ACC 377 - Chapter 2: Risks and Risk Assessment
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Risk
The likelihood of an unfavorable event occurring, including anything that can hinder a business from achieving its goals or cause a loss.
Differs by business type, size, industry, and location.
Drives innovation and competitive advantage.
Risk-Aware Culture
An environment characterized by leadership that…
Sets a risk-awareness tone at the top.
Encourages employees to discuss risk openly.
Aligns risk across all corporate initiatives.
Risk Assessment
A formal assessment that identifies, categorizes, and prioritizes individual risks in a company.
Used by management to decide how to manage risk.
Must know where risk exists in the organization structure.
Business Function
A high-level business area/department that performs business processes to achieve company goals.
Companies consider risk at this level.
More than one can be necessary for a single business process.
Broad function = Less specific identification of risk.
Portfolio View
A view of risk that examines risk at the entity level.
Profile View
A view of risk that examines risk at the granular level of a business function, process, or event.
Enterprise Risk Management (ERM)
The comprehensive process of identifying, categorizing, prioritizing, and responding to a company’s risks.
Involves creating formal risk assessments.
What are the 4 steps to assess and address risk?
Risk identification (assess).
Risk categorization (assess).
Risk prioritization (assess).
Risk response (address).
What is risk identification?
The process of identifying existing risks and their outcomes to identify the worst-case scenario.
Murphy’s Law 🡲 anything that can happen will happen.
Risk Statement
A formal summarization of a potential problem that needs to be addressed, including...
The issue (IS).
The possible outcome (DOES).
Should be granular enough to link to one source (internal or external).
What is risk categorization?
The process of categorizing risks based on their types to “fine-tune” the assessment.
Different risks in the same category = address with the same response.
Internal Risk
Occurs throughout the company’s operations and arises during normal operations.
Often preventable 🡲 use risk identification & management.
Can relate to external parties.
External Risk
Occurs outside of the organization and is NOT related to normal business operations.
Often unpredictable 🡲 no control/influence over them.
Can still be prepared.
What are the types of internal risk?
Operational risk.
Financial risk.
Reputational risk.
What are the types of external risk?
Compliance risk.
Strategic risk.
Physical risk.
Operational Risk
A type of internal risk that occurs during daily business operations and causes a breakdown in business activities.
Results from inadequate/failed procedures.
Most important for AIS.
Example 🡲 technological interruption.
Technology Risk
A subset to operational risk that exists when technological failures have the potential to disrupt business.
Cyber Risk
A subset of operational risk that occurs when an external part accesses company technology assets and performs unauthorized, malicious actions.
Financial Risk
A type of internal risk that refers to money going in & out of a company with the potential for loss of a substantial sum.
Increases with more debt accumulation.
Associated with financial transactions.
Examples 🡲 failed investments, purchases, loans, sales.
Reputational Risk
A type of internal risk that occurs when the reputation or good name of a company is damaged.
Can be both internal AND external.
Can lead to financial loss from lost customers and revenue (hard to quantify).
Example 🡲 data breach on the news.
Compliance Risk
A type of external risk that occurs when a company fails to follow regulations/legislation and is subjected to legal penalties.
Can lead to financial AND reputational loss.
Example 🡲 regulatory fines.
Strategic Risk
A type of external risk that occurs when a strategy becomes less effective.
Often inevitable 🡲 strategies must be constantly updated.
Example 🡲 beat by competitor (Blockbuster vs. Netflix).
Physical Risk
A type of external risk that poses a threat and is important to identify because the impact is usually high.
Easiest risk to understand.
Can lead to financial AND reputational loss.
Example 🡲 natural disasters, crime, physical damage.
Risk Inventory
A list of all known risks for a business that is compiled after identifying and categorizing risks.
Helps create a portfolio view of risk at the entity level.
What is risk prioritization?
The process of selecting the risks most likely to occur and have the biggest impact on the organization.
Ranked by severity 🡲 uses monetary value, historical data, & external benchmarks.
Limited resources = must address the most important risks first.
Risk Severity
The likelihood of risks occurring and their potential impact on the company.
Ranked with levels, scores, or dollar amounts.
Risk Likelihood
The estimated probability of a risk occurrence, ranked on a spectrum.
Risk Impact
The estimated damage that could be caused if a risk occurs - “consequence”.
The outcome of a risk.
Measured from low (1) to high (10).
Risk Likelihood Score
A quantitative approach to score risk based on its likelihood AND impact.
Higher score 🡲 Higher priority.
Risk Score = Likelihood Score x Impact Score.
Risk Matrix
A diagram that clarifies risk by helping users visualize variations in risk scores.
Allows management to plot risk AND adjust prioritization.
Used for risks that score the same.
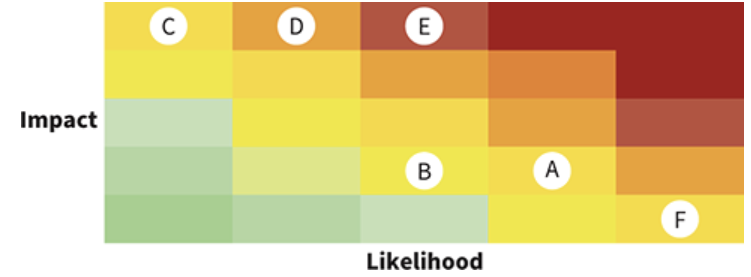
Heat Map
A type of risk matrix that uses different colors to represent values of data in a map/diagram format.
Used to show management which areas are the highest risk.
Risk Management
An area that requires critical thinking and decision-making skills.
Must understand the situation AND respond appropriately.
Determine how much residual risk is acceptable AND the most cost-effective response.
Risk Appetite
The amount of risk a company is willing to take on at a particular time.
Part of company culture.
Newer company = Higher appetite.
Inherent Risk
The natural level of risk that exists in a business process/activity if there are no risk responses in place.
Risk BEFORE implementing a risk response.
Includes likelihood & impact.
Residual Risk
The remaining risk posed by a business process/activity once a plan to respond is in place.
Risk AFTER implementing a risk response.
Has 2 types: target & actual.
Always exists at some level.
Compared to the risk appetite to determine if the risk response is adequate.
Target Residual Risk
The goal after implementing a risk response.
Actual Residual Risk
What really happens after the risk is addressed.
What is risk response?
The process of deciding how to address the prioritized risks.
Acceptance.
Avoidance.
Mitigation.
Transfer.
Risk Acceptance
A type of risk response that occurs when an inherent risk is present but the organization chooses NOT to act.
Can be small or unlikely to happen.
Can be large but org. has limited resources.
Risk Avoidance
A type of risk response that eliminates the risk by completely avoiding the events that cause the risk.
Avoid when it is significant AND highly likely to occur.
Difficult to completely avoid risk.
Risk Mitigation
A type of risk response that occurs when a company decides to accept the risk but minimize its impact if it occurs.
Most common risk response.
Allows companies to take on risk to gain advantage.
Risk Transfer
A type of risk response that involves shifting risk to a third party, who then assumes the liabilities.
Often done through contracts.
Involves associated costs 🡲 i.e. insurance premiums.