ANP W7 Integumentary System
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
What are the 2 primary layers of the skin? Describe each.
Epidermis → outer most portion; stratified squamous epithelial cells; avascular
Dermis → CT layer; vascular; has nerves and glands
How is the epidermis nourished?
By the capillaries in the dermis
What does a pink flush indicate? What does cyanosis indicate?
increased blood volume or increased bloody oxygen
Cyanosis = low blood oxygen; blueish gray skin colour
The dermis is composed of what kind of connective tissue?
Dense irregular CT → collagen and elastic fibres
What is a sudoriferous gland?
sweat gland - located in dermis layer
What are the 4 functions of the dermis layer of the skin?
protection
nourishment of epidermis
skin elasticity
sensory perception
What is the subcutaneous layer? Fx?
Hypodermis
composed of Areolar and adipose tissue
vascularized and has nerves
thickness varies
Fx:
Connects skin to underlying muscle
insulation
temperature regulation
sensory perception
Why is there no clear boundary between the hypodermis and the dermis?
Continuous bundles of elastic fibers connect them together
Accessory structures of the skin help protect it and give it more functions. What are 3 accessory structures of the skin?
Glands → sebaceous oil glands and sudoriferous (sweat) glands
Hair
Nails
Describe Sebaceous glands. Location, fx? What does it secrete?
Sac like gland associated with hair follicles
found every where except on palm of hands and soles of feet
secretes sebum → oily substance that lubricates skin and hair and prevents drying
**produces the Vernix caseosa a greasy white substance covering the fetus during the last trimester
What is the Meibomian gland?
Meibomian gland is a type of oil gland that helps lubricate the eyes.
What are the 2 types of sudoriferous glands? Describe each.
1. Eccrine glands
Widely distributed; most numerous on palms, soles, forehead
Secrete watery sweat (mainly water + salts) for thermoregulation
Open directly onto skin surface
2. Apocrine glands
Found in armpit, groin, areola of breast
Open into hair follicles
Become active at puberty; can produce odor when decomposed by skin bacteria
Secrete thicker, milky fluid (water, salts, proteins, lipids)
Describe sudoriferous gland. Fx?
Coiled-tube like gland that directly opens up to the skin or to a hair follicle. It is located in the dermis and hypodermis
fx:
body thermoregulation
eliminate wastes (salts)
What are some modified sudoriferous glands?
Ceruminous gland in the ear canal producing ear wax (cerumen)
Ciliary glands on the edge of eyelids
Mammary glands in breast
What is lanugo?
soft hair of fetus and newborns
What is the name of the involuntary smooth muscle that causes hair to stand up straight?
Arrector pili → also stimulates secretion of sebum
The hair follicle is a sheath of …?
Epithelial and connective tissue
What is the crescent-shaped area nearest the root on a nail called?
Lunula
What are the 4 major functions of the Integumentary System?
Protection - the body’s first line of defense
Protection against dehydration (drying)
Temperature Regulation
Collect sensory information
How does the skin act as the first line of defense to protect the body? (4)
An intact skin is a barrier against infection by microbes
Sloughing (shedding) of old, dead, surface skin removes pathogens
Protection against UV rays (melanin)
Sweat has some microbial characteristics
Defense against bacterial toxins and some harmful environ chemicals
How does the skin protect against dehydration? (2)
prevents excess water loss by evaporation
Keratin and sebum help to waterproof the skin and keep it moist and supple
How does the skin regulate body temperature? (3 mechanisms)
Regulation of sweat secretion
Regulation of blood flow near body surface
Shivering causes contraction of the arrector pili muscle → raised hair traps warm air near the skin
What type of senses is the skin able to detect? What type of nerve/receptor is responsible for each?
Pain → free nerve ending
Temperature → free nerve ending
Light touch and deep pressure → sensory receptor
Heat and Cold → thermoreceptor
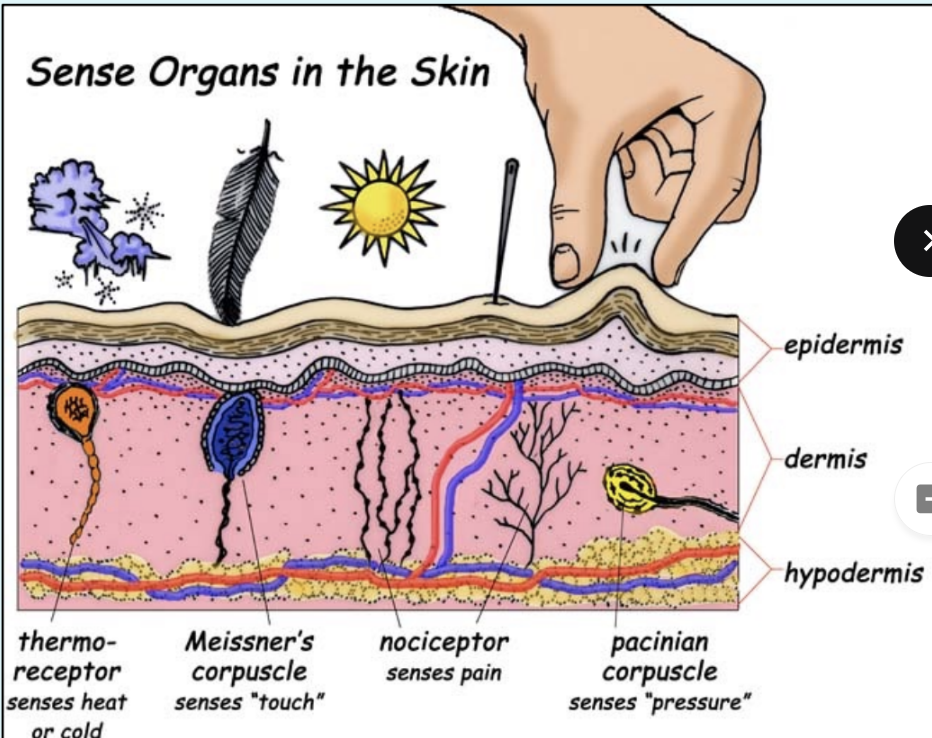
What contributes to the colour of skin?
Melanin → degree of brown pigment in the skin
Hemoglobin → blood in the surface of blood vessels (pallor =pale, flush=pink, cyanosis=blue)
Define Carotenoderma.
A skin discolouration where excess carotene in the blood gives the skin a yellow/orange colour.
carotene pigment obtained from vegetables
What pigment causes the skin to turn yellow when someone has Jaundice?
Bile pigments
Jaundice reflects impaired liver function, gall bladder problems abd or excess hemolysis (RBC death)
What are 4 conditions that Jaundice may be a symptom of?
Tumour pressing on bile duct
Virus that causes inflammation of liver (hepatitis)
Blood disease → RBC rapidly destroyed
Immaturity of liver (inability to process bilirubin)
How does the skin repair itself? (wound healing)
Wound healing only happens in areas with actively dividing cells. It beings after blood has clotted with an inflammatory response.
stem cells produce new tissue cells and BV
collagen produced by fibroblasts close the wound
arger injuries require more extensive growth which can lead to scars(cicatrix) and keloids
What 4 factors affect healing?
nutrition
blood supply
infection
age
What are the 4 classifications of burns? Describe each briefly.
First degree superficial
surface of epidermis only; minimal pain
skin is red and dry
Second degree superficial partial thickness
burn reached deep into the epidermis and part of the dermis
red, blistered painful
heals without scarring
Second degree deep partial thickness
burn through epidermis and dermis
tissue blistered, weeping, or dry if sweat glands damaged
less painful than superficial burns because of nerve damage
Third degree full thickness
burn through all layers of skin + some hypodermis; may include damage to muscle and bone
may require surgery, loss in digits or limbs
Of these 3 types of skin cancer, list them from most to least common.
Basal Cell carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma
Melanoma
**remember carcinoma is cancer of the epithelial tissue
What is Impetigo?
Bacterial infection of the skin caused by staphylococcal or streptococcal infection
What are 2 examples of a viral infection of the skin?
warts
herpes simplex virus
What is tinea?
a fungal infection of the skin
Define Dermatitis
general inflammation of the skin
Urticaria and eczema are exampels of what kind of disorder of the skin?
Acute inflammatory disorder
Describe Lupus erythematosus
Autoimmune disease of connective tissue
characterized by rough, raised, violent tinted papules on face/scalp only
Describe systemic sclerosis/scleroderma.
Unknown etiology; may be autoimmune disease of vessels and CT
thickening and tightening of skin
severe cases: impaired function, lack of facial expression
Describe Psoriasis
Chronic inflammatory condition with unknown cause; could be autoimmune or genetic
characterized by silvery scales
Describe Dermatographia
“Allergy to touching self”
Dermatographia is a skin condition where light scratching or pressure causes raised, red, itchy welts.
Also called “skin writing”
Caused by histamine release from mast cells in the skin
Usually harmless and often temporary
Define these types of Lesions: Macule, Papule, Pustule
Macule - flat and discoloured
Papule - small firm, raised lesion → large papule is a nodule
Pustule - pus filled lesion; infected vesicle
Define these types of Lesions: Vesicle, Plaque, Cicatrix and Keloid.
Vesicle - bulla/blister or small fluid filled sac
Plaque - Large, slightly elevated, flat surfaced legion often topped by scales.
Cicatrix - scar
Keloid - raised, irregular, tumour-like masses of collagen resulting from excess scar tissue formation