lab quiz 4 and 5 anatomy
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
respiratory volumes and capacities
The total capacity of the lungs is divided into various volumes according to their function in the intake or exhalation of air.
total lung capacity
Total lung capacity is the maximum amount of air the lungs can hold, including the residual volume. It is the sum of vital capacity and residual volume.
equation : TV + IRV + ERV + RV
inspiratory reserve volume
is the maximum volume of air that can be inhaled after a normal inhalation. It is an important measure of lung capacity.
functional residual capacity
the amt of air remaining in the lungs after a normal respirtation
EQUATION: RV + ERV
tidal volume
amt of air inspired or expired during normal, quiet respiration
expiratory reserve volume
the maximal amount of air which can be forcefully expired following normal respiration
residual volume
amt of air which remains trapped in the lungs after a maximal expiratory effect.
vital capacity
maximal amt of air that can be forcefully expired after a max inspiration
EQUATION : TV + IRV + ERV
inspiratory capacity
max amt of air which can be inspired after normal expiration
EQUATION : TV + IRV
spirometry
measurement of respiratory volumes; useful for evaluating changes in respiratory functions, can distinguish between restrictive diseases and obstructive pulmonary diseases
restrictive diiseases
effect lungs capacity to expand
obstructive pumonary disease
cause lungs to hyper inflate due to airway restriction
spirometer
instrument to measure respiratory volume
respiatory minute volume
tells us the amt of gas that flows in to or out of the respiratory tract in one minute
equation : tidal volume x respiratory rate
nomogram
graphical calculating device; used in clinical settings to predict probability of an event based on known relationships in treatment and care.
Heymer test of respiratory reserve
often a better index of respiratory reserve than is the traditional
vital capacity measurement. The principal value of these pulmonary measurements lies in following volume changes caused either by disease or recovery from a disease.
left-sided heart disease
found to have decreases vital capacity .When the heart's left ventricle is inefficient at pumping blood, blood can build up in the pulmonary veins and cause pulmonary edema. The buildup of fluid in the lungs reduces the amount of oxygen that can move through the lungs, causing shortness of breath, which, in turn, decreases vital capacity
polimyelitis or polio
a virus that infects an individual’s spinal cord and
causes paralysis. Paralysis of the respiratory muscles affects the individual’s ability to breathe on their own, which resulted in the development of the Iron Lung in the early 1900s
The _________ an individual’s breath-holding time, the ______ efficient their respiratory system is at maintaining their blood’s pH
longer ; more
modification of respiratory function
because of their importance, the concentration of O 2 and CO2 in the lungs and blood is finely regulated by variety of receptors, reflexes, and feedback processes which serve to control our respiration patterns.
receptors
Receptors are specialized proteins on cell surfaces or within cells that recognize and bind specific molecules, triggering a cellular response.
reflexes
reflexes Reflexes are automatic responses to stimuli that help protect the body from harm. They are controlled by the spinal cord and do not require conscious thought.
feedback processes
Feedback processes involve the exchange of information to regulate or control a system, allowing for adjustments to be made based on the received feedback.
dry gas meter
measures the volume of gas that passes through it (similar to the natural gas meter in your home) and keeps a cumulative total.
calculating tidal volume
divding toal air exhaled by the number of breaths made over the collection period
metabolic rate
(measured in ml O 2 consumed/min) can be determined by calculating the difference between the percentage of O2 in inhaled air (20.95%) and the percentage of O2 in exhaled air (measured by the oxygen analyzer), and then multiplying this percentage difference to the volume of air breathed during a measured time span (measured by the dry gas meter).
rate of oxygen consumption
equal to both
rate at which u obtain oxygen from the environment across respiratory exchange surface of the lungs (ventilation)
the rate at which ixygen is extracted from the blood going through capillaries of the metabolizing cells (perfusion)
ventilation- perfusion coupling
An individual can increase ventilation by increasing their respiratory rate and tidal volume, while perfusion can be increased by increasing their heart rate. Both can be calculated by measuring the flow (ml/min) of the medium (air or blood) and multiplying them by the amount of oxygen that is extracted per ml of medium that passes the exchange surface.
minute volume
flow of air in the respiratory system
cardiac output
flow of blood in the circulatory system
respiratory system
concentrations of oxygen in the inspired air (CO2 i) and the exhaled air (CO2 e)
circulatory system
concentrations of oxygens in the systemic arterial blood (CO2 a) and systemic venous blood (CO2 v).
rate of oxygen consumption equation
(Vm)(Co2i - Co2e)=(CO)(Co2a - C02v)
metabolic rate during exercise
Vo2 = (Vm)(Co2i-Co2e)
maximun oxygen content
Co2a = average hemoglobin concentration (G hb/ 100ml blood) x 1.34 ml o2/ g Hb
oxygen content of mixed venous blood at rest
Co2v= 0.6(Co2a)
resting cardiac output
CO = V02/(Co2a - Co2v)
resting stroke volume
SV = CO/HR
During exercise, the oxygen content of venous blood ______
FALLS
CALCULATING oxygen venous blood content
pulse pressure(resting). = stroke volume (resting)
pulse pressure (exercising) stroke volume (exercising)
cardiac output during exersice
COe = SV x HR
oxygen venous blood exercise
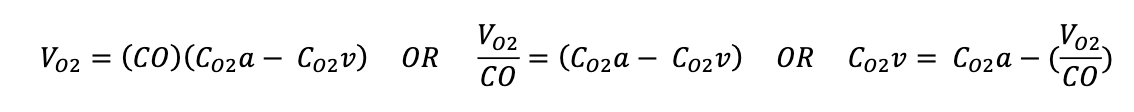
rate of respiration si controlled by
neural centers located in the medulla and pons
carbonic acid - bicarbontate mechanism
when carbon dioxide leaves the tissues and enters the blood cells, it combines with water to form carbonic acid. Shortly after it is formed, carbonic acid dissociates into bicarbonate and hydrogen ions. The bicarbonate ions diffuse out of the blood cells and into the plasma to become alkaline buffers, while the hydrogen ions combine with hemoglobin molecules within the cell and become neutralized. When carbon dioxide levels in the blood increase, there is an increase in the concentration of hydrogen ions causing a decrease in the blood’s pH (more acidic) until the body can stabilize pH by combining the hydrogen ions with bicarbonate ions. If the concentration of carbon dioxide in the blood decreases, there is a decrease in the concentration of hydrogen ions in the blood causing an increase in the blood’s pH (more alkaline) until more carbon dioxide enters the blood cells to form carbonic acid.
If we ________ the rate and depth of respiration (rapid, deep breathing), carbon dioxide
quickly becomes flushed out of the body as we are eliminating a larger concentration of carbon dioxide at a faster
rate
increase
If we________ the rate and depth of respiration (slow, shallow
breathing), carbon dioxide will accumulate in the blood as a smaller concentration of carbon dioxide is being
eliminated at a slower rate.
decrease
hyperventilation
occurs when an individual takes rapid and deep breaths that exceeds the body’s need
to eliminate carbon dioxide.
When the concentration of carbon dioxide in the blood becomes too low, the brain will force the body to
_______ the respiratory rate and _______ the tidal volume (slow, shallow breaths).
decrease / decrease
apnea
cessation of breathing
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
irreversibly decrease an indiviuals ability to force air out of lungs
asthma
result of inflammation in the bronchioles reducing the amount of oxygen that can reach the alveoli