BIO408 - TT1
1/90
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
Stephen Kuffler
Formed the first department of Neurobio in Harvard in 1966
Hippocrates
Idea of the brain as center for emotions and intelligence
Aristotle
Said the heart as centre of thought and emotions and the brain acts like a radiator
Galen
Brain is similar to the heart and so, its ventricles are like chambers of the heart
Vesalius
Still talked about the humoural theory - focus on ventricles
Descartes
Focus on ventricles - idea that they connect to control movement
18-19th Century Neurosci
Change from humoural theory to modern views due to increase in scientific process and methods
18th-19th Century Neurosci lead to the findings of
nerves as electrical wires
Different brain
Neutron doctrine - Cajal
Ventral Areas control
Motor functions
Dorsal Areas control
Sensory functions
4 Basic types of signal potentials
Resting membrane potentials, receptor potentials, Synaptic potentials, action potentials
Resting Membrane potential
baseline for all cells - don’t carry info and sre ‘static’
Receptor potentials
small amplitudes that are sensory inputs turned into electrical inputs → touch to signal
Synaptic Potentials
Synapse at neurons where its information from one neuron/area to another
Action potentials
largest amplitudes and are fixed in waveform → quickest form of signalling
Neural signals occur when
ions create electrical charges that move by ion [C] gradient
Ion levels in a cell
K = 100mM in side, 5mM out
Na = 15mM inside, 150mM out
Cl = 13 mM inside, 150mM out
Ca = 0.0002mM inside, 2mM out
Active transporters
ATPase pup
Ion exchanger
Need energy from ATP or [C] gradients of other ions
ATPase Pumps
Na/K pump = low Na in, high K in
Ca2+ pump = low Ca in
How does the Na/K ATPase pump work?
conformation change that allows Na binding and ATP binds
pump becomes phosphorylated → P only and pump closed
conformational change to release Na out and K binds from outside
Pump phosphorylated and loses P
ATP binds to let K inside and Na binds again
restart
How many Na/K get bound/let out or in?
3 Na out and 2 K in
How do Ion exchangers work?
Use the energy of the Na/K [C] gradients made from ATPase pumps
What are the two main categories of ion exhangers?
Antiporters and co-transporters
What are two types of Antiporters and how do they work?
Na/Ca exchanger - keep Ca low inside
Na/H exchanger. -regulates pH - H out
These work in opposite directions, where one ion goes inside, and the other out
What are the 3 types of co-transporters and how do they work?
Na/K/Cl co-transport - Cl inside
K/Cl - co-transport - regulates Cl out
Na/NTs co-transport - synapses
These work by ions moving in the same direction in or out
How are ion gradients established?
ion gradients
ion channels
Why ion channels?
They allow ions to diffuse down their [C] gradients high to low and are selectively permeable
Is resting membrane pot Vm = 0?
NO! thats why we have ion channels, they control RMP
What if we had no ion channels?
Then no e- potential - so no resting membrane
How is the RMP created?
K moves across [C] gradient - chemical pot
Then ± charges re-distribute and causes to build up e- potential around membrane
will lead up and countinue to flow until eq.potential of K = negative
then Na also flows and has + potential(not exactly eq.pot in the cell)
Chemical potential is the
flow of ions
Electrical potential is the
flow of charges
The Nernst Equation
z = ion charge
ion out = outside ion [C]
ion in = inside ion [C]
![<p>z = ion charge</p><p>ion out = outside ion [C]</p><p>ion in = inside ion [C]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/cb789efd-88de-4e6c-99b6-7cdffdeff077.png)
If there was only one type of ion channel then resting
Vm equals to eq.potential of that ion
What is the E ion for the major 3 ion types?
K = -80 mV
Na = 62 mV
Cl = -65 mV
The smaller the ion-out/ion-in ratio is, the
more negative the Eion is
Goldman=Hodgkin-Katz equation
Vm = 62log(permeability out of ions)/(permeability of ions in)
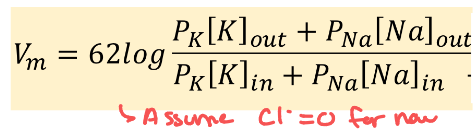
What is an assumption of Goldman equation?
Cl = 0
In a cell, Vm is closer to the eq.potential of the ion that is
more permeable
if PK/PNa = 40, then
Vm = closer to K, so more (-)
What are 2 categories of ion channels?
Leakage channels
Gated ion channels
What do voltage-gated ion channels do?
They open at the action potential, increasing permeability of their ion
How do the Na voltage gated ion channels work?
Opens early when a positive stimulus comes by to trigger a more + potential and opens Na quickly
How do the K voltage-gated channels work?
Open late after the Na channel and slow to close - slow to open and close, lead to hyperpolarize
What are the 4 steps of the AP
Rising Phase = Na increases
Overshoot = Na at max, K opens
Falling = Na decreased and K reaches max
Undershoot = Na inactive and K decreases
What are the two feedback groups of the AP
+ feedback = Na increase → keeps opening and opening(until it eventually has no more Na channels to open) = self-sustaining
- feedback = K channels open to hyperpolarize membrane and restore to RMP
How does the AP Propogate?
By the nodes of Ranvier - jumps → as the signal moves through the axon, it activates the next channels(because of Na) and decreases in past channels(because of K)
What are the 5 steps of the AP propogation?
AP starts at axon hillock - Na channels
Cytoplasm is conductive to allow Ap to move
Depolarization of volt-gated Na channels downstream
repeat of process to propagate AP
AP moves to terminal via Na and not backwards due to K
What are the 3 types of ligand-gated channels?
NTs
Proton(H+)
Second messengers - Ca, cAMP
What are thermoreceptors?
Detect changes in temperature, hot or cold - also capsaicin for heat receptors
What are mechanoreceptors?
Detect pressure stimuli, sound, distortion of cytoplasmic membrane.
Synaptic transmission needs:
AP and synaptic potentials - pre and post synapse stuff
What are the 2 types of synapses?
Electrical and Chemical
What are electrical synapse?
Flow of ions - narrow gaps, very closely connected synapses, no vesicles and low receptor selectivity
What are chemical synapses?
Flow of NTs → have larger gap junctions, vesicles, and more selective receptors
Why are electrical synapses special?
They are muchhh faster than chemical ones - minimal delay in sending signal
With electrical synapses, there is increased(word for togtherness)
synchrony and connection of communication → bidirectional
What are 2 unique things about chemical synapses?
Greater gap and specialized receptors on post-synapse
What are the 6 events during pre-synapse?
AP comes to axon terminal
NTs made and ready in vesicles
Ca channels open up by depolarization
[Ca] influx
Ca and synaptogmins cause vesicles to fuse with synaptic membrane
NTs leave via exocytosis
Why is Ca so important?
Ca triggers NT release - without it, no signal to post-synapse - needed and is sufficient for synaptic transmission
What are the 6 post-synapse events?
NTs exocytosis into synapse
NTs bind to post-synaptic receptors
open/close channels
IPSP/EPSP
NTs removed from synapse
NTs stored into vesicle on pre-synapse
What are the 2 types of NT receptors?
Ionotropic and metabotropic
What are ionotropic receptors?
They are like ion channels - open once receptor binds → 3 step process
What are metabotropic receptors?
Use GCPRs to open - ligand gated and 4-5 steps
What are the differences between iontotropic and metabotropic receptors?
Ionotropic = faster, use nicotinic acetyl, and encode info
Metabotropic = slower, musacrinic, and excitability and NT release
What are excitatory synapse?
Use glutamate, +, AMPA receptors, and Na flow to dep.
What are inhibitory synapses?
Use GABA, -, Cl flow, and hyperpolarize
What is the threshold for AP firing?
-40mV
What is synaptic summation?
When many signals come in at once to fire AP
What is synaptic temporal sumamtion?
When signals come in one after the other - timed summation
What are the 2 parts of a neuron?
Soma and neurite(axon/dendrites)
What are 3 types of neurons Cajal found?
purkinje, pyramidial, ganglion
Why are pyramidial neurons special?
They can be located and branch into many areas of the brain
Non-pyramidial neurons are
interneurons - one area
Bitufted neurons
have 2 sides f dendrites, ex. pyramidial neurons
What are some neuron axon shapes?
Basket - round axon shape
Chandelier = axons fall
What are some gene classifications of neruons?
GABA = Parvalbumin, somatostatin
Ca = Calbindin, calretinin
VGAT, GAD = GABA (package and making)
ChAT = Ach
What are the 4 types of neuron firing?
non-acomodating = doesn’t increase/decrease = same
accomodating = firing decreases with time
Fast spiking = fast burst then decreases
Irregular = no certain way or pattern
What firing do pyramidial cells use?
use glutamate, VGLUTS, and all 4 types
What firing do basket cells use?
GABA, parv, VGAT, GAD = fast and non-accomodating
What do martinotti cells use to fire?
GABA, Somato, VGAT, GAD = reg. and accommodating
What is the knee jerk reflex?
Uses the motor and sensory neurons to jerk knee when hit
What are the steps to the knee jerk reflex?
hit knee, sensory neurons active in spinal cord - internuerons - inhibit flexor
motor neurons activate extensor, relax flexor
leg extends
What are 5 ways to study neurons?
Extracellular recording
intracellular recordings
Ca functional imaging - use GFP, Ca, calmodulin binding etc
Using Gene tools like Cre-LoxP, cre recombinase excisons
Scaning tools
What is synaptic plasticity?
Strengthen of connections over time
What are the 2 types of plasticity?
LTM and STM
What is STM?
Short-term - so after 1 AP = facilitation
What does STM use?
increases Ca = more NTs in pre-synapse to allow AP firining
What is synaptic depression?
What increases tetanic stimulation arises, depletion of vesicle pool, less NTs to leave, and depression of AP
What is post-tetanic potentiation?
when increase tetanic stimulation lets more Ca in → instead of depletion
What is LTP?
Long-term potentiation - on a longer scale → lasts for a longer time