Year 9 Biology 2025
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
Ecology
The study of how living things interact with each other and their environment.
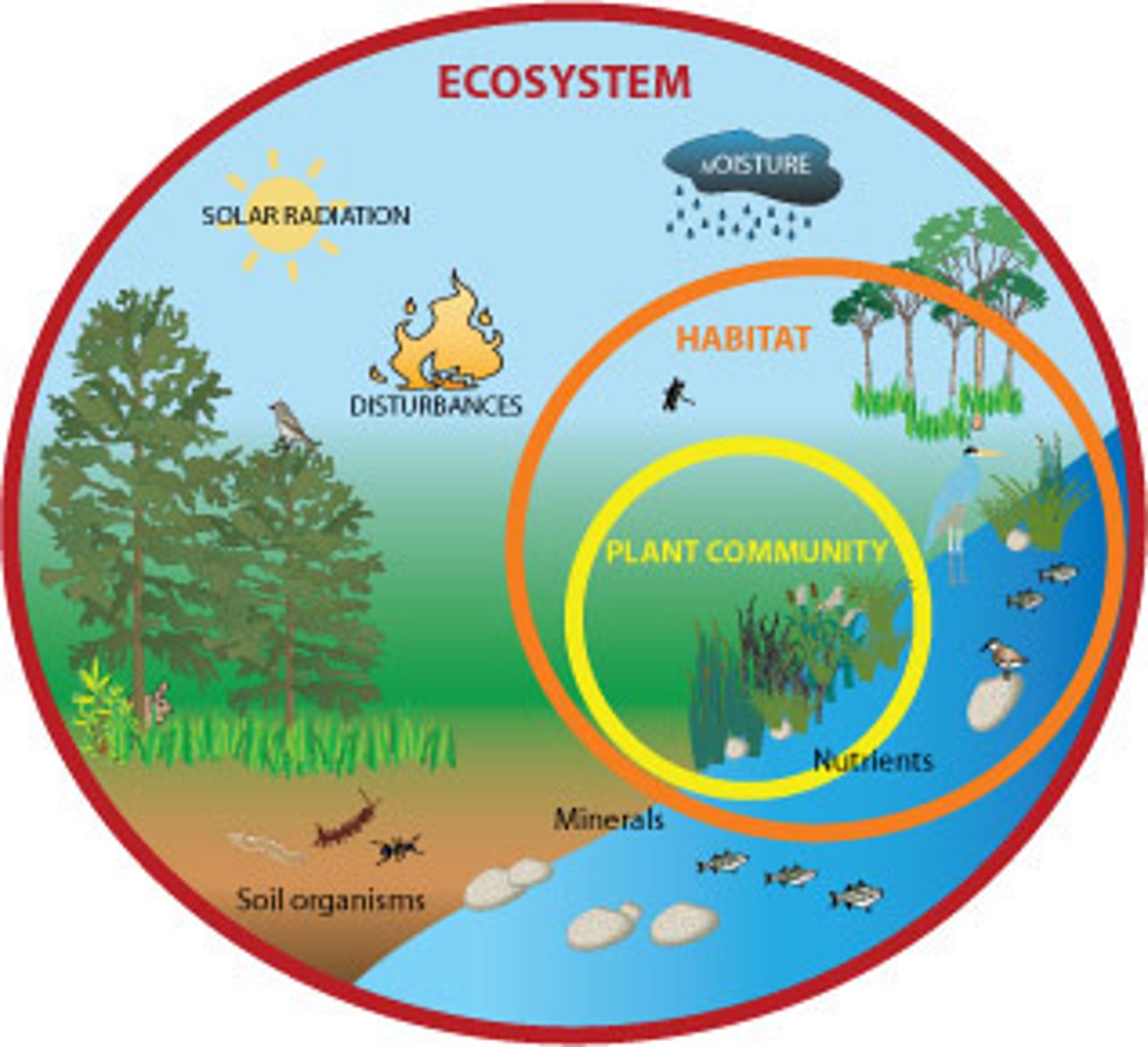
Ecosystem
A community of living things and their non-living surroundings working together.
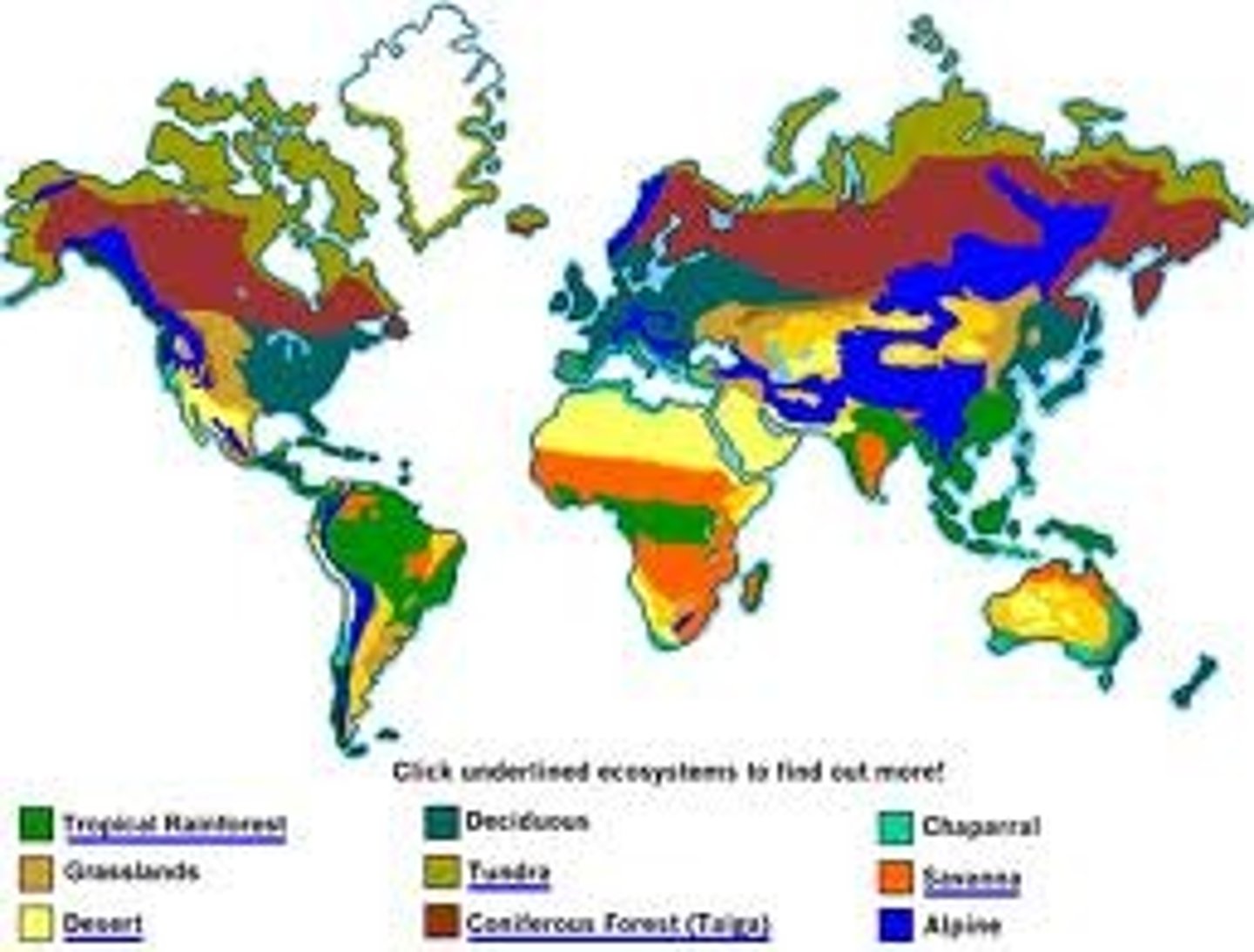
Biome
A large region with a specific climate and types of plants and animals (e.g., desert, rainforest).
Community
All the different species living together in one area.
Population
A group of individuals of the same species living in one place.
Habitat
The natural home or environment of an organism.
Competition
When organisms fight for the same resources like food, water, or space.
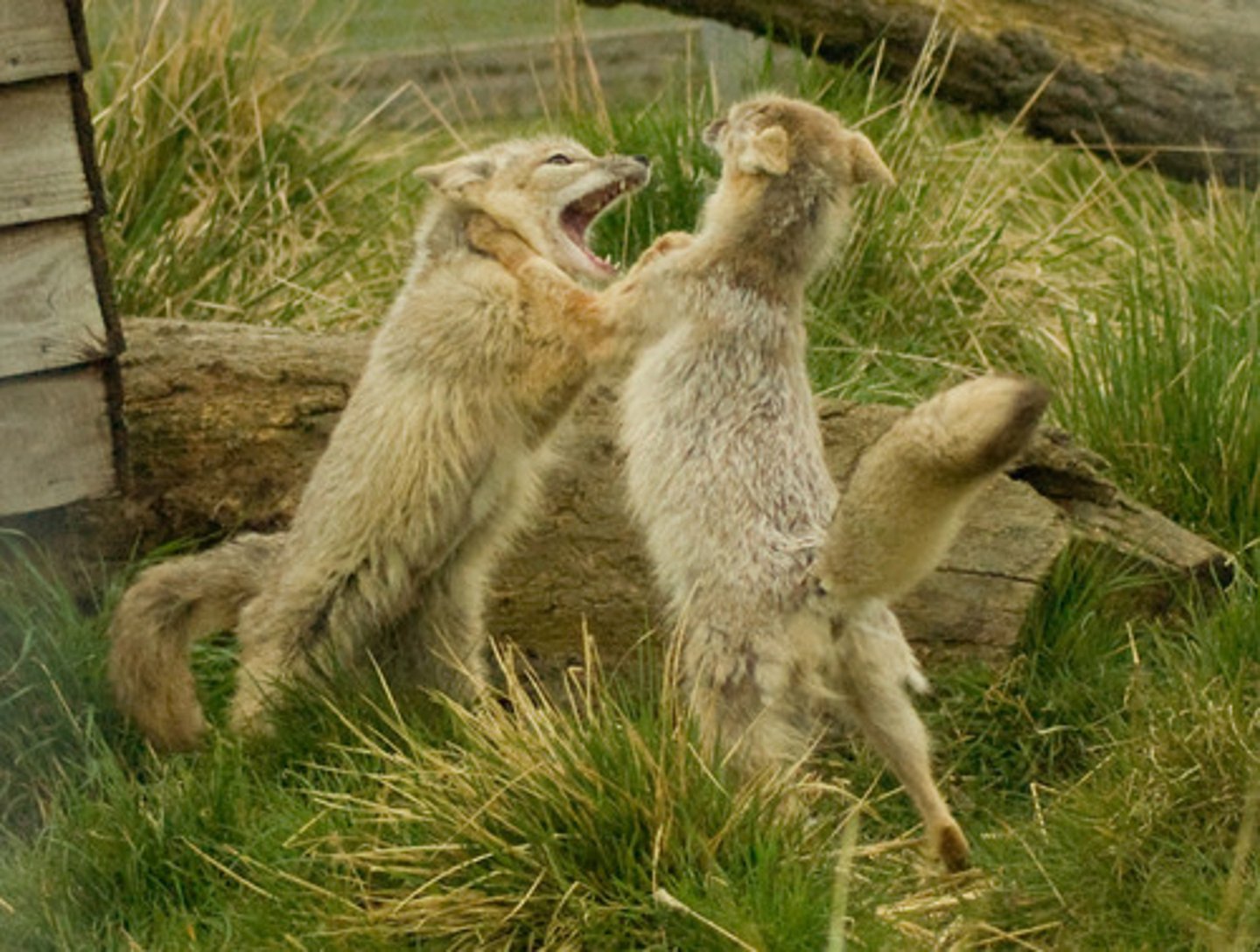

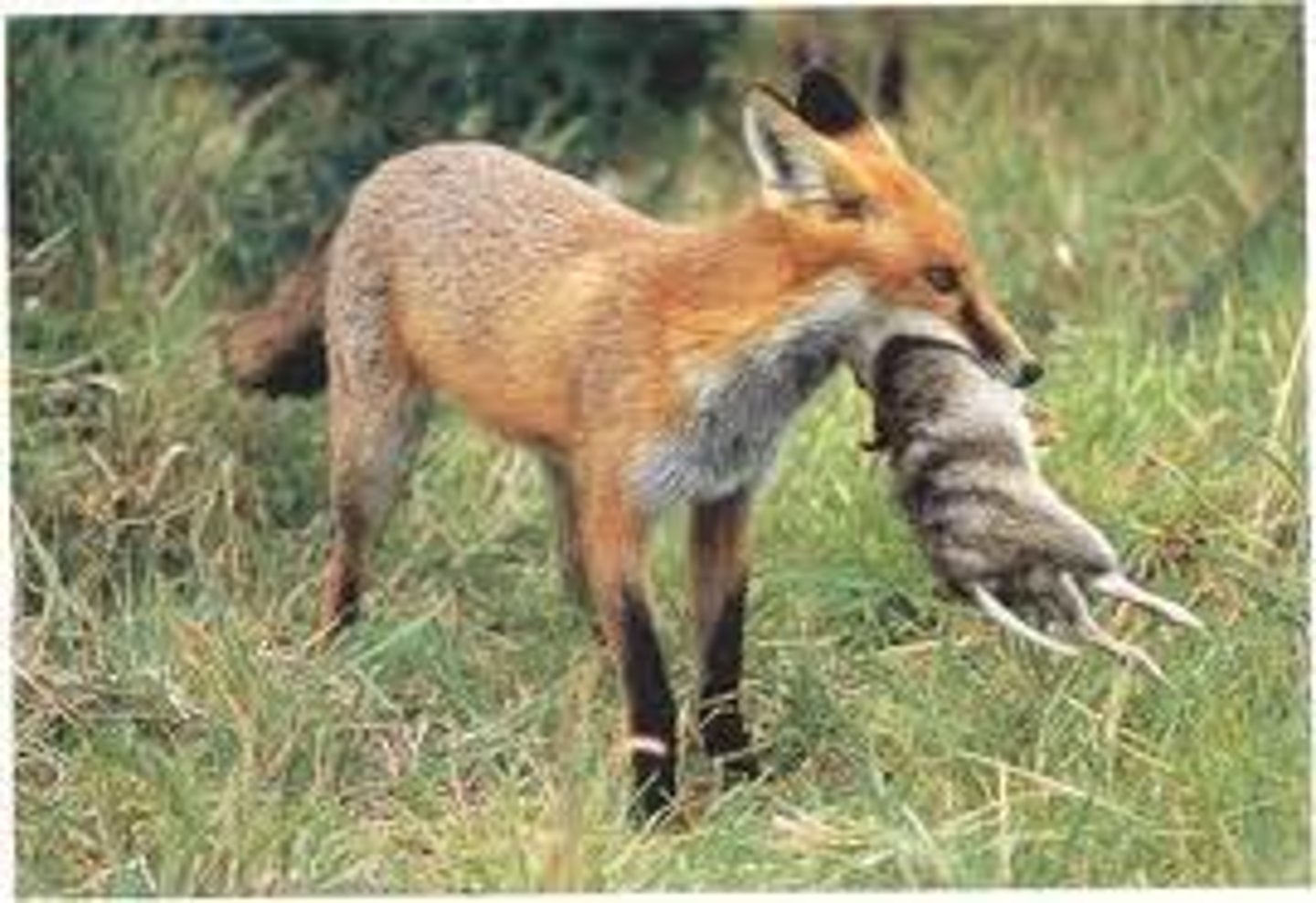
Predation
When one organism (the predator) hunts and eats another (the prey).

Symbiosis
A close long term relationship between two different species.
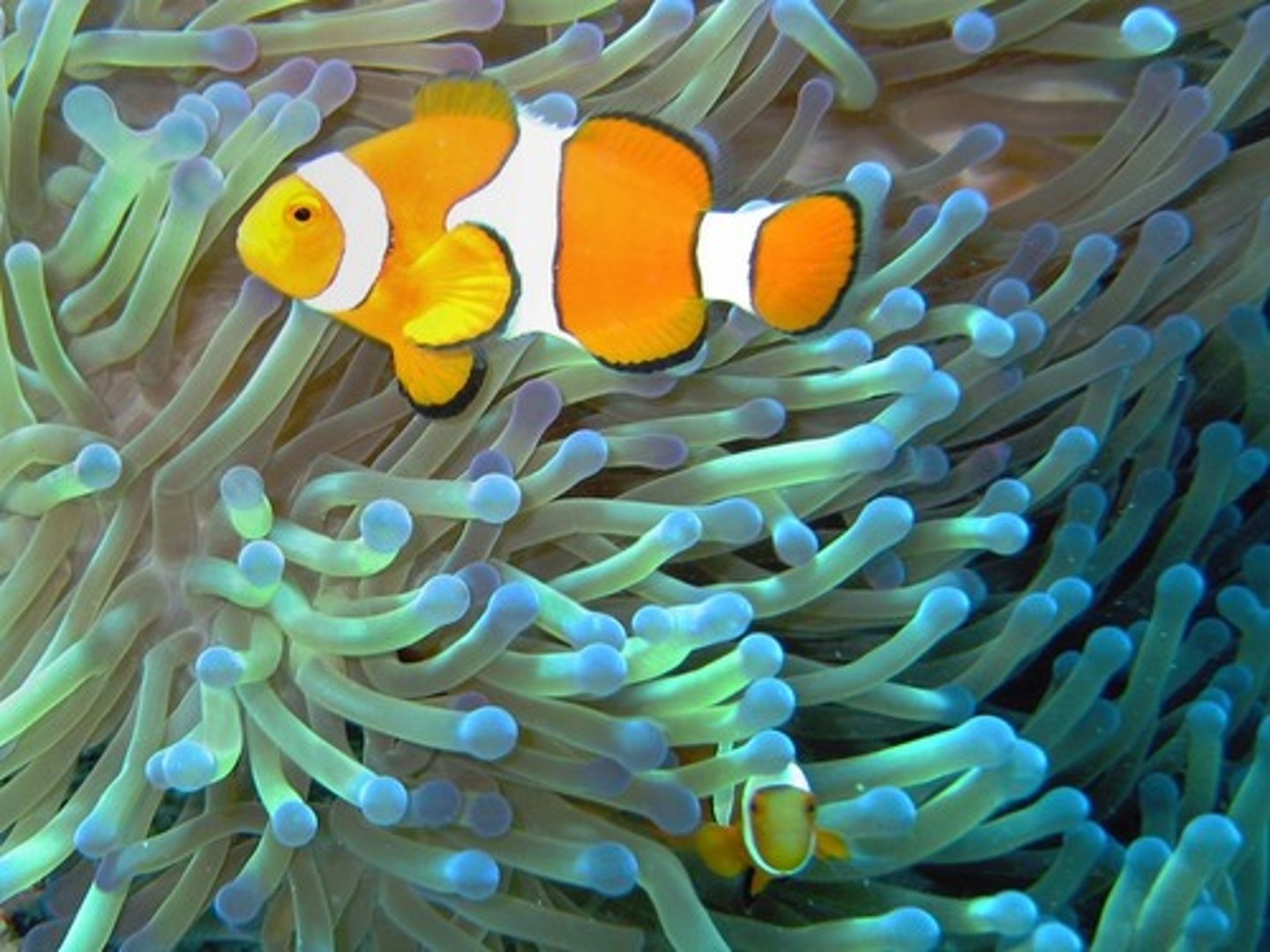
Mutualism
A type of symbiosis where both species benefit.

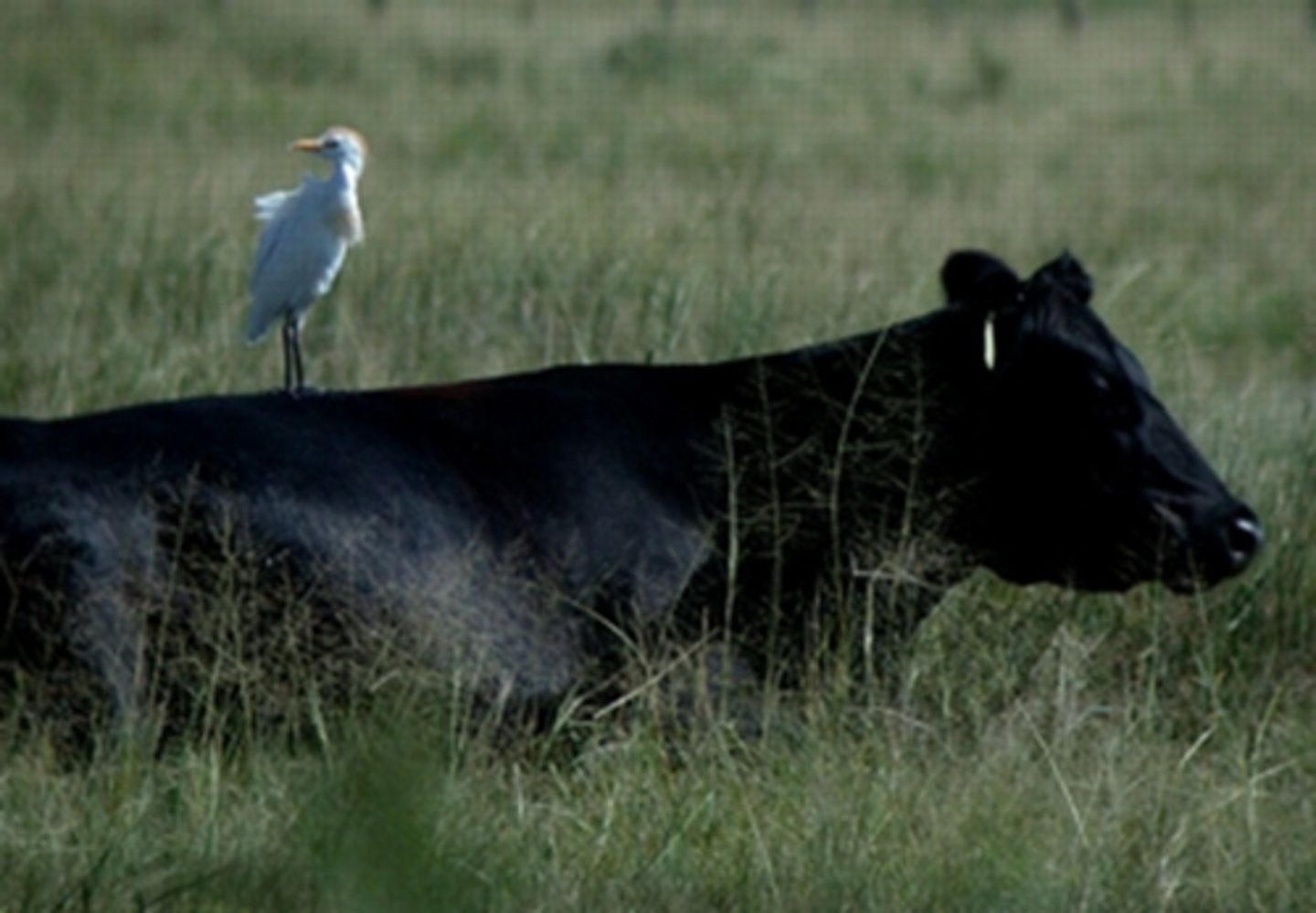
Commensalism
A relationship where one species benefits and the other is not affected.

Parasitism
A relationship where one species benefits and the other is harmed.

Trophic level
A step or level in a food chain (e.g., producer, primary consumer, secondary consumer).
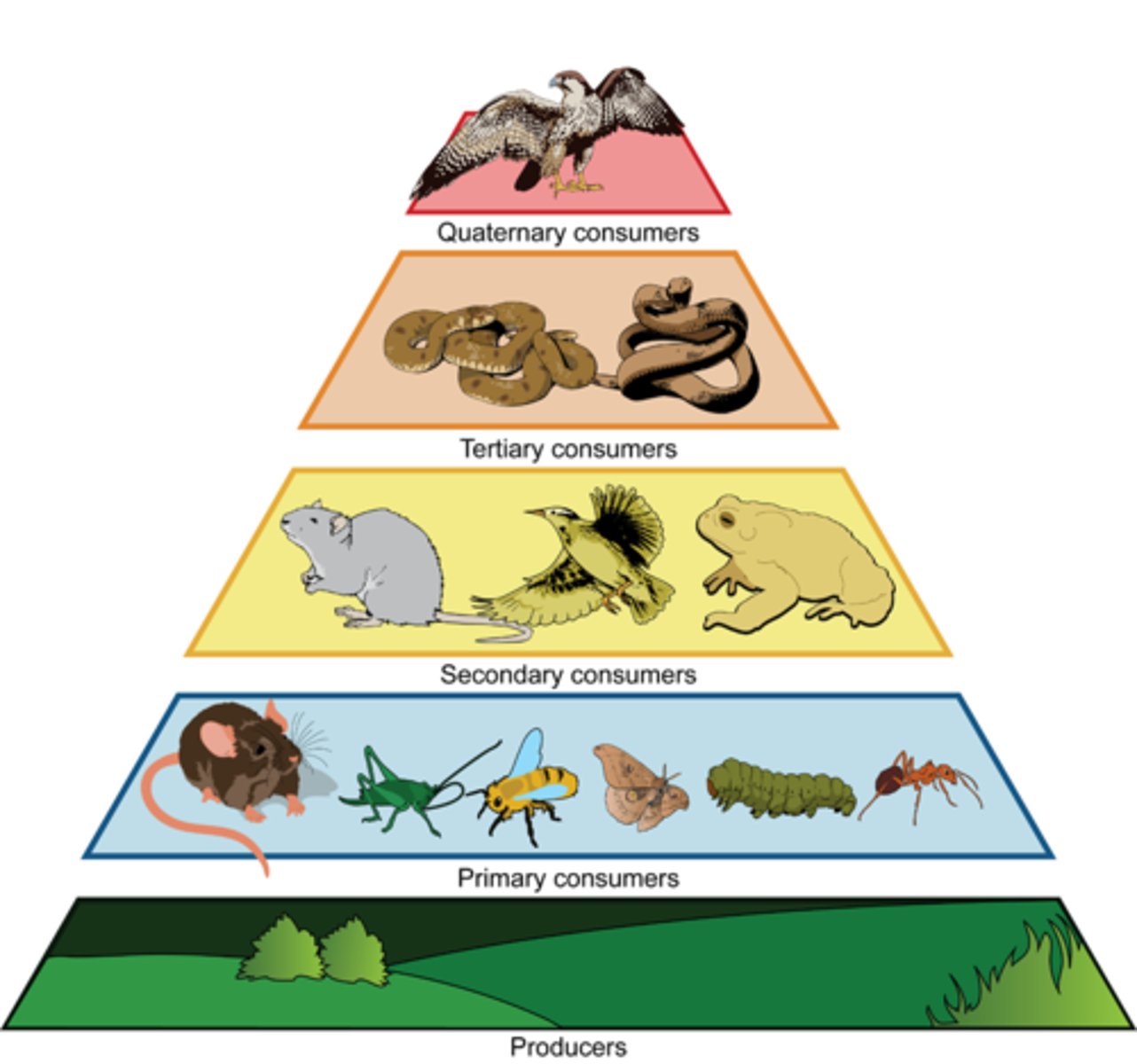
Heterotroph
An organism that gets its food by eating other organisms.

Autotroph
An organism that makes its own food, usually by photosynthesis.

Biomass
The total mass of living material in an area or ecosystem.
Chemical energy
Energy stored in the bonds of chemical substances like glucose.
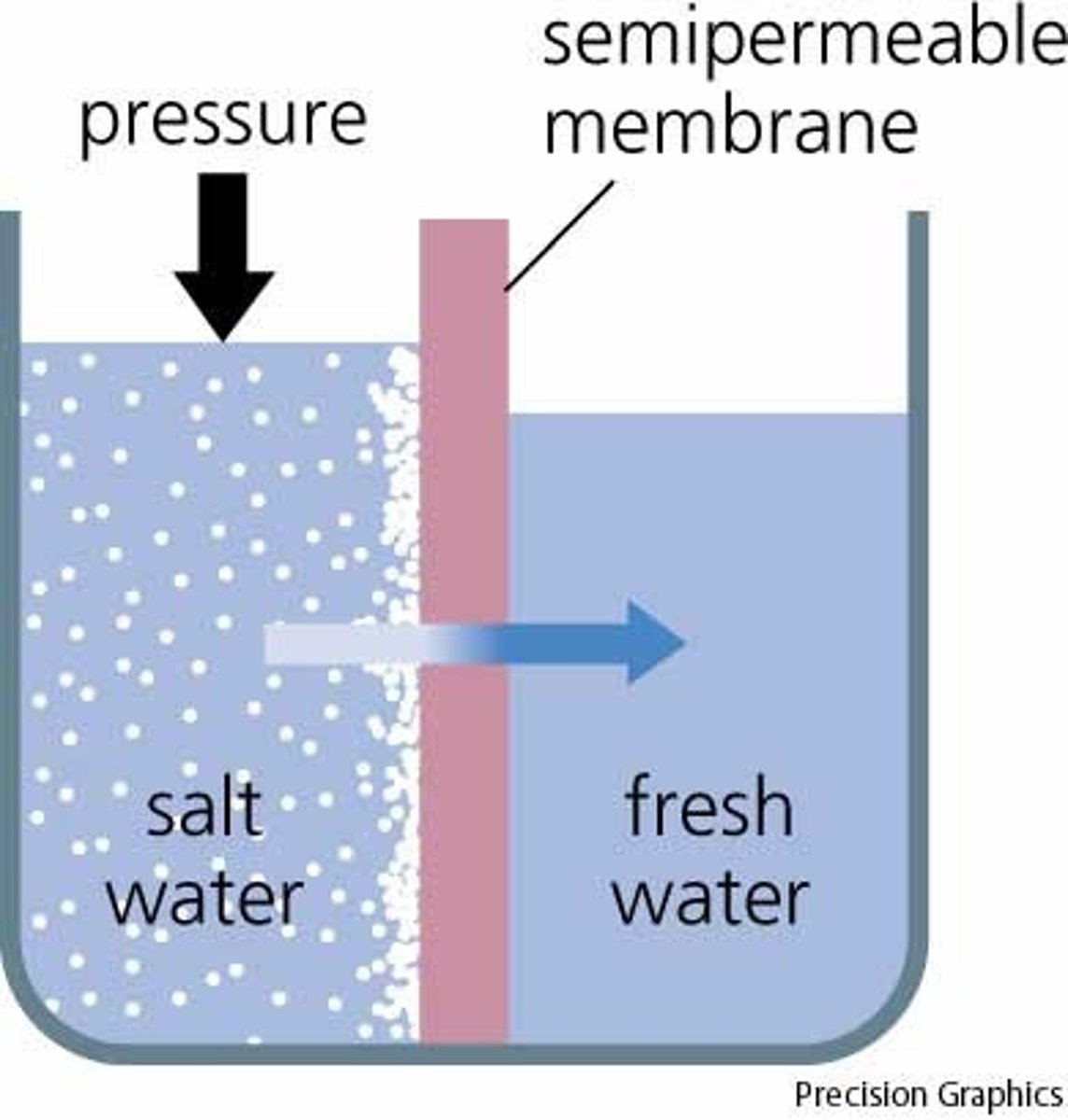
Osmosis
The movement of water across a membrane from an area of low concentration to high concentration.
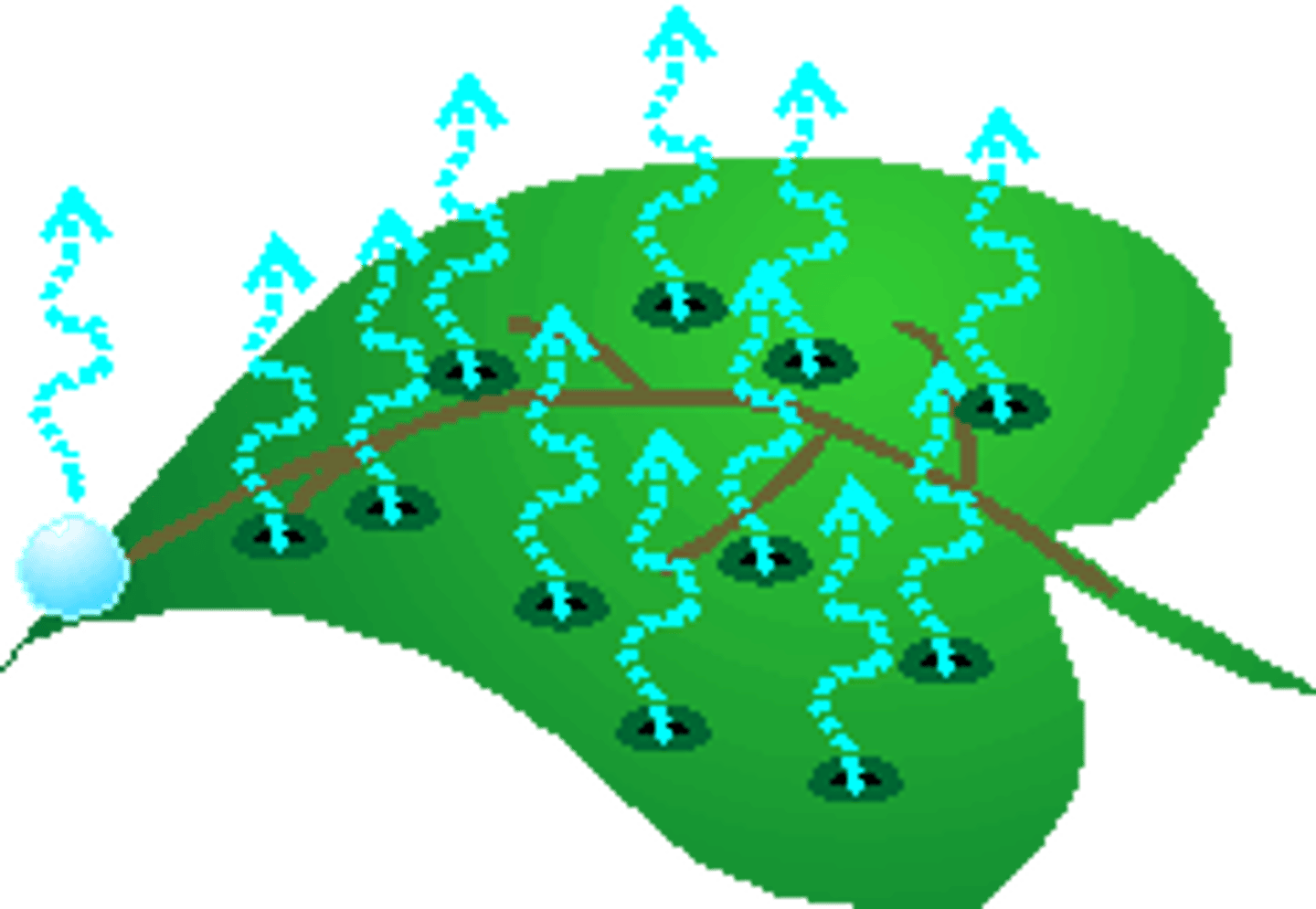
Transpiration
The process of water moving through a plant and evaporating from the leaves.
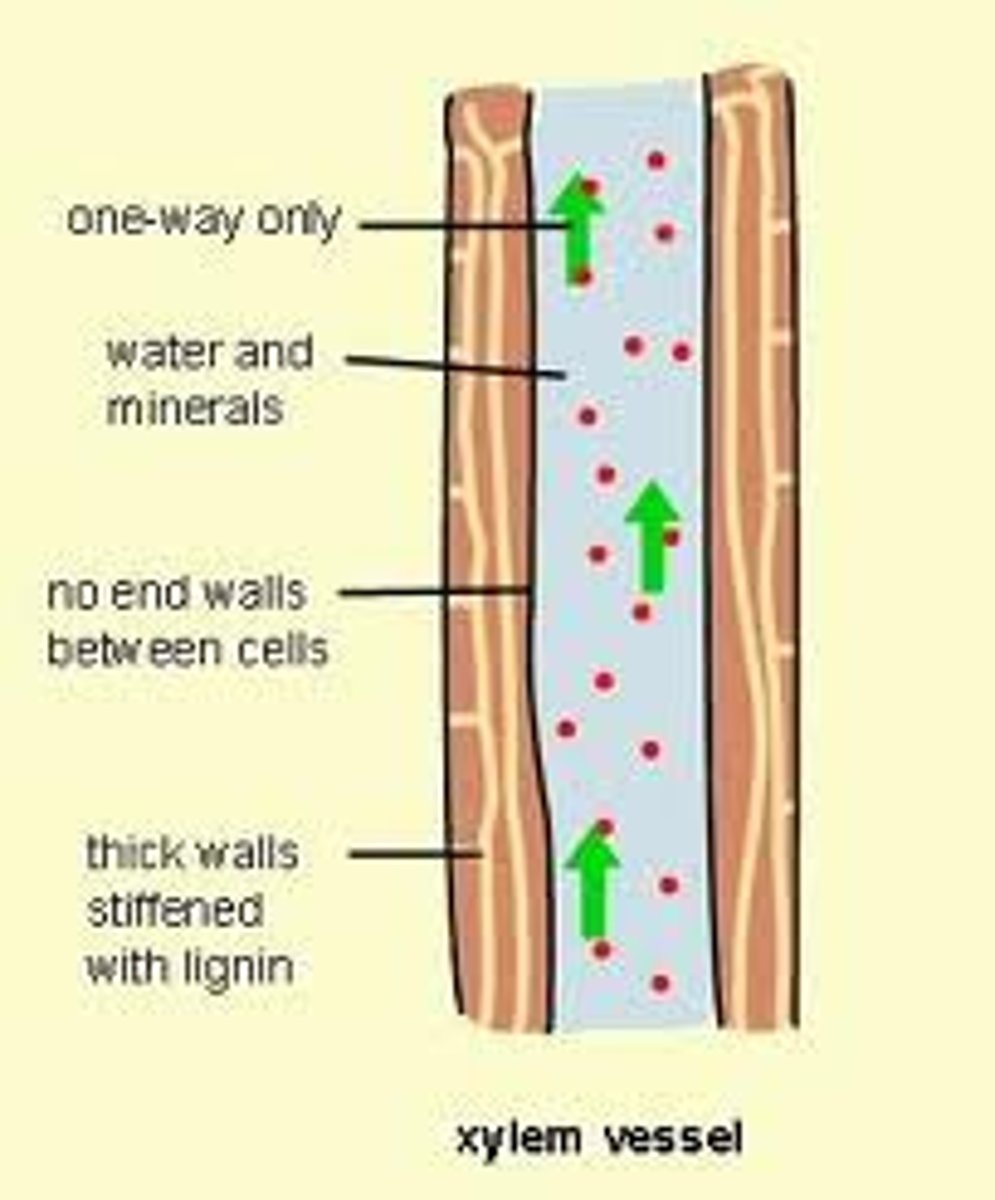
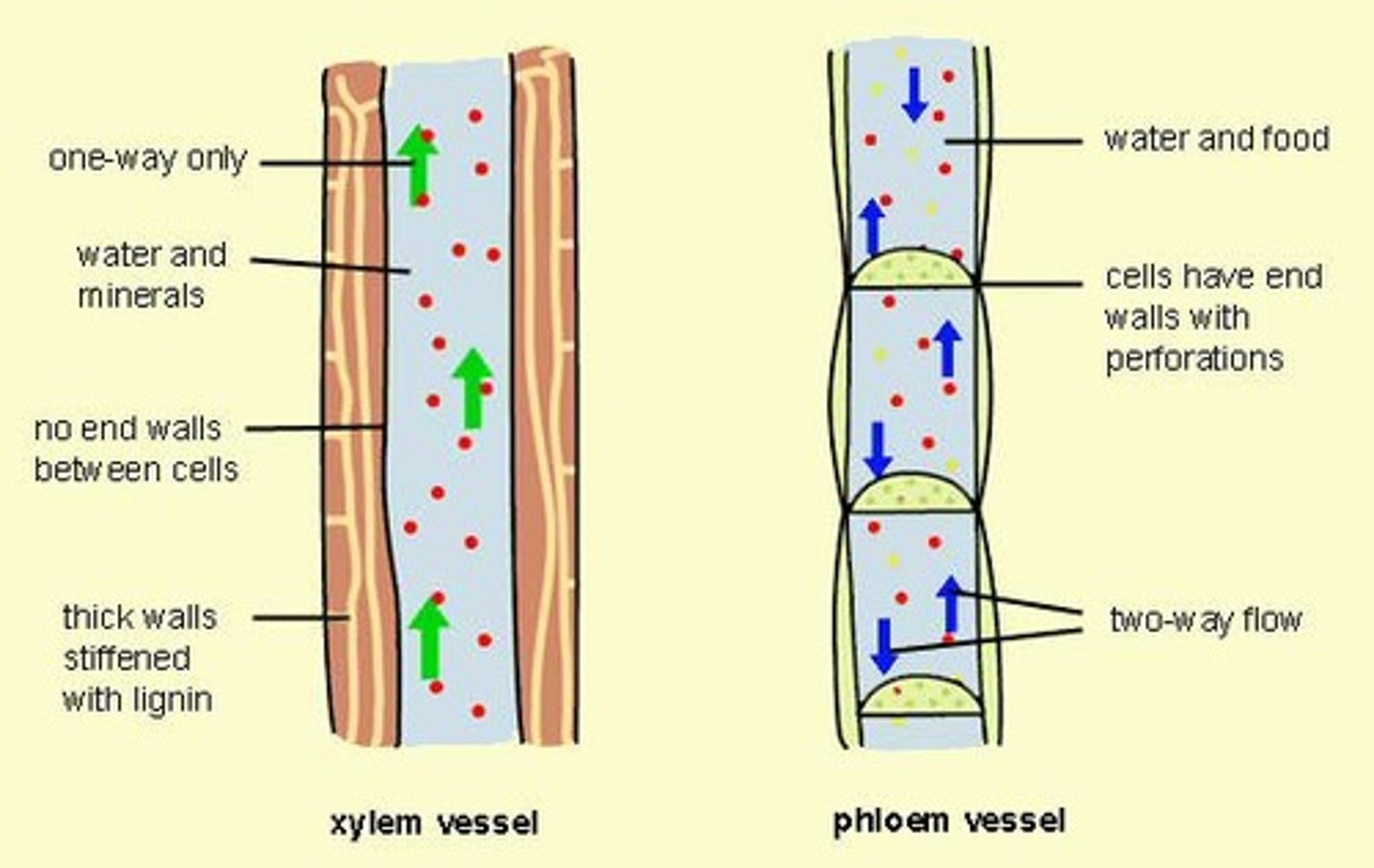
Xylem
Plant tissue that carries water and minerals from roots to leaves.
Phloem
Plant tissue that transports sugars and nutrients around the plant.
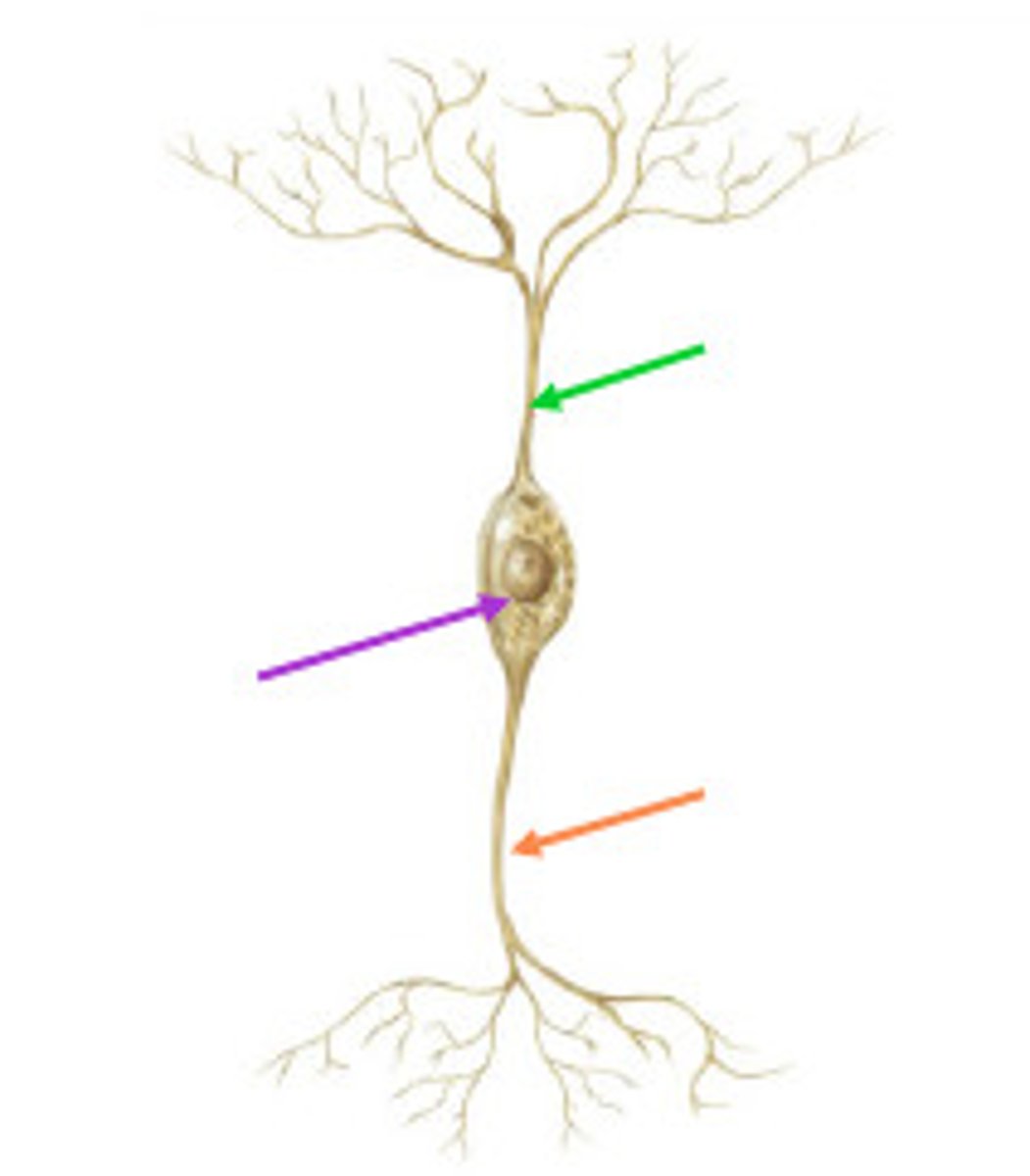
Neuron
A nerve cell that carries messages around the body.
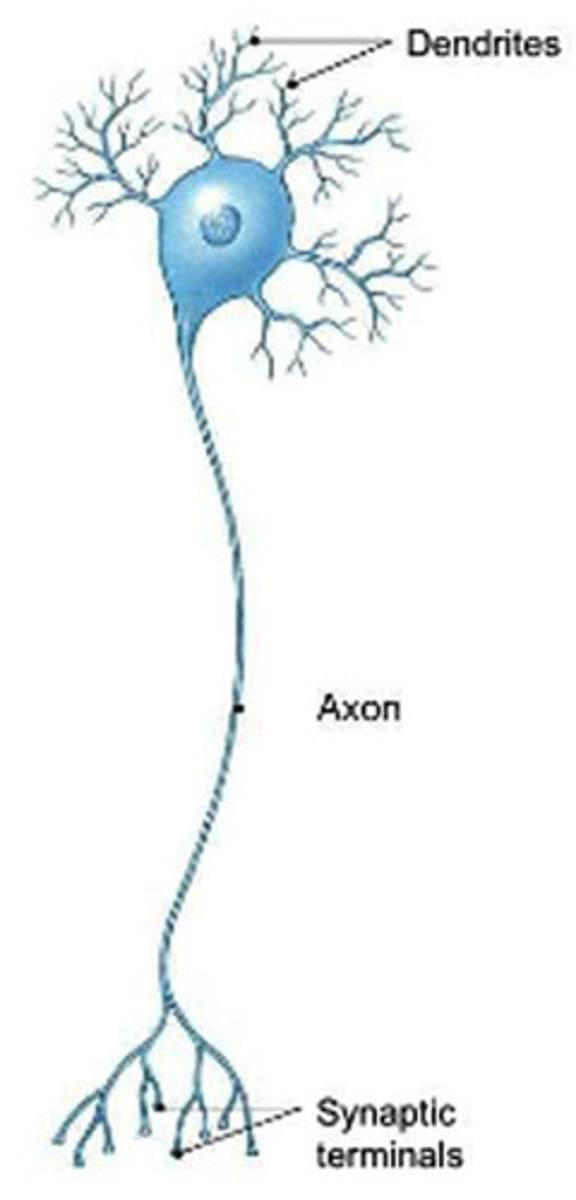
Axon
The long part of a neuron that carries electrical messages away from the cell body.
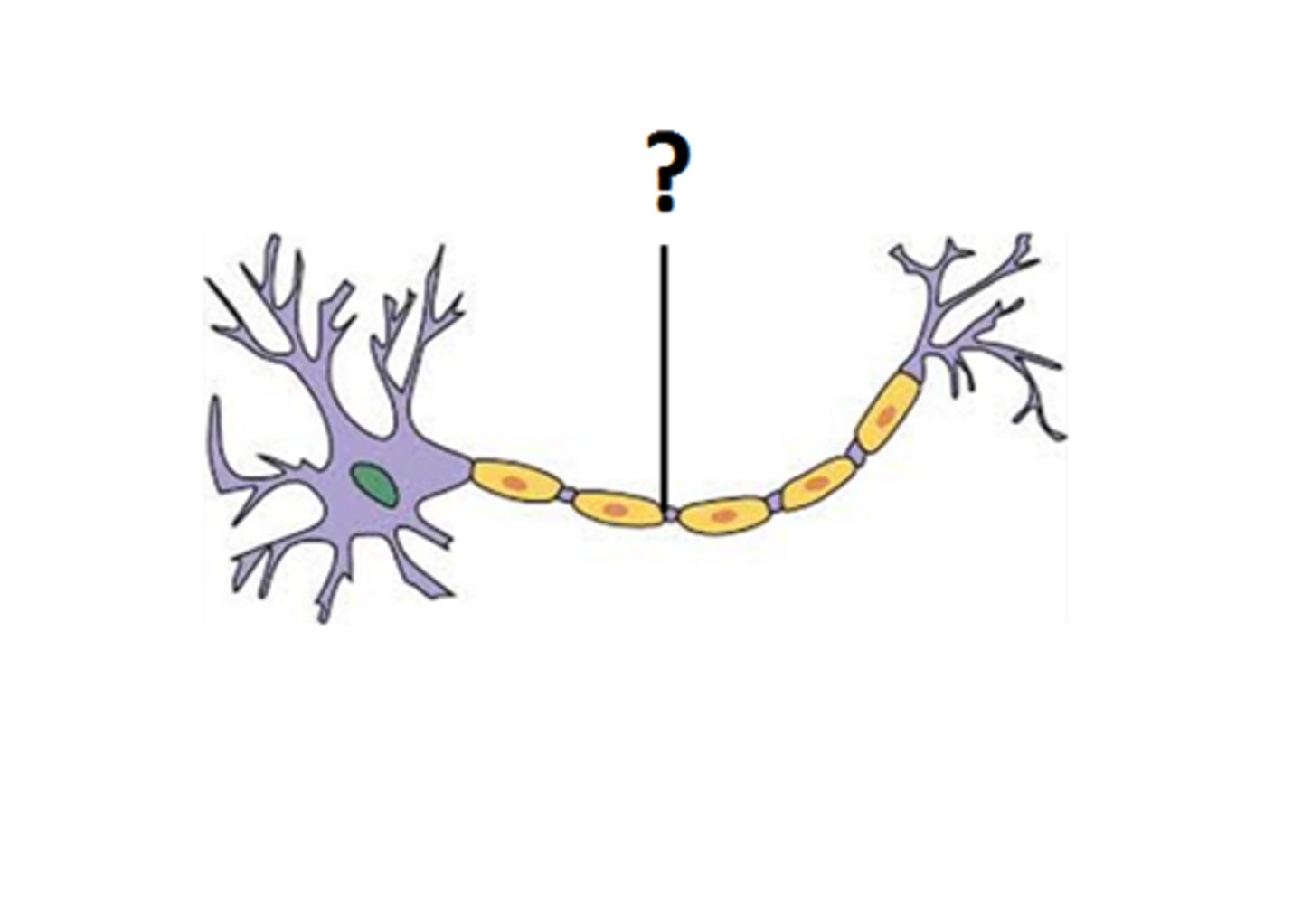
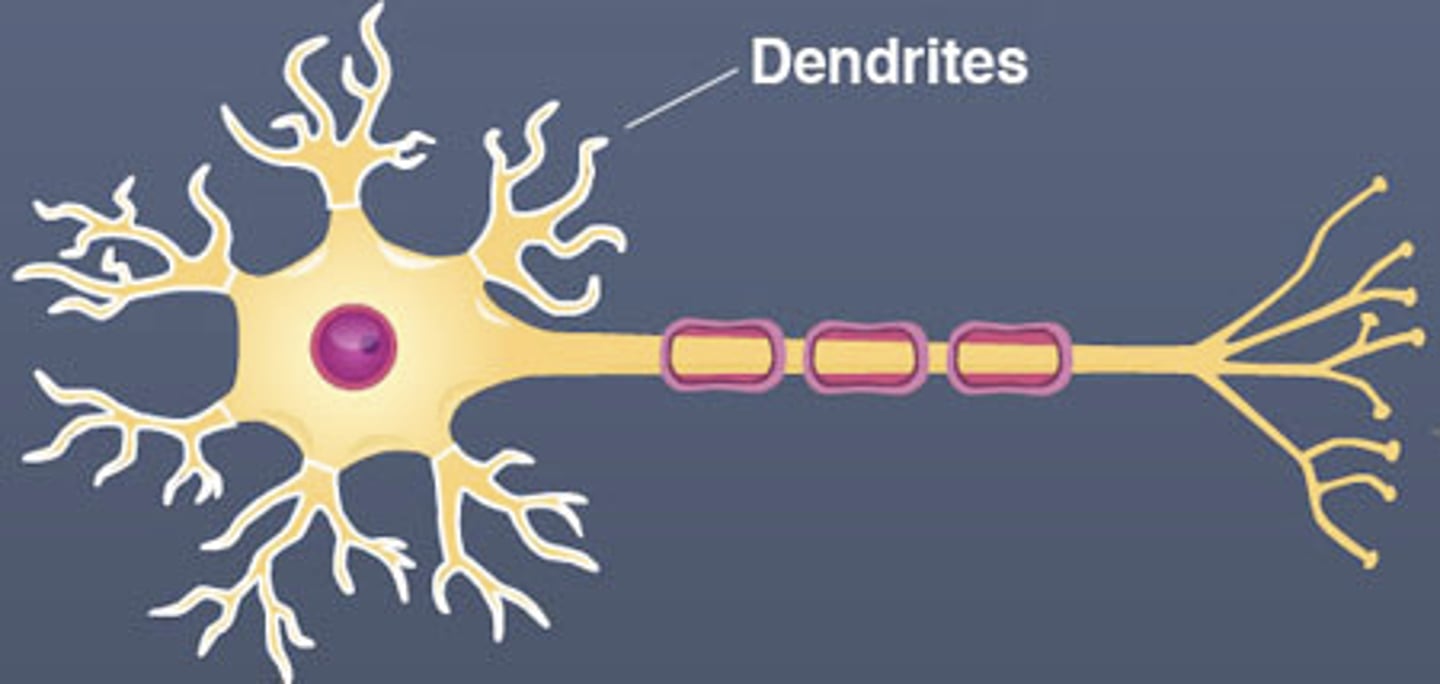
Dendrite
Branch-like parts of a neuron that receive signals from other cells.
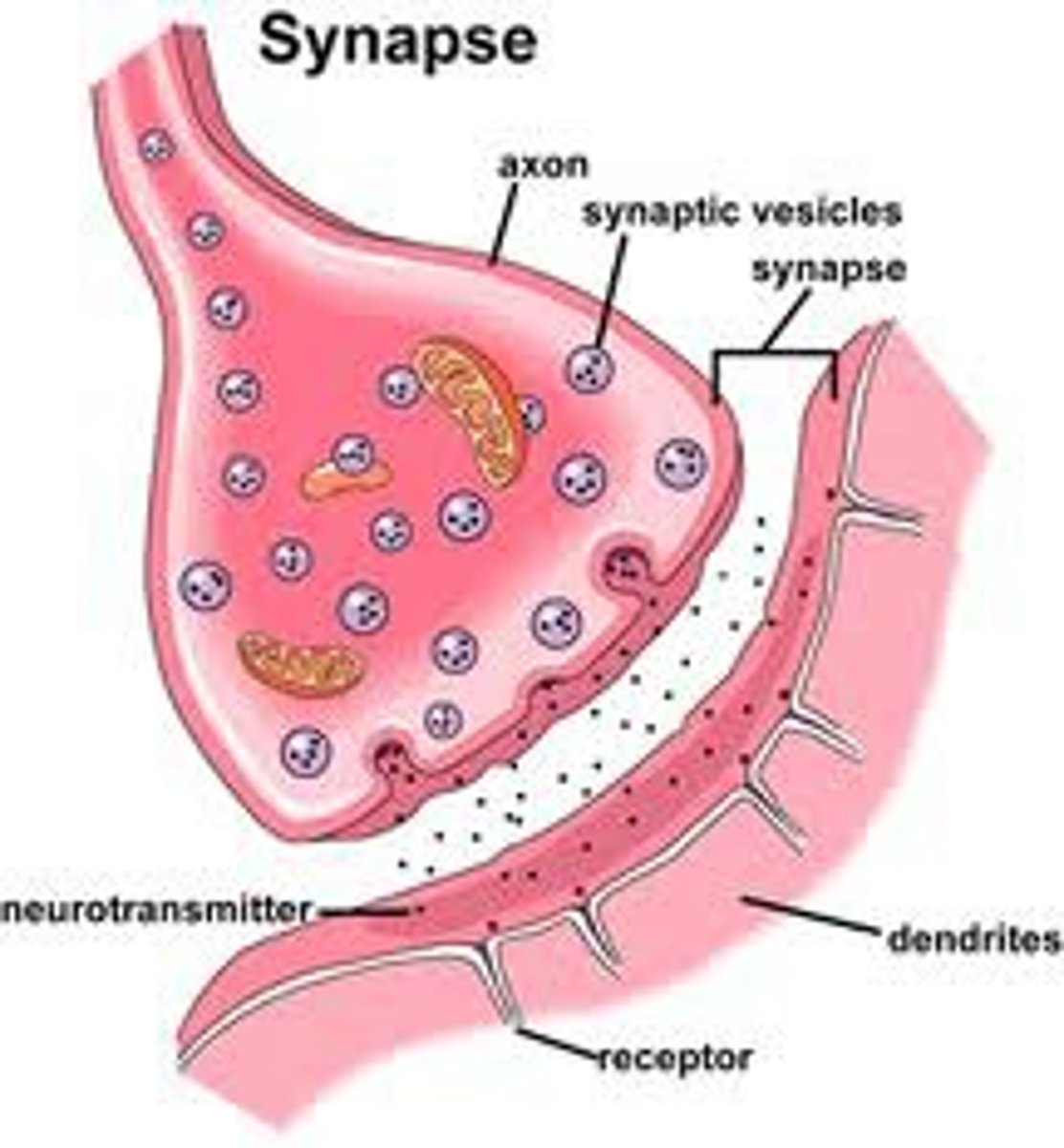
Synapse
The tiny gap between neurons where messages are passed using chemicals called neurotransmitters.
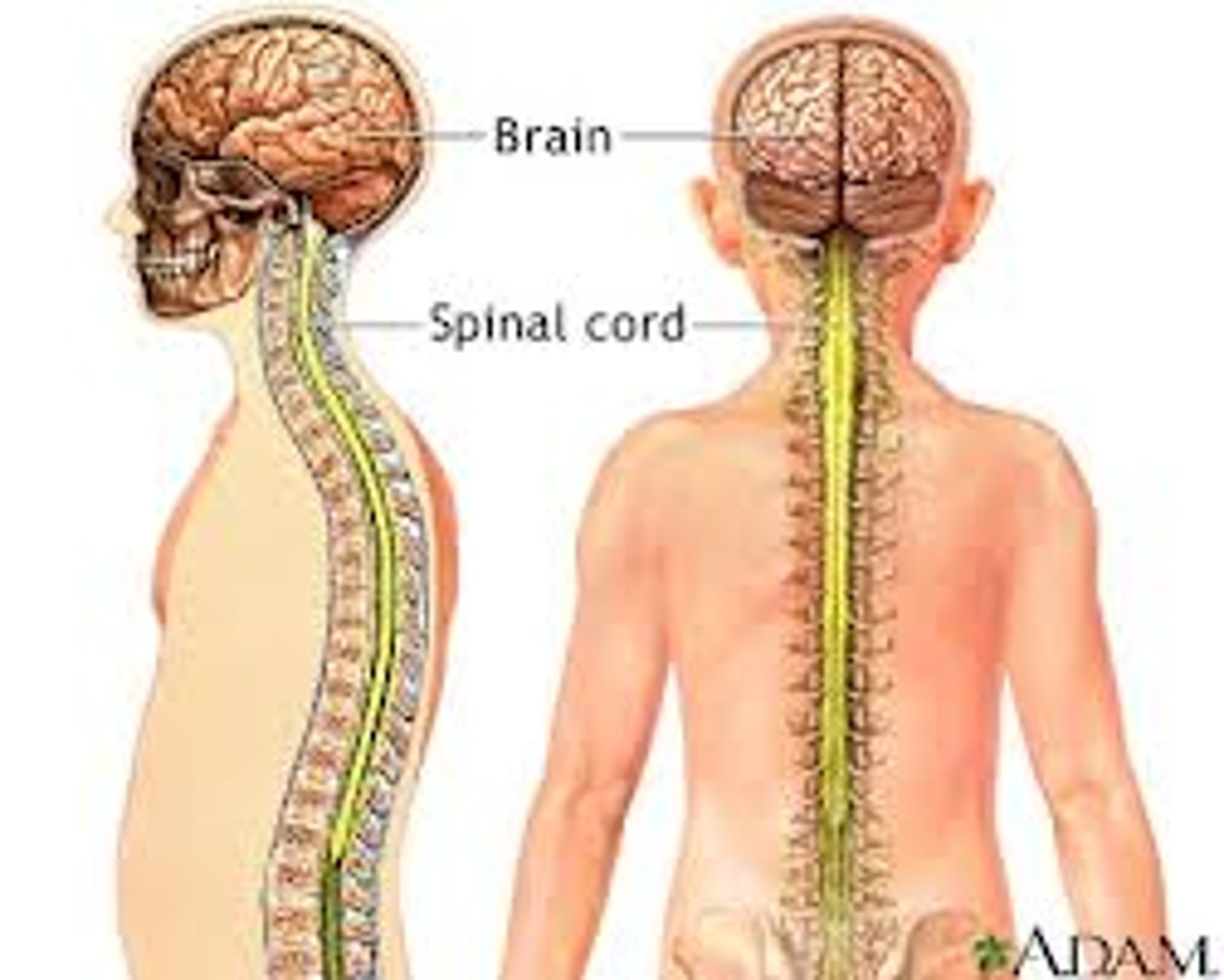
Central Nervous System (CNS)
The brain and spinal cord; it controls most body functions.
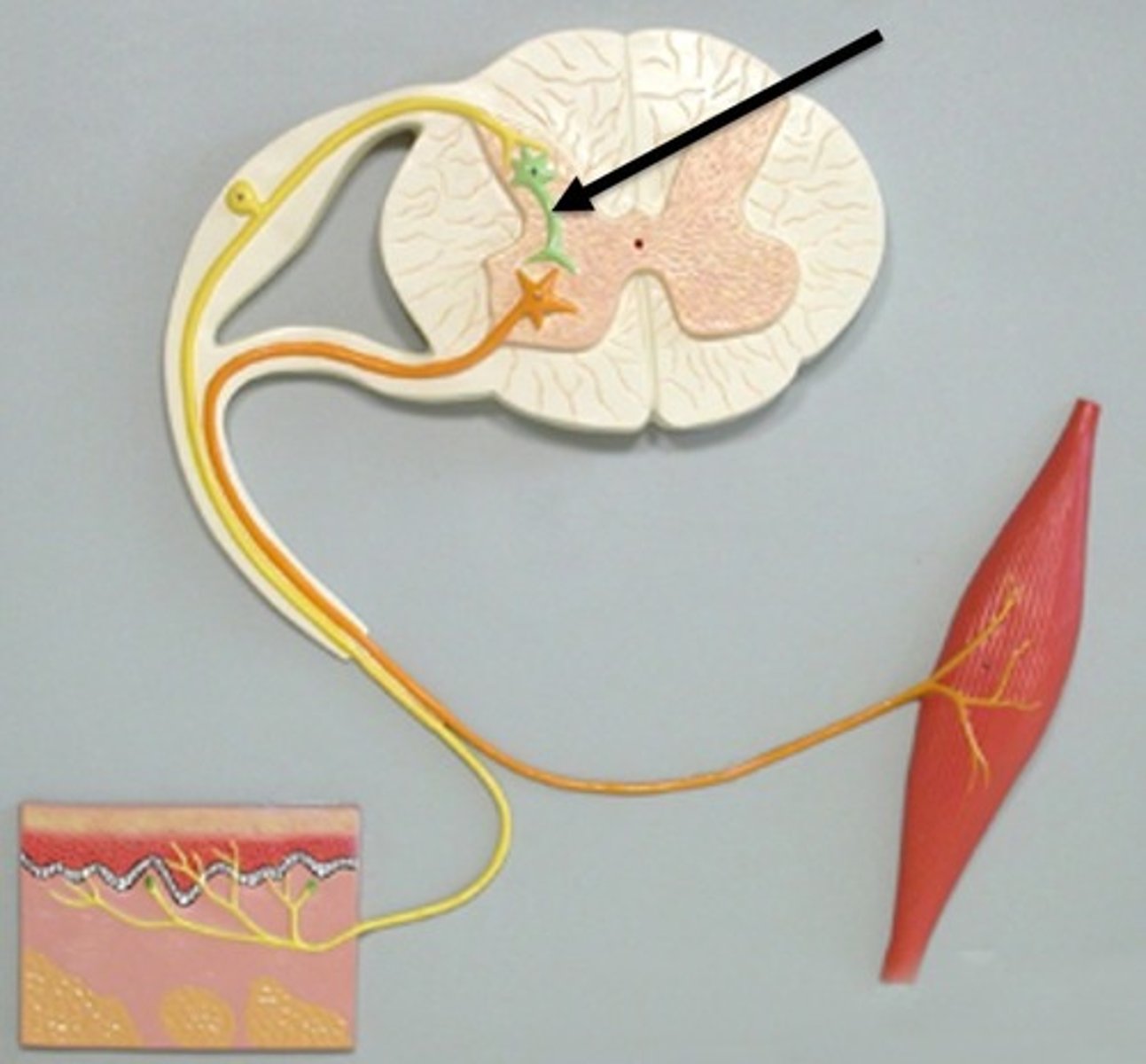
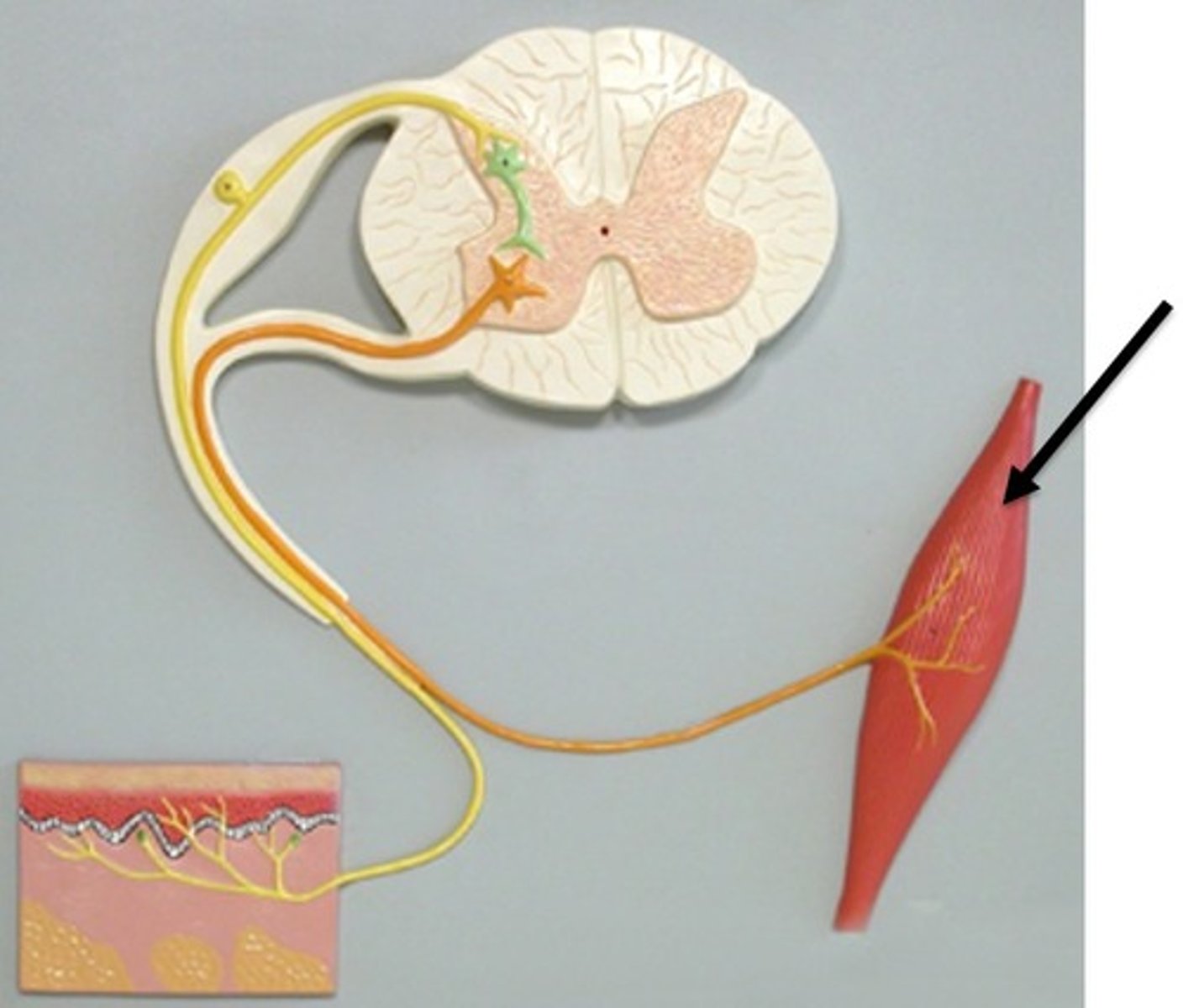
Reflex arc
The pathway that controls an automatic, fast response to a stimulus.
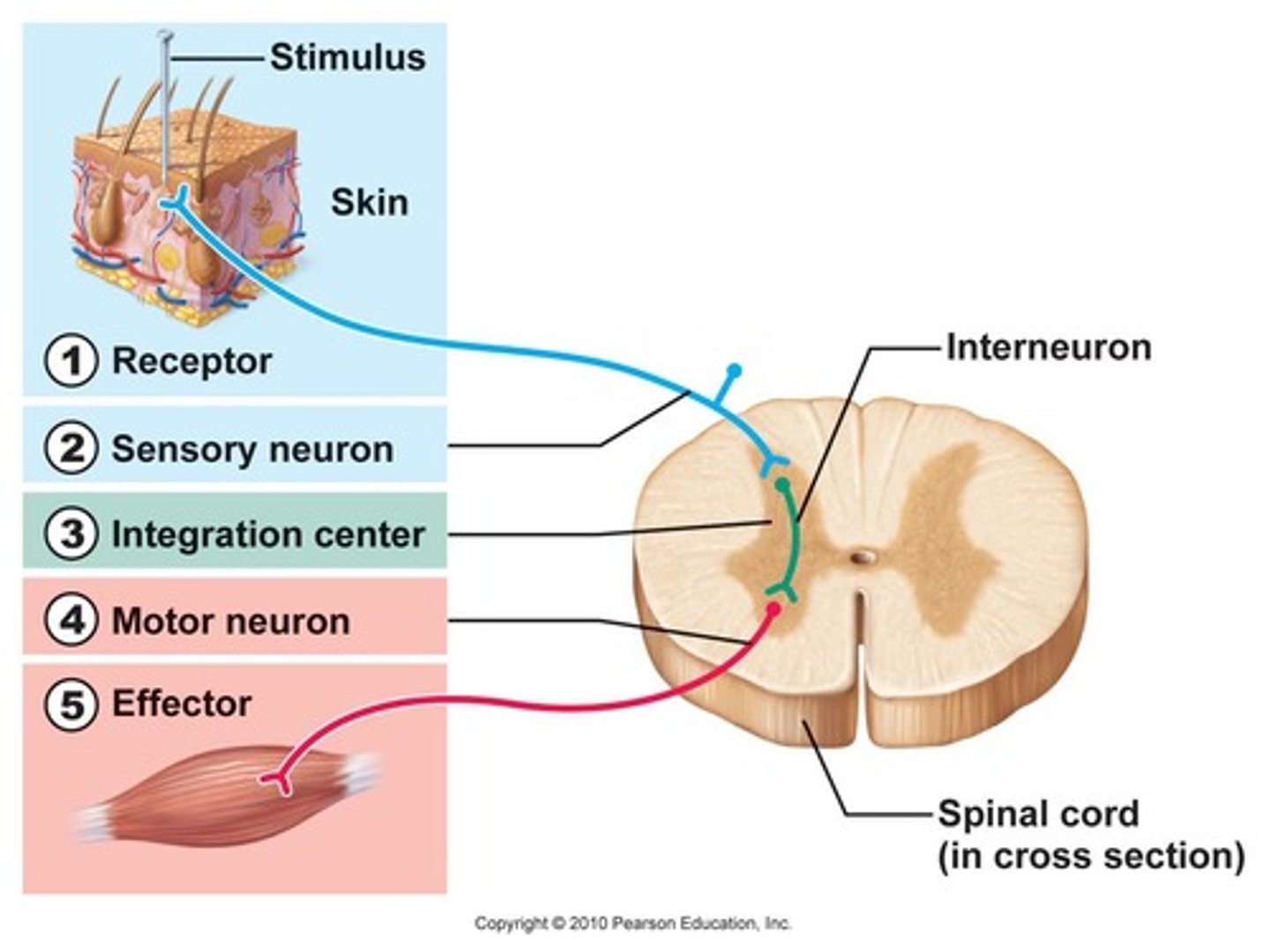
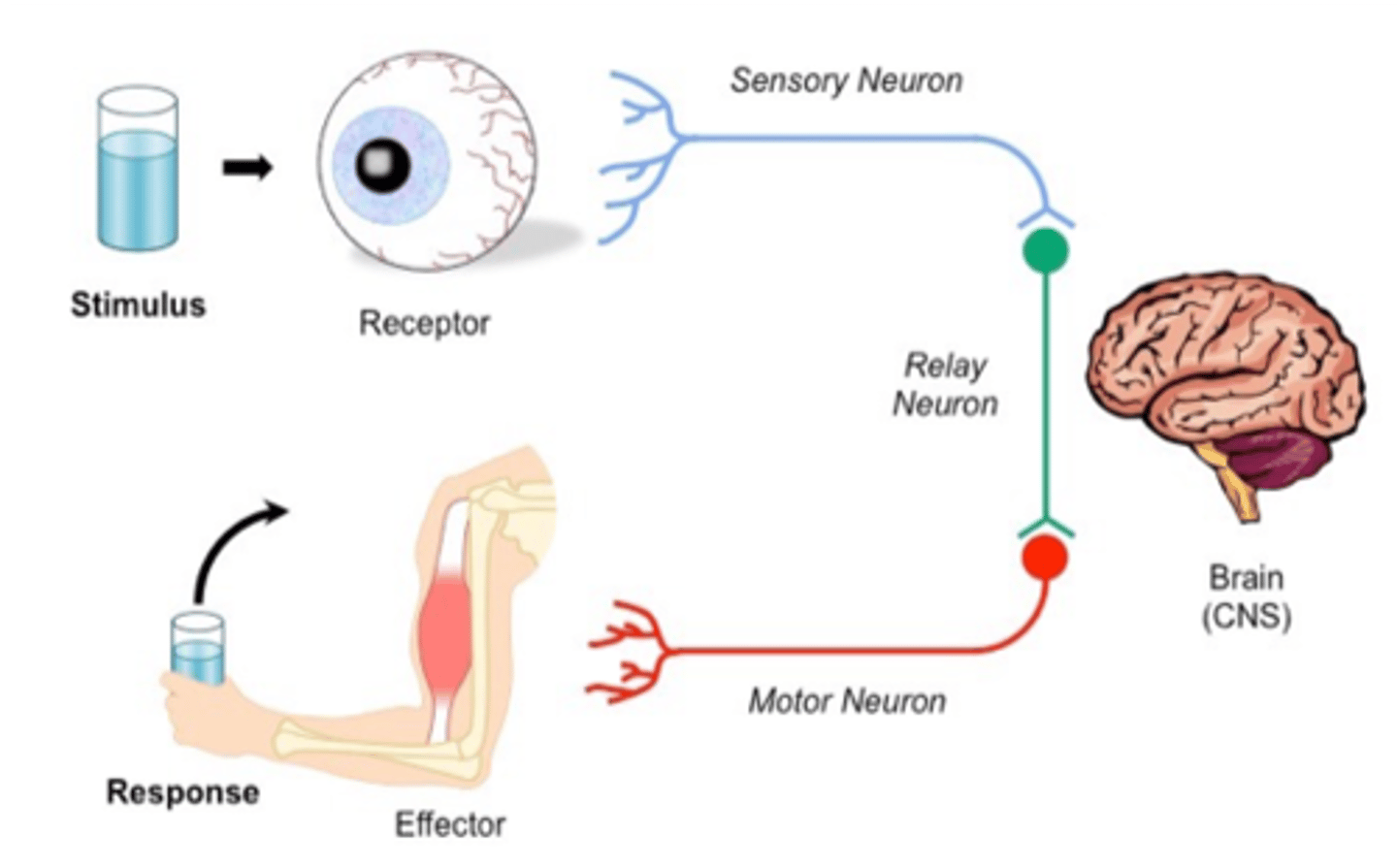
Stimulus
A change in the environment that causes a response.
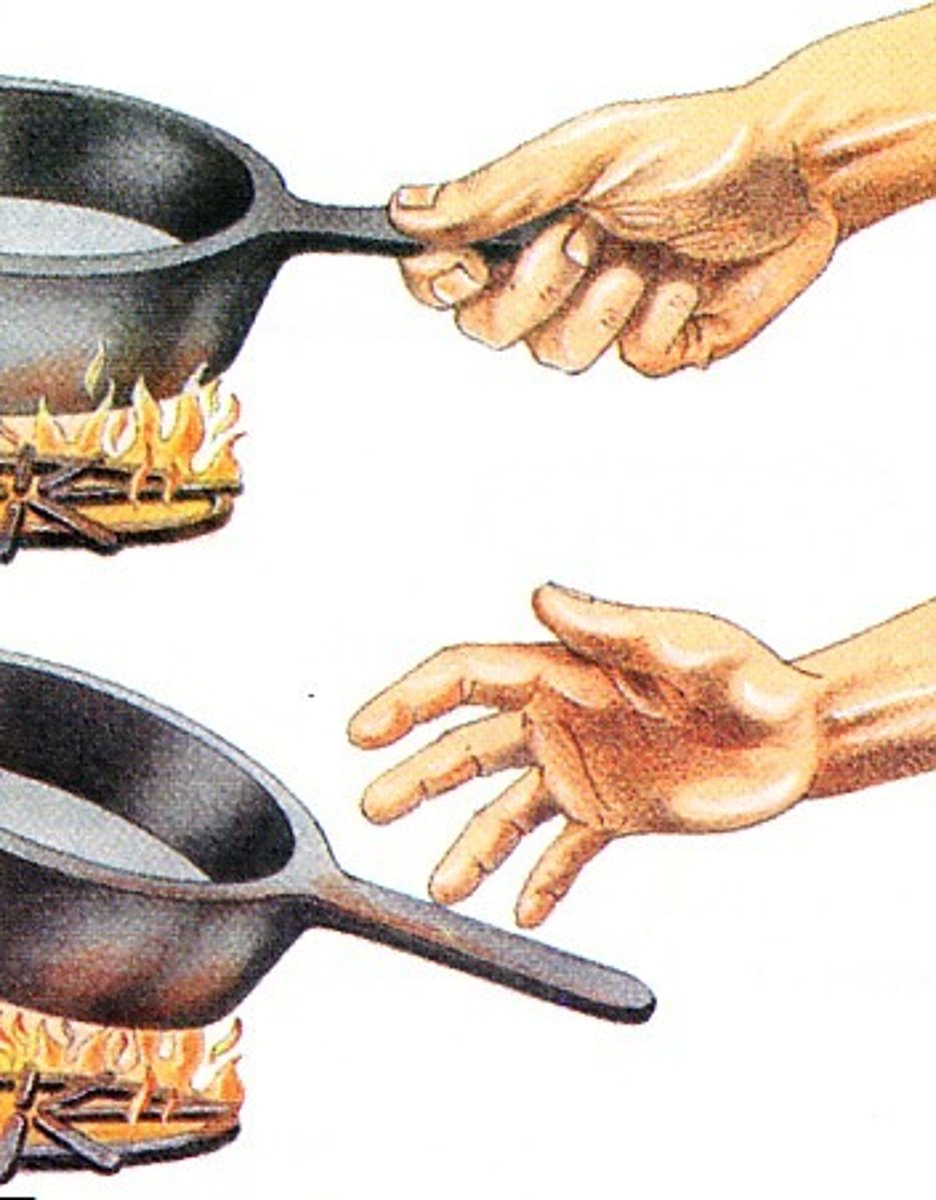

Receptor
A structure that detects a stimulus (e.g., in the eyes, skin, or ears).
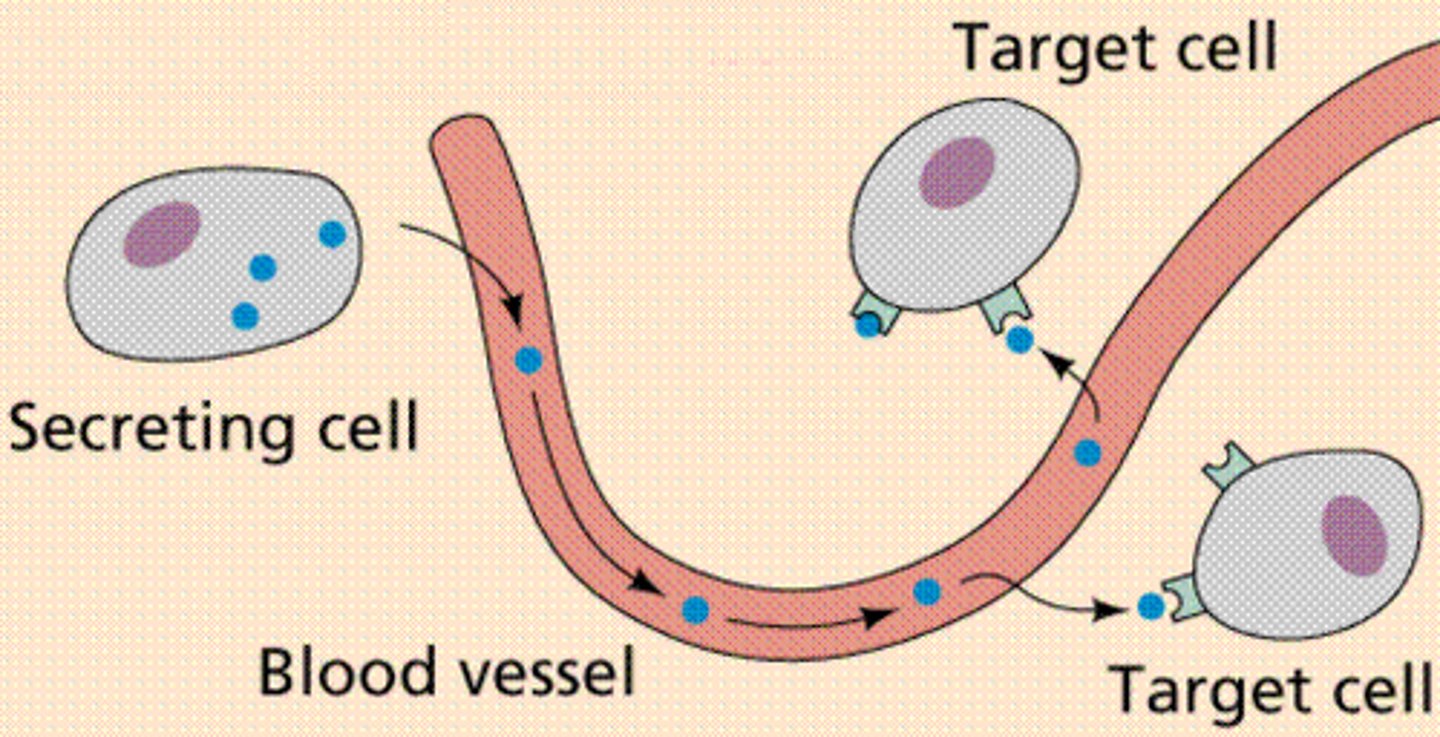
Hormone
A chemical messenger made by glands that travels in the blood to control body functions.
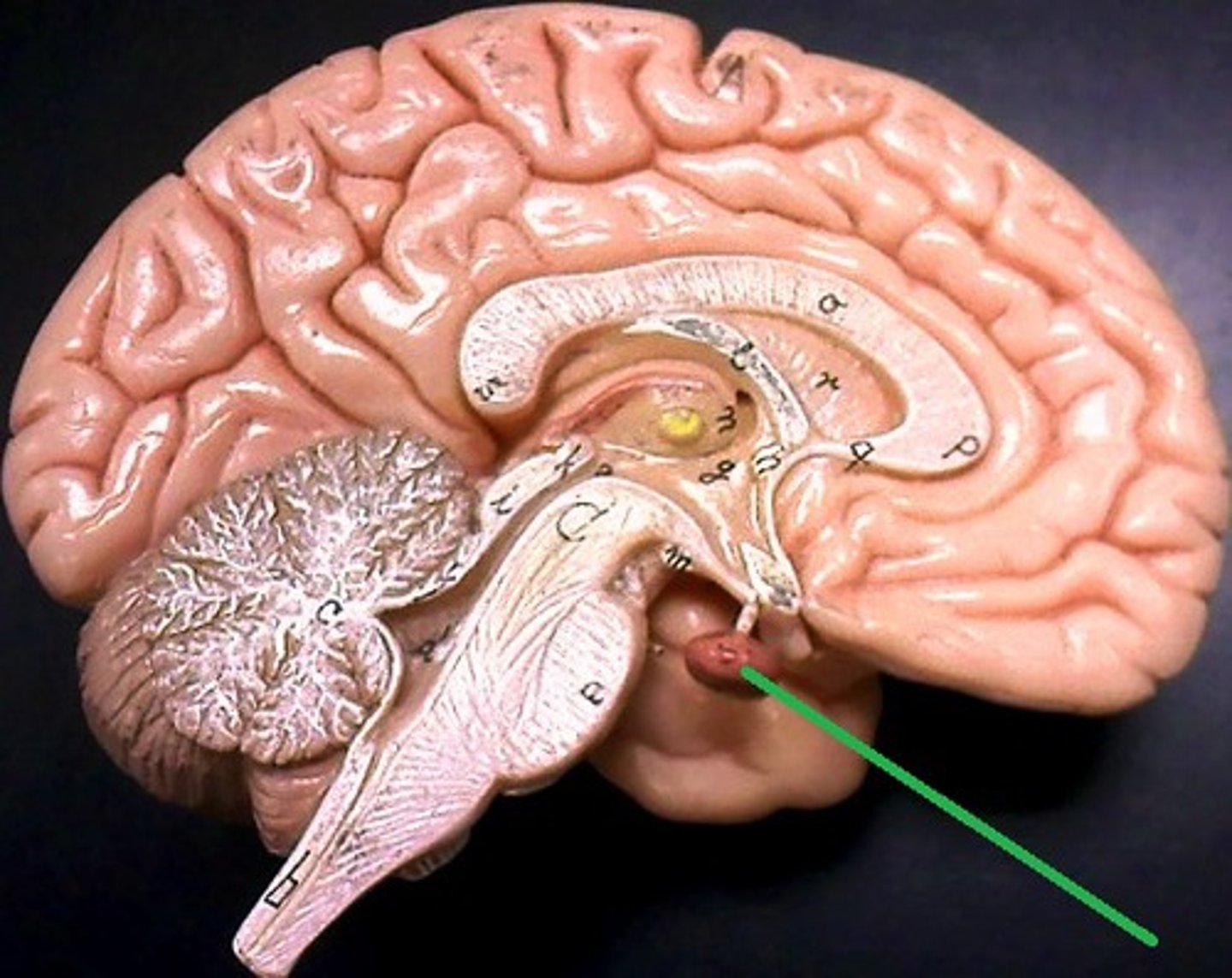
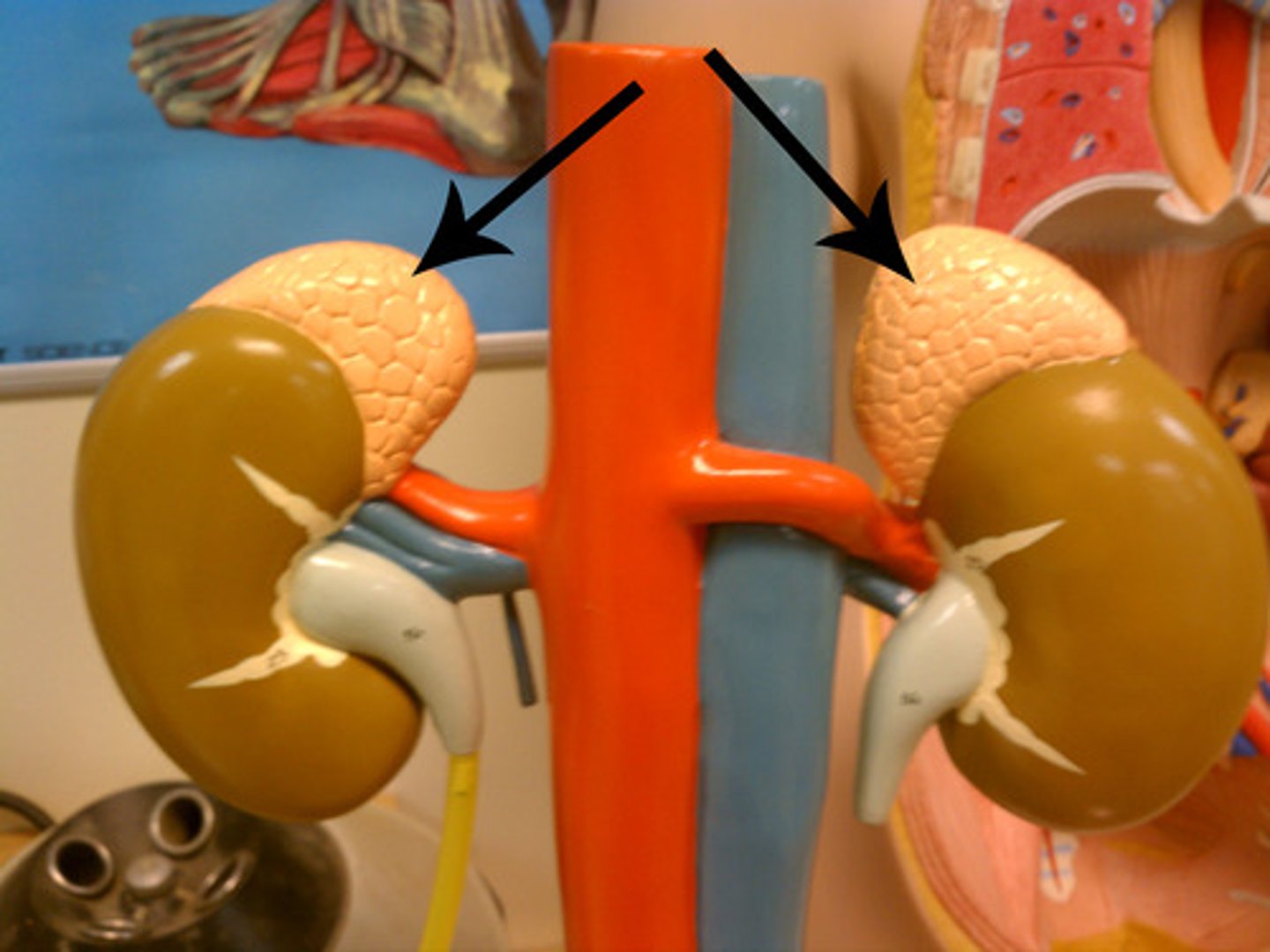
Pituitary
The "master gland" that controls other glands and many body processes.
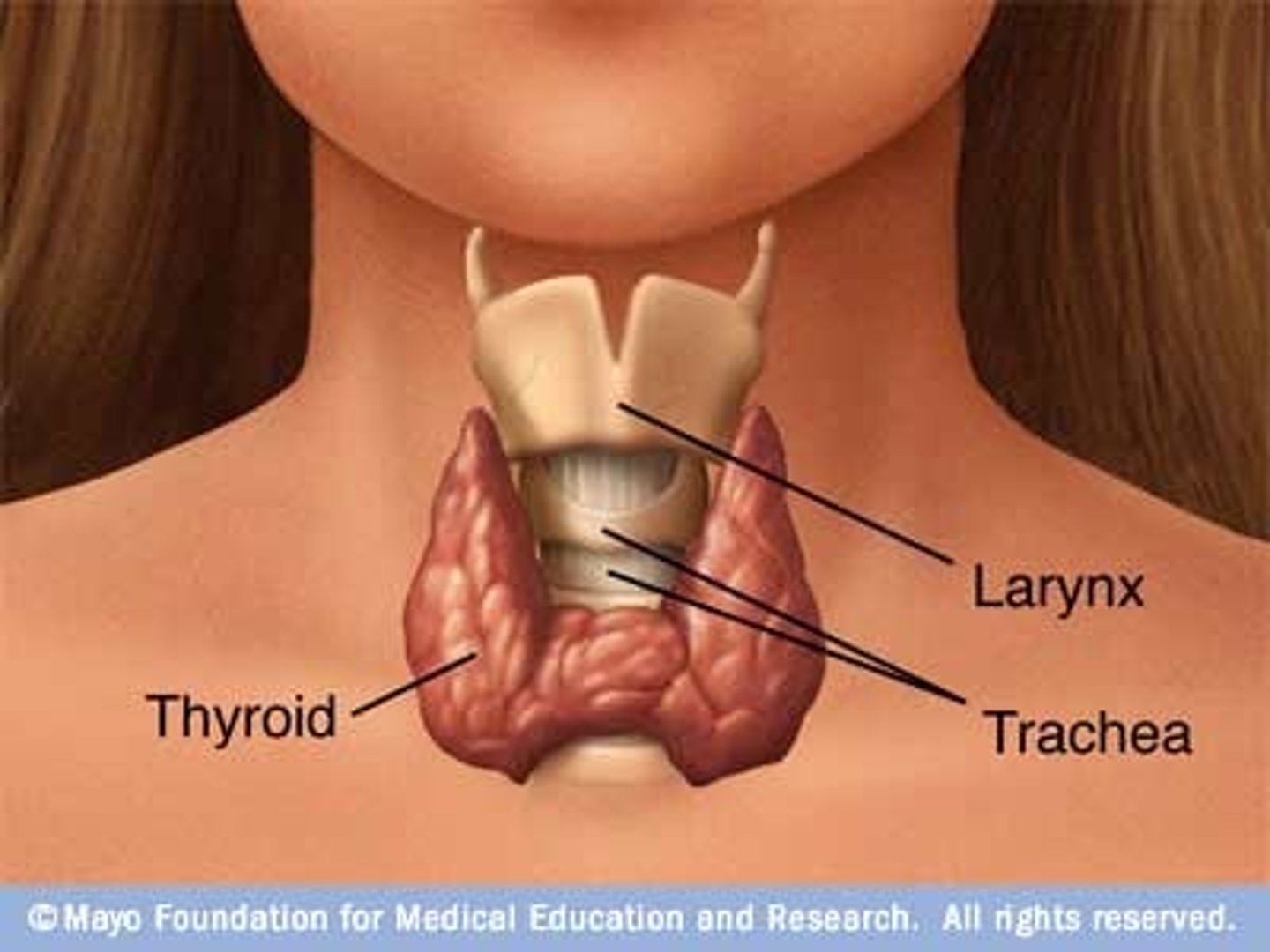
Thyroid
A gland in the neck that controls metabolism and energy use.
Adrenal Glands
Glands that release adrenaline to prepare the body for "fight or flight."
Sensory neuron
Carries messages from receptors to the CNS.
Relay neuron (interneuron)
Passes messages within the CNS (brain and spinal cord)
Motor neuron
Carries messages from the CNS to muscles or glands (effectors).
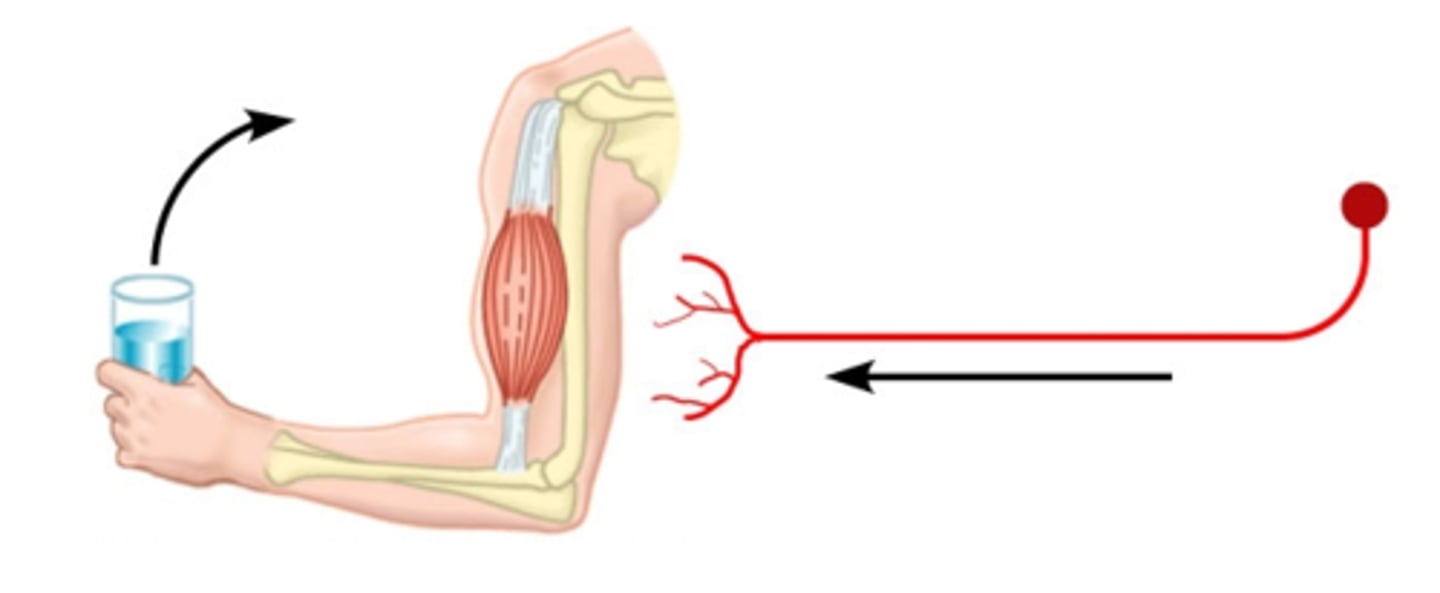
Effector
A muscle or gland that responds to a message from the nervous system.
Glucose
A simple sugar used by cells for energy.
Oxygen
A gas needed for cellular respiration.
Carbon dioxide
A gas produced as a waste during respiration. Removed through exhalation.
Water
A product of respiration and essential for life processes.
Energy
The ability to do work; released during respiration.
Homeostasis
Keeping internal conditions (like temperature or blood sugar) stable.
Negative feedback
A process that reverses a change to keep conditions stable.
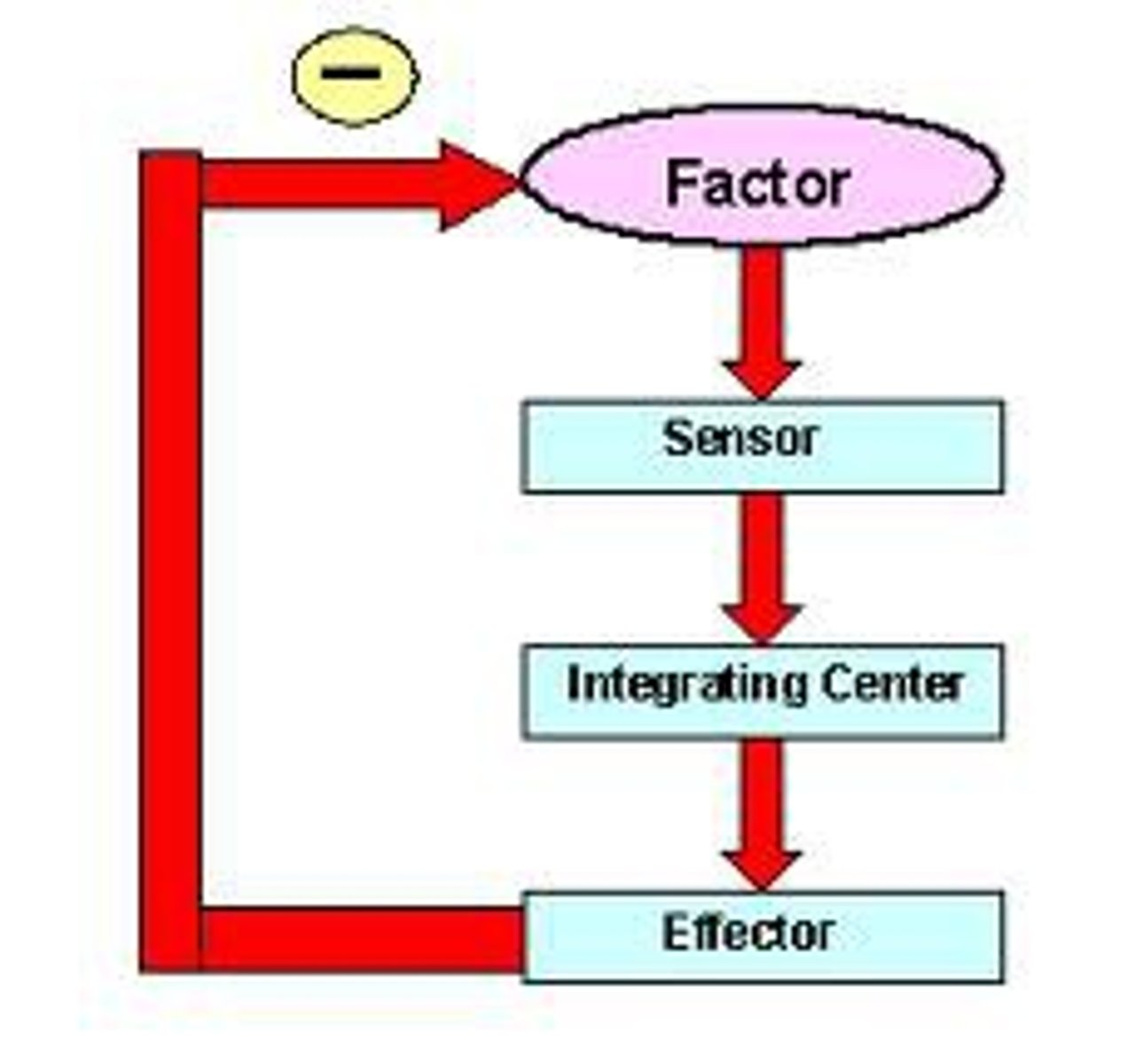
Stimulus response model
Describes how the body detects and responds to changes (stimulus → receptor → modulator → effector → response).
Modulator
The control centre that processes information and sends instructions (e.g., brain or spinal cord).
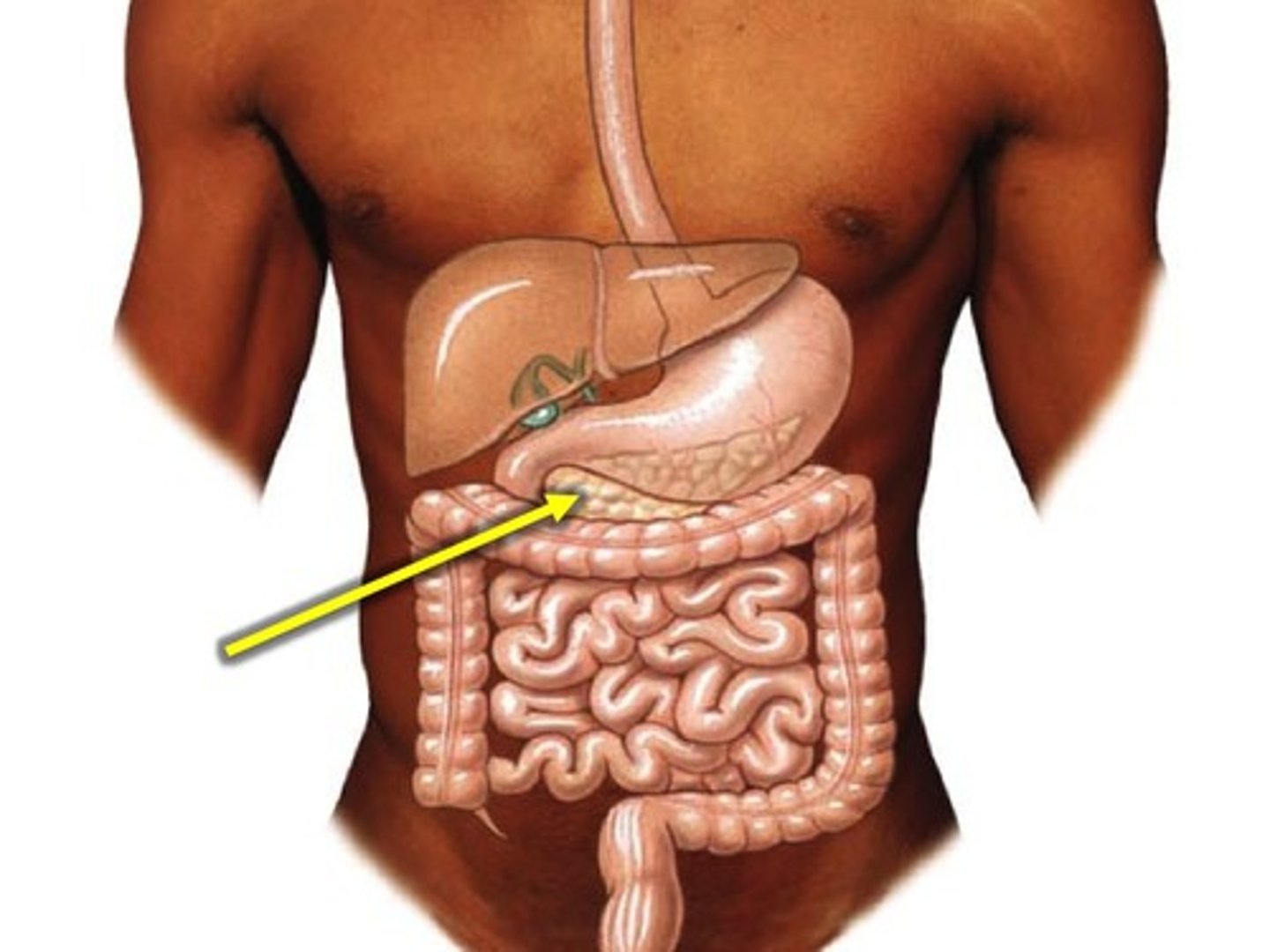
Pancreas
An organ that helps control blood sugar by producing insulin and glucagon.
Glycogen
The stored form of glucose in the liver and muscles.
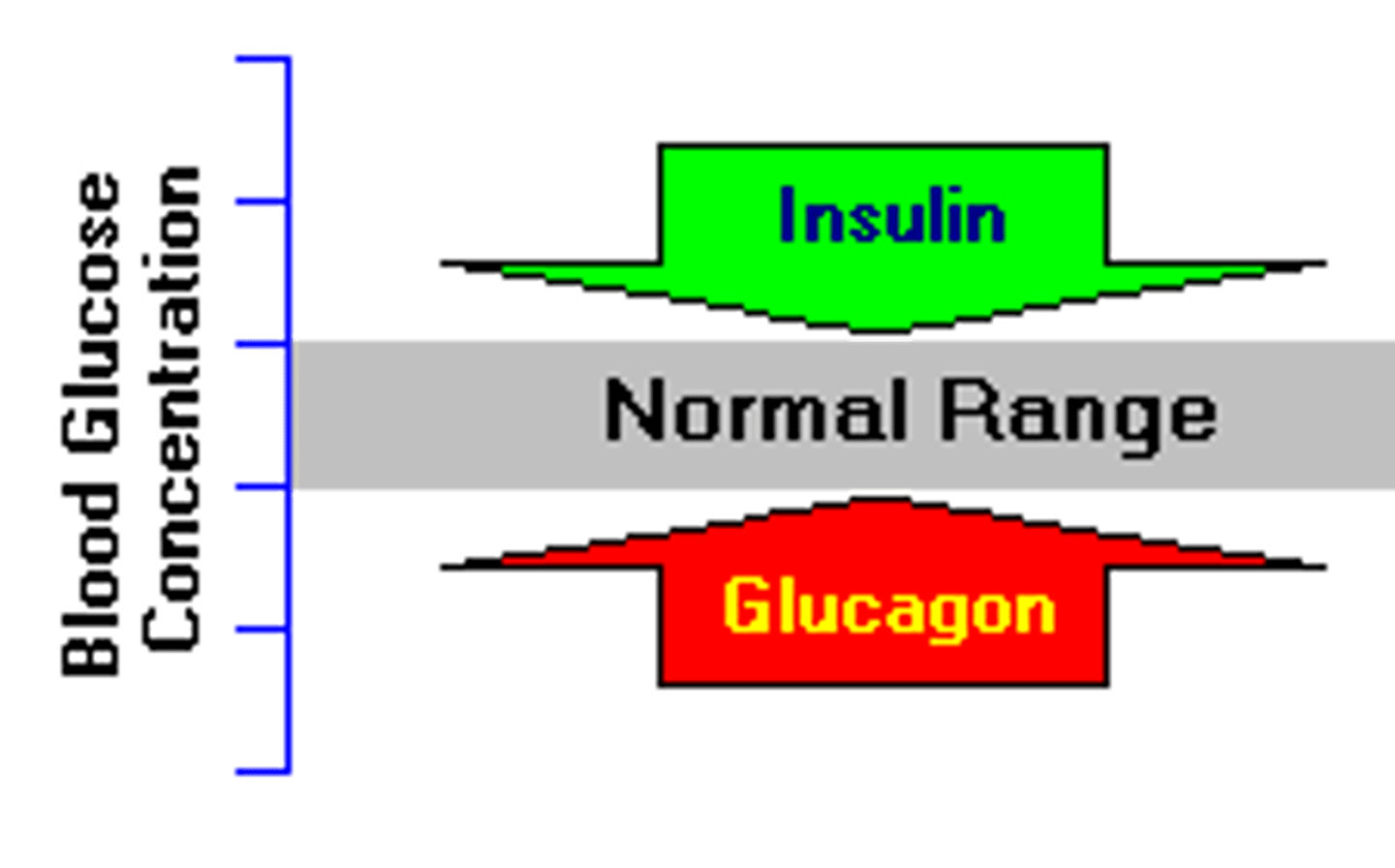
Insulin
Hormone that lowers blood sugar levels.
Glucagon
A hormone that raises blood sugar levels.
Hypothalamus
Part of the brain that controls temperature, hunger, and other automatic functions.
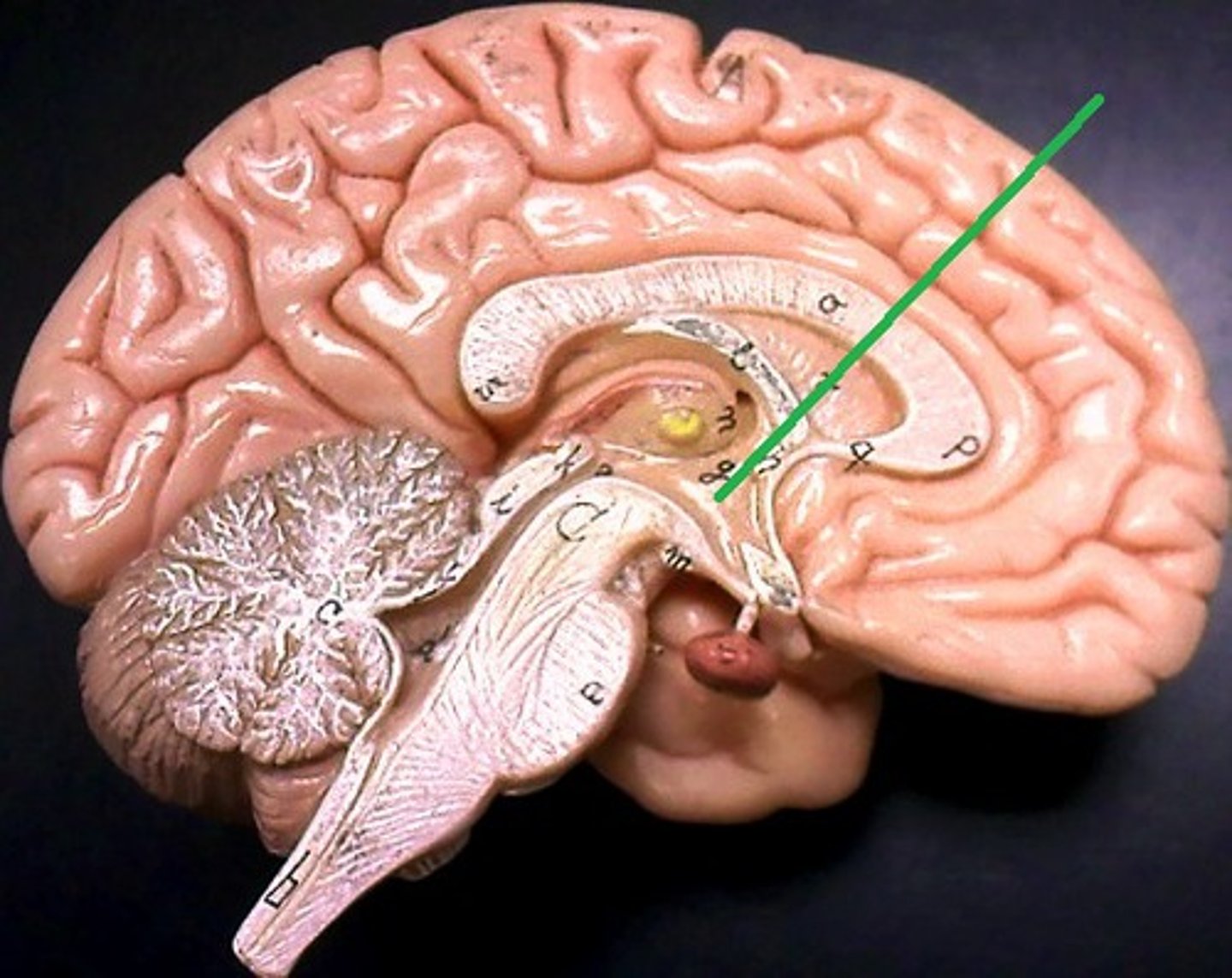
Mucous
A sticky substance that traps dust and germs.
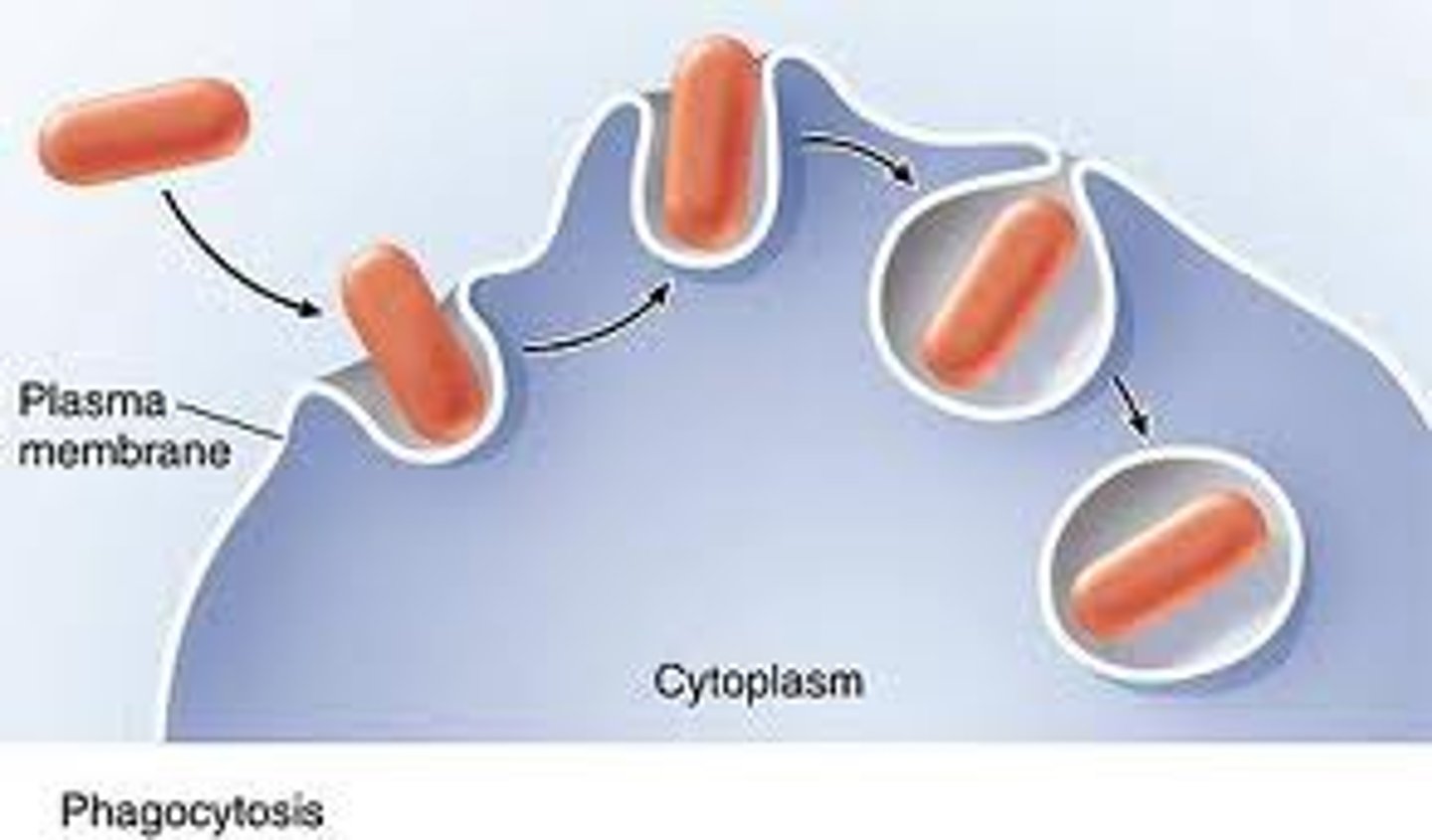
Phagocytosis
When white blood cells surround and engulf (eat) harmful microbes.
Antigen
A molecule on a pathogen that triggers an immune response.
Antibodies
Proteins made by the immune system to attack specific antigens.
Lymphocytes
White blood cells that produce antibodies and help fight infection.
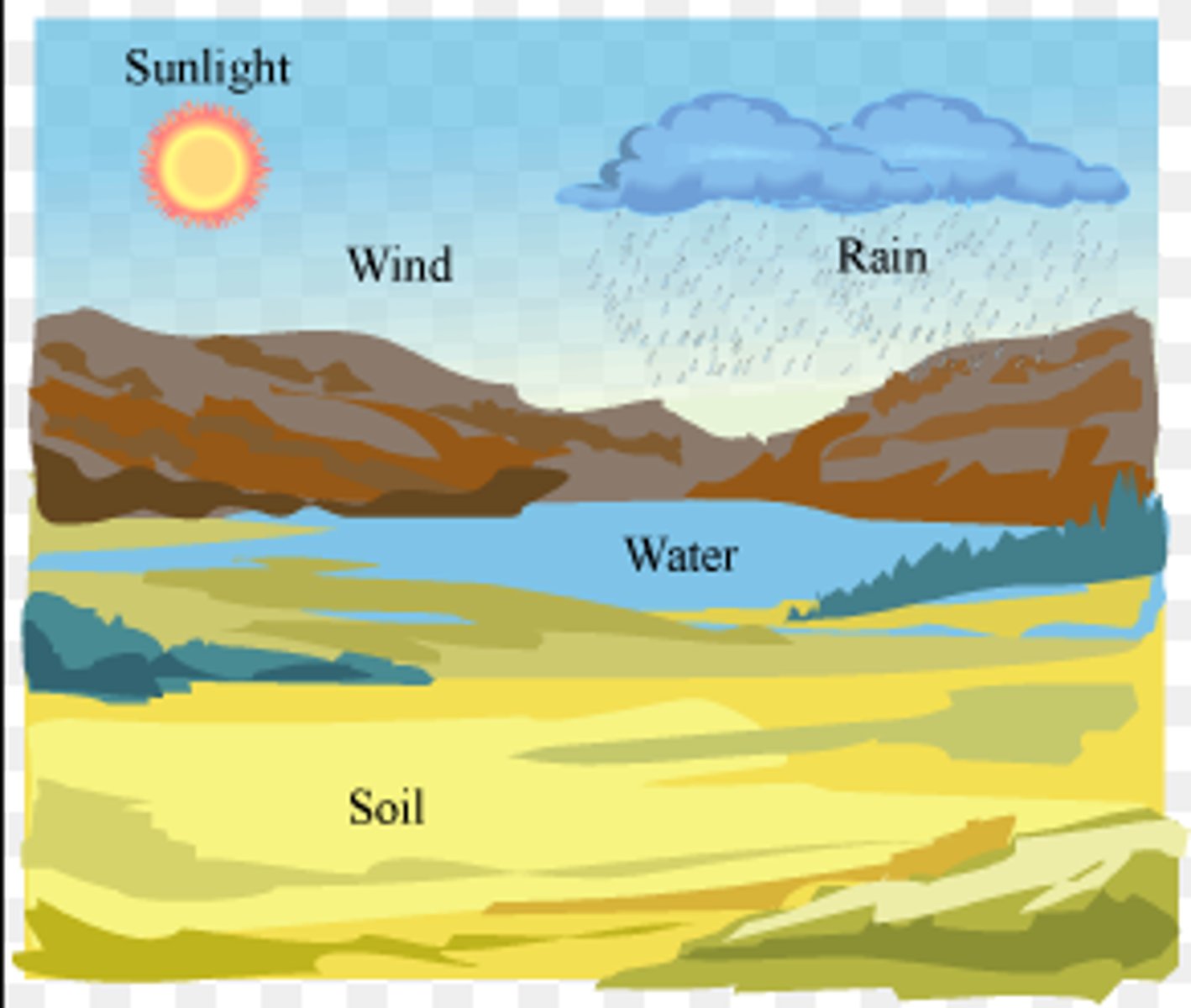
Abiotic Factors
The non-living parts of an environment such as sunlight, temperature, water, and soil.
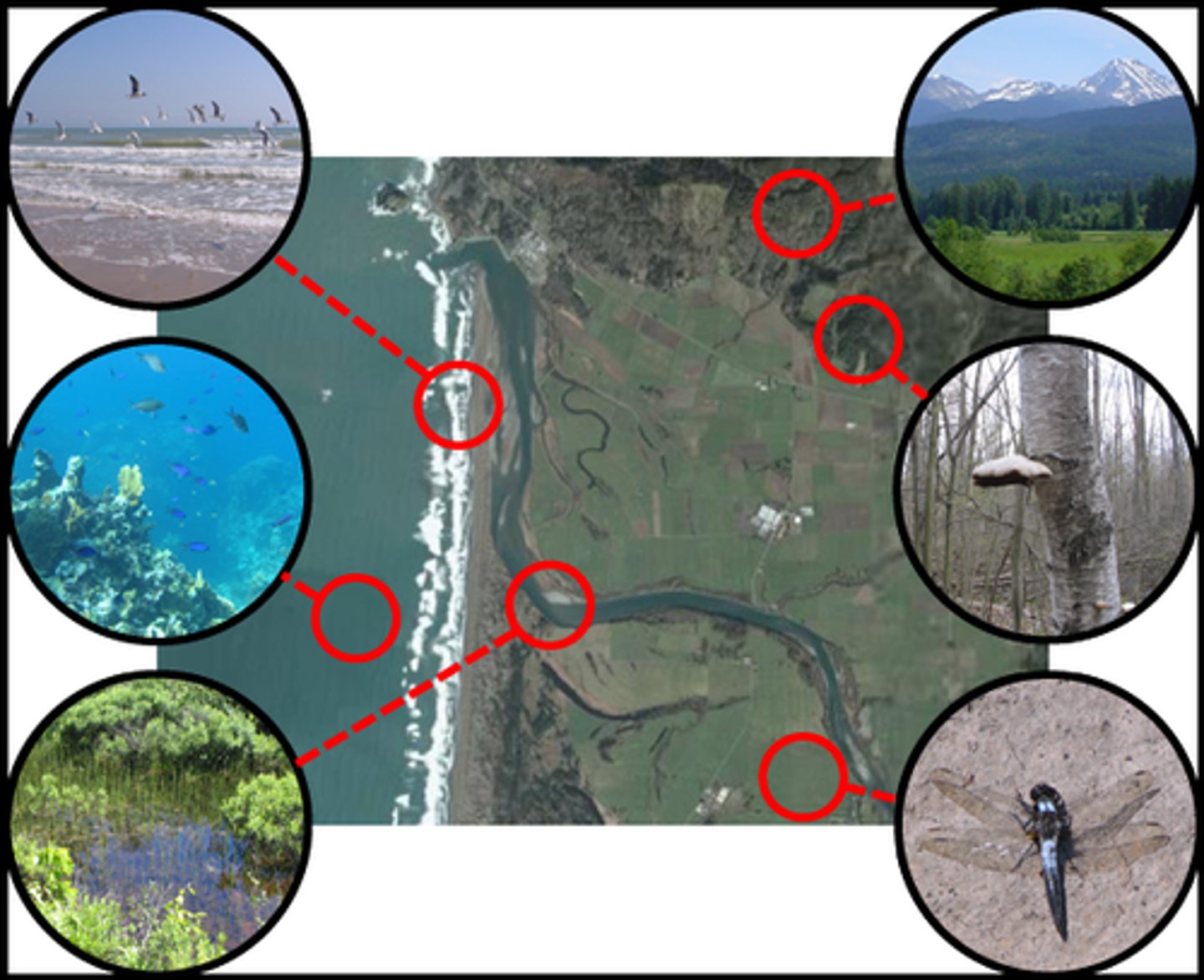
Biotic Factors
Fire-stick farming
A traditional Indigenous Australian practice of using controlled burns to manage the land, promote new plant growth, and attract animals for hunting.
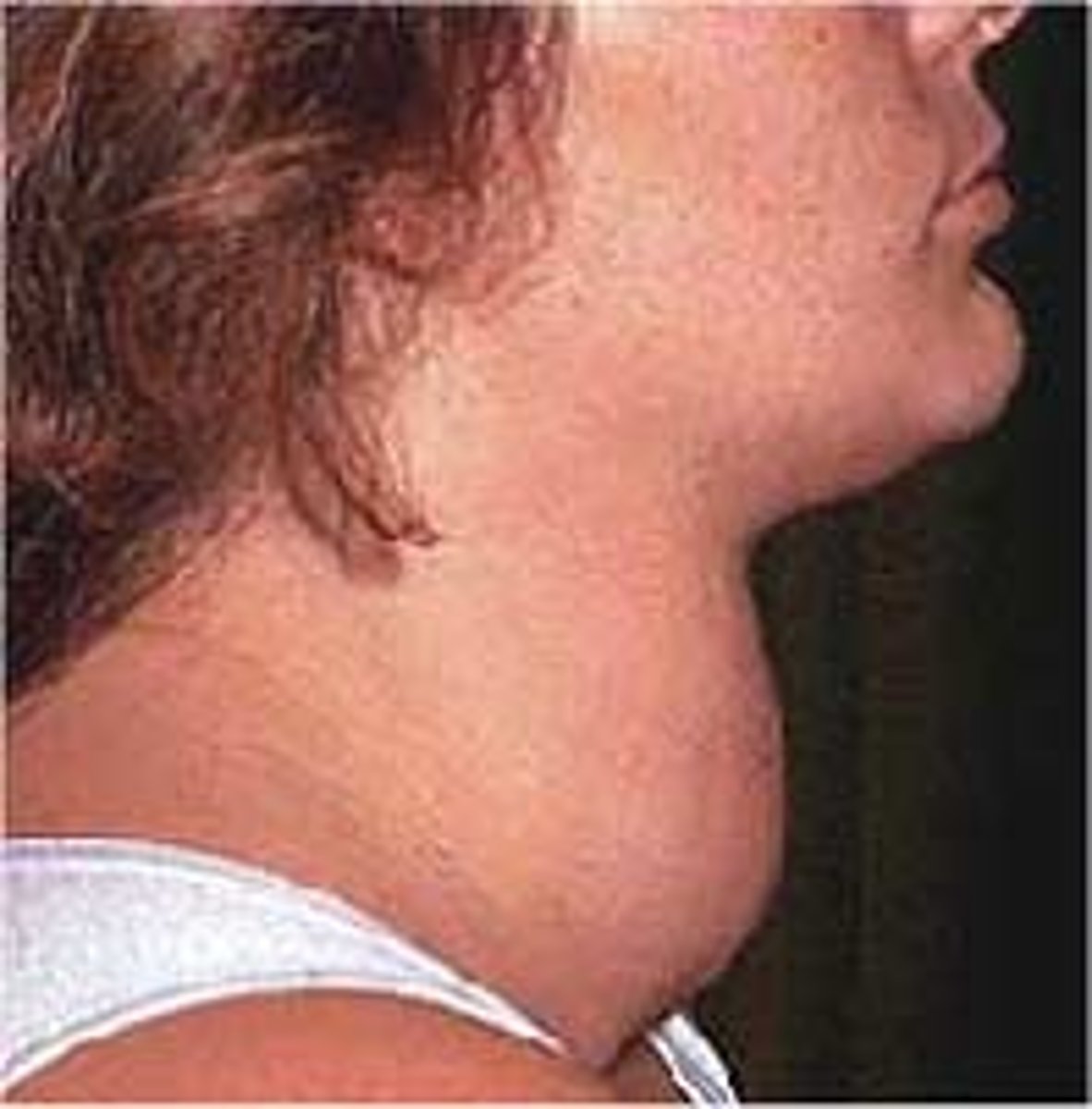
Goitre
An enlargement of the thyroid gland, usually caused by a lack of iodine in the diet or other thyroid problems.
Estrogen
Produced by the ovaries in females, responsible for the development of female secondary sexual characteristics and regulation of the menstrual cycle.
Testosterone
Produced mainly by the testes in males, responsible for the development of male secondary sexual characteristics and supporting sperm production.
Thyroxine
Hormone produced by the thyroid gland, which controls metabolism, growth, and development in the body.
Melatonin
Produced by the pineal gland in the brain, which helps regulate sleep.