biology topic 2.1 molecules to metabolism
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
understandings
molecular biology explains living processes in terms of the chemical substances involved.
carbon atoms can form four bonds allowing a diversity of compounds to exist
life is based on carbon compounds including
carbohydrates
lipids
proteins
nucleic acids
metabolism is the web of all enzyme catalyzed reactions that take place withing a cell or organism
anabolism is the synthesis of complex molecules including the formation of macro molecules from monomers by condensation reactions.
catabolism is the breakdown of complex molecules into simpler molecules including the hydrolysis of macro molecules into monomers
carbohydrates
provides energy for cell processes, allows storage for energy
example
monosaccharides,
disaccharides,
poly,
glucose,
lipids
used to store energy: fat in humans (saturated, solid at room temp), oils in plants (unsaturated fats, liquid at room temp), C,H,O
proteins
essentia, for cell processes
nucleic acids
DNA or RNA.
smallest protein=amino acids,
(20 unique and naturally occurring ones)
C,H,O,N,P
1 amino acid+ 1 amino acid=
dipeptide
nucleitide
5 base sugar
carbon,
phosphate base,
nitrogen base
metabolism
sum of all chemical reactions that occur in a living thing, catalyzed reactions, how fast it takes to grow things like hair, nails, etc
catabolism
breakdown of complex molecules into simpler molecules including the hydrolysis of macromolecules into monomers
(ie digestion of food, respiration)
anabolism
synthesis of complex molecules from simpler molecules, including the formation of macromolecules from monomers by condensation reactions
(ie photosynthesis, protein synthesis)
carboxyle group
c = O, - O,H

hydrocarbon chain

dipeptide

1 glycerol + 3 fatty acids
1 triglycerol
3 fatty acid chains and 1 glyceride
triglyceride
glucose + glucose
MALTOSE
glucose +fructose
SUCROSE
glucose + galactose
LACTOSE
polysaccharides consist of which monosaccharides linked together?
starch,
chitin,
glycogen,
cellulose
which end of water molecule contains positive charge?
hydrogen end
three examples of a monosaccharide
glucose,
galactose,
fructose
three examples of a disaccharide
maltose
lactose
sucrose
three examples of a polysaccharide
starch
cellulose
glycogen
which carbohydrate in animals functions to store energy till needed by its metabolism?
glycogen
three parts of a nucleotide
sugar deoxyribose, a base (ATCG), phosphate group
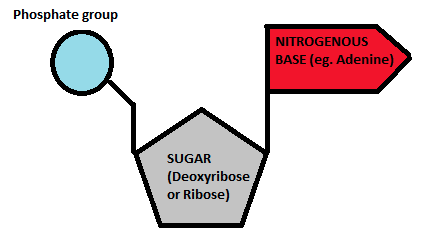
nitrogen bases of DNA molecule?
adenine
guanine
cytosine
thymine
define ENZYME
proteins which
act as biological catalysts of chemical reactions,
speed up metabolic reactions,
do not become part of end product
where is the active site?
on the enzyme
three factors that can alter an enzyme's activity
temperature,
pH levels, -
substrate concentration
if a protein becomes denatured, what has happened to it?
their bonds have broken
enzyme shape and overall structure is disrupted and no longer the same
three components of RNA molecule?
phosphate group,
nitrogen base,
5 carbon sugar
what elements are in fatty acids AND glycerol?
carbon,
hydrogen
oxygen
what elements are present in amino acids?
carbon,
hydrogen,
oxygen,
nitrogen
describe the difference between an amino acid molecule and protein molecule
amino acids make up proteins, therefore a protein is a chain of multiple amino acids.
the type of protein depends on the variable group of the amino acids
glucose molecule
saturated vs unsaturateded fatty acid molecule
 Saturated fatty acids have hydrocarbon chains connected by single bonds only. Unsaturated fatty acids have one or more double bonds.
Saturated fatty acids have hydrocarbon chains connected by single bonds only. Unsaturated fatty acids have one or more double bonds.
ribose diagram

polymer which contains a-glucose
starch
glycogen
amylose
amylopectin
polymer which contains ribose
ribonucleic acid
RNA
Distinguish between the formation and breaking down of a polymer.
in polymer formation, condensation reaction occurs but in the breaking down of a polymer a hydrolysis reaction occurs
in polymer formation, one molecule of water
is produced but in the breaking down of a polymer water molecules are split/added
polymer formation is an anabolic reaction and breaking down a polymer is a catabolic reaction
Compare and contrast carbohydrates, lipids and proteins.
Carbohydrates | Proteins | Lipids | |
|---|---|---|---|
Organic macromolecules | Organic macromolecules | Organic macromolecules | |
Formed by condensation reaction | Formed by condensation reaction | Formed by condensation reaction | |
Composed of C, H, and O | Composed of C, H, O, N and sometimes S | Composed of C, H, and O | |
Monomers are monosaccharides | Monomers are amino acids | Made out of fatty acids and glycerol |