Exam 2
1/120
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
121 Terms
What are the major inhibitory amino acids
GABA and Glycine
What is GABA made from? Via what?
Glutamate via glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD)
GABA is transported into vesicles via _____
Vesicular GABA transporters (VGAT)
GABA is removed from the synaptic cleft by...... (3 types of transporters)
GAT-1, GAT-2, GAT-3
Removal on neurons:
GABA is either reloaded into vesicles or metabolized to glutamate and succinate by GABA aminotransferase (GABA-T)
Removal on astrocytes:
Glutamate is converted to glutamine by glutamine synthetase --> glutamine can be released by astrocytes ---> taken up by neuron & converted back to glutamate --> remade into GABA
To raise GABA at synapse:
- Block GABA-T (gaba stays & does not get picked up)
- Block GAT1, 2, or 3
What happens to GABA release if you block GAD
decreased production of GABA --> less available in synapse
What about blocking the vesicular transporter (GABA)
GABA is not present to be released (decreased GABA release)
Why won't precursors to GABA work?
Glutamate: excitatory
Glutamine: too standard of a precursor (used for others)
GABA A channels:
-Move ____ into cell
- ________ and ______ occurs at the postsynaptic cell
- __#_ subunits - Various combos of ___ subunits:
1. Cl-
2. Hyperpolarization
3. four: α, β, γ, δ
Both Benzos and barbiturates are......
both have different what kind of binding sites
PAMS & allosteric (binds outside active site)
BZD increases _______ of opening (only if ___ subunit is present)
BZD _____ a subset of GABAa receptors
frequency, γ, potentiate
barbiturates increase ______ of opening
duration
Both BZD & barbiturates have broadly ____ effects but _______ are much stronger.
depressive, barbiturates
NAMS at BZD promote.......
anxiety, arousal, & seizures
Vigabon
- treatment for epilepsy
- responsible for converting GABA transported into neurons into glutamate
-prevents GABA metabolism = increased presynaptic GABA levels
- can affect vision ---> impacts GABAergic interneurons in the retina.
Carbamazepine
- treatment for epilepsy
-Stabilizes inactive state of sodium channels
- reduced neuronal firing
-potentiates SOME GABAa receptors
Lamotrigine
- treatment for epilepsy
-a sodium channel blocker
Ketogenic Diet and Epilepsy: potential mechanisms
- net increase of GABA levels --> suppresses neuronal firing
- inactivation of VGLUT --> less loading GABA in vesicles = lower GLU levels
-altered levels of other NTs (NE, adenosine or 5-HT)
-antioxidant effect
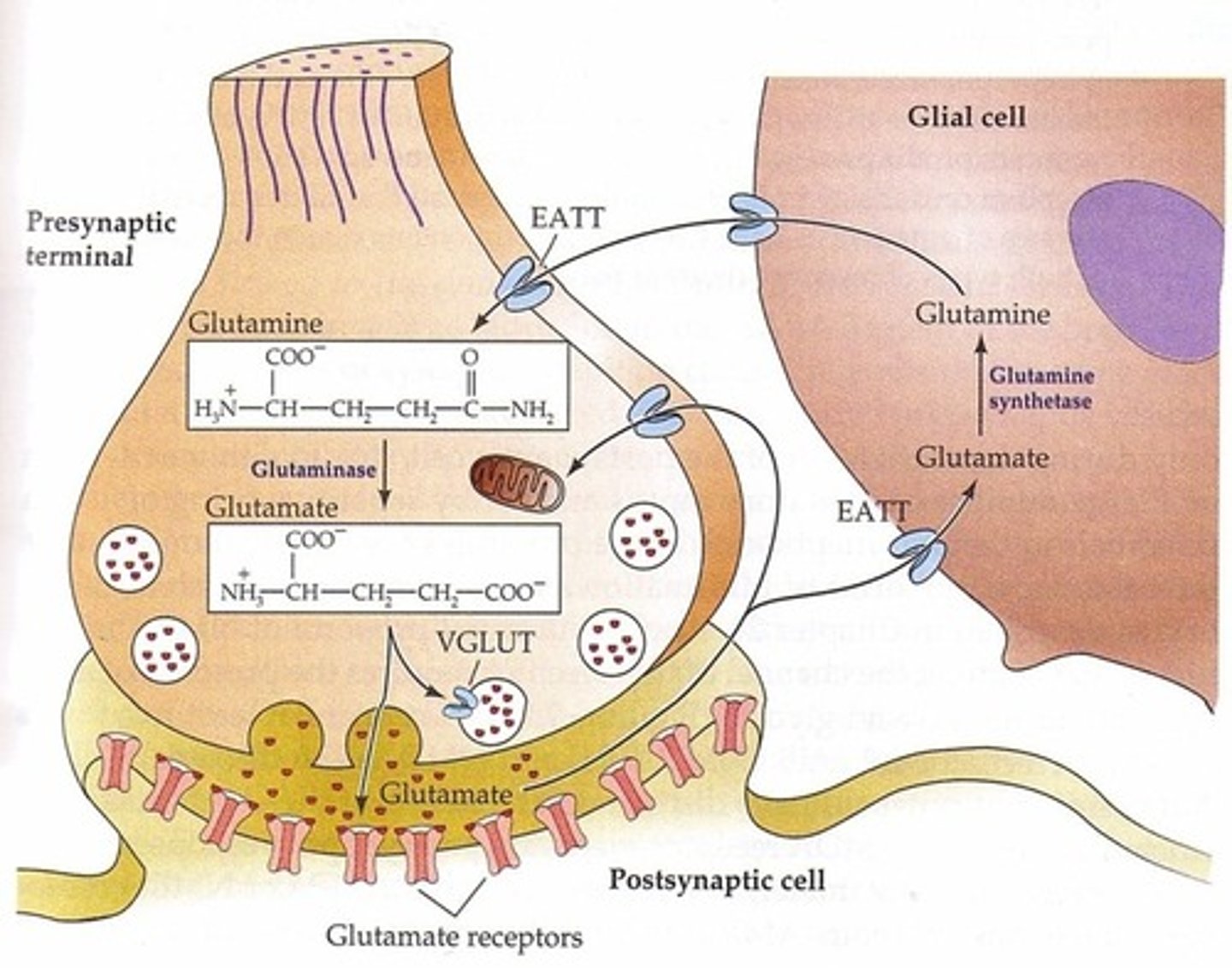
Glutamate Cycle
-EAAT1 & 2 located on astrocytes
-EAAT3 located on presynaptic terminal of neuron
Astrocyte: GLU --> glutamine synthase --> glutamine -> goes through glutamine transporters --> neuron terminal
Neuron terminal Glutamine --> Glutaminase --> Glutamate
VGLUTs load glutamate through vesicles: GLU--> EAAT3 --> VGLUT --> Glutamate in vesicle
VGLUT1 knockout mice
survive birth but begin to die during the third week of life
VGLUT2 knockout mice
die immediately after birth
VGLUT3 knockout mice
are viable but completely deaf; the inner hair cells of the cochlea use glutamate as the neurotransmitter
VGLUT blockers
should reduce levels of GLU released --> used to treat excitotoxicity
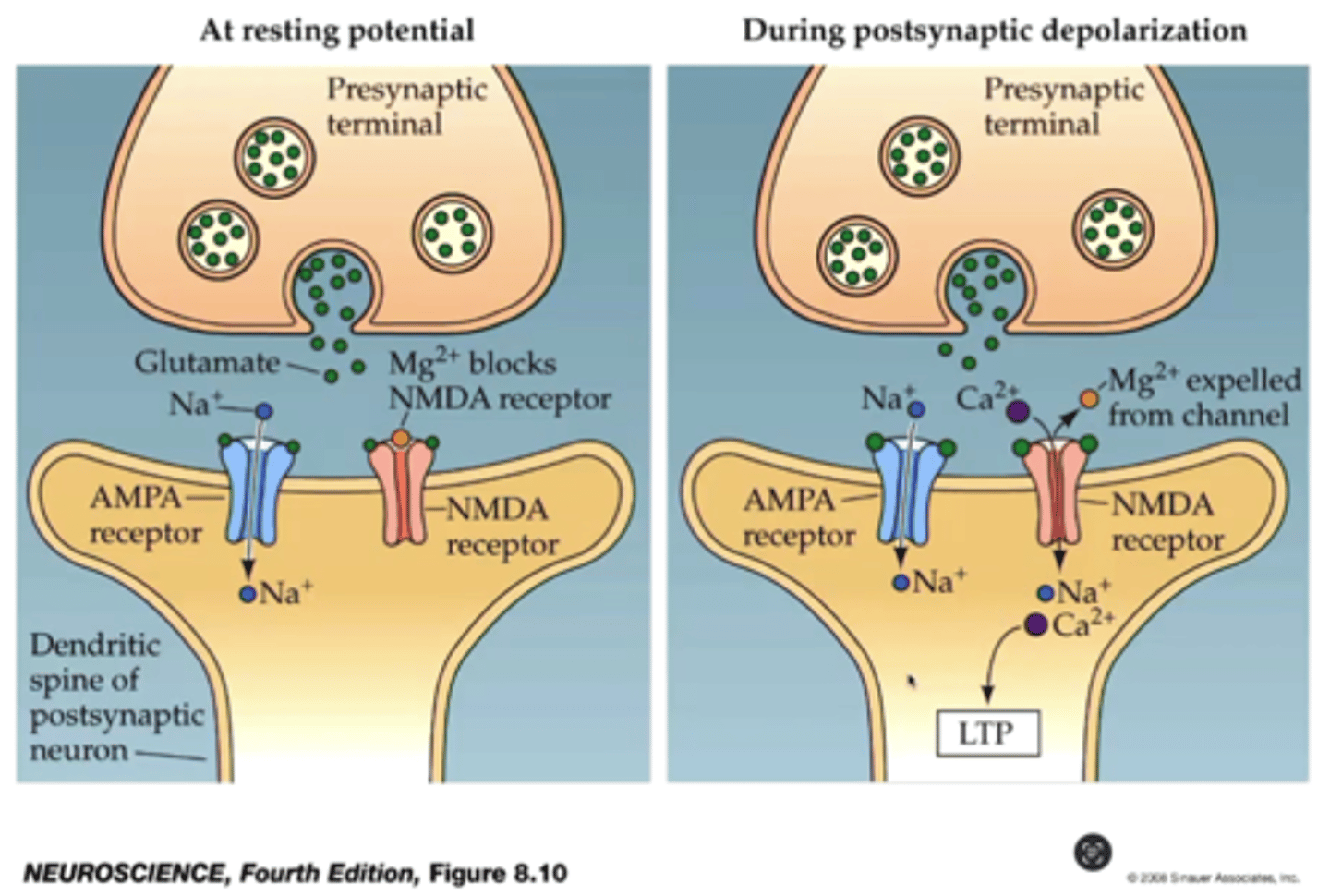
NMDA & Long term potentiation
-NMDA receptor is located at post synaptic terminal & responds to GLU
-NMDA has a Mg2+ ion block
- Presynaptic AMPA receptors are activated --> allows influx of Na+
- At sufficient depolarization Mg2+ block is lifted from NMDA Channels
- subsequent stimuli allows for Na+ and Ca2+ influx through NMDA
-Ca2+ is linked to induction of long-term enhancement of signaling at the spine (LTP)
AMPA-kines
drugs that enhance action of AMPA receptors
- maybe by reducing rate of desensitization
- maybe by acting as a PAM
- works in animal models & mixed results in humans
increased neurotransmission --> facilitate LTP --> increase cognitive function (thought to be used in neurodegenerative diseases)
Zinc and NMDA-sensitive glutamate-gated channels (two mechanisms)
Zinc directly inhibits
1) High-affinity binding to N-terminaldomains of Glu NR2A subunits reduceschannel open probability
2) Low-affinity voltage-dependent binding topore-lining residues blocks the channel
Doogie Mouse
NMDA receptor geneticaly altered to stay open longer, allowing more calcium influx, more robust LTP, and enhanced memory
NR2B subunit of NMDA receptor --> over expressed -> greater ratio of NR2B subunits = longer NMDA receptor opening
note: more sensitive to certain forms of pain
Necrosis
Uptake: cell contents are ingested by macrophages with significant inflammation
Membrane: Loss of membrane integrity with cell lysis occurring
Organelles: organelle swelling + lysosomal leaking & random degradation of DNA
Apoptosis
Size: cellular shrinkage with one cell being affected
Uptake: cell contents ingested by neighboring cells with no inflammatory response
Membrane: membrane blebbing & Apoptotic bodies forming
Organelles: mitochondria release prop-apoptotic proteins with the presence of chromatin condensation and non-random DNA degradation.
How can ischemia cause an increase in glutamate release:
Ischemia = temporary stoppage of blood flow/oxygenation to tissue
- lack of O2 --> interferes with ATP production
- when ATP dependent ion pumps fail --> cell is depolarized
-voltage gated Ca channels open = intercellular Ca2+ levels rise
- stimulates glutamate release --> AVALANCHE
- glutamate activates AMPA & NMDA receptors --> Ca2+ influx in downstream neurons
-excitotoxicity
- second wave: cells that die of necrosis release glutamate into interstitial space, also exciting neighboring cells. --> advantage of having microphages/microglia absorb dying cells
Once blood flow returns --> reperfusion injury --> increased permeability of blood vessels = inflammatory response.
Caffeine as an antagonist
blocks activity
what type of receptors are Adenosine A1
G i/o coupled
what type of receptors are Adenosine A2a
Gs coupled
what type of receptors are Adenosine A2b
G s/q coupled
what type of receptors are Adenosine A3
G i/q coupled
Caffeine at higher doses
-Inhibition of phosphodiesterase: increase cAMP =paralysis in insects
- Blocking of GABAa receptors
- Stimulation of Ca2+ release
- enters toxic range
Malignant hyperthermia
inherited disorder that causes a severe reaction to certain anesthetics
Treatment for malignant hyperthermia
Dantrolene
What genetic mutation is associated with malignant hyperthermia?
Mutation affecting the RYR1 protein in skeletal muscle
What are the two sites on the RYR1 protein responsible for controlling calcium concentration?
A-site and I-site
What is the function of the A-site on the RYR1 protein?
Mediates RYR1 opening with high affinity for calcium
What is the function of the I-site on the RYR1 protein?
Mediates RYR1 closing with low affinity for calcium
What role does magnesium play in the function of the RYR1 protein?
Causes RYR1 protein to close by acting on the I-site
MH: triggering agents
Caffeine, halothane, etc.
- acts by drastically increasing the affinity of the A-site for Ca while simultaneously decreasing the affinity of the I-site in mutant MH proteins.
- Also includes a greatly decreased affinity for Mg.
End result of triggering agents (MH)
increased Ca release due to lowered activation and heightened deactivation threshold.
Most & Least Potent hallucinogens
Most: LSD
Least: Mescaline
How are most hallucinogens administered
they are ingested
Duration of Hallucinogen Effects
begins at 30-90 mins --> LSD trip can last for 6-12 hours
- smoked DMT & Sativa: felt in secs --> peaks in minutes --> gone in an hour
2C-x
Family of psychedelic phenethylamines originally synthesized byAlexander Shulgin
• Early pesticide work with Dow Chemical
• Systematically tested compounds on himself
PCP and ketamine binding site/receptors
noncompetitive antagonists at NMDA receptors
inside the receptors ion channel, separate from the site at which glutamate or NMDA binds
Chronic Use of PCP or Ketamine: negative effects
- Urological signs: bladder pain and incontinence
-deficits in memory/ other cognitive functions
- Grey and White matter abnormalities (chronic ketamine)
-Repeated administration of high doses of ketamine = apoptotic cell death in developing brains of rats and monkeys
This is concern because Ketamine is a common anesthetic agent for pediatric procedures
How can you increase catecholamine synthesis?
administering a precursor
example: LDOPA & treating parkinson's disease
Pathway to dopamine and NE
tyrosine --> TH --> DOPA --> AADC --> DA--> DBH --> NE
Alpha-methyl-para-tyrosine (AMPT)
Blocks TH --> prevention of catecholamine synthesis
After catecholamine synthesis.........
- catecholamines are packaged into vesicles
OR
- is broken down --> decreased levels = sedation and depression
What drug blocks VMAT 2 & 2
reserpine
What type of receptor subtypes are present in DA-ergic system? How many?
- metabotropic
- 5
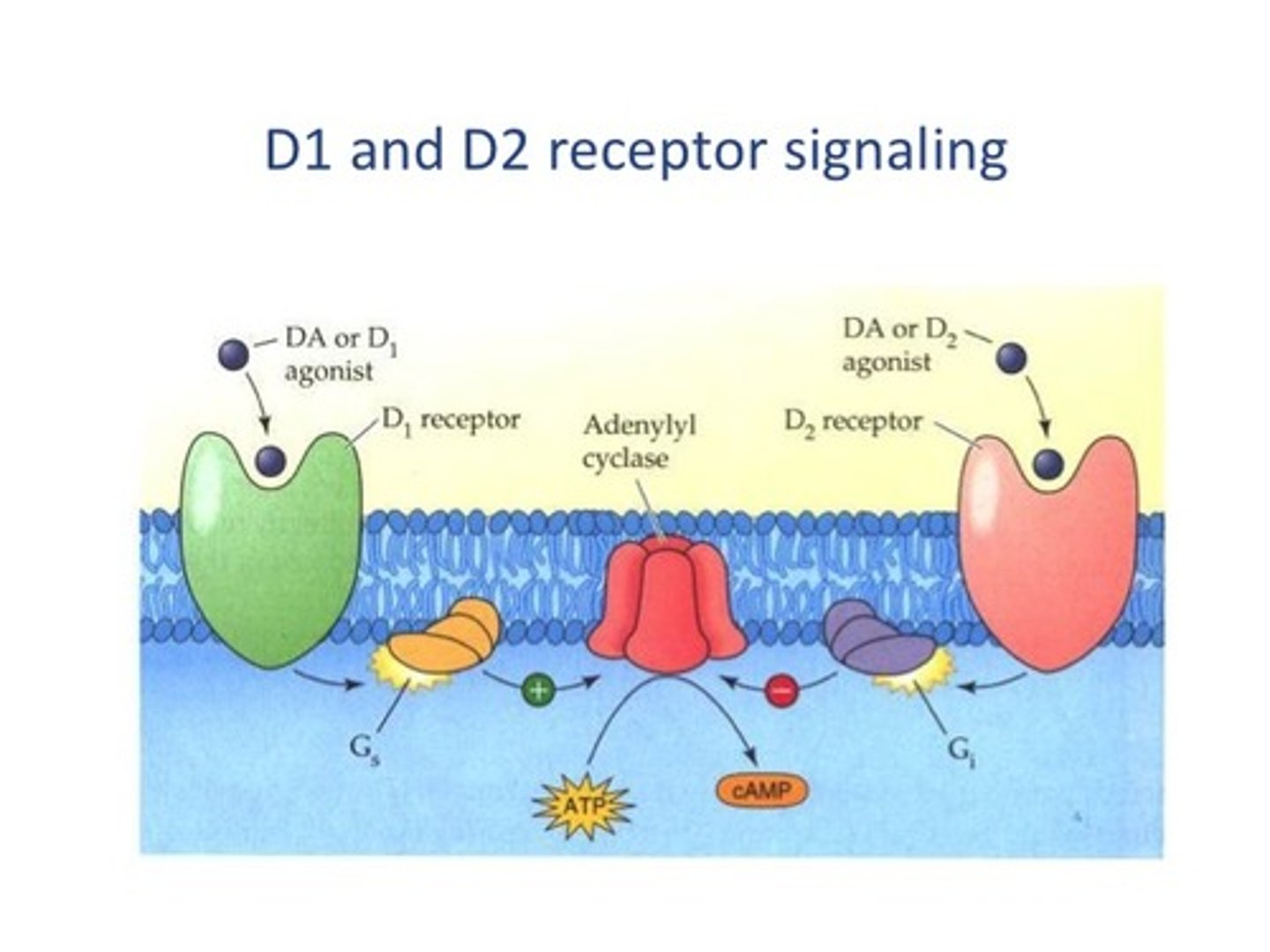
D1 & D5 (G...... coupled)
Gs coupled
also know as "D1 like"
D2, D3, D4 receptors
separate family --> Gi/o coupled
Also know as "D2 like"
dopaminergic system: D1 & D2 signalling
alpha1 receptors (four main areas)
1. Blood vessels: vasoconstriction, increased BP, increased contractibility of the heart
2. eye: Mydriasis (dilation)
3. bladder: relaxation
4. prostate: contraction
alpha2 receptors (two main areas)
1. blood vessels: decreased blood pressure
2. smooth muscles (GI tract): decreased GI tone and motility
beta1 receptors (2 main areas)
1. heart: increased heart contraction and increased heart rate
2. kidney: increased renin secretion, increased angiotensin, and increased blood pressure
beta2 receptors (4 main areas)
1. smooth muscle (GI tract): decreased GI tone and motility
2. Lungs: bronchodilation
3. uterus: relaxation of uterine smooth muscle
4. Liver: activation of glycogenolysis, and increased blood sugar
Alpha1 Adrenergic Blockers
opposite functions of sympathetic nervous system --> decreased smooth muscle contraction and blood vessel dilatation
treats hypertension and benign prostatic hyperplasia
Beta1
main subtype of the heart
propranolol: what does it block? What does it do?
blocks β-receptors in the heart, reducing contractile force
makes anxiety FEEL less overwhelming
How do you make serotonin
Tryptophan —> TH —> 5-HTP —> AADC —> 5HT—> serotonin
What will given Tryptophan do?
increase production of 5HT
Serotonin Cycle:
5-HT released by vesicles —> 5HT transporter (SERT) takes it back into serotonergic neuron —> Transported into vesicles by VMAT2—> Metabolized by MAO to 5-HIAA
What is the target for SSRIs
SERT
What does reserpine do as a VMAT2 blocker
Depletes 5-HT —> is then broken down when not protected in vesicles
Which MAO is located in neurons vs gilal cells?
MAO-A is located in neurons, MAO-B is located in gilal cells.
Serotonin receptors and appetite (reduced food intake)
5-HT1B or 5-HT2C receptor agonists, and 5-HT6 antagonists produce
hypophagia (reduced food intake)
Serotonin receptors and appetite (increased food intake)
5-HT1A agonists can lead to hyperphagia (increased food intake).
Where are 5-HT3 receptors located?
On the peripheral terminals of the vagus nerve
Chemo and 5-HT3 receptors
induces vomiting
antagonists can be used to treat the nausea
Pathological Aggression
Prevalent in men —> comorbidity with a lot of things such as substance abuse, depression, and anxiety disorders.
Pathological aggression: threat perception and risk assessments
alteration can affect aggression —> reactive aggression associated with poor recognition of facial cues
Pathological aggression: circuit
amygdala —> orbito frontal and orbital prefrontal cortex (OPF cortex)
Lesion of the OPF cortex……
massive agression
Arsenic toxicity: target organs
Blood, Kidneys, CNS, digestive, and keratinized tissues
Arsenic has a high affinity for a…..
sulfhydryl chemical group (thiol)
Amino acids that contain sulfur:
cysteine and methionine
Where are skin affects of arsenic seen at
hands and feet
Arsenic poisoning: impedes….. and may also alter……
DNA repair system & DNA methylation (alters gene expression)
Brain barrier to prevent metal insults from blood beyond the BBB
choroid plexus (CP)
True or false: Cadmium can cross BBB
true
cd concentration in blood is about —— times higher than found in the brain cortex
2.5x
the CP contains abundant WHAT binding ligands
metal
BBB and CP structures in young Individuals…. does it make it easier or harder for Cd to reach the brain
NOT FULLY DEVELOPED & EASIER —> DEVELOPMENTAL TOXIN
Itai Itai disease
Chronic Cd poisoning that happened in japan
1912-1942
‘it hurts it hurts’ disease
Cd orginated from downstream of major mining site
Link to Cd was not id’ed until 1968
softening of the bone as Cd substitutes Ca
Dimercaprol: what is it?
BAL
drug of choice fr treatment of gold, lead, arsenic, copper, and mercury toxicity
used as an antidote to the chemical weapon Lewisite
How is Dimercaprol administered
Deep IM injection
Dimercaprol: What does it do?
- Extracellular and intracellular cation scavenged
• Enhances fecal and urinary elimination
• Diffuses into brain and RBC's
IS TOXIC ITSELF WITH A NARROW THERAPEUTIC RANGE
What else is Dimercaprol useful for?
Apparently also useful for some snake-bites
• Zinc-dependent metalloproteinases in viper venom
• Chelates the zinc
EDTA
second line of treatment for lead toxicity
more effective when given early in acute poisoning
CHELATES ONLY EXTRACELLULAR LEAD
may also induce CNS toxicity if BAL therapy not initiated first
EDTA —> when does therapy start? How is it administered?
4 hrs after BAL is given
Only given via IV by continuous infusion