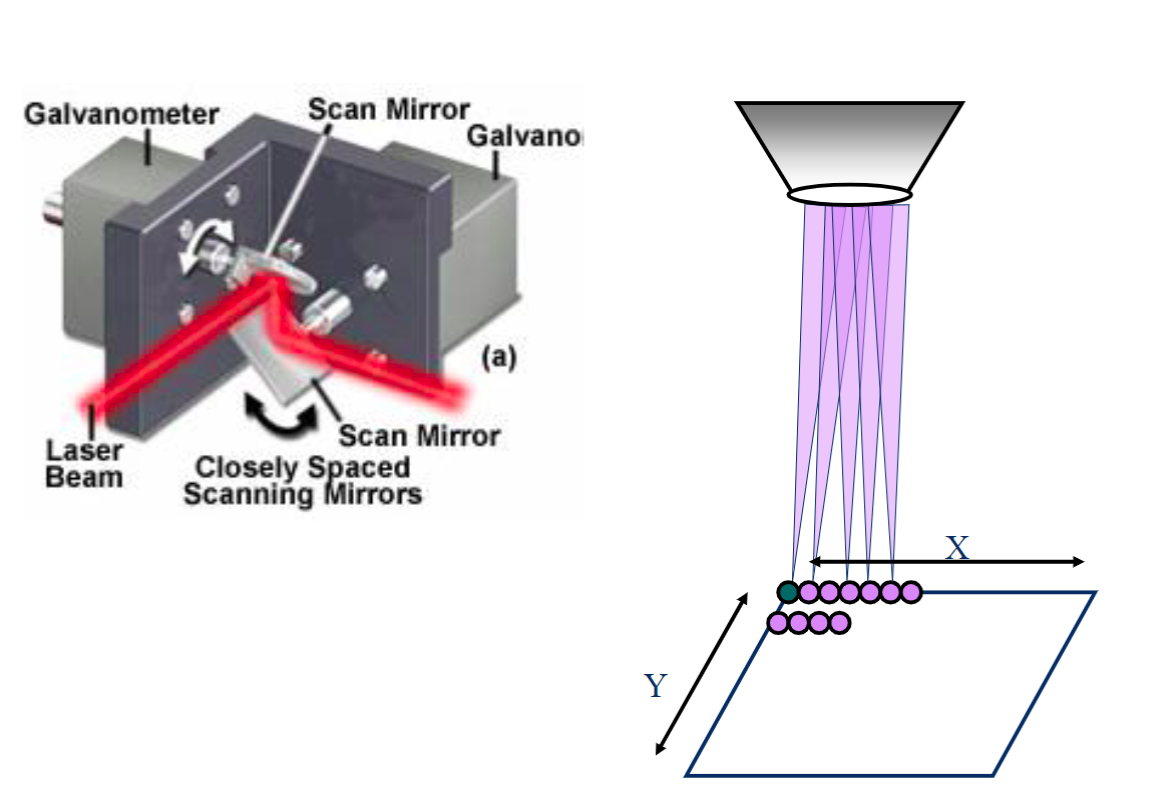
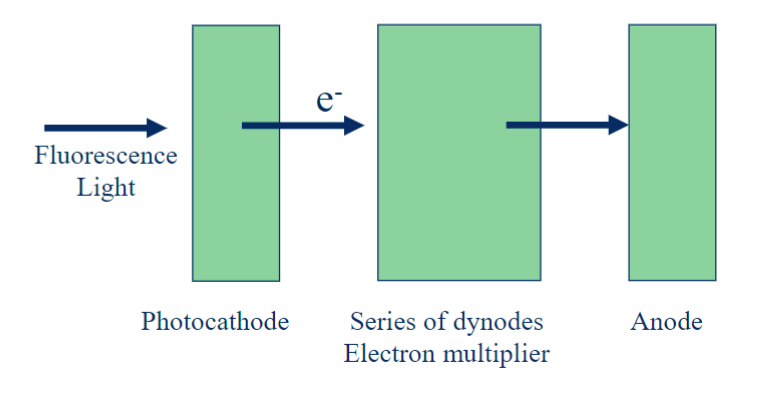
photo multiplier tube (PMT)
used as photodetectors (image formation)
confocal scanning
X and Y Scan Mirrors (galvo mirrors) - controls the exact position of the laser within the field of view of the sample
AOTF - microsecond shuttering and intensity control of the laser (turn of / on intensity of laser)
2 types of point scanning
1) uni-directional -standard scan is left to right, more accurate
2) bi-directional - rapid scanning, but can produce jagged edges within the image (scanning mirrors have to slow down/speed up before/after turns). This has been fixed by having galvo mirrors start outside of field of view
bi-directional better for live cells (moving)
resonance scanning
Probably won’t need for fixed but maybe for live
Some scopes only have galvo some have both where you can choose
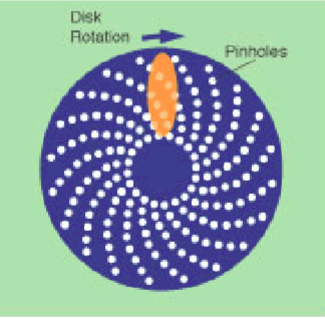
multi-point scanning confocal (spinning disk)
two spinning disks with dichroic mirror between the two disks
camera detection instead of PMT
can illuminate more than one point at a time
what problem arises with multipoint-scanning confocal
missing laser- only a little bit of laser going in holes
original not good for biology but is good for lasers
advantages of spinning disk confocal
1) Speed - depends on spinning disk rate and camera readout rate (less res. for spinning)
2) sensitivity - quantum efficienty of cameras about 95% (PMT is 25-50%)
3) reduced photobleaching - low intensity longer exposure (inverse for point scanner)
point scan confocal advantages
1) optical sectioning- adjustable pinhole apeture; optimize for each objective and wavelength . Spinning disk does not have adjustable pinhole apeture, optimized for 100x objective, and green excitation only. Out of focus light can cross into other pinholes
2)multi-color imaging - multiple PMT detectors, simultaneous detection. Spinning only has single ccd camera and sequential detection
3) region of interest scanning/bleaching - scan mirrors/AOTF permit regional scan/bleach. Spinning disc is limited to FOV, no point bleaching
When might spinning disck be useful?
live cell imaging over time and rapid 3d imaging over time
reason: reduced photobleaching and faster scan speeds
photomultiplier tubes design
includes a photocathode, a focusing electrode, an electron multiplier (dynode), and an electron collector (anode)
photocathodes types
multi-alkali photocathode detector (standard) - highly sensitive in UV range and not as easily damaged
GaAsP (gallium arsenide phosphide detector) - highly sensitive throughout visible wavelength range. Can be easily damaged by intense light
PMT dynamic range
the range of detectable intensities that the PMT can record
dimmiest - below is zero. This is the offset value
upper limit (brightest) - above this is saturation. Determined by gain
what do PMT detectors convert fluorescence density into
a digital intensity value
bit depth
bit depth determines the number of increments or intensity levels between zero and saturation for a PMT
actual intensity value is recorded by the PMT is determined by the bit depth
doesn’t matter for pretty pics but does matter for quantifying
Look-Up Table (LUT) (color assignment)
image displayed on the monitor is not a “true” color image
color is a pseudo color chosen by the user. defined by LUT
It maps color intensity to th efluorescence intensity detected by the PMT
kalman averaging
high detector gain settings will create random bright spots or noise in the image
this is due to random electrons generated and detected within the PMT detecto (not true signal from sample)