Bonding test Study Guide
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Cations
Formed by losing all valence electrons
Positively charged
Alkali metals(Group 1A), Alkaline earth metals (Group 2A), Group 3A
Anions
Formed by gaining 1 or more valence electrons
negatively charged
Group 5A, Group 6A, Halogens ( Group 7A)
Polyatomics
Ammonium: NH4 1+
Acetate: C2H3O2 1-
Hydroxide: OH 1-
Cyanide: CN 1-
Nitrate: NO3 1-
Bicarbonate: HCO3 1-
Carbonate: CO3 2-
Sulfate:SO4 2-
Chromate: CrO4 2-
Phosphate:PO4 3-
Naming Polyatomics
Ate - Base
Ite - Minus 1 oxygen
Per- plus 1 oxygen
Hypo ite - Minus 2 oxygen
Naming Ionic
First name metal, then non-metal
Transition metals use Roman numerals as well as Tin and Lead
Non-transition metals with known charges are just the element name, as well as silver, zinc, and cadmium
For non-metals, just add ide to the end unless polyatomic
( to figure out subscripts, write the charges and then cross them)
Naming Covalent
use charge to determine charges.
The first non metal does not use mono
second non metal uses all prefixes and adds ide to the end
Prefixes
mono
di
tri
tetra
penta
hexta
hepta
octa
nona
deca
Properties of ionic compouds
ions are strongly bonded
structure is rigid
high meting points because of strong forces between ions
brittle
Ionic conductivity
conductivity requires charges that move
Solid (S): will not conduct
liquid (L): will conduct
dissolved in water(Aq): will conduct
Gas(s): Will not conduct
Metalic Bonding
two metals
Electrons are held loosely and free to move through a solid (Sea of electrons). Electrons are mobile
The attraction between cations and the sea of delocalized electrons
Solid (S): will conduct
liquird (L): will conduct
dissolved in water(Aq): will not conduct
Gas(s): Will not conduct
Metalic Properties
Malleable
Ductile - drawn into wires
Good conductors of heat
Good conductors of electricity
Sigma and Pi in Covalent Bonds
Single - 1 sigma
Double - 1 sigma, 1 pi
Tripple - 1 sigma, 2 pi
As the number of bonds grows, the bond grows shorter and stronger, the presence of pi brings the atom closer.
Ionic Bond
The transfer of valence electrons from cations to anions or metals to nonmetals
Covalent Bond
Sharing of a pair of valence electrons between anions or two non metals
cannot conduct electricity
Molecular structure
The central atom will be the least electronegative and the atom that there is the least amount of
Hydrogen will not be a central atom it is typically halogens
Diagramming molecular compounds
Count up valence electrons for each atom
Draw bonds and subtract 2 electrons for each bond
add additional electrons
If the octet/ duet rule is not met, try double bonds.
Boron will be happy with 6 and Hydrogen will be happy with 2
Formal charge
To make sure that the bonds are correct
Valence electrons - (the dots and lines added together) = 0
Bonding domains
Number of elements around the center
Non bonding domains
number of electron lone paires
Lone pairs + elements
Number of electron domains
Linear
Bonding domains : 2
nonbonding domains: 0
Number of electron domains: 2
Bond angle: 180
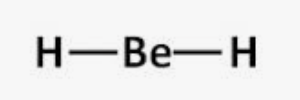
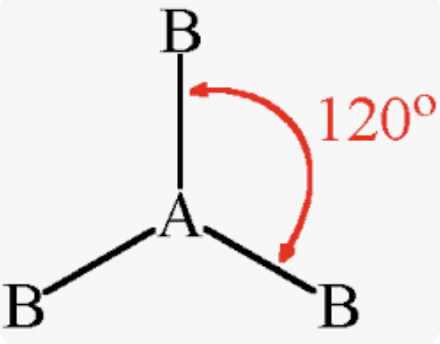
Trigonal Planar
Bonding domains : 3
nonbonding domains: 0
Number of electron domains: 3
Bond angle: 120
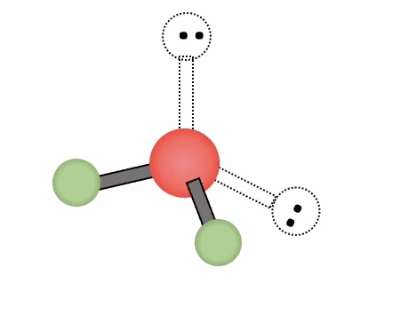
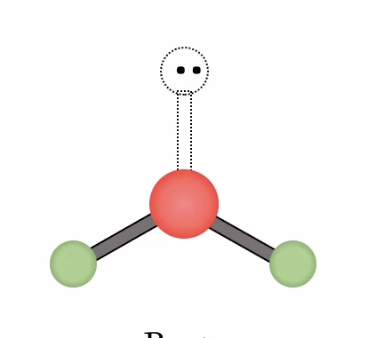
Bent ( single lone)
Bonding domains: 2
nonbonding domains: 1
Number of electron domains: 3
Bond angle: 117.5
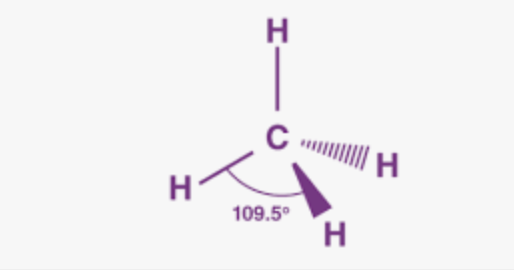
Tetrahedral
Bonding domains: 4
nonbonding domains: 0
Number of electron domains: 4
Bond angle: 109.5
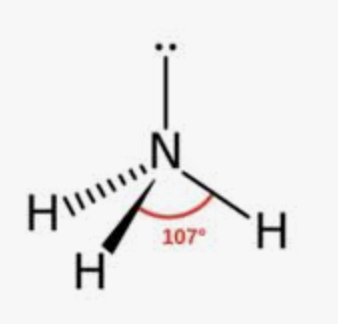
Trigonal Pyramidal
Bonding domains : 3
nonbonding domains: 1
Number of electron domains: 4
Bond angle: 107
Bent (Double lone)
Bonding domains: 2
nonbonding domains: 2
Number of electron domains: 4
Bond angle: 104.5