Neuroanatomy
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/116
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:58 PM on 11/15/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
117 Terms
1
New cards
What were Golgi and Cajals most important findings via silver staining?
- Golgi -> Neurons are all connected in a big network, like a spider web. This the reticular theory
- Cajal -> There are small gaps between neurons that now call synapses (Neuronal doctrine)
- Cajal -> There are small gaps between neurons that now call synapses (Neuronal doctrine)
2
New cards
What are the CNS and PNS responsible for?
CNS - Brain and S.cord
PNS - Spinal and cranial nerves
They communicate with each other to elaborate incoming information via senses (eg) and respond to it via motor
PNS - Spinal and cranial nerves
They communicate with each other to elaborate incoming information via senses (eg) and respond to it via motor
3
New cards
What are the 4 main cell types in the brain visible with a microscope?
Neurons, ODCs (myelin prod), Astrocytes (for support), Microglia (immune cells of the brain)
4
New cards
What are the folds in the skull where the brain sits called?
Fossae
5
New cards
What are the holes in the skull used as passages for cranial nerves and vessels?
Foramina
6
New cards
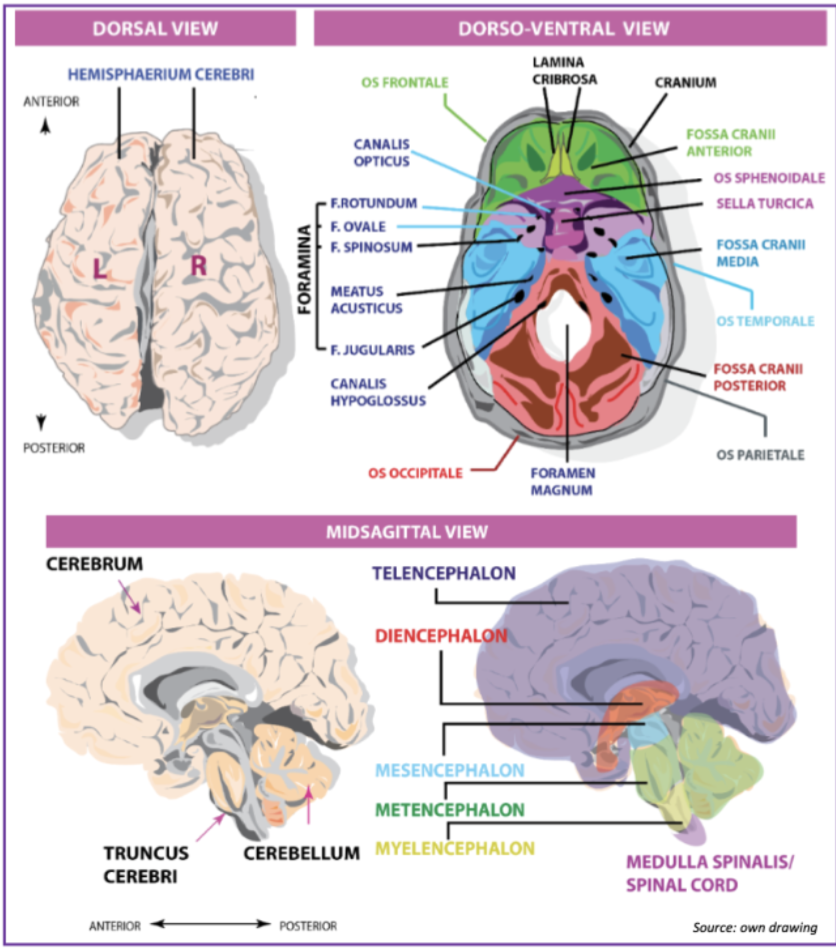
What are the three main fossa and what is their function (visible from a dorso-ventral view)?
1. Anterior - holds part of the frontal lobe
2. Medial - holds parts of the temporal lobes
3. Occipital - holds the occipital lobe and cerebellum
2. Medial - holds parts of the temporal lobes
3. Occipital - holds the occipital lobe and cerebellum
7
New cards
What is the function of the sell turcica? and where does it connect to the frontal/anterior fossa?
- Present in the centre of the brain (coronal)
- Holds the optic chiasm, mammaliary bodies, part of the diencephalon
- The Sphenoid is where the connection is
- Holds the optic chiasm, mammaliary bodies, part of the diencephalon
- The Sphenoid is where the connection is
8
New cards
What foramen allows the passage of the trigeminal nerve?
The foramen ovale and spinosum
9
New cards
What foramina allow passage of olfactory nerve and spinal cord respectively?
- O.nerve via Lamina Cribrosa
- S. cord and occipital fossa via foramen magnum
- S. cord and occipital fossa via foramen magnum
10
New cards
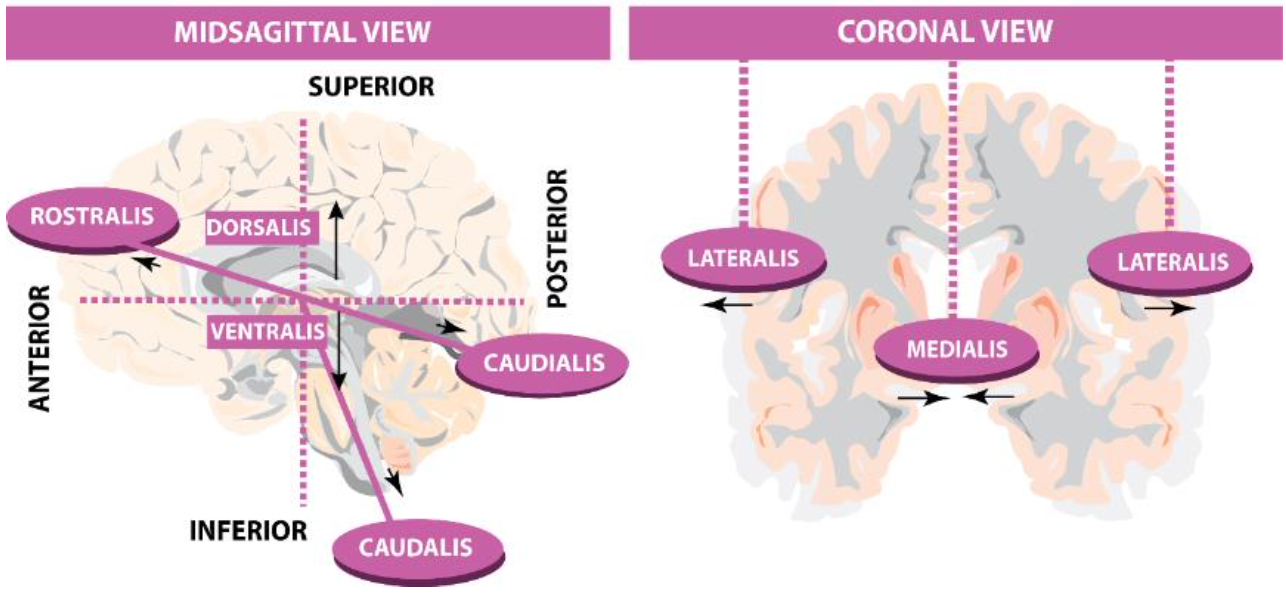
What are the three most commonly used axes in neuroanatomy?
- Coronal (most common)
- Saggital
- Horizontal
- Saggital
- Horizontal
11
New cards
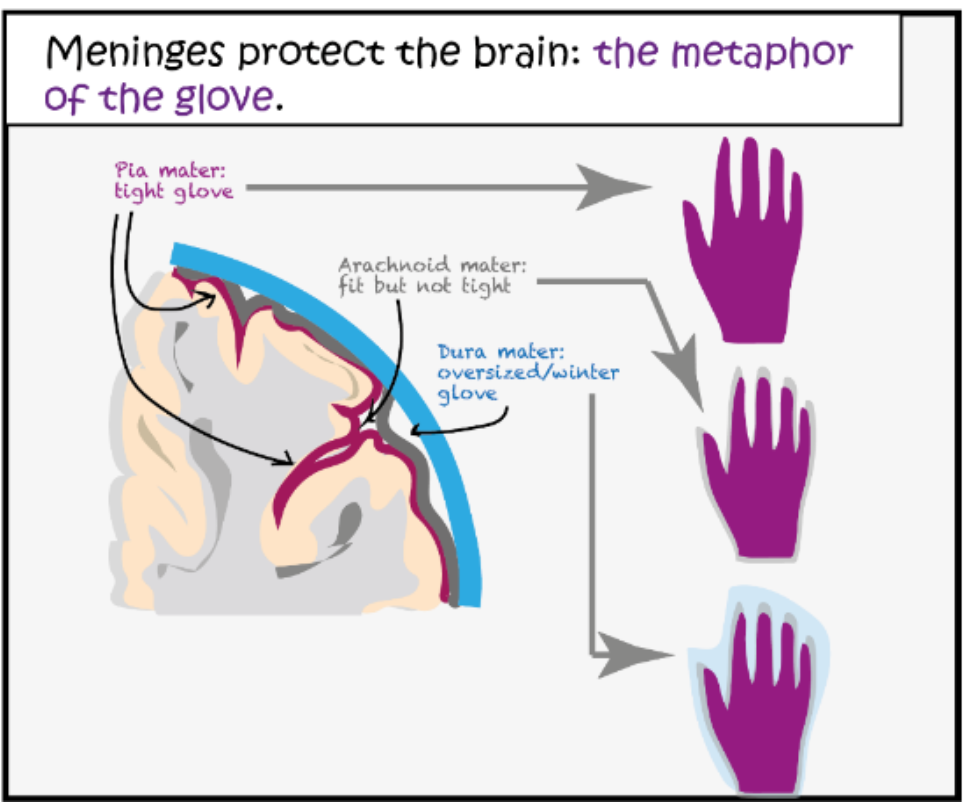
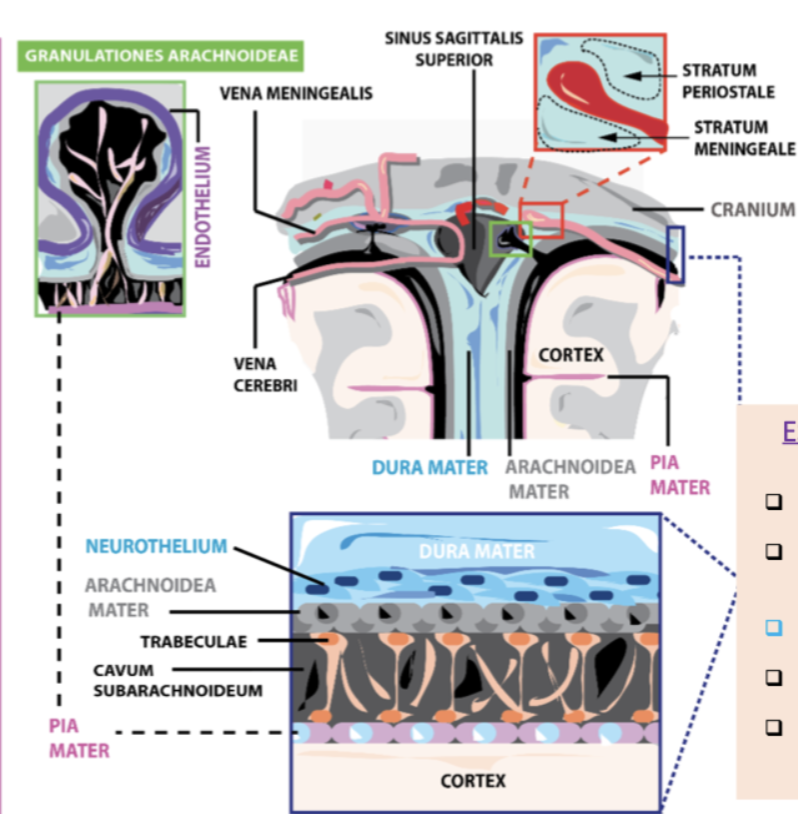
What are the 3 layers in which the meninges are organised for protection of the brain? What metaphor is used to describe this?
Dura - Arachnoid - Pia matter (from out to in)
Metaphor - 3 gloves on each other
Pia is tight on the brain, Arachnoid is fit but not tight, Dura is oversized and doesn't go in as much as the other two
Metaphor - 3 gloves on each other
Pia is tight on the brain, Arachnoid is fit but not tight, Dura is oversized and doesn't go in as much as the other two
12
New cards
The dura mater in the encephalon is divided into what 2 layers?
osteal (closer to skull) and meningeal (closer to brain) layers
13
New cards
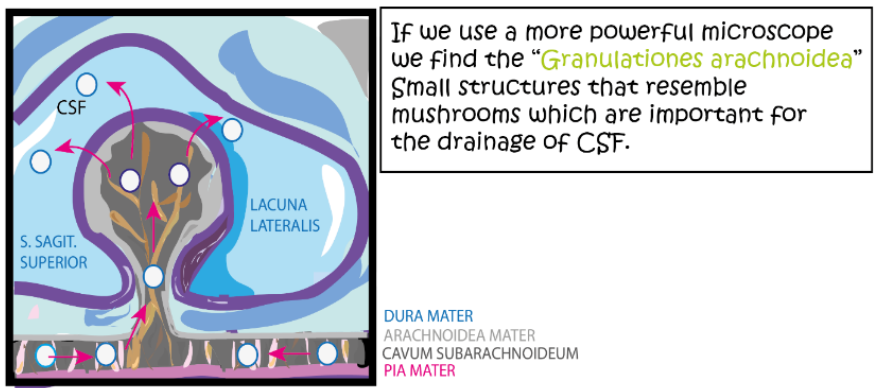
What is the space between the arachnoid and the Pia called? What is its function?
The subarachnoid space, along with arachnoid, it makes granulations that drain the CSF to the sinuses/ventricles of the brain
14
New cards
What arteries supply the brain with O2?
- Common carotid
- Vertebral artery
- Vertebral artery
15
New cards
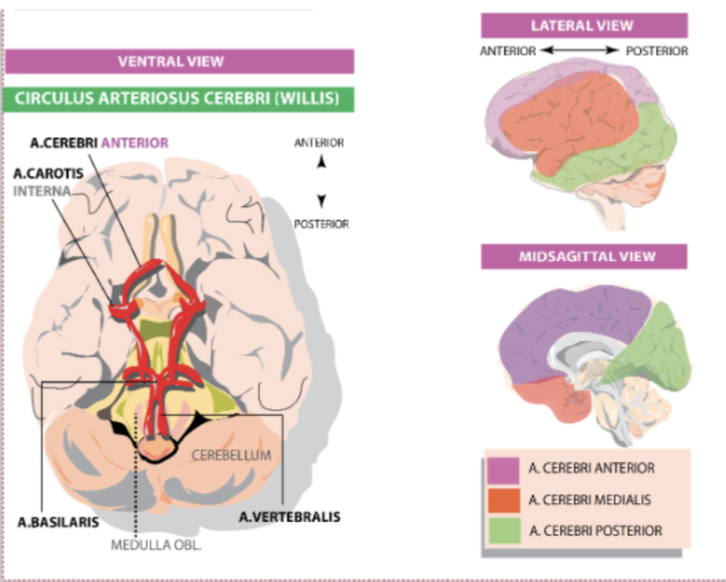
Where does the basilar artery come from? It joins with the carotid to form what structure?
Two vertebral arteries converge into the basilar artery which then converges with the carotid into the Circle of Willis.
16
New cards
What is an example of Redundancy in the brain?
The circle of willis, it prevents lack of blood in case of damage to one of the cranial arteries by doubling their circulation (redundant)
17
New cards
What 3 arteries branch out from the COW? And what parts of the brain do they supply?
Anterior (medial part of brain) - Middle (lateral part) - Posterior cerebral (occipital)
18
New cards
Where is the CSF produced and what does it provide the brain?
- Its made in an invagination of the Pia called the Choroid Plexus
- The fluid is full of sodium, Ca, Mg, Glucose
- The fluid is full of sodium, Ca, Mg, Glucose
19
New cards
There are 4 ventricles in the brain, how are they organised?
2 lateral ventricles, one per hemisphere
3rd ventricles connects the 2 ventricles
4th at the level of the cerebellum/pons
3rd ventricles connects the 2 ventricles
4th at the level of the cerebellum/pons
20
New cards
What structure is between the lateral and the 3rd ventricles? Function?
Foramen of Monro, allows communication between them.
21
New cards
The cerebral aqueduct is present between the 3rd and 4th ventricle, what is its function?
Its a connecting tube that spreads CSF throughout the brain and spinal cord
22
New cards
What tube follows the S.cord along to supply it with CSF?
Central Canal
23
New cards
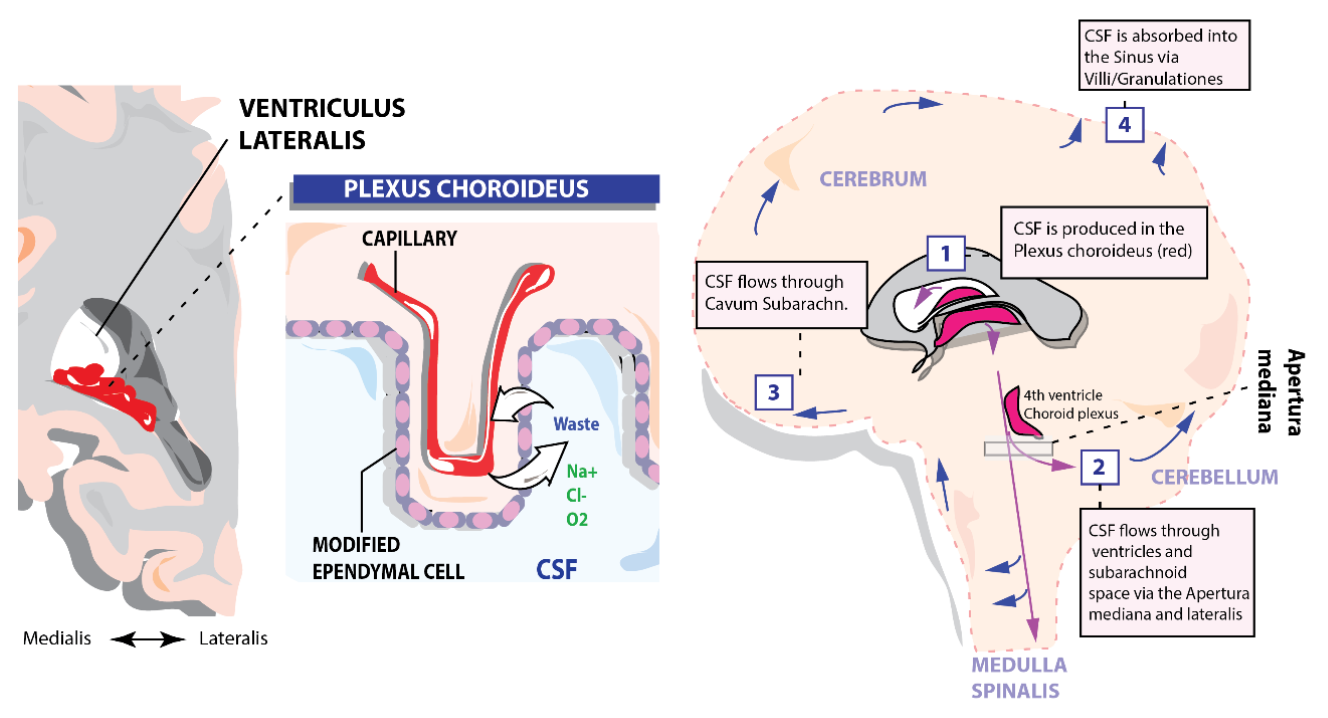
What is the pathway. of CSF supply?
24
New cards
What is the buoyancy principle?
The CSF feeds the brain cells and protects It from the bouncy principle by reducing its mass by about 90%
25
New cards
What happens to the CSF after its been used in the brain?
It gathered in the subarachnoid space and sent to the sinuses via granulations.
26
New cards
What is the role of sinuses in the brain and what are they made of?
They are located in specific parts of the brain and they convey CSF AND Blood from venous capillaries to drain it outside the NS. Their walls are made of dura mater
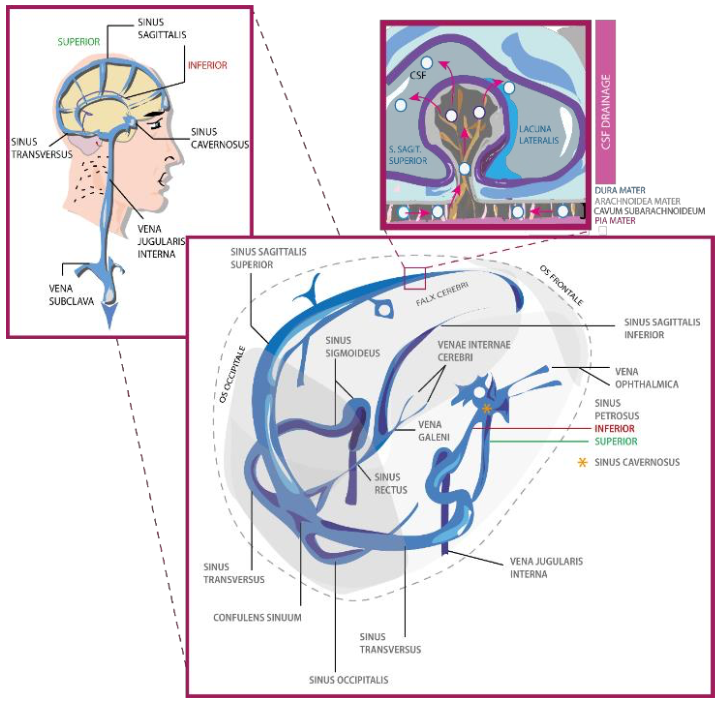
27
New cards
No drainage of CSF will cause...?
Hydrocephalus
28
New cards
What are the main sinuses ?
Superior and Inferior Sagittal, Transverse, Sigmoidal
29
New cards
After the CSF is sent to the sigmoidal sinus, what vein does it use to leave the CNS?
Jugular
30
New cards
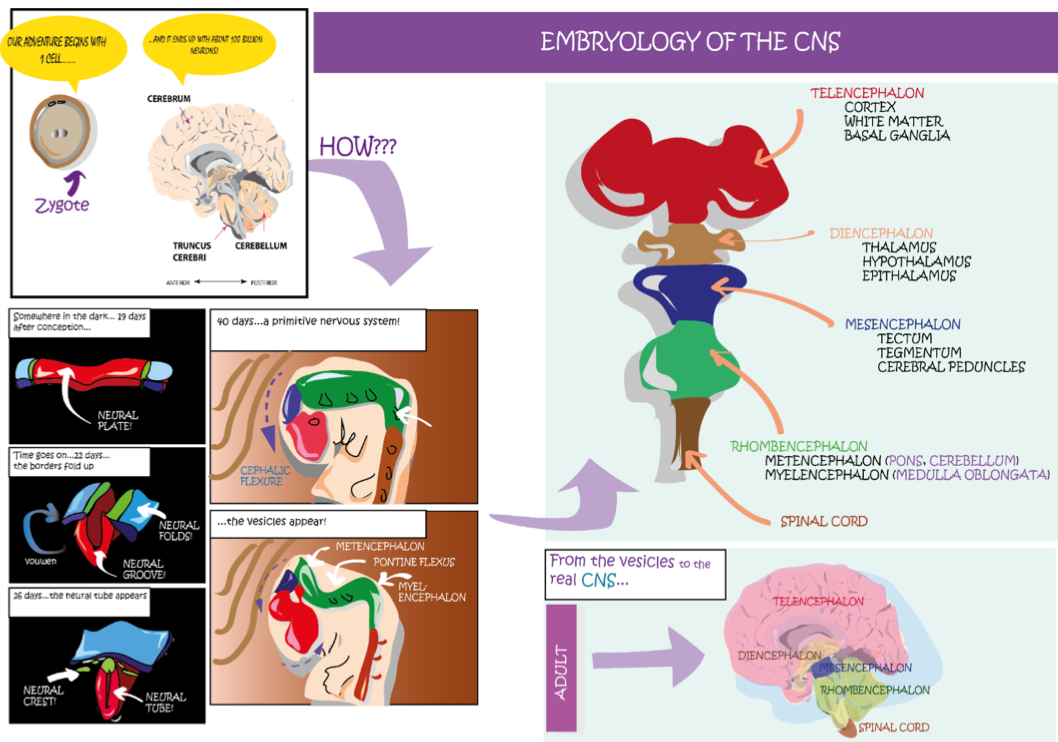
Embryology of the brain in 5 main steps
1. Day 19, Neural plate --> Neural groove on day 22 (hole is rudimental central canal from which ventricles will arise)
2. Day 40, Flexure of frontal part
3. Flexure of pontine structures
4. Finally, the main vesicles appear from these modifications to form a proper NS
5. Telencephalon, Diencephalon, Mesencephalon, Rhombencephalon (which separates into the Metencephalon and Myencephalon)
2. Day 40, Flexure of frontal part
3. Flexure of pontine structures
4. Finally, the main vesicles appear from these modifications to form a proper NS
5. Telencephalon, Diencephalon, Mesencephalon, Rhombencephalon (which separates into the Metencephalon and Myencephalon)
31
New cards
What structures can be found in the telencephalon?
- Cortex
- White matter
- Basal Ganglia
- White matter
- Basal Ganglia
32
New cards
What part of the brain can the thalamus and hypothalamus be found in?
Diencephalon (also the epithalamus)
33
New cards
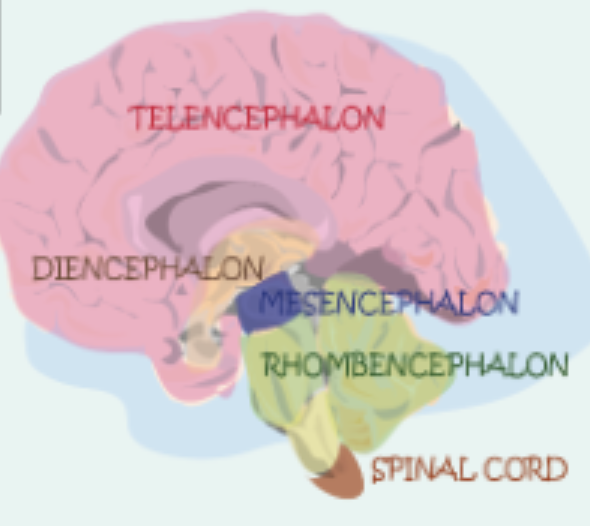
The pons, cerebellum and medulla oblongata are found where?
Metencephalon (p,c) and Myencephalon (M.O)
34
New cards
What is the most developed structure in the brain and why?
The telencephalon, because it hosts the neocortex which plays are role in (most) complex brain function like cognitive ability
35
New cards
How is the cortical surface of the brain minimised to fit in the skull?
The neocortex is full of circumvolutions, visible in the telencephalon as "lobes"
36
New cards
What are the visible lobes of the brain ? Name all 4
Frontal - Parietal - Temporal - Occipital
37
New cards
What are the 2 less visible/more internal lobes in the brain?
Insular - Limbic
38
New cards
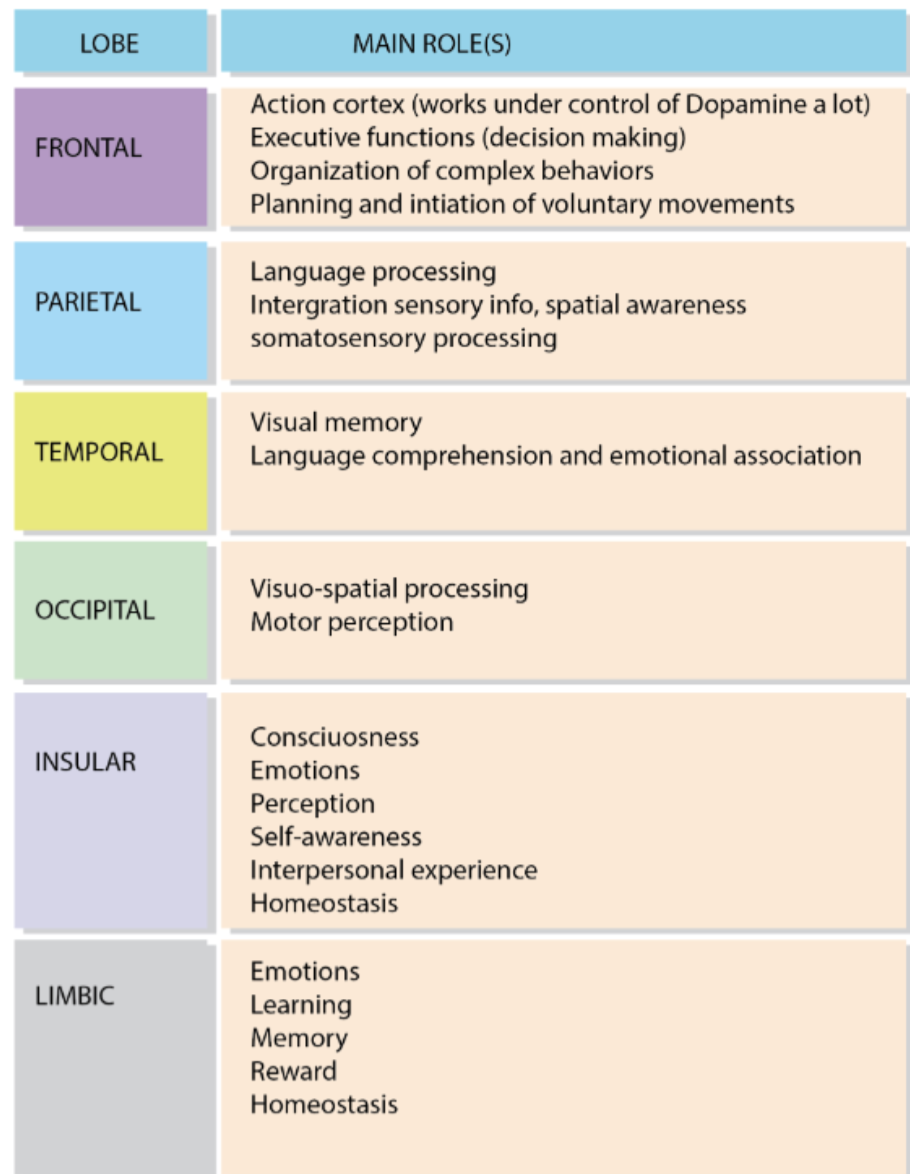
What are the main functions of the 6 lobes in the brain?
39
New cards
What are the two structures responsible for production of speech and language comprehension respectively ?
Broca (in the GFI) & Area of Wernicke (in the GTS)
40
New cards
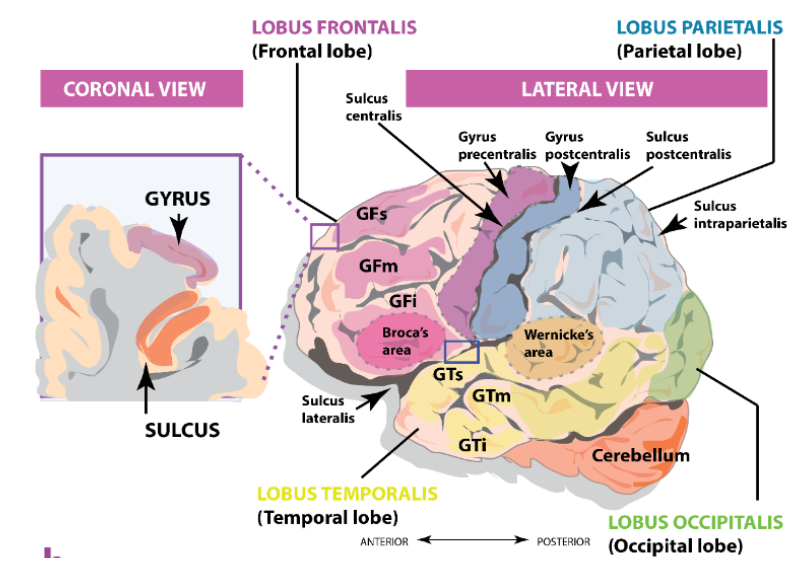
The frontal and temporal lobes are further subdivided into...
Superior, medial and inferior gyrus
41
New cards
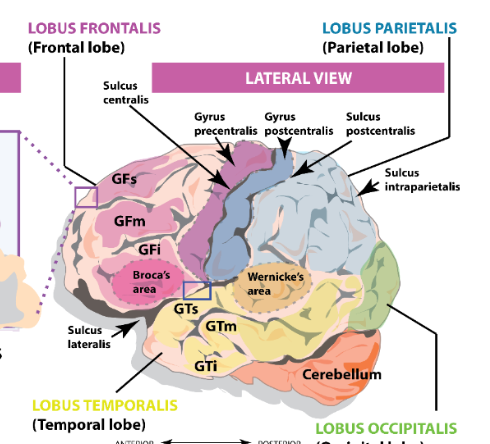
Where does the M1 and S1 reside?
in the pre and post central sulcus of the frontal and parietal lobes. Purple and blue in the figure
42
New cards
What sulcus divides between the frontal and the parietal lobe ?
Central sulcus
43
New cards
What divides the frontal and parietal lobes from the temporal lobe?
Lateral Sulcus
44
New cards
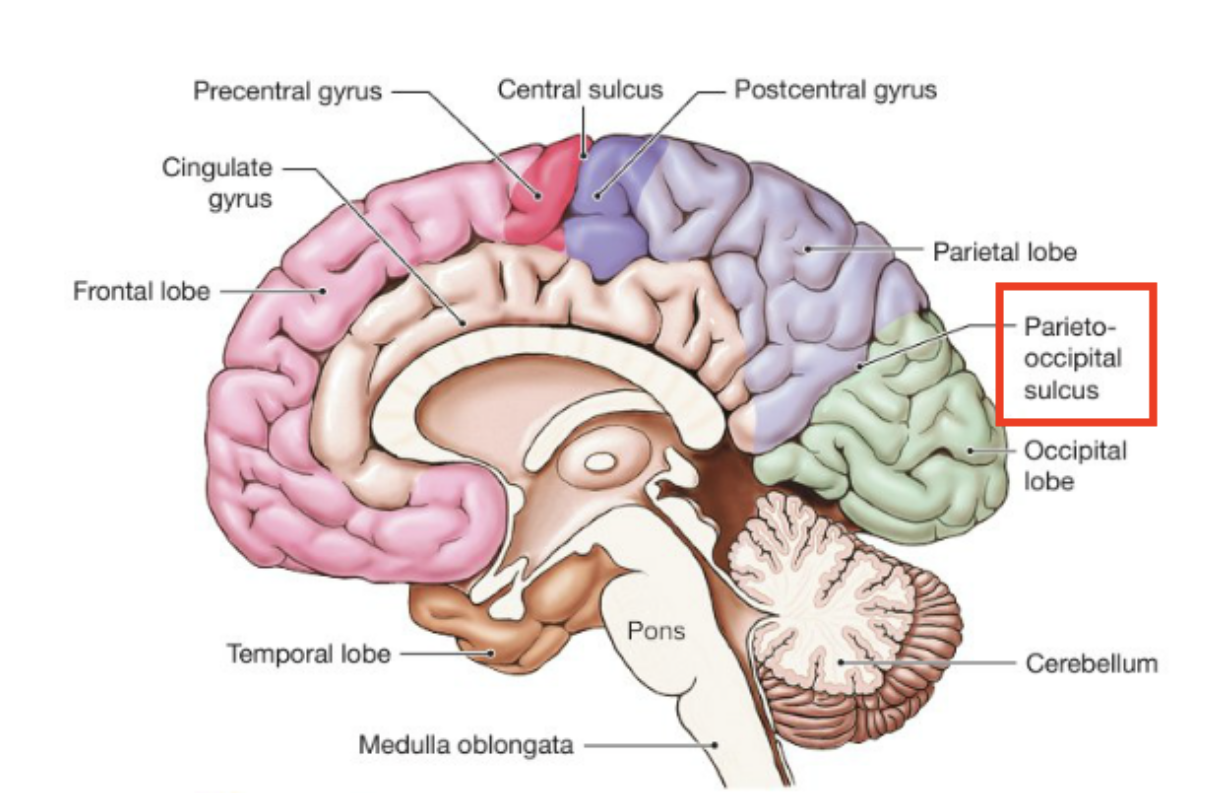
What structure is only visible via midsagittal plane ?
Parietoccipital sulcus, borders between the parietal and occipital lobe
45
New cards
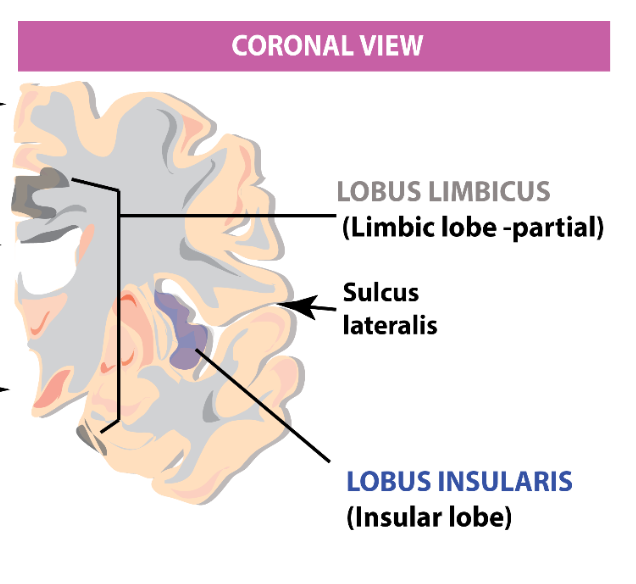
The insular lobe is visible when what lobes are separated?
Frontal and temporal
46
New cards
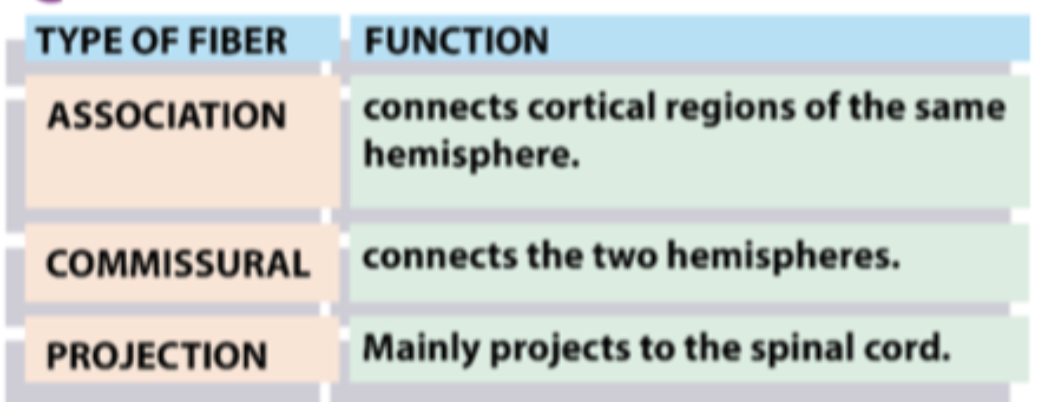
What are the three types of white matter fibers?
Association
Commissural
Projection
Commissural
Projection
47
New cards
The fibers of WM mainly function to...
allow communication between
Brain regions
Brain and S.cord
Brain regions
Brain and S.cord
48
New cards
What do association fibers connect?
Different cortical regions with each other on the same hemisphere
49
New cards
What fibers of WM connect the cortex to s.cord?
Commissural
50
New cards
Give an example of an association and a commissural fiber?
- Sup/Inf longitudinal fascilicus
- Corpus callosum
- Corpus callosum
51
New cards
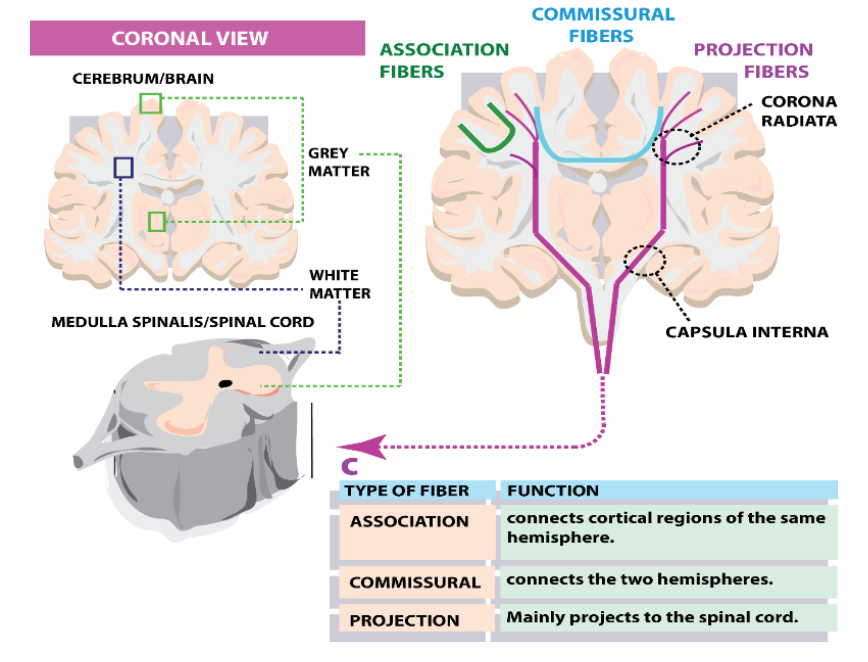
Projection fibers function and pathway
Made by fibers leaving the cortex, and converging into the corona radiata. They reach the pyramid in the myencephalon via the internal capsula to then reach the s.cord and relay motor info to muscles
52
New cards
what is a component of grey matter NOT present in WM?
Neuronal cell bodies
53
New cards
What is the main function of subcortical structures in the telencephalon ?
They support the function of the cortex
54
New cards
Give an example of a subcortical structure
Basal Ganglia
- Globus Plallidum
- Dorsal striatum
- Non-telencephalic substantia nigra
- Globus Plallidum
- Dorsal striatum
- Non-telencephalic substantia nigra
55
New cards
What structures make up the diencephalon?
Thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus
56
New cards
How are the thalamus and epithalamus connected?
via inter-thalamic adhesion at the level of the 3rd ventricle
57
New cards
What is the function of the thalamus?
Picking up incoming sensorial info (except olfactory) and dispatching it to parts of the cortex
58
New cards
What structures of the thalamus does transduction of visual stimuli entail?
- Pulvinar (back of the thalamus)
- Lateral Geniculate nucleus
- Lateral Geniculate nucleus
59
New cards
What structure of the thalamus does transduction of auditory stimuli entail?
- Medial Geniculate nucleus (projects to auditory cortex)
60
New cards
What are the three main structures of the mesencephalon and what are their main functions?
- A portion of the cerebral peduncles --> passage of WM to s.cord (and back)
- S. nigra --> involved in dopaminergic control of the basal ganglia and planning/initiation of motor functions
- Periaqueductal gray (PAG) -> GM encompassing the cerebral aqueduct involved in processing pain
- S. nigra --> involved in dopaminergic control of the basal ganglia and planning/initiation of motor functions
- Periaqueductal gray (PAG) -> GM encompassing the cerebral aqueduct involved in processing pain
61
New cards
Raphe is an important WM structure in the myencephalon, why?
Serotonin transmission, affected by hallucinogens
62
New cards
From what structure does the pyramid arise from and why is it important?
From the myencenphalon, its a critical WM region that connects the motor cortex with the s.cord, and the scored with the thalamus for somatosensory control of incoming info
63
New cards
What two important structures arise from the metencephalon?
Pons, Cerebellum
64
New cards
Describe the pons functionality with its structure
its a rhomboid structure where the majority of cranial nerve nuclei are, these innervate the head and the neck
65
New cards
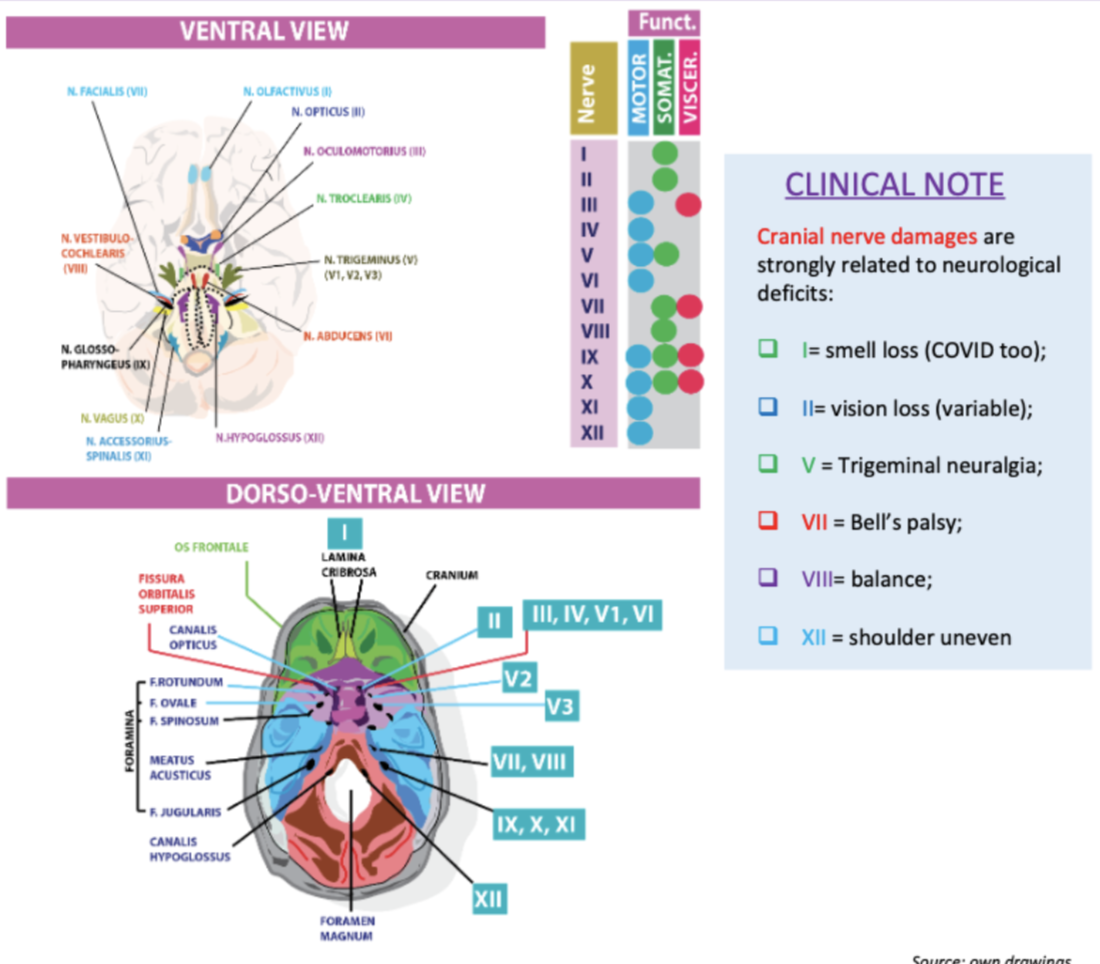
What functions do the nerves 1,2,4 and 6 have?
?
66
New cards
The S.cord is mostly made of GM and WM, what are it's primary functions?
- The GM part contains somatosensory neurons and ventral horn motor neurons
- It receives incoming somatosensory info from somatic branch of spinal nerves
- It responds with motor info to the motor components of the nerves -> muscles
- It insists on keeping these two pathways separate
- It receives incoming somatosensory info from somatic branch of spinal nerves
- It responds with motor info to the motor components of the nerves -> muscles
- It insists on keeping these two pathways separate
67
New cards
How do reflexes happen?
By virtue of interneurons present between the dorsal and ventral horns, motor responses are automatically produced after specific somatosensory stimulations
68
New cards
Voluntary movement is mainly governed by which 2 tracts? What are their main functions?
Pyramidal - Extrapyramidal
Initiation of voluntary movement - Muscle tone, balance, posture..etc
Initiation of voluntary movement - Muscle tone, balance, posture..etc
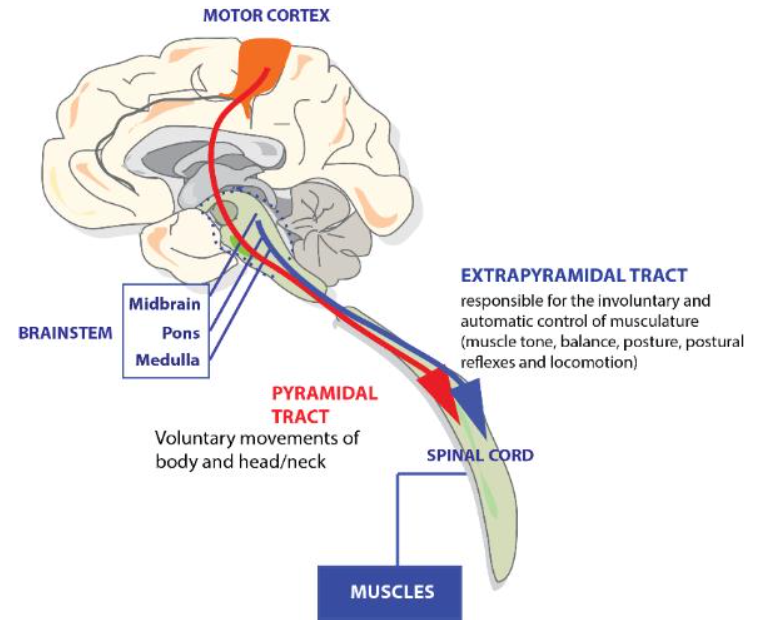
69
New cards
Where do the pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts originate from?
Pyramidal neurons in the motor cortex - brainstem
70
New cards
How does planning and initiating voluntary movement happen and what structure is mainly involved ?
Primary motor cortex (M1) - via a long bundle of axons directly connected to the s.cord.
71
New cards
What is the homunculus principle?
That some muscles need more cells to coordinate them (represented by the S1 > M1)
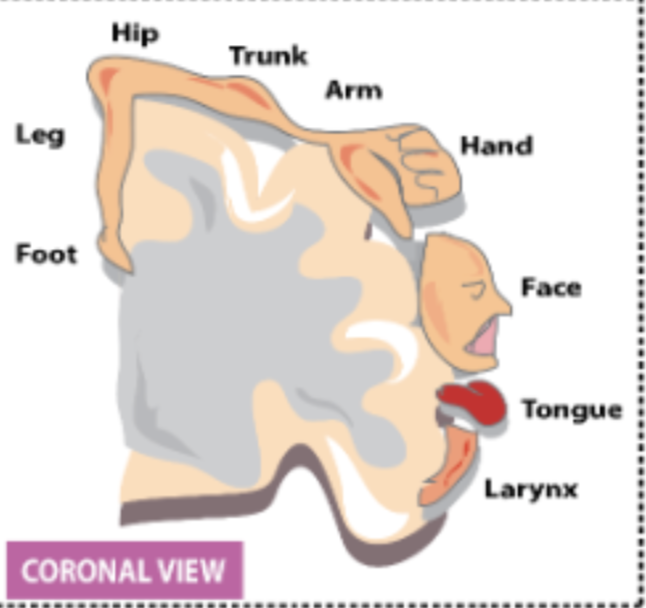
72
New cards
What important structure is found in the central gyrus and what is its function?
The primary somatosensory cortex (S1), involved in somatosensory elaboration of incoming info from the body.
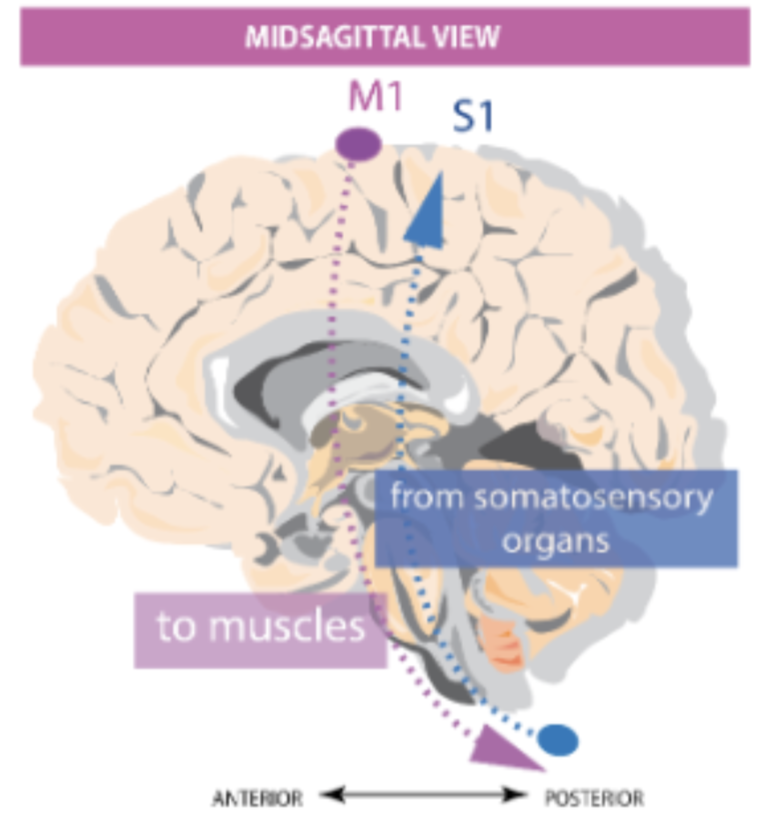
73
New cards
Directions of the descendent and ascendant pathways
D -> M1 to S.cord
A -> S.cord to S1
A -> S.cord to S1
74
New cards
What structures support M1 and S1 ? How?
Primary cortices - specific movement initiation and somatic elaboration
Association cortices
Premortor cortex to support M1
Secondary motor cortex (S2 for S1)
Association cortices
Premortor cortex to support M1
Secondary motor cortex (S2 for S1)
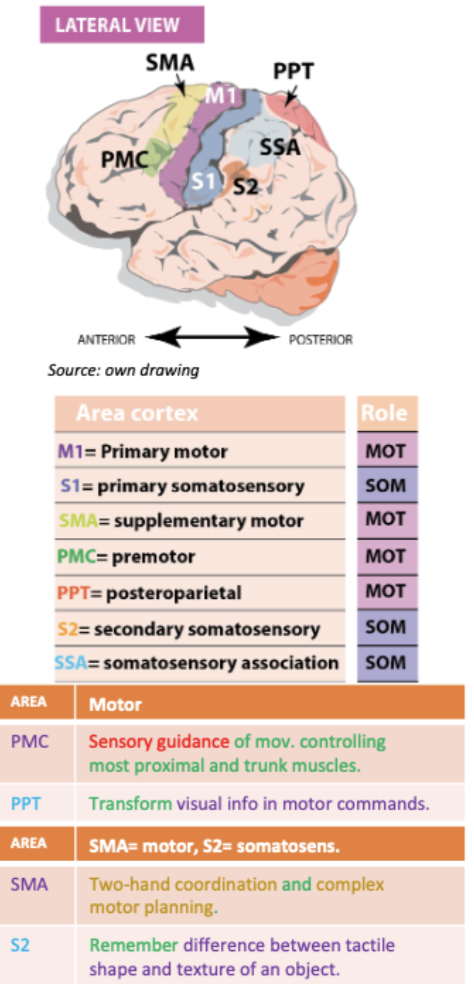
75
New cards
What is unique about the cortico-spinal tract that emerges from M1?
M1 axons from pyramidal neurons DONT STOP until they reach the s.cord associated with a specific part of the body - No extra synapses
76
New cards
Name the structures involved in the cortico-spinal tract in order of impulse direction
Corona radiata - Internal capsule - cerebral peduncles - Pyramid (in the myencephalon)
77
New cards
How can we explain the decussation of fibers after impulse reaches the pyramid?
Axons from left hemisphere target the right side of the s.cord and vice versa. We don't know why
78
New cards
Which cortico-spinal tract interacts with distal vs proximal muscles?
90% of descending fibers cross-over at lateral cortico-spinal tract -> distal
the rest at ventral cortico-spinal tract --> proximal
the rest at ventral cortico-spinal tract --> proximal
79
New cards
What is responsible for the movement of the head and neck?
Corticobulbar tract, from M1 to pons and mes (many nuclei for cranial nerves)
80
New cards
What are gnostic and vital stimuli responsible for respectively?
Fine touch and proprioception
Temperature and pain processing
Temperature and pain processing
81
New cards
How is the gnostic stimuli organised?
via the dorsal column-medial lemniscus pathway that originates in the s.cord and travels down to the thalamus
82
New cards
What happens when the s.cord senses fine touch via s.nerves? 2 steps
1. it sends this info ipsilateral to the pyramid, where there are synapses in 2 structures: fasciculus cuneatus & gracialis + decussate (structure in contralateral thalamus).
2. Then from the thalamus 3rd order neurons send info to S1 and pals
2. Then from the thalamus 3rd order neurons send info to S1 and pals
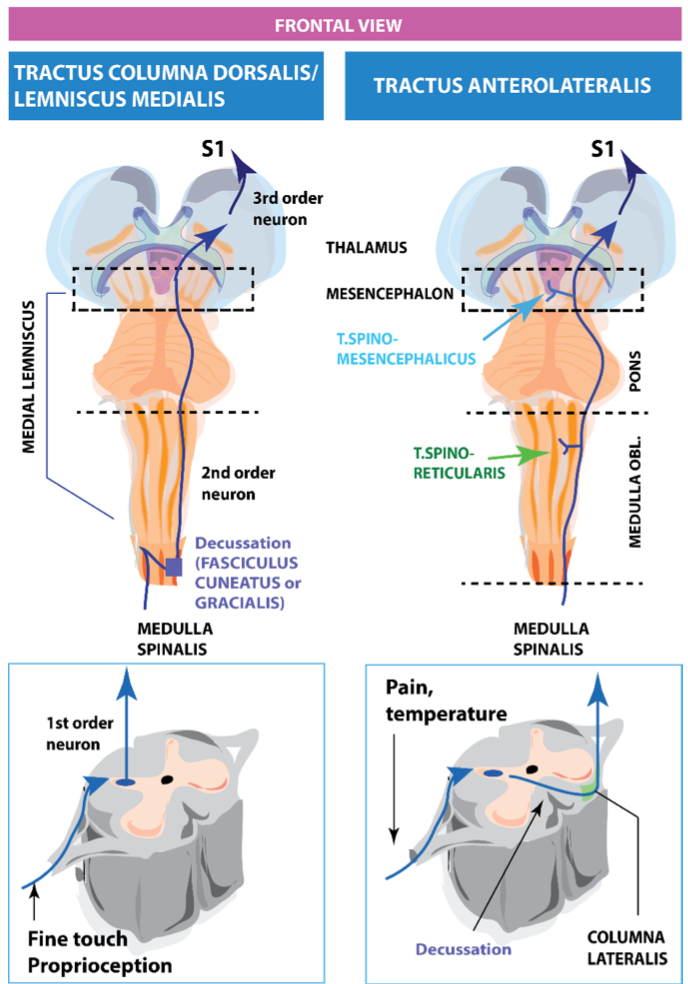
83
New cards
Pain and temp are processed using what pathway?
Anterolateral
84
New cards
Order of anterolateral pathway from s.cord
s.cord - pyramid - thalamus - S1
85
New cards
What are the 2 routes that the anterolateral pathway can branch into ?
1. Route forming the spinoreticular (neuro-vegetative response to pain
2. Spinomesencephalic (goes to PAG)
2. Spinomesencephalic (goes to PAG)
86
New cards
What is the function of the basal ganglia relative to M1?
Advisors, support in modulating motor behaviour
87
New cards
What are the basal ganglia of the telencephalon called?
- Dorsal striatum (caudate and putamen)
- Globus pallidum
- Globus pallidum
88
New cards
The diencephalic basal ganglia are known as
Subthalamic nucleus
89
New cards
The basal ganglia are also spread throughout the mesencephalic, what are they called here?
Substantia nigra
90
New cards
What are the 5 main functions of the basal ganglia?
1. Initiation of movement
2. Mov Scaling
3. Mov Sequencing
4. Switching Mov
5. Selection/inhibition of competing motor prog
2. Mov Scaling
3. Mov Sequencing
4. Switching Mov
5. Selection/inhibition of competing motor prog
91
New cards
What 2 pathways does the GB rely on for fluidity of movement?
Direct - goes directly to thalamus, disinhibit M1
Indirect - stops at sub thalamic nucleus before thalamus to inhibit M1
Indirect - stops at sub thalamic nucleus before thalamus to inhibit M1
92
New cards
What structure decides on which pathway the BG should use? How does this work?
SN pars compacta, mesencephalic dopamine neurons that send projections to the putamen which express excitatory D1 receptors (stimulating the direct pathway while inhibiting the indirect pathway)
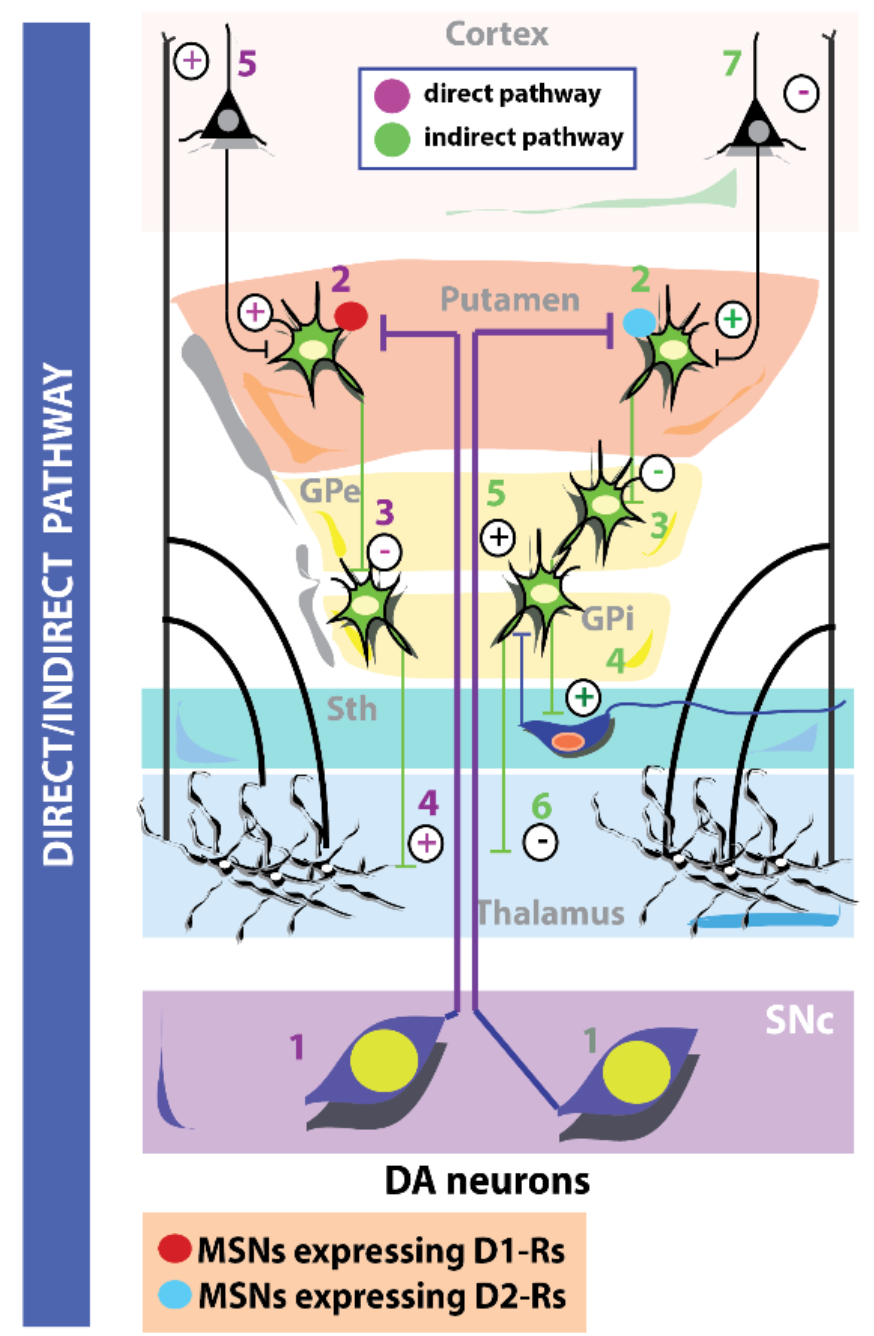
93
New cards
How is the indirect pathway inhibited?
Expression of D2 inhibitory receptors in putamen cells
94
New cards
What causes PD?
Destruction of DA neurones in the SN - Switch between pathways is not accurate. Direct pathway can't be activated and indirect pathway can't be inhibited due to under expression of D2 inhibitory receptors
95
New cards
The cerebellum is organised in three regions, what are they? and what are their main functions?
1. Archicerebellum (Balance/Cordination)
2. Paleocerebellum (Integration between sensory inputs and motor commands)
3. Cerebrocerebellum (cognitive functions eg speech, attention)
2. Paleocerebellum (Integration between sensory inputs and motor commands)
3. Cerebrocerebellum (cognitive functions eg speech, attention)
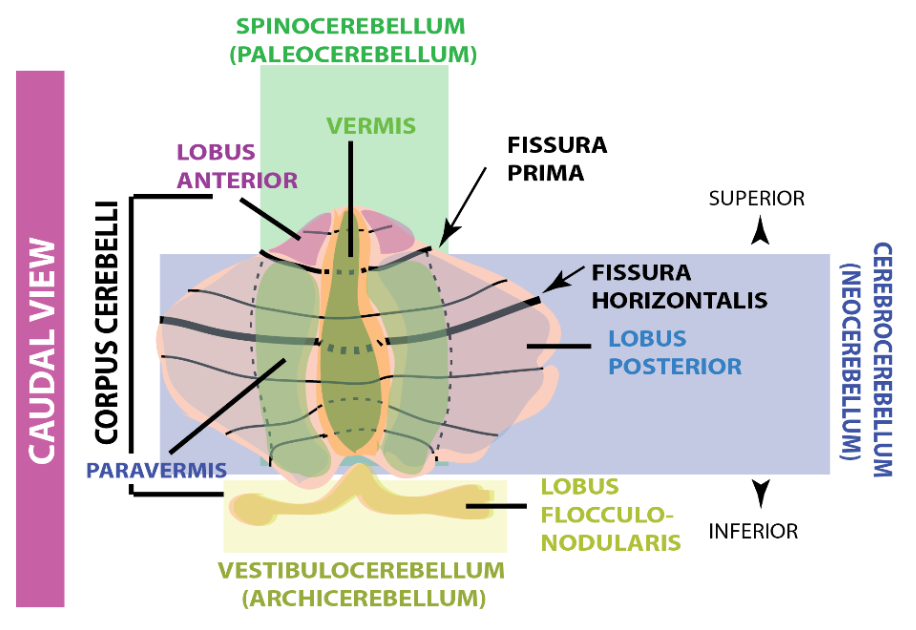
96
New cards
The ventral tegmental area is a supportive structure of which system? What is it orchestrated by?
Limbic, by dopa
97
New cards
What system is involved in reinforcing properties of natural stimuli as well as drugs of abuse?
Mesolimbic system
98
New cards
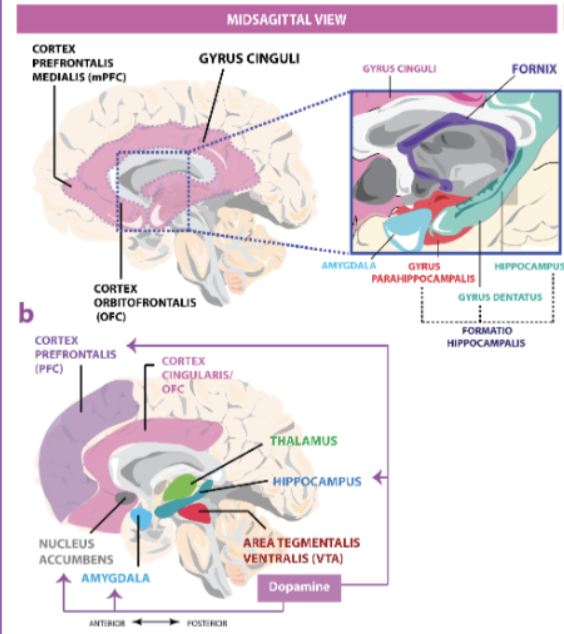
What kind of gyrus can we find in the limbic system?
Gyrus cinguli
99
New cards
What is the main function of the hippocampus?
long-term memory consolidation
100
New cards
The Ammon's horn (CA) is divided into 4 regions. What are the 6 important structures they entail?
From CA1 to CA4 we find the dentate gyrus + subiculum + pre and parasubiculum + entorhinal cortex (place cells for spatial navigation) + Parahippocampal gyrus = hippocampal formation