Thalamus
1/72
Earn XP
Description and Tags
KIN 4571 Final Exam
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
Thalamus
Part of the Diencephalon rostral to the brain stem that:
receives sensory info
processes sensory info
interprets sensory info
integrates sensory info with cognitive processes (ex. memory)
gives meaning to our environment - perception
contains many nuclei, which:
receive specific afferent info
project to specific areas in cortex
lower level
Thalamus:
receives sensory info
processes sensory info
higher level
Thalamus:
interprets sensory info
integrates sensory info with cognitive process (ex. Memory)
Thalamus
What is the green arrow pointing to?
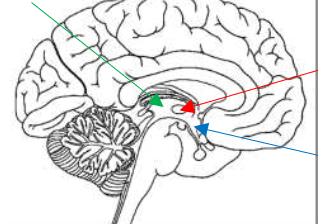
Interthalamic adhesion
What is the red arrow pointing to?
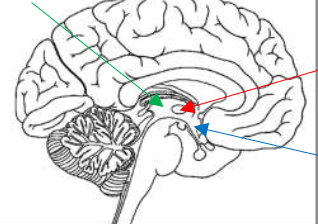
Hypothalamus
What is the blue arrow pointing to?
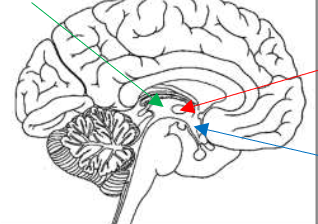
Coronal
This is the _______ section through the forebrain
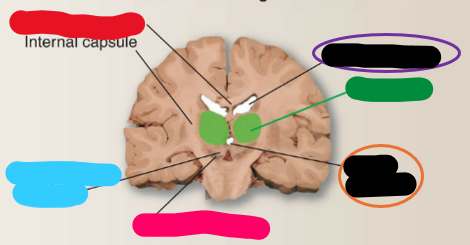
Corpus callosum
What is the red structure?
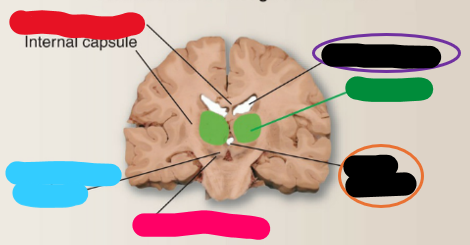
Subthalamic nucleus
What is the blue structure?
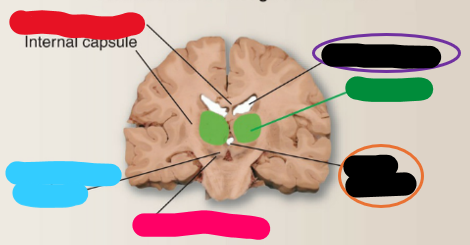
Substantia nigra
What is the pink structure?
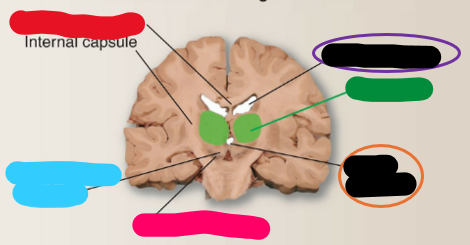
Third ventricle
What is the orange structure?
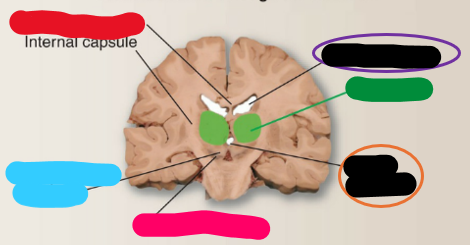
Thalamus
What is the green structure?
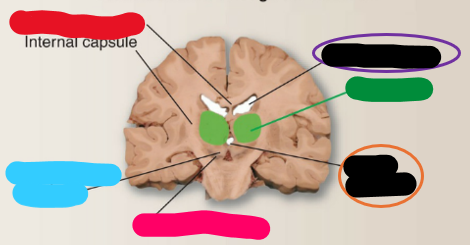
Lateral ventricle
What is the purple structure?
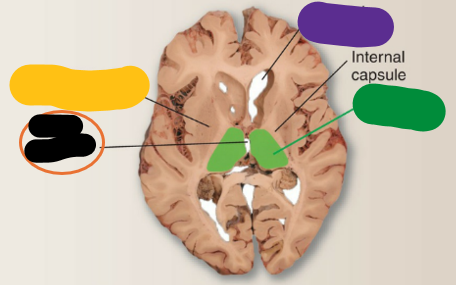
horizontal
This is the _________ section through the forebrain
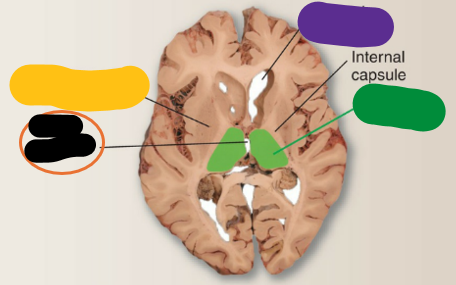
Putamen and Globus pallidus
What is the yellow structure?
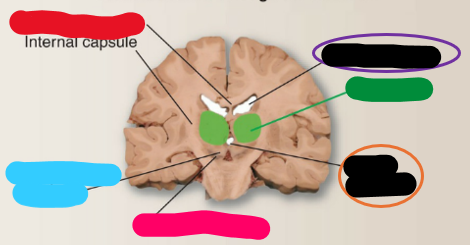
Third ventricle
What is the orange structure?
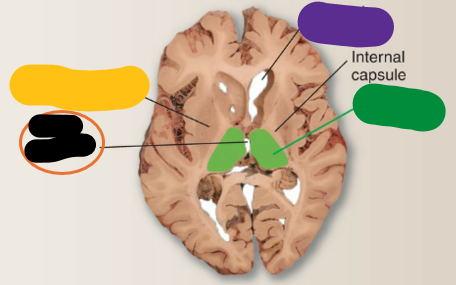
Thalamus
What is the green structure?
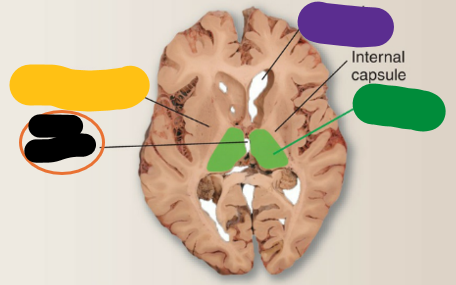
Lateral ventricle
What is the purple structure?
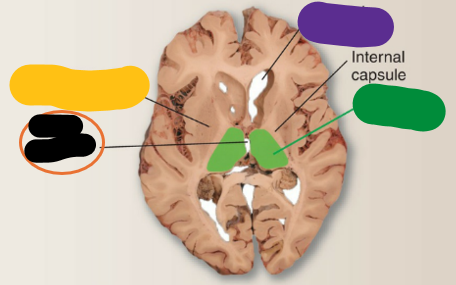
Interthalamic adhesion
known as the “eye of the bird” since it is the dot on the Thalamus
top
The first and second (left and right lateral) ventricles are on _______ of the Thalamus
between or underneath
The third ventricle is in _________ the Thalamus
Medial Lemniscus Pathway
Receptor: joint, cutaneous, muscle
Sensation: joint position, touch, pressure (body)
Cross over: medulla
Spinal Cord: posterior column (Fasciculus Gracilis and Fasciculus Cuneatus)
Brain Stem: Neuleus Gracilis and Neuleus Cuneatus → Medial Lemniscus
Thalamus: Ventral Posterolateral Nucleus (VPL)
Cerebral Cortex: Primary Somatosensory
Spinothalamic Tract
Receptor: skin receptor
Sensation: pain, temperature, itch, light touch (body)
Cross over: anterior white commissure at S.C.
Spinal Cord: anterolateral spinothalamic tract
Brain Stem: anterolateral spinothalamic tract
Thalamus: Ventral Posterolateral Nucleus (VPL)
Cerebral Cortex: primary somatosensory
Trigeminothalamic Pathway
Receptor: facial receptor
Sensation: facial sensation
Cross over: medulla
Spinal Cord: N/A
Brain Stem: CN V → Trigeminal Nucleus → Trigeminothalamic Tract
Thalamus: Ventral Posteromedial Nucleus (VPM)
Cerebral Cortex: primary somatosensory
Trigeminothalamic Tract
The ___________ does not go through the S.C.
Medial Lemniscus Pathway
Senses joint position, touch, pressure (body)
Spinothalamic Tract
senses pain, temperature, itch, light touch (body)
Trigeminothalamic Pathway
facial sensation
Medial Lemniscus and Trigeminothalamic
Crosses over at the medulla
Spinothalamic Tract
Crosses over at the anterior white commissure at the S.C.
Ventral Posterolateral Nucleus (VPL)
medial lemniscus and spinothalamic terminate here at the thalamus
Ventral Posteromedial Nucleus (VPM)
Trigeminothalamic terminates here at the thalamus
posterior
The bumps are _________
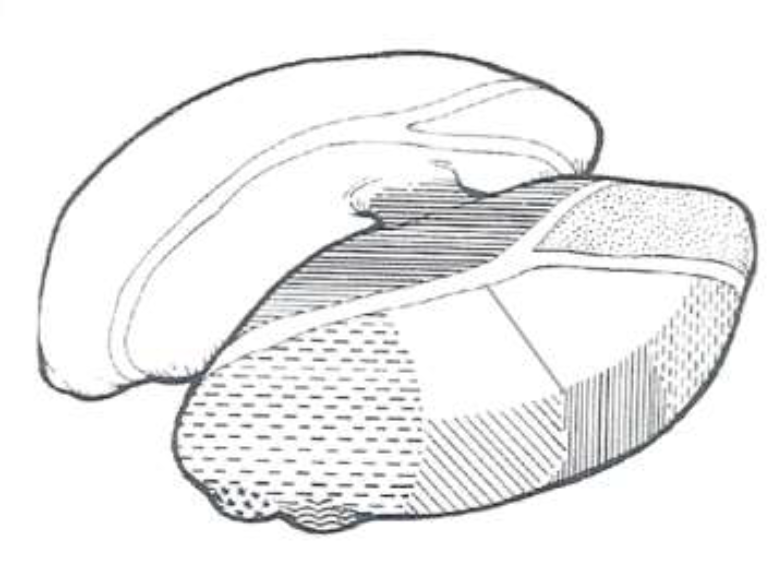
anterior
The top of the Y is __________
Internal medullary lamina
What is the black arrow pointing to the Y-shape?
white (axons)
The internal medullary lamina is made up of _______ matter (______)
Interthalamic adhesion
What is the black arrow pointing to the middle of the thalamus?
no
Is the Interthalamic adhesion needed to function normally?
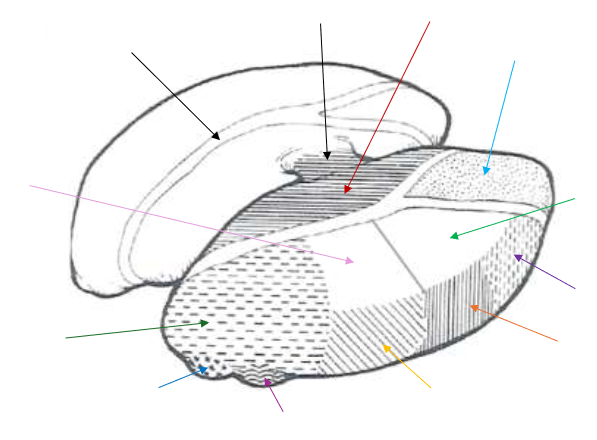
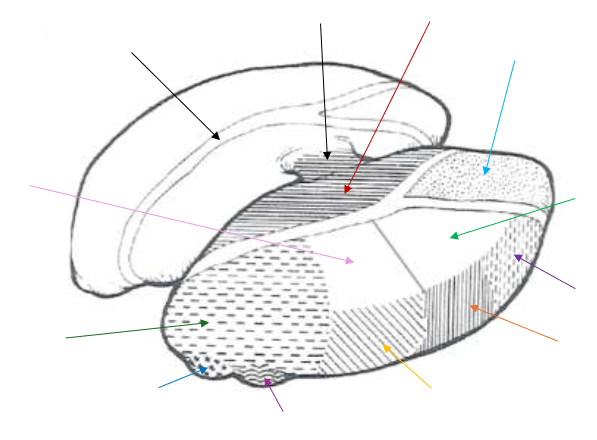
Medial Nucleus
What is the dark red arrow pointing to near the middle?
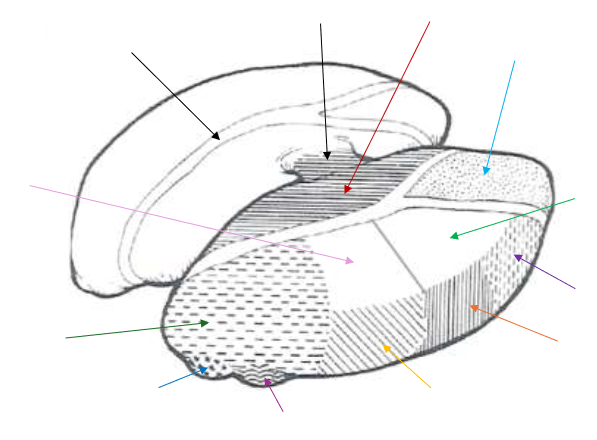
Anterior Nucleus
What is the light blue arrow pointing to near the top right?
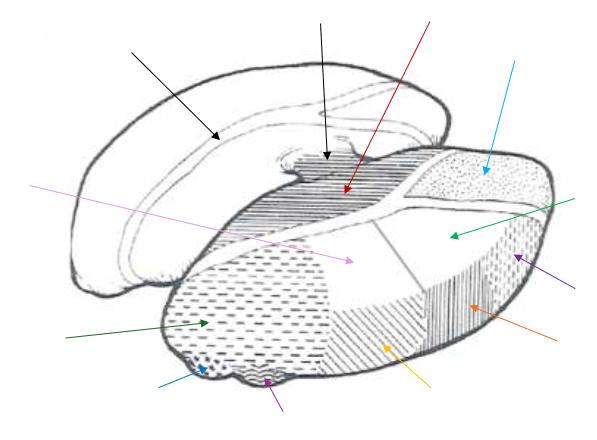
Lateral Dorsal (LD) Nucleus
What is the light green arrow pointing to?
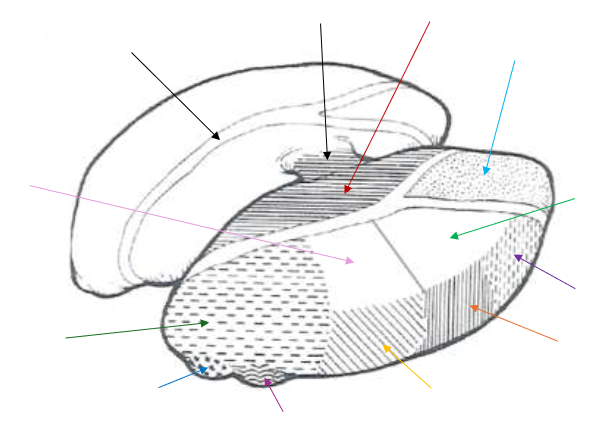
Ventral Anterior Nucleus
What is the purple arrow pointing to near the top?
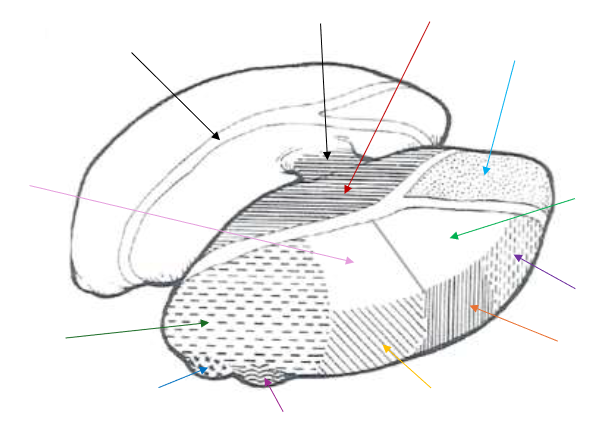
Ventral Lateral Nucleus
What is the orange arrow pointing to?
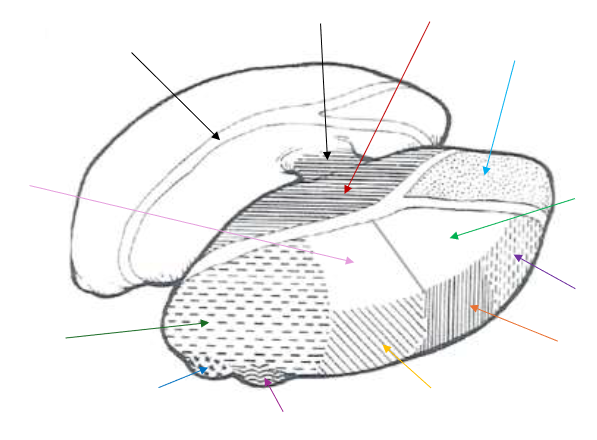
Ventral Posterior Nucleus
What is the yellow arrow pointing to?
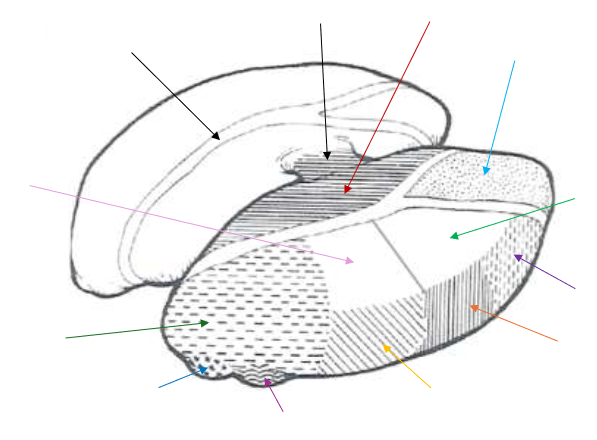
Ventral Posterolateral and Ventral Posteromedial
The Ventral Posterior Nucleus is split up into what two parts?
Lateral Geniculate Nucleus
What is the magenta arrow pointing to near the bottom?
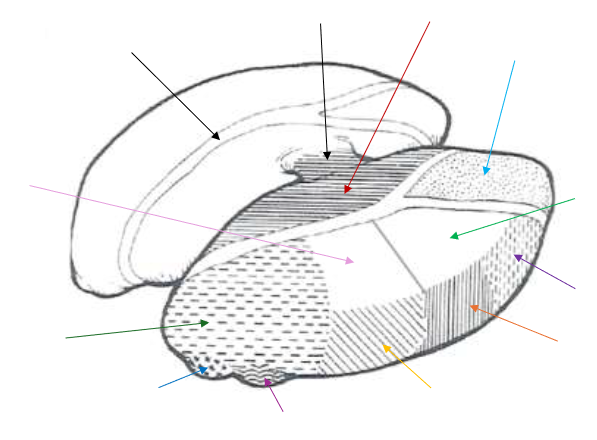
Medial Geniculate Nucleus
What is the dark blue arrow pointing to near the bottom?
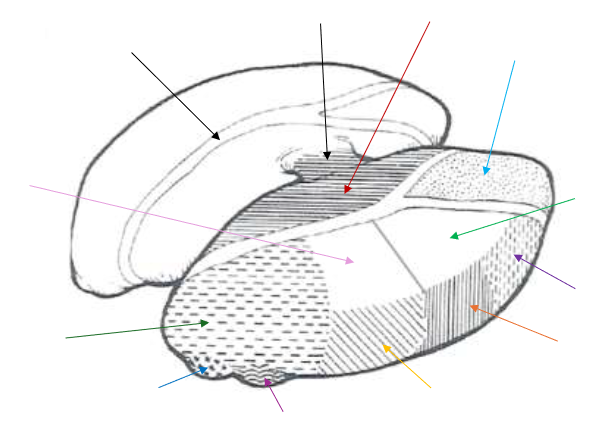
Pulvinar Nucleus
What is the dark green arrow pointing to near the bottom?
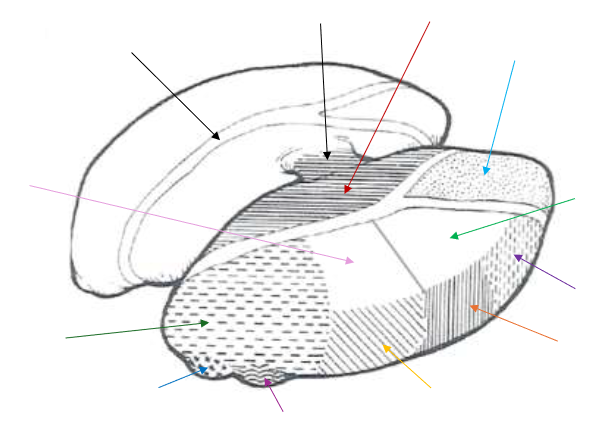
Lateral Posterior (LP) Nucleus
What is the light pink arrow pointing to?
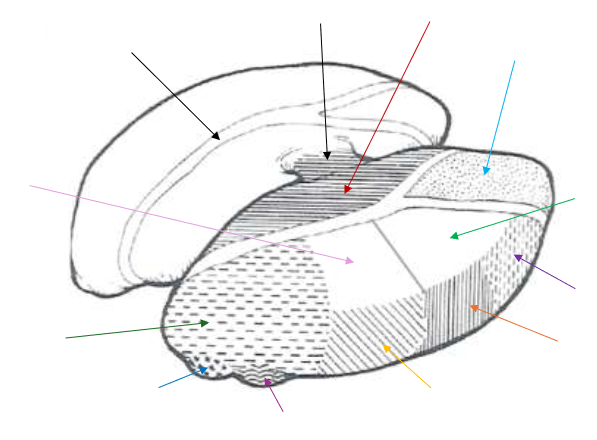
Association Nuclei
Medial, Pulvinar, Lateral Posterior
from cortex
receives info from cerebral cortex and sends info to other parts of cerebral cortex
pulvinar
The lateral posterior (LP) nucleus sends info to the __________ nucleus (they have the same cortical lobe and function)
Specific/Relay Nuclei
anterior, lateral dorsal, ventral anterior, ventral lateral, ventral posterior, lateral geniculate, medial geniculate
from periphery/subcortical
relay receives info from the peripheral and relays it to the cerebral cortex
anterior
The lateral dorsal (LD) nucleus sends info to the __________ nucleus (they have the same cortical lobe and function)
Medial
Cortical Lobe: frontal
Function: cognitive/executive
Pulvinar and Lateral Posterior
Cortical Lobe: parietal
Function: sensory association
Anterior and Lateral Dorsal
Cortical Lobe: limbic (cingulate)
Function: memory/motivation
Ventral Anterior and Ventral Lateral
Cortical Lobe: frontal (motor cortex)
Function: motor control/coordination
Ventral Posterior
Cortical Lobe: parietal
Function: sensory
Lateral Geniculate
Cortical Lobe: occipital
Function: visual
Medial Geniculate
Cortical Lobe: temporal
Function: auditory
Sensory
__________ Disorders of the Thalamus
problems distinguishing stimuli
type
location
intensity
Hemianopsia (hemianopia)
thalamic pain syndrome
neuropsychological problems
Hemianopsia
vision loss of one side (damage to lateral geniculate)
Thalamic Pain Syndrome
every sensation is painful
Motor
_________ Disorders of the Thalamus
sensory ataxia
dyskinesia
chorea
tremors
dystonia
Sensory Ataxia
no motor coordination
Dyskinesia
involuntary motion
includes:
dystonia
chorea
tremors
Chorea
jerky movements
tremors, dystonia
Dystonia
change in muscle tone
Thalamic Syndrome
A combination of sensory and motor disorders. Includes:
thalamic pain syndrome (sensory)
hemianesthesia (sensory)
hemiparesis (motor)
Hemianesthesia
loss of sensation on one body side
Hemiparesis
weakness on one body side
Thalamus related motor disorders
includes:
dystonia
hemiparesis
tremors
sensory ataxia
chorea
Thalamus related sensory disorders
includes:
hemianopsia
hemianesthesia
thalamic pain syndrome
problem distinguishing stimuli