3.3 Physics Waves
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
Fill in the gaps: T_____ waves have particles that move __________ to the direction of the wave
Transverse waves have particles that move at right angles to the direction of the wave
Fill in the gaps: L_____ waves have particles that move __________ to the direction of the wave
Longitudinal waves have particles that move parallel to the direction of the wave
What is superposition?
Superposition is the resultant wave of multiple waves being at the same place at the same time, so is the vector sum of the individual waves.
What is diffraction?
Diffraction is the radiating out of wavefronts as they pass around a barrier or move through a gap.
When does constructive interference occur?
When 2 peaks or 2 troughs arrive at the same point at the same time and are in phase.
When does destructive interference occur?
When a peak and trough arrive at the same point at the same time and are out of phase.
What does it mean if two waves are coherent?
It means they have the same amplitude and frequency and are always exactly in phase.
What is the equation for beat frequency?
Fb= | F1-F2 |
What are beats?
Beats are the periodic and repeating loud and soft sounds heard when two sound waves of slightly different frequencies interfere with each other.
Fill in the gaps:
Explain why beats form-
When 2 ____ waves of slightly different __________ ________, ___________ regions of __________ and _________ interference cause a ________ and ________ ______.
When 2 sound waves of slightly different frequencies combine, alternating regions of constructive and destructive interference cause a periodic and repeating pattern.
What are nodes?
Nodes are points on a standing wave that are always at rest (skinny point)
What are antinodes?
Antinodes are points in a standing wave with the greatest displacement (fat point)
The distance between 2 adjacent nodes (or antinodes) is=
half the wavelength
What is the general frequency equation for standing waves on strings and waves in fully open pipes?
fn=nv/2L where n= the number harmonic
Name the pairs of names for the first 3 possibilities for standing waves on strings and waves in fully open pipes:
Fundamental- 1st harmonic
1st overtone- 2nd harmonic
2nd overtone- 3rd harmonic
Name the pairs of names for the first 3 possibilities for standing waves in half-open pipes:
Fundamental- 1st harmonic
2nd overtone- 3rd harmonic
4th overtone- 5th harmonic
For standing waves on a string what is the same as the number of the harmonic?
The number of antiodes
For waves in fully open pipes what is the same number as the number of the harmonic?
The number of nodes
for standing waves on strings and waves in fully open pipes, λ=
2L/n
For waves in half open pipes what is the same number as the number of the harmonic?
The number of nodes + number of anodes - 1
What is the general frequency equation for waves in halfopen pipes?
fn=nv/4L where n= the number harmonic
For waves in half open pipes, λ=
4L/n
In order to observe interference of light…
the light sources must emit light waves that are coherent (maintaining constant phase with each other) and monochromatic (have the same wavelength/colour).
What type of light device coherent and monochromatic?
A laser
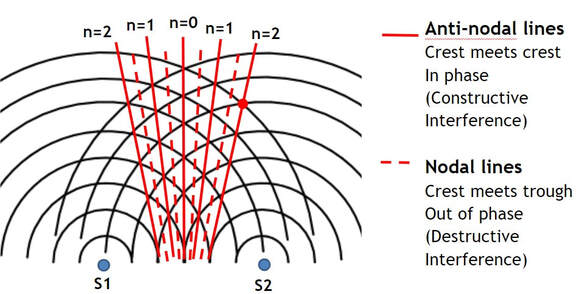
Describe anti-nodal lines for interference of light:
The positions where light waves reinforce from constructive interference of waves that are in phase, resulting in bright light. (maximum)
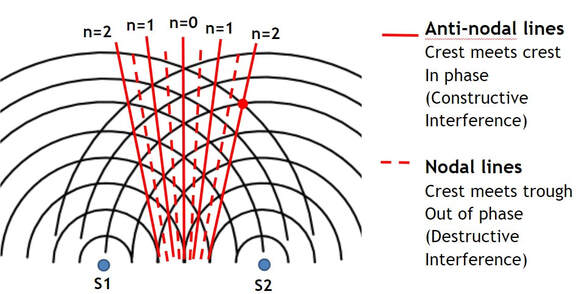
Describe nodal lines for interference of light:
Positions where light waves cancel out from the destructive interference of waves that are fully out of phase, resulting in no light. (minimum)
When do bright bands form on a screen?
When the antinodal line intersects the screen and when the path difference of light from the slits to the screen is a whole number of wavelengths.
When do dark bands form on a screen
When the nodal line intersects the screen and when the path difference of light from the slits to the screen is a half number of wavelengths.
What affect will shining a longer wavelength of light have on bands?
Bands will be further apart
What affect will shining a shorter wavelength of light have on bands?
Bands will be closer together
What affect will increasing the separation of the slits have on bands?
Bands will be closer together.
What affect will decreasing the separation of the slits have on bands?
Bands will be further apart.
What affect will moving the screen closer to the slits have on the bands?
Bands will be closer together.
What affect will moving the screen further away from the slits have on the bands?
The bands will be further apart.
In two source interference questions, what does λ stand for?
The wavelength in metres of the light through the slits.
In two source interference questions, what does θ stand for?
The angle from the central band to the nth band on the screen.
In two source interference questions, what does x stand for?
The distance from the central band to the nth band on the screen.
In two source interference questions, what does L stand for?
The distance in metres from the slits to the screen.
In two source interference questions, what does n stand for?
The order of the bright band. The central band has an order of 0
In two source interference questions, what does d stand for?
The distance in metres between the slits
What is a useful equation to link x and L?
tantheta = x/L
Fill in the gaps to explain what would be observed on the screen if the wavelength of the light decreased:
A _______ wavelength results in the pattern of ____ and _____ bands being ______ together. The ____nodes (______ bands) are created when the ____ __________ between the ____ of light from the two slits is equal to a _____ wavelength. When the wavelength is _______, the path difference to ____ an antinode will be ____, so the _________ will be bunched ______ together.
A smaller wavelength results in the pattern of dark and light bands being closer together. The antinodes (bright bands) are created when the path difference between the rays of light from the two slits is equal to a whole wavelength. When the wavelength is smaller, the path difference to form an antinode will be less, so the atinodes will be bunched closer together.
Fill in the gaps to explain what would be observed on the screen if the spacing between the slits was decreased:
A ________ spacing between the _____ would result in the pattern of ______ and ____ bands being _______ apart. The ____nodes (______ bands) are created when the path __________ between the ____ of light from the two slits is equal to a _____ wavelength. When the slits are ______ together, a ______ angle is needed to the get the ____ path difference, as the rays of light start off ______ together, so the antinodes will spread _______ apart at ______ angles.
A decreased spacing between the slits would result in the pattern of bright and dark bands being further apart. The antinodes (bright bands) are created when the path difference between the rays of light from the two slits is equal to a whole wavelength. When the slits are closer together, a larger angle is needed to the get the same path difference, as the rays of light start off closer together, so the antinodes will spread further apart at larger angles.
When can the equation nλ=dx/L be used?
When the angle between the central antinode and the adjacent antinode is small.
For diffraction gratings, d=
1/N where N is lines per metre
Fill in the gaps:
For ___________ gratings, bright bands are _______, and more _______ than in a ______ slit experiment due to ____ point sources so more positions of __________ interference. Bright bands are also ______ due to more sources so more points of _________ interference.
For diffraction gratings, bright bands are thinner, and more distinct than in a double slit experiment due to more point sources so more positions of destructive interference. Bright bands are also brighter due to more sources so more points of constructive interference.
As the number of slits increases, the fringes: (4)
get more defined (sharper)
get narrower
pattern gets brighter overall (more gaps for light to go through)
have same central maximum
Fill in the gaps to explain trends with increased number of slits:
As the number of _____ increases, the number of _______ with the right path __________ for CI increases, making the fringes ________. At the same time, the _____ required for CI becomes more _______ and so the fringes become _______. The amount of destructive interference _________ and so the ______ get wider, making the maxima ________.
As the number of slits increases, the number of sources with the right path difference for CI increases, making the fringes brighter. At the same time, the angle required for CI becomes more precise and so the fringes become sharper. The amount of destructive interference increases and so the minima get wider, making the maxima narrower.
Where is sound intensity the greatest for two source sound interference?
At the central maximum (anti-nodal line)
Fill in the gaps to explain what would happen to the loud sounds along a line if the two speakers emit a lower frequency:
A lower frequency sound has a ______ wavelength. The 1st ____ position from the ______ occurs when the ____ difference is 1 __________, so will now be at a _____ angle from the centre. A larger _____ means the ____ positions are _______ apart.
A lower frequency sound has a longer wavelength. The 1st loud position from the centre occurs when the path difference is 1 wavelength, so will now be at a larger angle from the centre. A larger angle means the loud positions are further apart.
Fill in the gaps to explain what would happen to the loud sounds along a line if the distance between two speakers is increased:
The 1st loud position from the centre occurs when the path ___________ is _ wavelength. When the speakers are ______ apart, a _______ angle from the centre is needed to achieve a ____ difference of 1 wavelength. A _______ angle means the loud positions will be _____ together.
The 1st loud position from the centre occurs when the path difference is 1 wavelength. When the speakers are further apart, a smaller angle from the centre is needed to achieve a path difference of 1 wavelength. A smaller angle means the loud positions will be closer together.
What is resonance?
Resonance is when the amplitude of oscillations increases when the driver frequency is equal to the natural frequency (the frequency the system would oscillate at without the driver).
How does the angle affect doppler shift for a source passing an observer?
As theta increases, the component of Vs pointing towards the observer decreases. =100% when theta=0 and o% when theta=90º
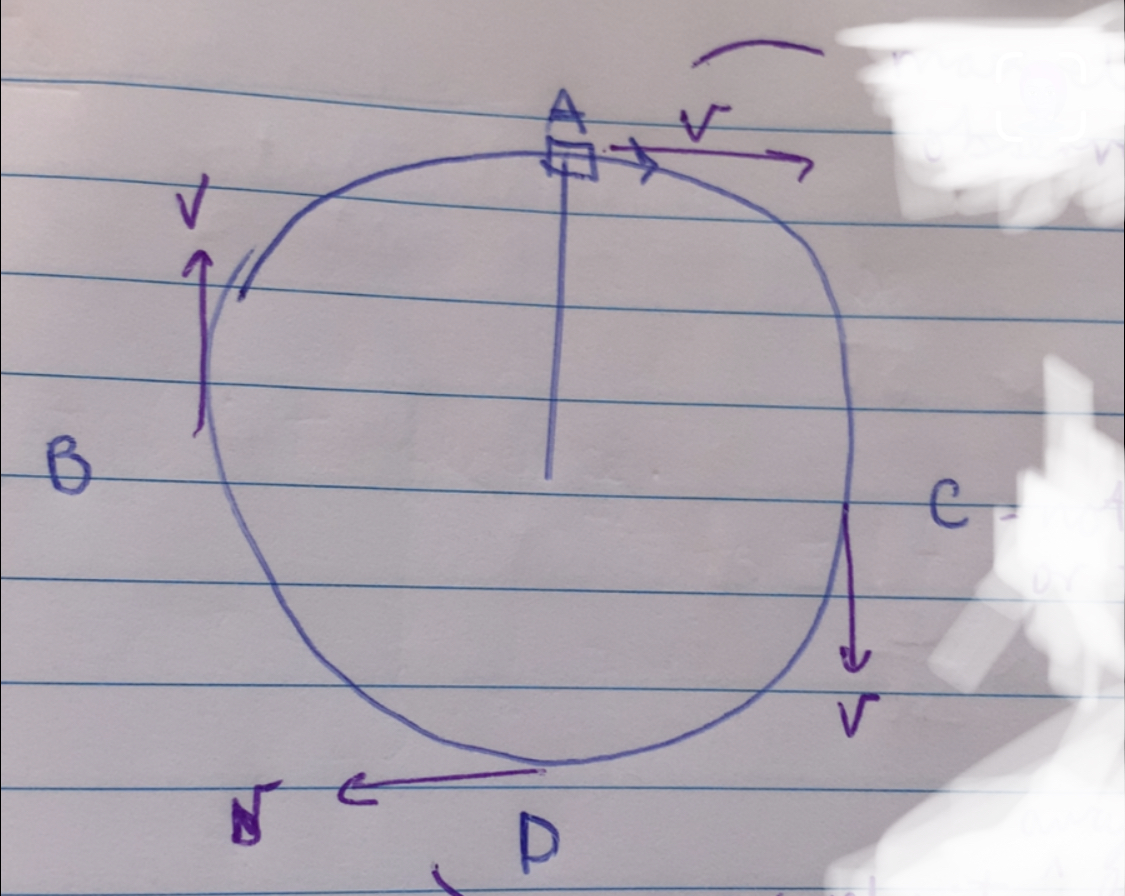
Explain the f’ in positions A and C if the observer is on the right of the diagram:
A- max velocity towards observer so f’ is highest
C- not moving away of towards so f’=0 so no doppler shift
Shorter wavelength=
= higher frequency= higher pitch
longer wavelength=
= lower frequency= lower pitch
What is the doppler effect?
The Doppler effect is the shift in frequency of a wave whenever there is relative motion between the wave source and the observer.
Fill in the gaps to explain ambulance towards child doppler effect example:
The child hears a ________ frequency sound that is ______ than the _________ heard by the driver. This is because __________ arrive at the child with a _______ wavelength than those _______ by the siren as the ambulance _______ up on wavefronts that were emitted slightly _______.
Note that the wave _____ of the sound waves remains ________.
The child hears a constant frequency sound that is higher than the frequency heard by the driver. This is because wavefronts arrive at the child with a shorter wavelength than those emitted by the siren as the ambulance catches up on wavefronts that were emitted slightly earlier.
Note that the wave speed of the sound waves remains constant.
When is a doppler effect observed (speed)?
A doppler effect is observed when the speed of the source is slower than the speed of the waves.
Fill in the gaps:
What happens if a wave source travels at the speed of sound?
The wavefront ____________ _____ up causing a buildup of ________ (a _____ wave) ______ the source. An observer does ___ hear a sound until the _____ wave arrives. The ______ change in pressure is experienced as a ____ noise or ‘_____ ____’.
The wavefront compressions bunch up causing a buildup of pressure (a shock wave) behind the source. An observer does not hear a sound until the shock wave arrives. The sudden change in pressure is experienced as a loud noise or ‘sonic boom’.
Fill in the gaps:
What happens if a wave source travels faster than the speed of sound?
If a wave ______ travels ______ than the speed of sound then the sound waves _____ _____ up to the source. The _____ wave has a ____ shape. The _____ wave is heard whenever the ____ passes over the observer.
If a wave source travels faster than the speed of sound then the sound waves never catch up to the source. The shock wave has a cone shape. The shock wave is hear whenever the cone passes over the observer.
What sign is the Vs in the equation for f’ when the source is coming towards the observer?
f’ > 0 so -Vs
What sign is the Vs in the equation for f’ when the source is going away from the observer?
f’ < 0 so +Vs
What is necessary for an even number harmonic to form?
An even number of quarter wavelengths.