2.4 Price Elasticity of Demand
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
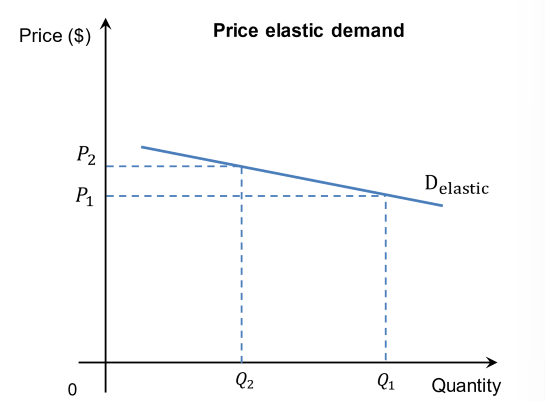
When is demand elastic? Explain and show its graph
If there is a relatively large change in the quantity demanded for price elastic a product following a relatively small change in its price. ( customers are responsive to changes in price.)
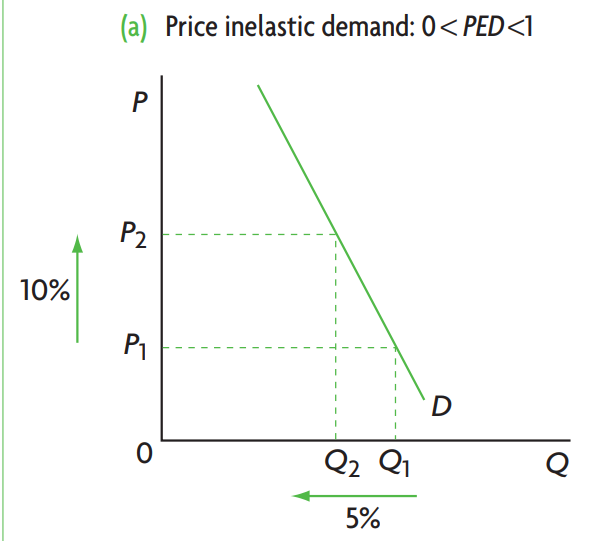
When is demand inelastic? explain its graph
If a price change causes a relatively small or insignificant change in the quantity demanded. (customers are irresponsive )
How does proportion of consumers income spent on a product effect its elasticity?
The greater the proportion of consumers income spent on a good or service, the more price elastic a product tends to be.
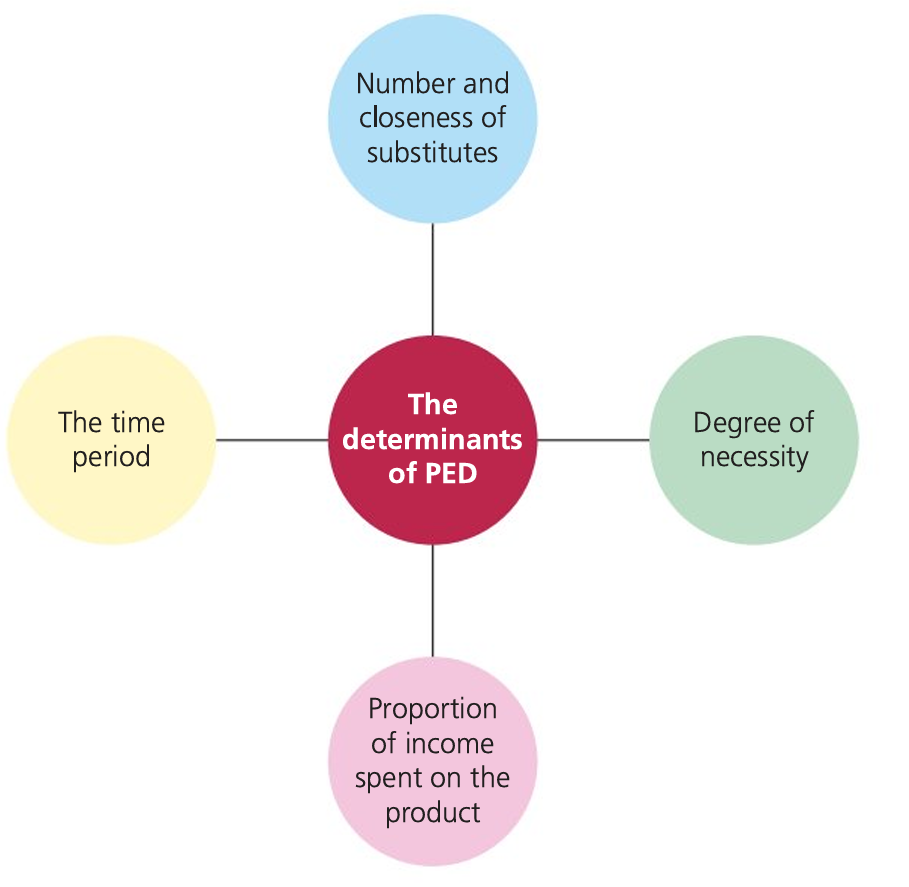
Detriments of PED
TINS
T- Time
I- Income
N- Necessity
S- Substitutes
How does the availability of a substitute product affect its elasticity?
Elastic products:
The more and easily available close substitutes for a product, the higher the price elasticity of demand (PED).
Consumers can readily switch to different substitute products or brands if there is a small change in the price.
a small change in price leads to a relatively larger change in quantity demanded.
If the price of a product like Fanta increases, consumers can easily switch to other soda brands like Tango, Orangina,
Inelastic Demand Examples:
Products with few or no substitutes (e.g., private education, prescribed medicines) often have price inelastic demand.
A small change in price causes a smaller percentage fall in quantity demanded because consumers have limited or no choice
High switching costs for customers, such as lengthy contracts for mobile phone services, can make demand price inelastic.
Reducing Substitute Availability:
Firms can deliberately attempt to reduce the number and closeness of substitutes to increase the opportunity costs of switching to rival brands. if there is high cost involved, demand is relatively price inelastic.
How does the degree of necessity effect the price elasticity of a product?
If a good is a necessity, quantity demanded is less responsive to a change in its price and demand is expected to be more price inelastic. Food products can be considered necessities; as such quantity demanded is not very responsive to price changes.
If a good is addictive, such as cigarettes and alcoholic drinks, it is more difficult to reduce consumption following an increase in price. Therefore, demand is expected to be more price inelastic.
How does the proportion of income spent effect the price elasticity of a product?
The greater the proportion of consumers real income spent on a good or service, the more price elastic demand will be, ceteris paribus.
Consumers are highly responsive to price changes for products that constitute a substantial part of their income, such as jewelry, sports cars, and overseas holidays.
Conversely, if a product represents only a small proportion of people's income, price increases have a minimal impact on their spending.
For example, even with a 50% price increase in items like toothpicks or safety matches, the quantity demanded may only fall by 10%, indicating price inelasticity due to the small proportion of income affected.
How does the time spent effect the price elasticity of a product?
Over a short period of time demand is more price inelastic but it becomes more price elastic as time goes on
As consumers are able to make adjustments and find substitutes, reducing consumption further.
The longer the time period after a price change, the more price elastic demand is likely to be
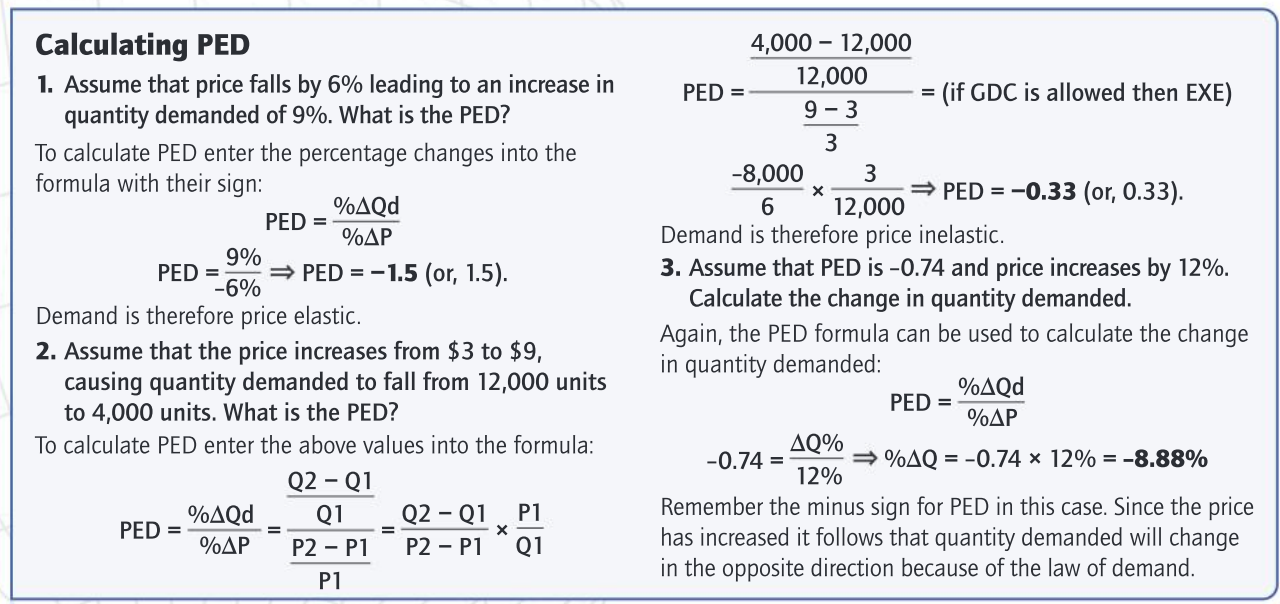
Formula for calculating the PED
percentage change in quantity demanded/ percentage change in price demanded
What are the degrees of PED and what value corresponds to it?
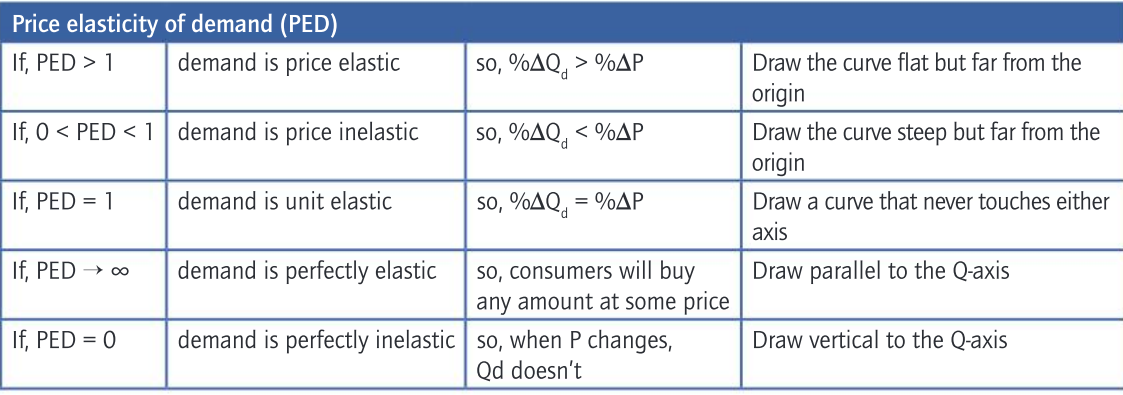
Does a term being more broadly defined mean its elastic or inelastic?
inelastic
How to calculate total revenue?
P x Q
(p1 x Q1 ) + (P2 x Q2)
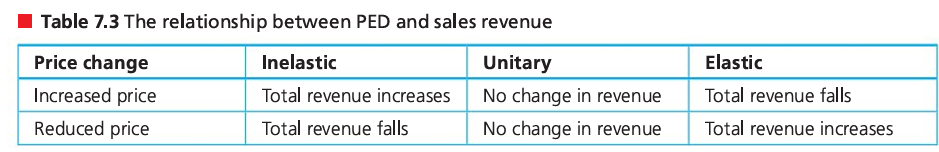
How is the total revenue effected when demand is price elastic?
quantity demanded changes proportionately more than price and total revenue changes in the same direction as quantity demanded.
• If P rises, Q falls proportionately more; therefore TR falls.
• If P falls, Q rises proportionately more; therefore TR rises.
How is the total revenue effected when demand is price inelastic?
quantity demanded changes proportionately less than price. Thus, the change in price has a bigger effect on total revenue than does the change in quantity demanded and total revenue changes in the same direction as price.
• If P rises, Q falls proportionately less; therefore TR rises.
• If P falls, Q rises proportionately less; therefore TR falls
the relationship between PED and sales revenue
The importance of PED for firms
Price elasticity of demand (PED) guides firms in pricing strategies. Firms with inelastic demand can implement price discrimination, charging different prices to different customer segments. For instance, cinemas and airlines adjust prices based on demand elasticity (when demand is price inelastic almost during holidays they hike their prices), maximizing revenue.
The importance of PED for government decision-making
Governments use PED in taxation policies. Taxes on demerit goods like cigarettes and alcohol, which have inelastic demand, can discourage consumption and generate significant tax revenue. Firms understand they can pass most of the tax burden to consumers due to the inelastic nature of these goods. This knowledge informs government policies, ensuring minimal impact on industries producing such goods.