QC1 LEC MIDTERMS: Chemical Reactions used in Titrimetry
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
105 Terms
Formula for Titer Value
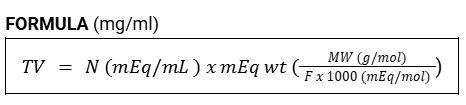
Standardization
The determination of the concentration of a solution (N or M)
Standardization
Accomplished by the use of another standard solution known as SECONDARY STANDARD or by the use of known purity substance as PRIMARY STANDARD
Primary Standard
Solid substance used for direct standardization of a solution
Formula for Primary Standard
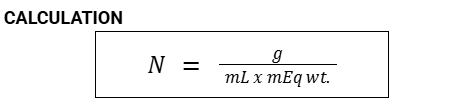
Secondary Standard
Liquid substance
Solution of known concentration
Formula for Secondary Standard
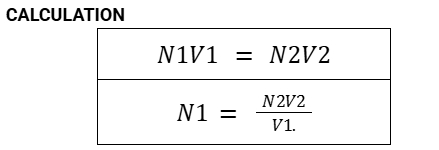
KHP (Potassium Hydrogen Phthalate)
Sulfamic Acid
Primary Standard of NaOH
Phenolphthalein
Indicator of NaOH
Sodium Carbonate
Primary Standard of HCl
Phenolphthalein
Indicator of HCl
NaCl (Sodium Chloride)
Primary Standard of Silver Nitrate
Potassium Chromate
Indicator of Silver Nitrate
Calcium Carbonate
Primary Standard of EDTA
Hydroxynaphthol
Indicator of EDTA
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid
EDTA
Sodium Oxalate
Standard Solution of Potassium Permanganate (KMnO4)
Arsenic Oxide (As2O3)
Primary Standard of Iodine
Starch
Indicator of Iodine
Benzoic Acid
Primary Standard of Sodium Methoxide
Thymol Blue
Indicator of Sodium Methoxide
Arsenic Oxide (As2O3)
Primary Standard of Ceric Sulfate
Orthopenanthroline
Indicator of Ceric Sulfate
Sodium Tartrate
Primary Standard of Karl Fisher Reagent
Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH)
Secondary Standard of HCl
Ferric Allum
Indicator of Ammonium Thiocyanate (NH4SCN)
Silver Nitrate (AgNO3)
Secondary Standard of Ammonium Thiocyanate (NH4SCN)
Iodine
Secondary Standard of Sodium Thiosulfate (Na2S2O3)
Starch
Indicator of Sodium Thiosulfate (Na2S2O3)
Burette
Pipette
Volumetric Apparatus: To Deliver
Volumetric Flask
Graduated Cylinder
Volumetric Apparatus: To Contain
Burette
Graduated glass tubes of uniform bore throughout the whole length
Burette
Closed at the bottom by glass or stopcock
Read at lower meniscus (for clear solutions)
MOHR
GEISSLER
Types of Burette
MOHR
Type of Burette:
For bases
A length of tubing connects a separate tip
Economical
GEISSLER
Types of Burette:
Acid burette
Built in stopcock
Expensive but more accurate
Direct Titration
Residual Titration
Types of Titrations
Direct Titration
One titrant used; one volumetric solution
Residual Titration
For compounds that reacts too slowly with the titrant and with poor solubility
Used when direct titration is not practicable
Used if volatile substances are involved
Residual Titration
Two titrants; two volumetric solution
1st VS
1st VS or 2nd VS: added in excess
2nd VS
1st VS or 2nd VS: used to titrate the excess
Blank Determination
Process of repeating the procedure but omitting the sample
Neutralization
Precipitation
Oxidation-Reduction
Complexation
Chemical Reactions used in Titrimetry
Reactions must proceed to completion.
Reaction must proceed in a stoichiometric manner.
Suitable endpoint detecting device must be available
For direct titration, reaction must be rapid so a sharp endpoint is achieved.
4 requirements that must be met if reaction is used
Neutralization
A Chemical process in which an acid (proton donor) reacts with a base (proton acceptor) [Bronsted-Lowry Theory]
Bronsted-Lowry Theory
What theory states that an acid (proton donor) reacts with a base (proton acceptor)
Acid
Acid or Base: Proton Donor
Base
Acid or Base: Proton Acceptor
Water and Salt
Determine the Product
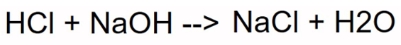
Indicator
Are complex organic compounds used to:
Determine endpoint
Determine the pH
Indicate that a desired change in pH has been effected
0 - 2.0
pH Range: Malachite Green
2.9 - 4.0
pH Range: Methyl Yellow
3.0 - 4.6
pH Range: Bromophenol Blue
3.2 - 4.4
pH Range: Methyl Orange
4.0 - 5.4
pH Range: Bromocresol Green
4.2 - 6.2
pH Range: Methyl Red
5.2 - 6.8
pH Range: Bromocresol Purple
6.0 - 7.6
pH Range: Bromothymol Blue
6.8 - 8.2
pH Range: Phenol Red
7.2 - 8.8
pH Range: Cresol Red
8.0 - 9.2
pH Range: Thymol Blue
8.0 - 10.0
pH Range: Phenolphthalein
9.3 - 10.5
pH Range: Thymolphthalein
Yellow
Green
Acid & Base: Malachite Green
Red
Yellow
Acid & Base: Methyl Yellow
Yellow
Blue
Acid & Base: Bromophenol Blue
Pink
Yellow
Acid & Base: Methyl Orange
Yellow
Blue
Acid & Base: Bromocresol Green
Red
Yellow
Acid & Base: Methyl Red
Yellow
Purple
Acid & Base: Bromocresol Purple
Yellow
Blue
Acid & Base: Bromothymol Blue
Yellow
Red
Acid & Base: Phenol Red
Yellow
Red
Acid & Base: Cresol Red
Yellow
Blue
Acid & Base: Thymol Blue
Colorless
Red
Acid & Base: Phenolphthalein
Colorless
Blue
Acid & Base: Thymolphthalein
3 drops
Rules for Using Indicator: Use ____ of indicator TS unless otherwise directed
Strong Acid
Determine: Strong Acid, String Base, Weak Acid, or Weak Base
Hydriodic Acid (HI)
Strong Acid
Determine: Strong Acid, String Base, Weak Acid, or Weak Base
Hydrobromic Acid (HBr)
Strong Acid
Determine: Strong Acid, String Base, Weak Acid, or Weak Base
Hydrochloric Acid (HCl)
Strong Acid
Determine: Strong Acid, String Base, Weak Acid, or Weak Base
Sulfuric Acid (H2SO4)
Strong Acid
Determine: Strong Acid, String Base, Weak Acid, or Weak Base
Nitric Acid (HNO3)
Strong Acid
Determine: Strong Acid, String Base, Weak Acid, or Weak Base
Chloric Acid (HClO3)
Strong Acid
Determine: Strong Acid, String Base, Weak Acid, or Weak Base
Perchloric Acid (HClO4)
Weak Acid
Determine: Strong Acid, String Base, Weak Acid, or Weak Base
Acetic Acid (CH3COOH)
Weak Acid
Determine: Strong Acid, String Base, Weak Acid, or Weak Base
Oxalic Acid (C2H2O4)
Weak Acid
Determine: Strong Acid, String Base, Weak Acid, or Weak Base
Hydrofluoric Acid (HF)
Weak Acid
Determine: Strong Acid, String Base, Weak Acid, or Weak Base
Hydrogen Cyanide (HCN)
Strong Base
Determine: Strong Acid, String Base, Weak Acid, or Weak Base
Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH)
Strong Base
Determine: Strong Acid, String Base, Weak Acid, or Weak Base
Potassium Hydroxide (KOH)
Weak Base
Determine: Strong Acid, String Base, Weak Acid, or Weak Base
Alanine (C3H5O2NH2)
Weak Base
Determine: Strong Acid, String Base, Weak Acid, or Weak Base
Ammonia (NH3)
Weak Base
Determine: Strong Acid, String Base, Weak Acid, or Weak Base
Methylamine (CH3NH2)
Weak Base
Determine: Strong Acid, String Base, Weak Acid, or Weak Base
Pyridine (C5H5N)
Hydrochloric Acid
Sulfuric Acid
Standard Acid Solution
Hydrochloric Acid (HCl)
Standard Acid Solution:
Preferably used in titration of compounds that yield a precipitate if used with H₂SO₄
Ex: Barium Hydroxide
Sulfuric Acid (H2SO4)
Standard Acid Solution:
Preferable in hot titrations (HCl is volatile if heat is applied)
Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH)
Potassium Hydroxide (KOH)
Barium Hydroxide (Ba(OH)2)
Standard Basic Solutions
NaOH, KOH, Ba(OH)₂
Absorb CO₂ in the air thereby changing rapidly in conc.