Dr. Li Partition
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
define partition/distribution coefficient
its the measure of the ability of a compound to distribute in two immiscible phases
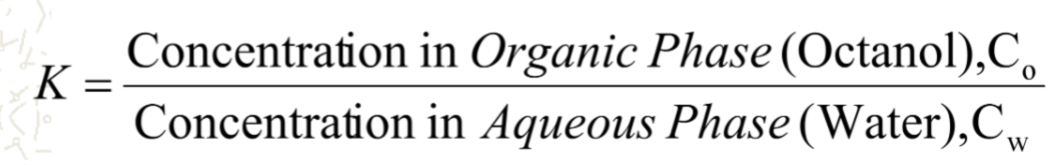
what does this equation defined as?
defined as the partition/ distribution coefficient
define partition coefficient
distribution of an unionized compound between two immiscible liquid phases at equilibrium
often expressed as Log P or K
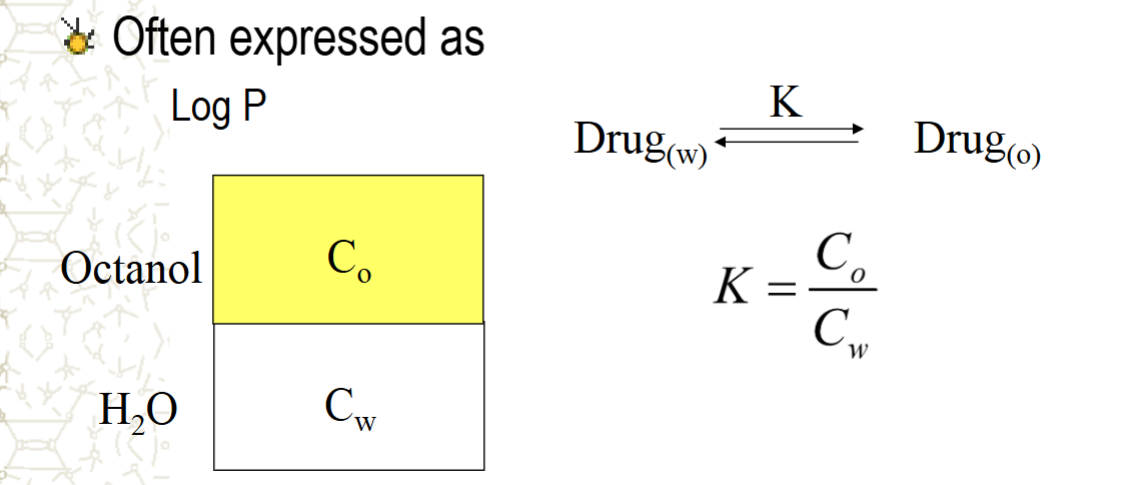
what do these equations signify?
partition coefficients
what happens when log = 0?
equally soluble in water and partition solvent
what happens when log is = 1 or higher (+) numbers?
more soluble in partition solvent
what happens when log is = -1 or any (-) numbers?
more soluble in water
how do you determine partition coefficient?
typically in octanol and water
some other solvents used for organic phase
chloroform, ether, hexane
what is the partitioning of weak electrolytes?
expression of partition coefficient is valid for non-electrolytes
expression of distribution coefficient takes ionized species into account
liquid phase only unionized form of drug
aqueous phase contains both ionized and unionized form of drug existing in equilibrium
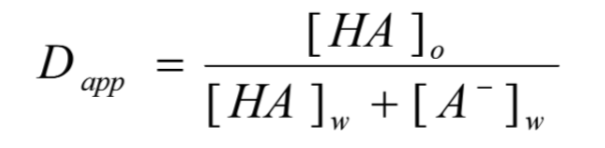
what does this equation identify?
partitioning of weak electrolytes
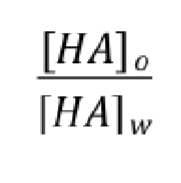
what does this equation identify?
partition of weak electrolytes between organic and aqueous phase
[HA]w in water ionizes to [H+] + [A-]
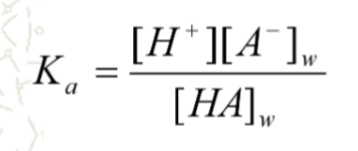
what does this equation identify?
partition of weak electrolytes between organic and aqueous phase
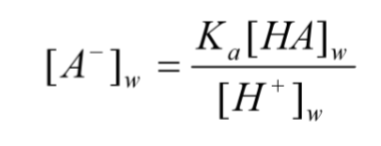
what does this equation identify?
partition of weak electrolytes between organic and aqueous phase
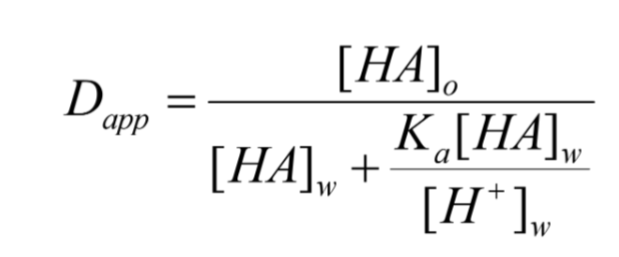
what does this equation identify?
partition of weak electrolytes between organic and aqueous phase
what is K and D
distribution constant
same for unionized compound
K relates to unionized or neutral compounds
D is only used for ionizable compounds
D is pH dependent
what is extraction?
the efficiency with which one solvent extracts a compound from another immiscible solvent is dependent upon the distribution and is used in
isolation of pure compounds from crude mixtures
separation of analytes from plasma samples during pharmacokinetic studies
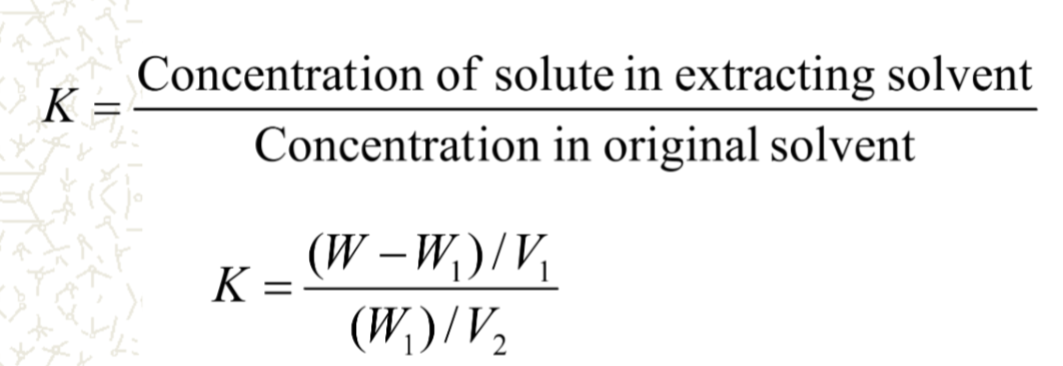
what does this equation refer to?
extraction
W and W1 = weight of solute added
V1 and V2 are volumes of extracting and original solvents
what is multiple extraction?
extraction efficiency can be improved by extracting multiple times using same volume of extracting solvent
what is the range for good oral absorption?
logP = 0-3
what does it mean when you have a high logP (log P > 4)
retained in lipophilic region, e.g. deposit in cellular membrane or fatty issue
what does is mean for a low log P?
highly water soluble and poor permeation across biological membrane