Chapter 9: Muscular System: Histology and Physiology
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
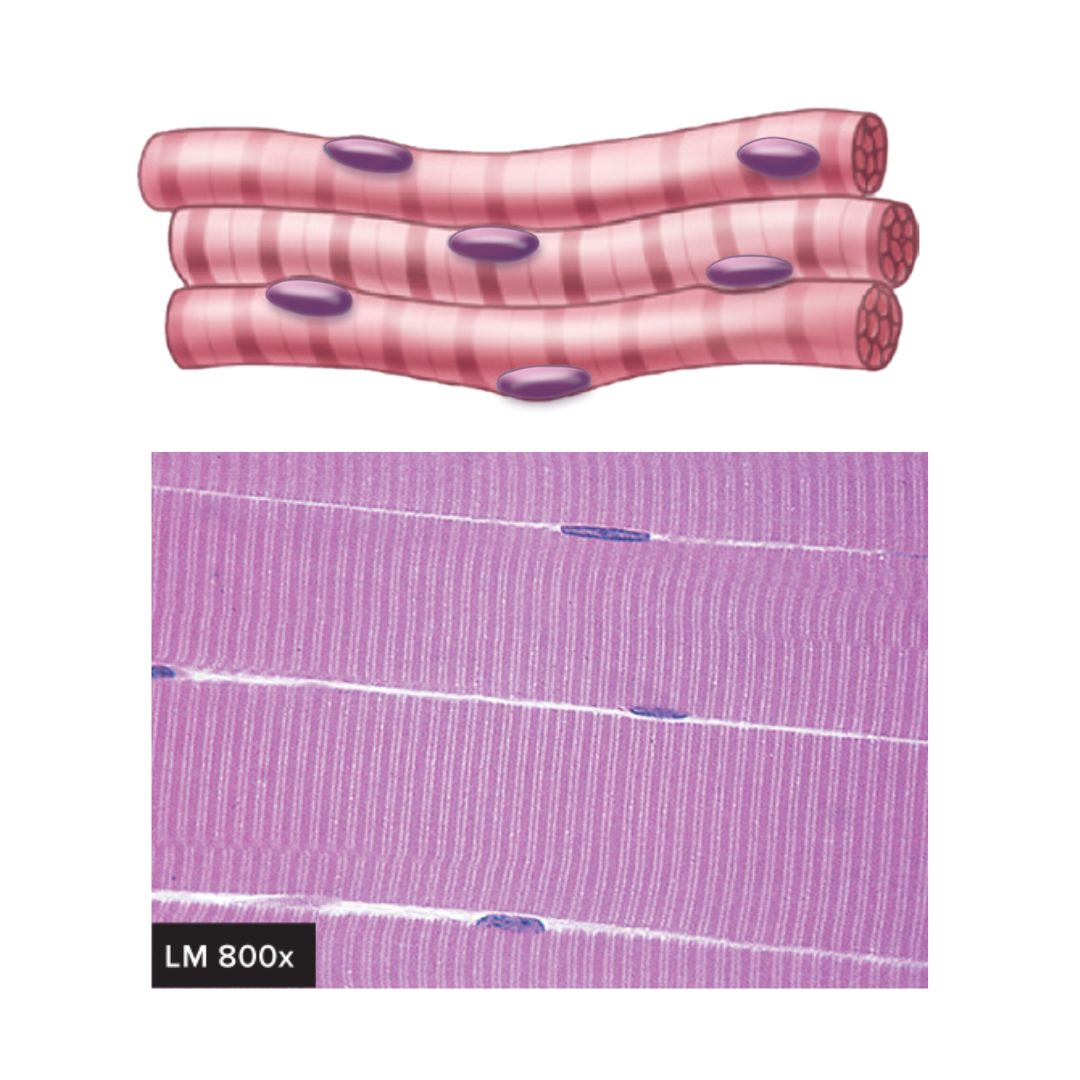
skeletal muscle
9.1: Functions of the Muscular System
attached to bones
very long and cylindrical
multinuclear, peripherally located
striations
voluntary and involuntary control (reflexes)
controls body movement

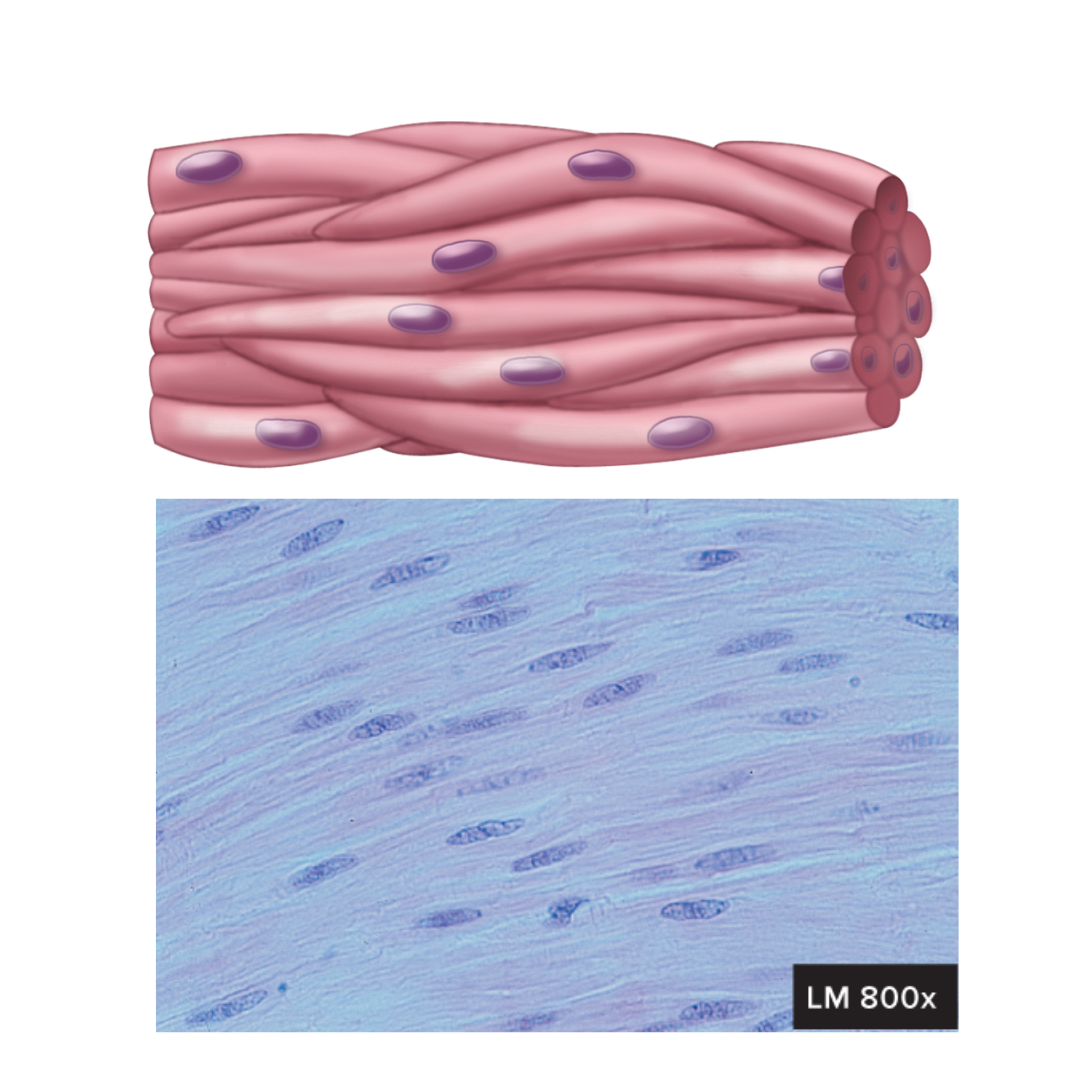
smooth muscle
9.1: Functions of the Muscular System
walls of hollow organs, blood vessels, eyes, glands, and skin
spindle-shaped
uninuclear, centrally located
gap junctions join some visceral cells together
involuntary control
some are capable of spontaneous contraction
moves food through the digestive tract, empties the urinary bladder, regulates blood vessel diameter, moves hair, etc
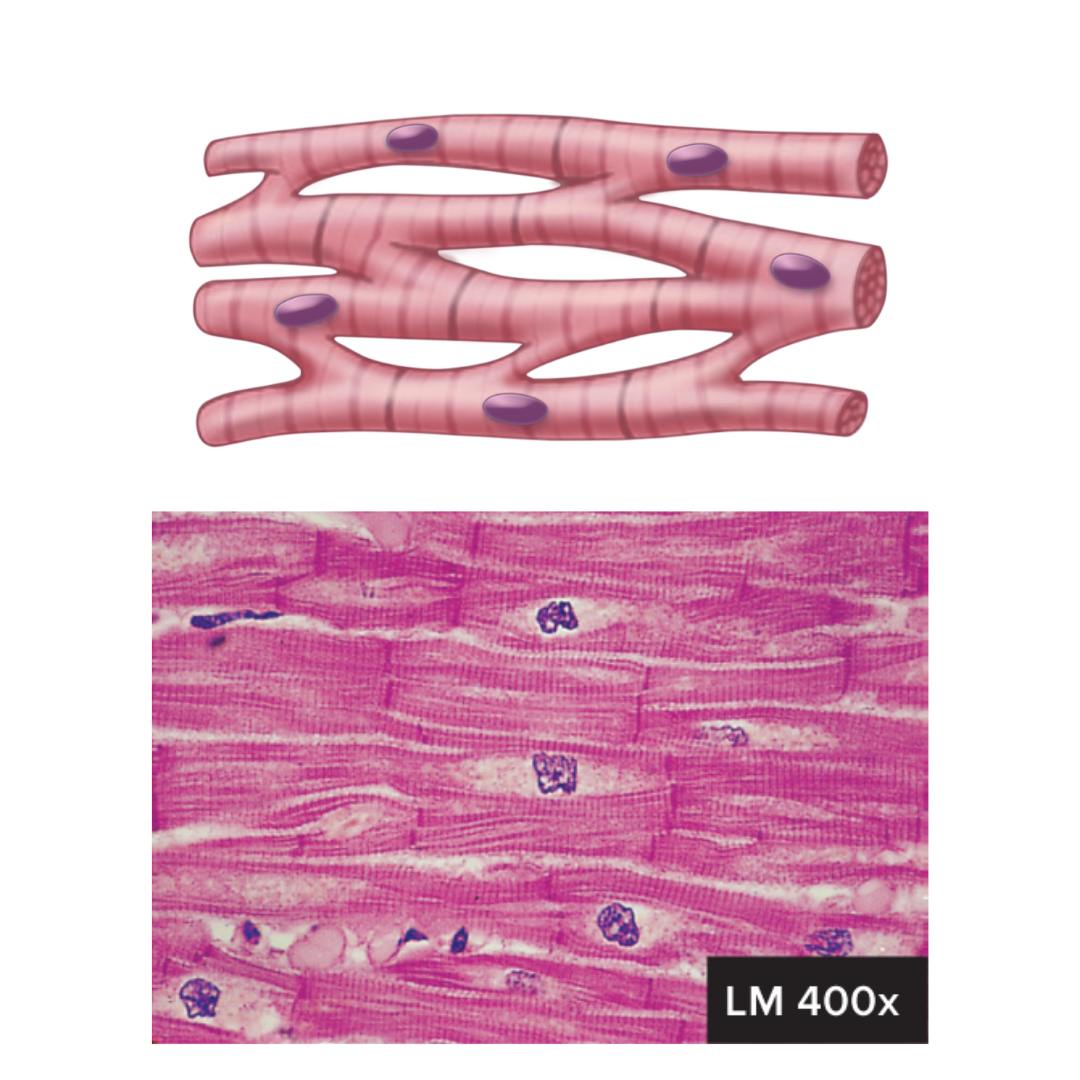
cardiac muscle
9.1: Functions of the Muscular System
located in the heart
cylindrical and branched
uninuclear, centrally located
intercalated disks join cells to one another
striations
involuntary control
capable of spontaneous contraction
pumping blood; contractions provide the major force for propelling blood through blood vessels
functions of the muscular system
9.1:
movement of the body
maintenance of posture
respiration
production of body heat
communication (speaking, gesturing, writing, etc)
constriction of organs and vessels
contraction of the heart
contractility
9.2: General Properties of Muscle Tissue
the ability of the muscle to shorten forcefully
excitablity
9.2: General Properties of Muscle Tissue
the capacity of muscle to respond to an electrical stimulus
extensibility
9.2: General Properties of Muscle Tissue
muscle can be stretched beyond its normal resting length and still be able to contract
builds contractility
elasticity
9.2: General Properties of Muscle Tissue
the ability of the muscle to recoil to its original size after it has been stretched
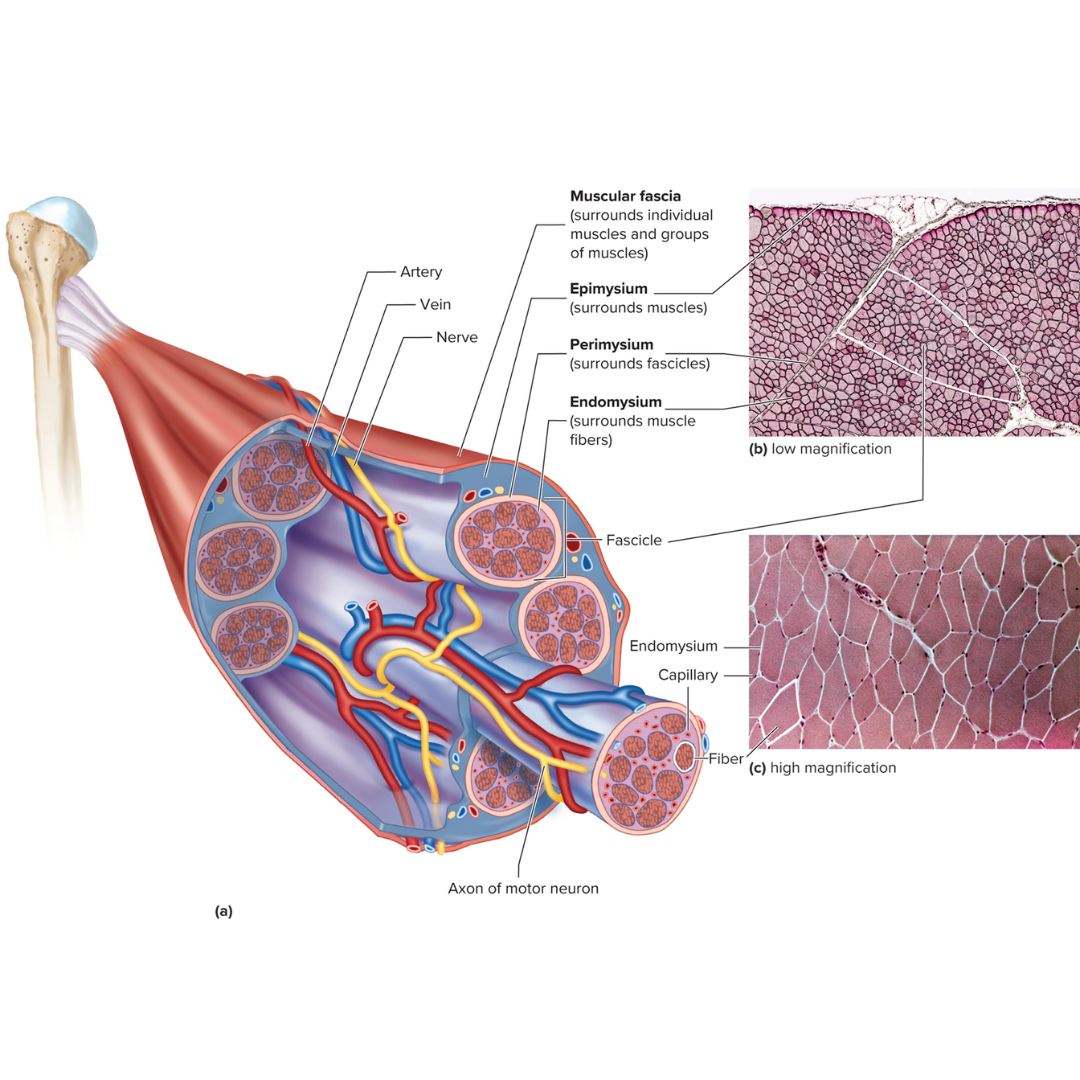
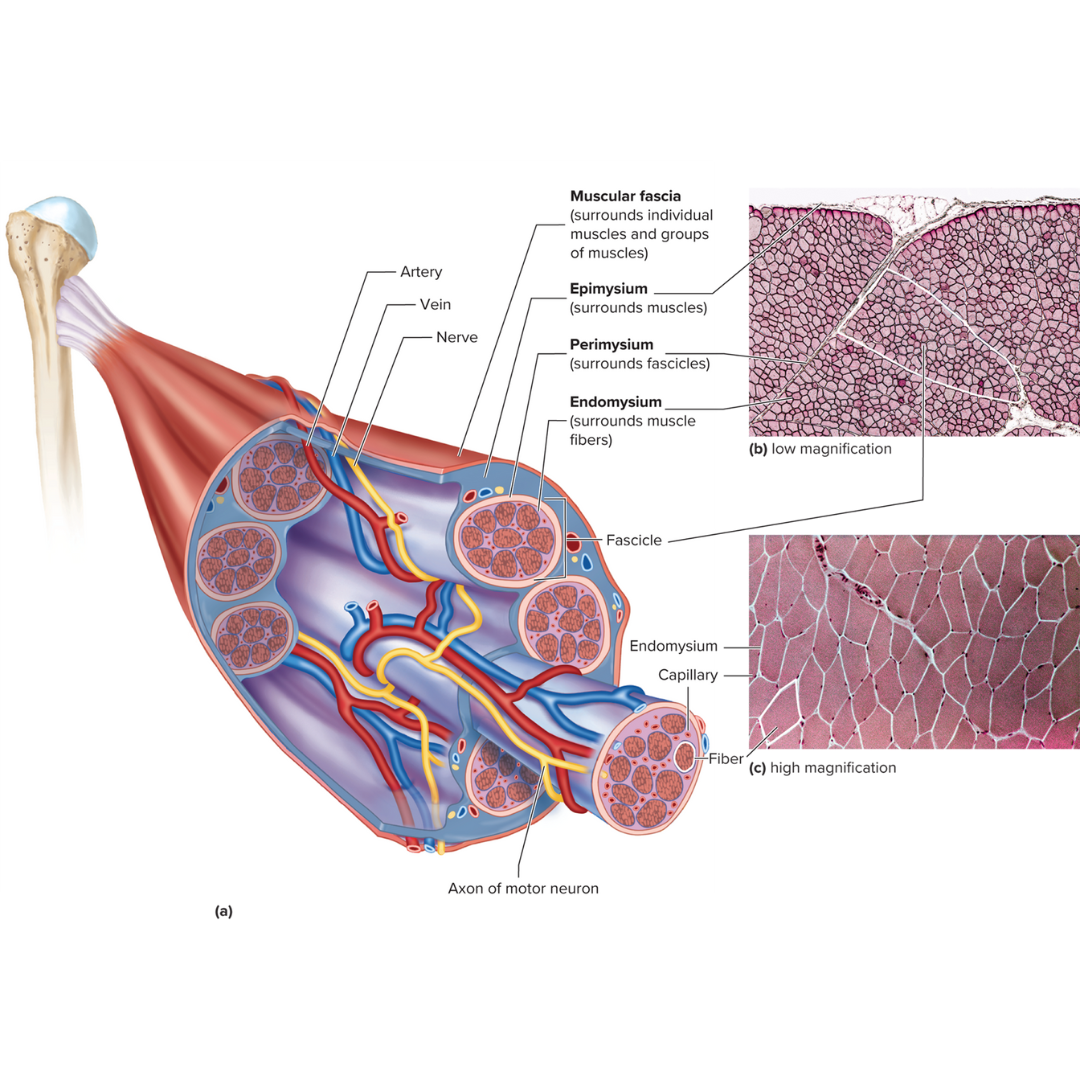
connective tissue layers covering skeletal muscle
9.3: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy
epimysium
perimysium
endomysium
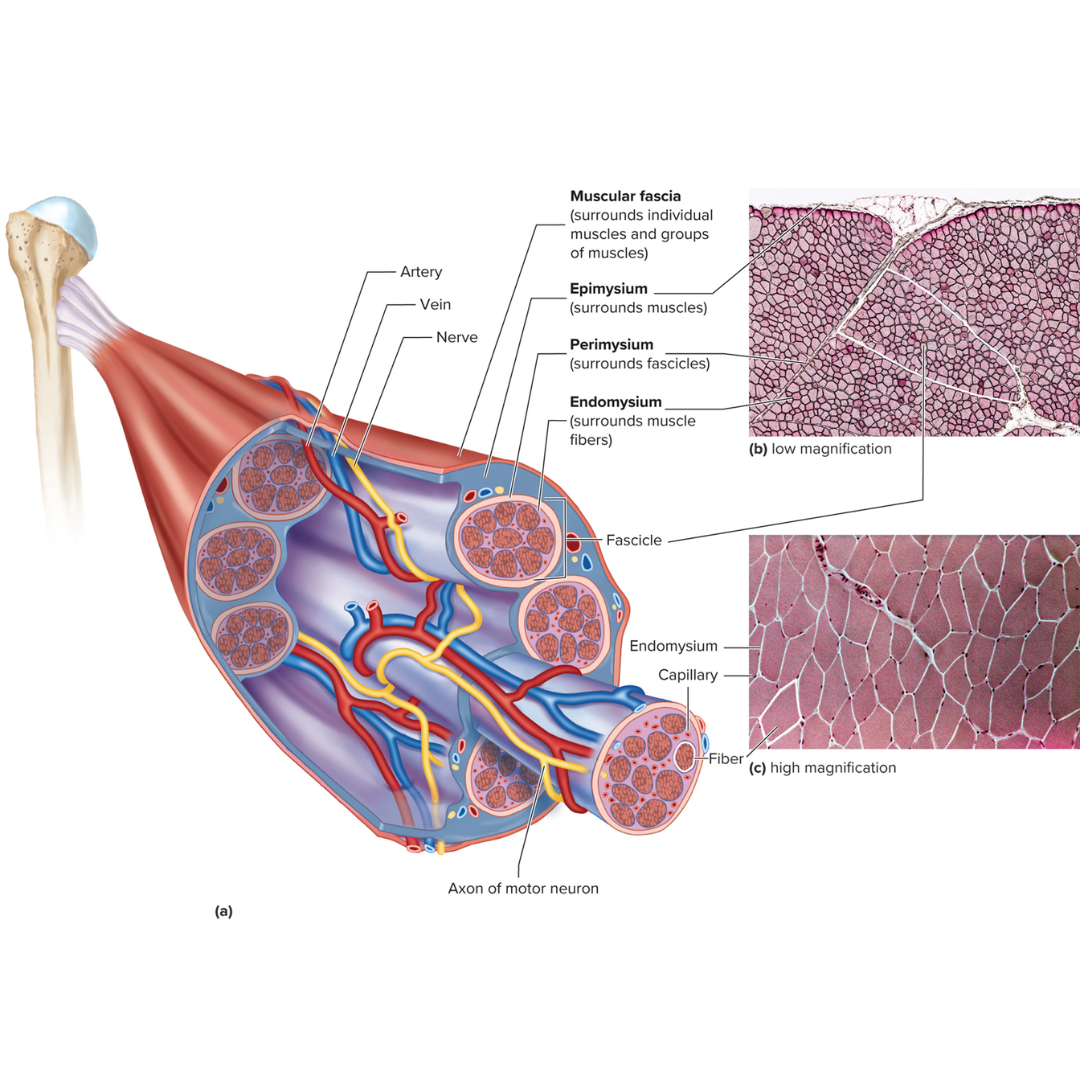
muscle fascia
9.3: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy
the layer of connective tissue between adjacent muscles and between muscles and the skin
epimysium
9.3: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy
Fibrous envelope surrounding a skeletal muscle; surrounds muscles
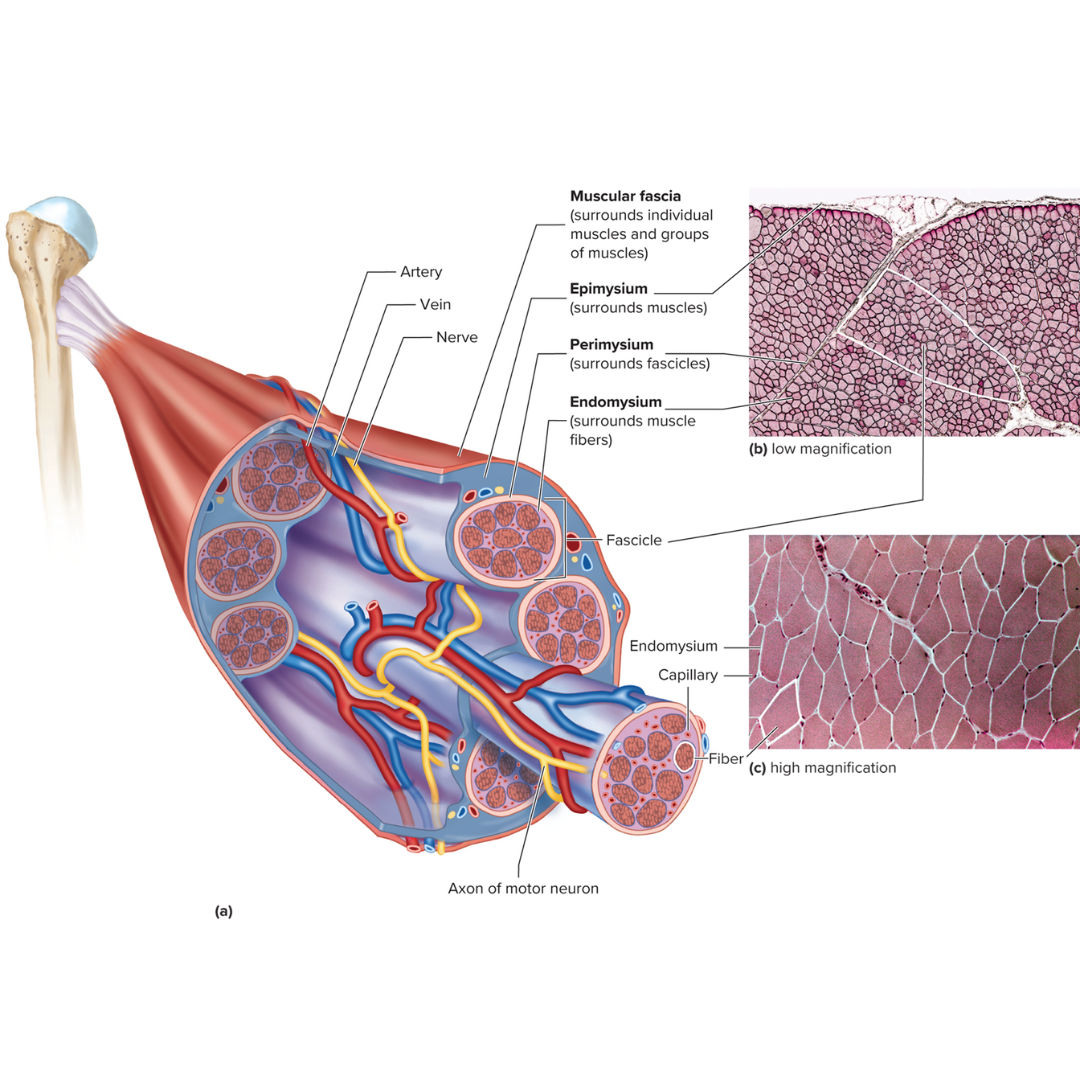
fascicles
9.3: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy
little groups of muscle fibers that are bundled together
wrapped in the perimysium
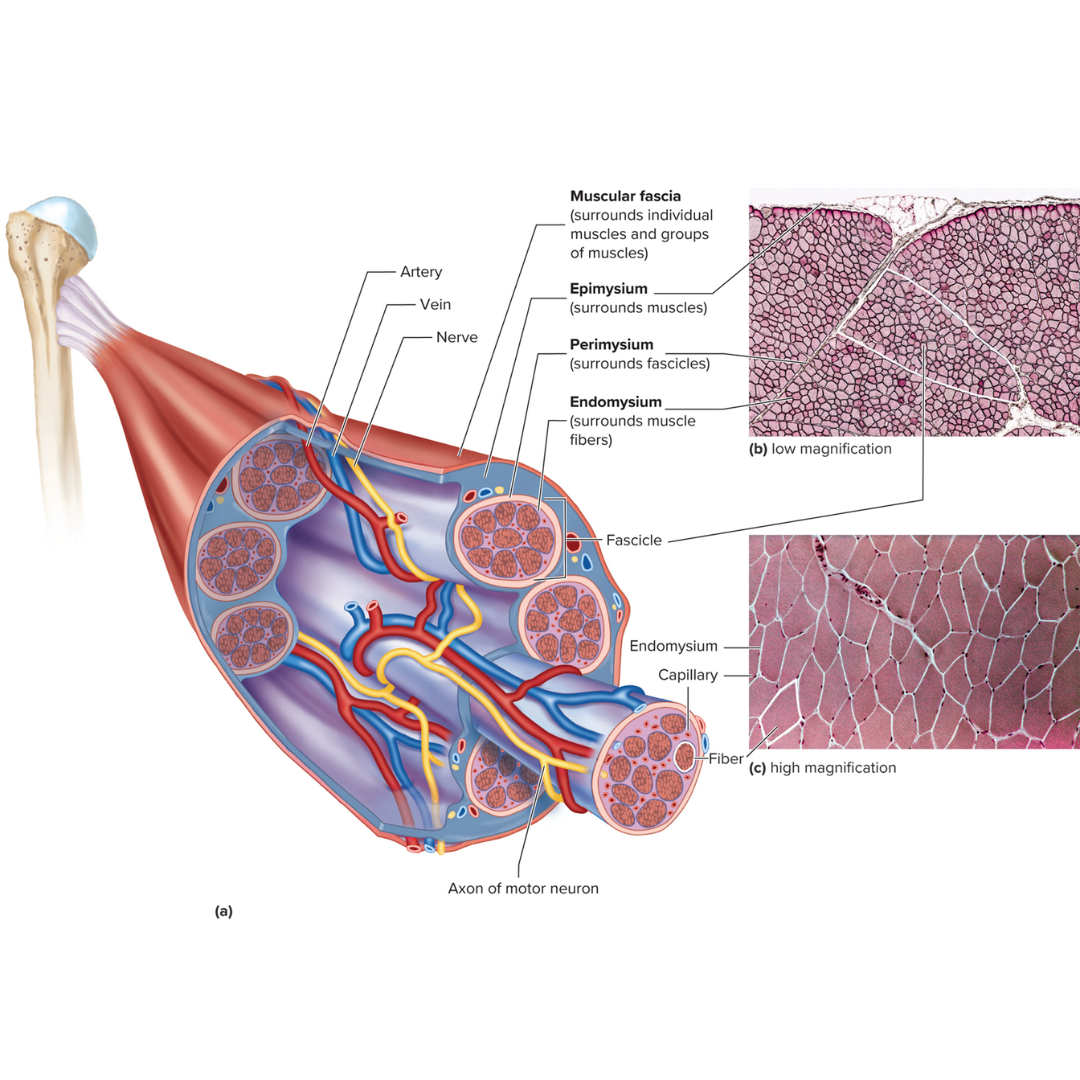
perimysium
9.3: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy
Fibrous sheath enveloping a bundle of skeletal muscle fibers; surrounds fascicles
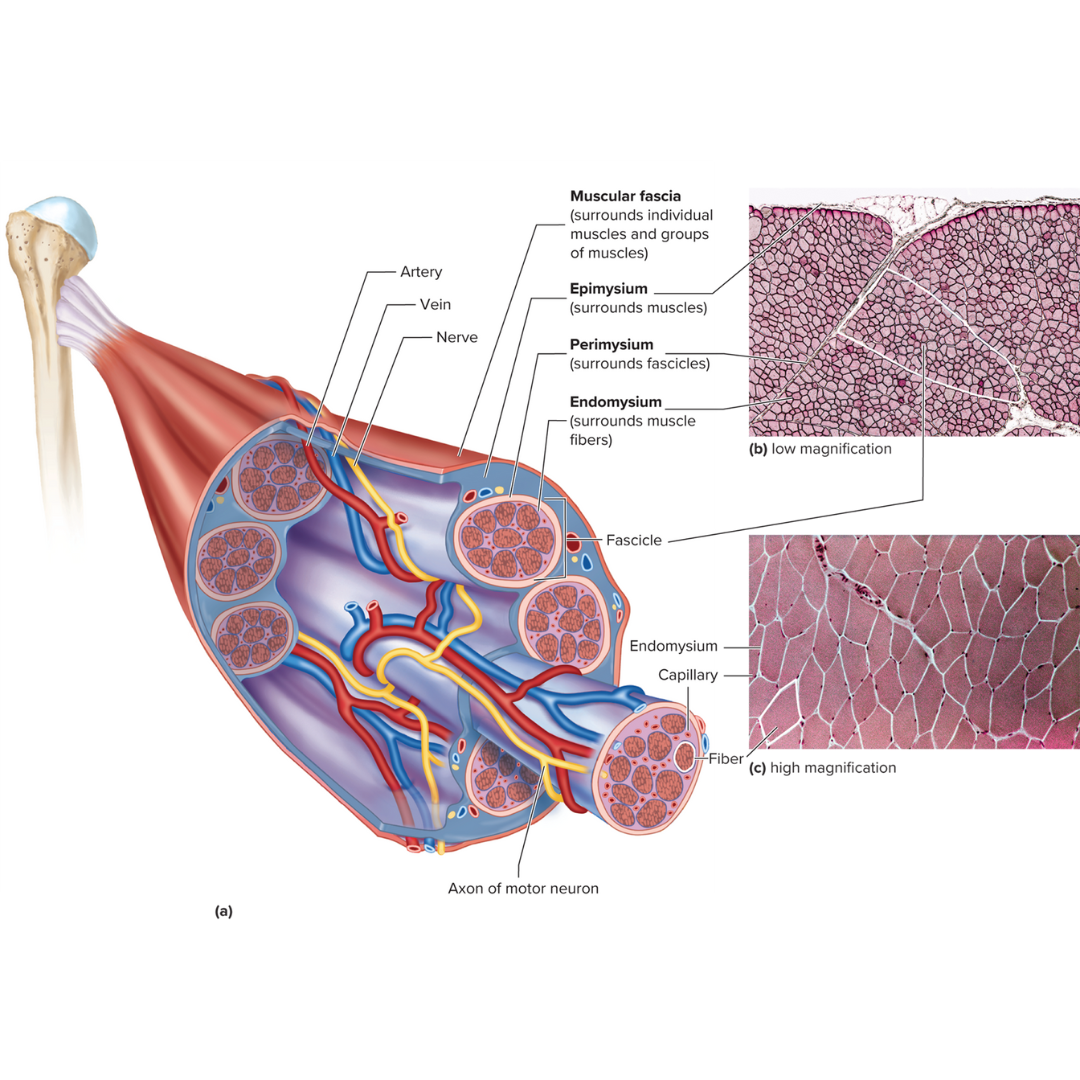
endomysium
9.3: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy
Fine connective tissue sheath surrounding a muscle fiber; surrounds muscle fibers
tendon
9.3: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy
band or cord of dense connective tissue that connects a muscle to a bone or another structure.
aponeuroses
9.3: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy
a flattened fibrous membrane binding the muscles together or connecting them to other parts of the body such as bone or skin
muscle fiber
9.3: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy
muscle cell
myoblasts
9.3: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy: Fibers
Primitive, multinucleated cell with the potential to develop into a muscle fiber
striated
9.3: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy: Fibers
Striped; marked by stripes or bands
hypertrophy
9.3: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy: Fibers
an increase in the size or volume of muscles due to the enlargement of individual cells
two main aspects to muscle contraction
9.3: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy: Fibers
an electrical component
a mechanical component
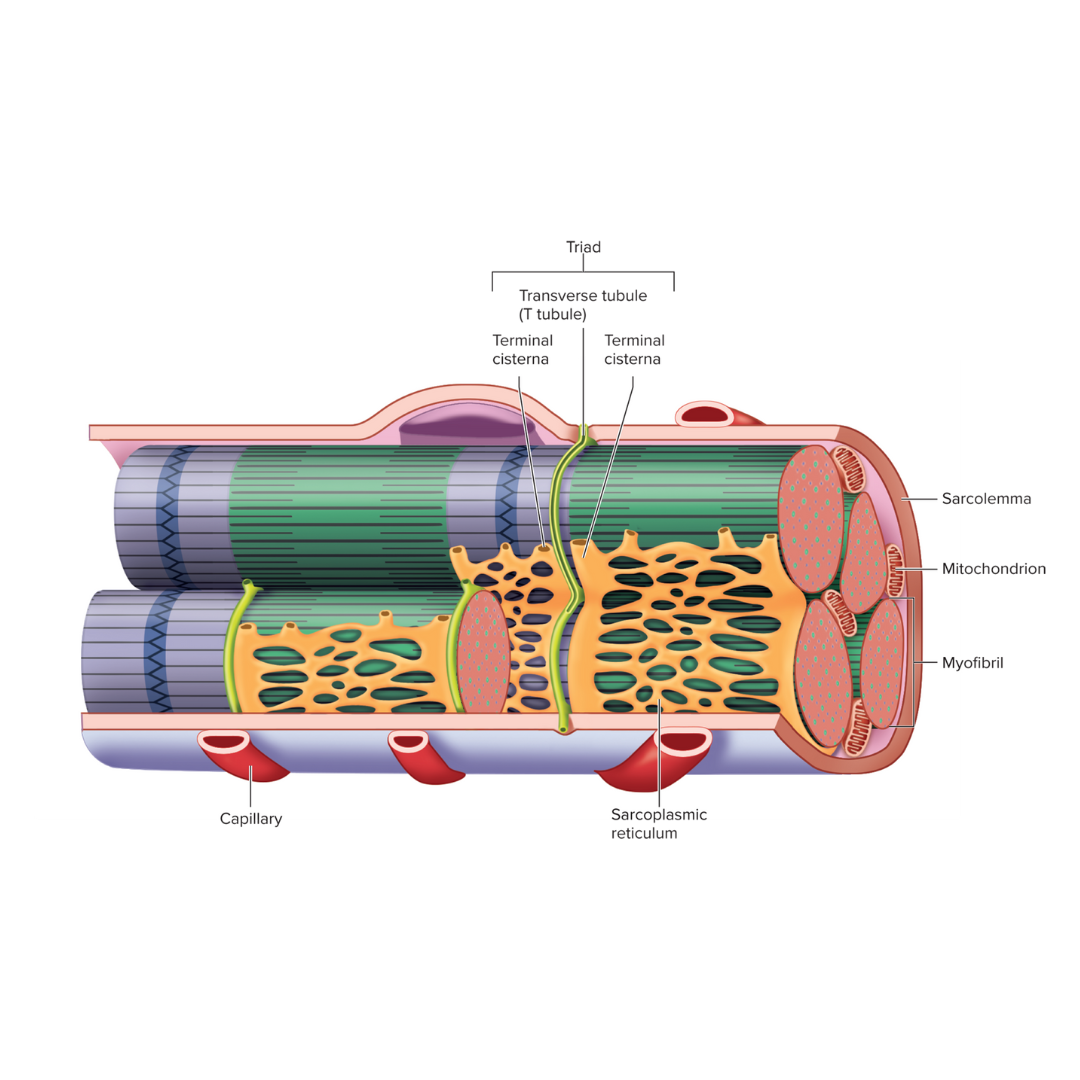
electrical component structures
9.3: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy: Fibers
sarcolemma
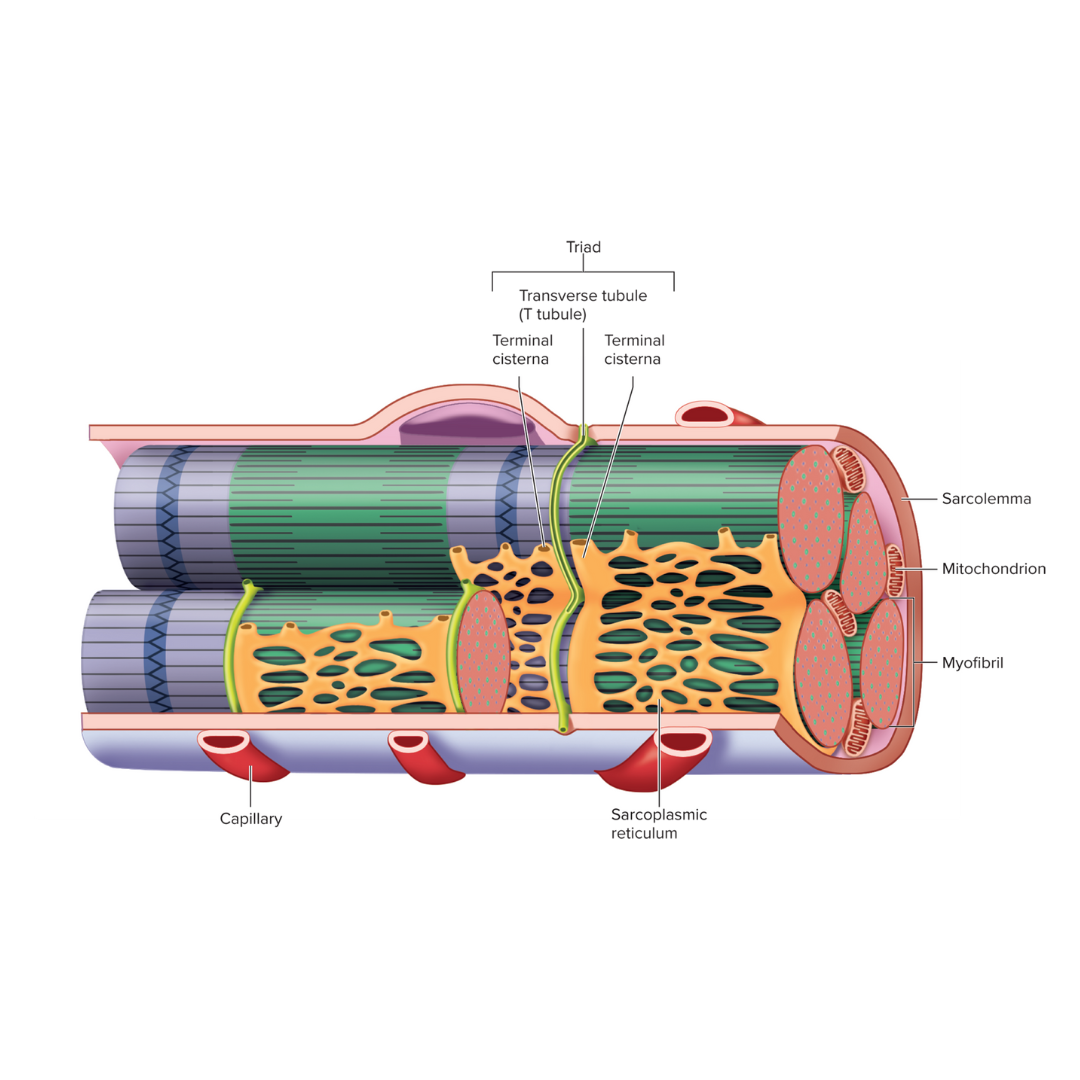
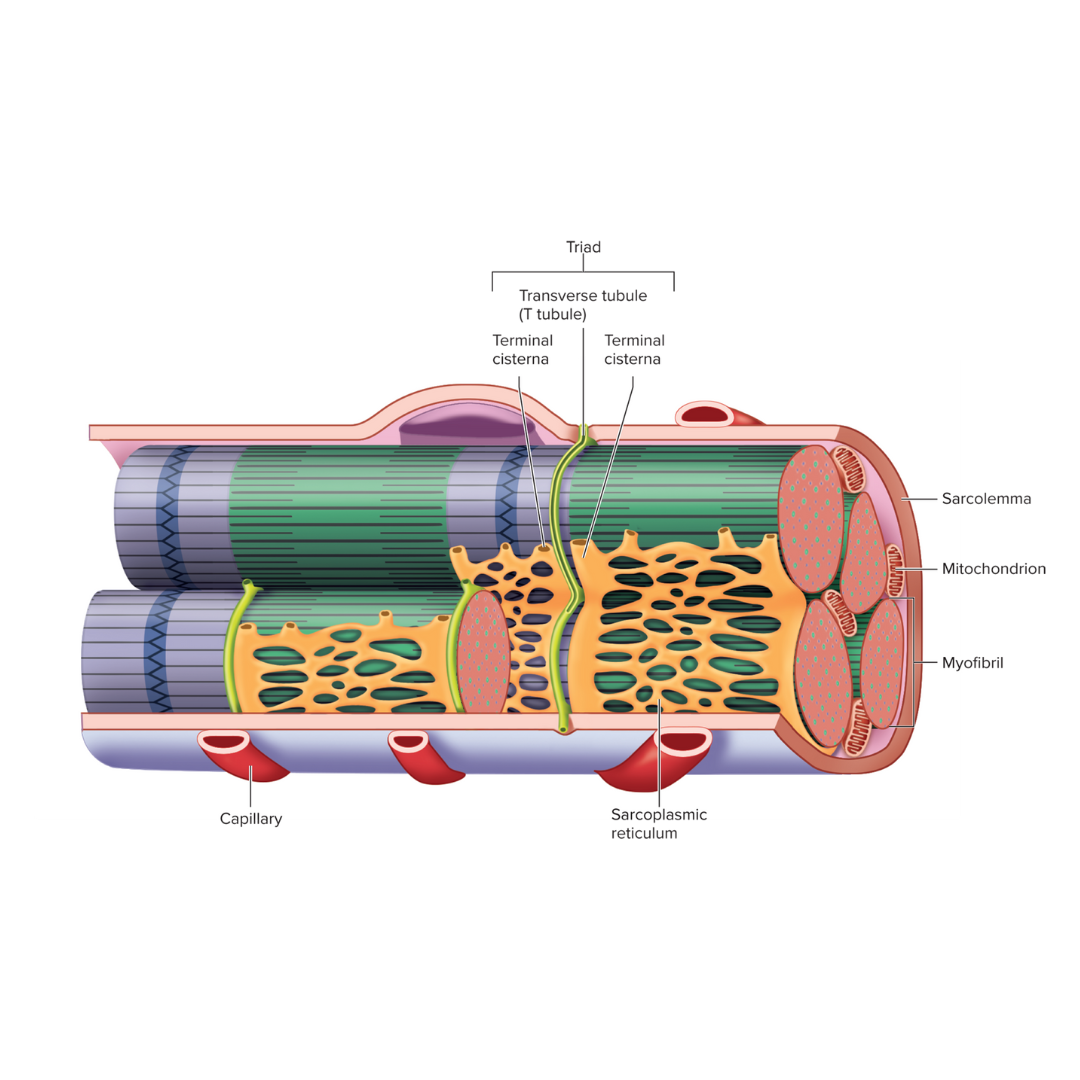
Transverse tubules (T tubules)
sarcoplasmic reticulum
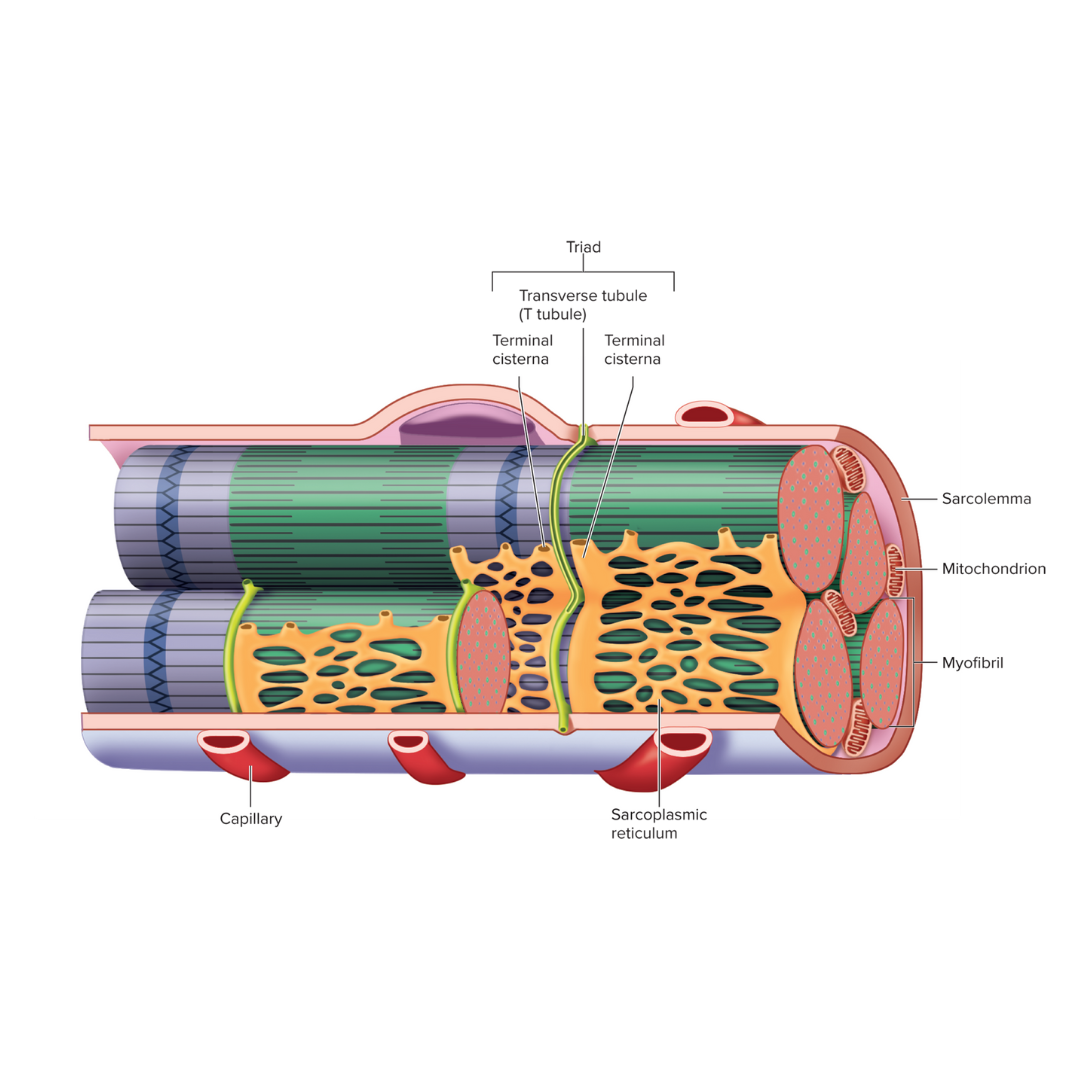
sarcolemma
9.3: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy: Fibers ⚡
The plasma membrane of a muscle fiber; an electrical component
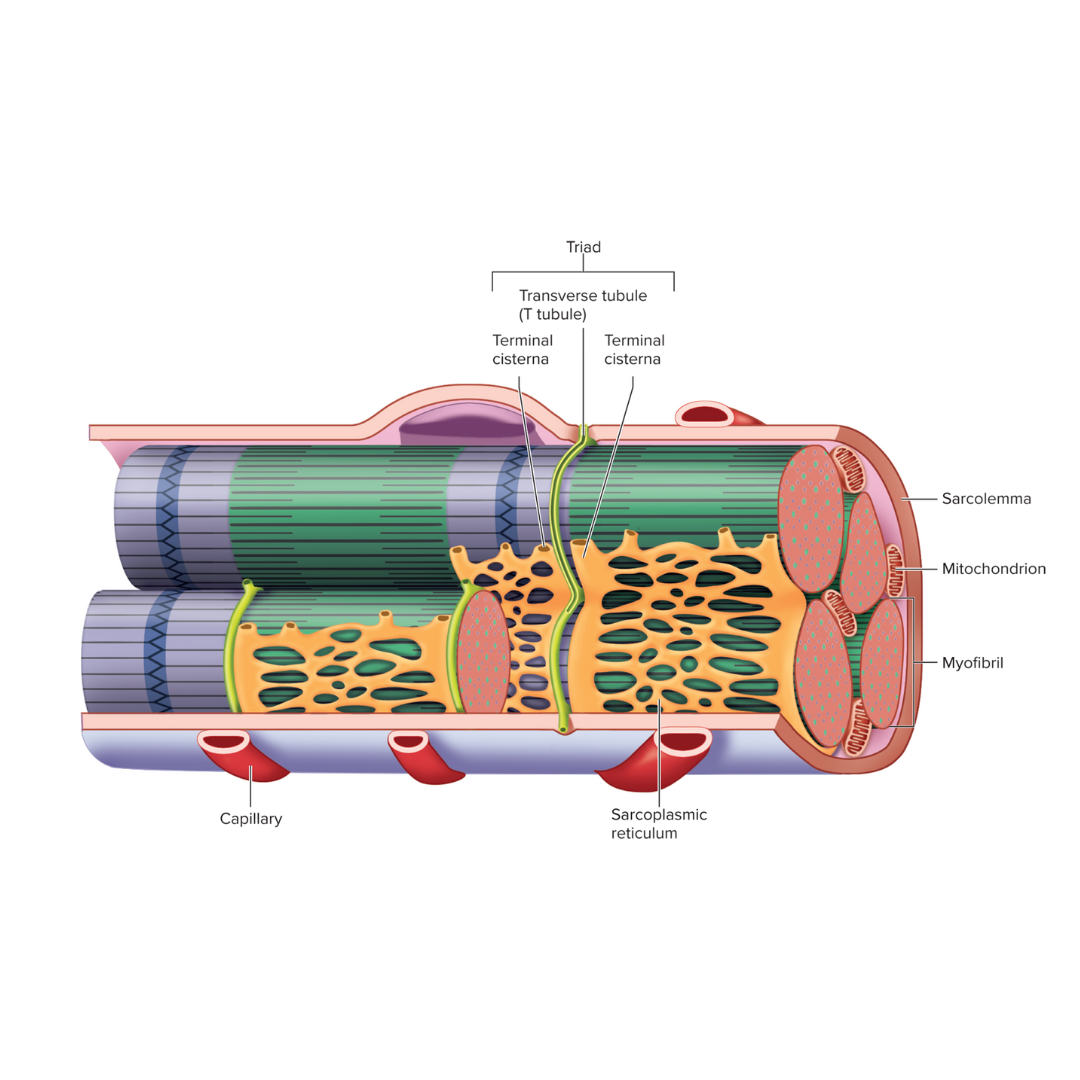
Transverse tubules (T tubules)
9.3: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy: Fibers ⚡
injection point for the sarcoplasmic reticulum to get its contents (calcium) into the cell
conduct action potentials deep into the muscle fiber
an electrical component
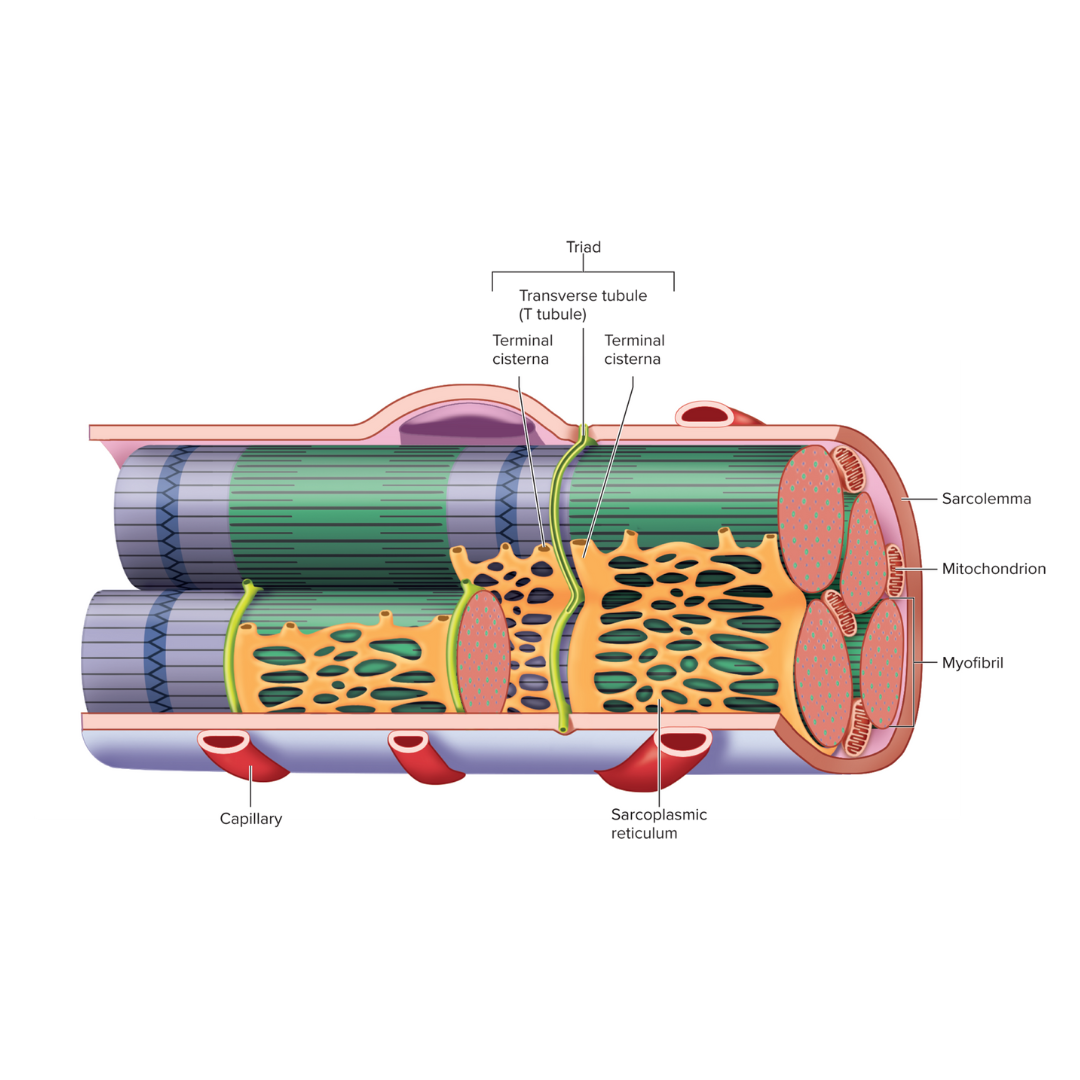
sarcoplasmic reticulum
9.3: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy: Fibers⚡
Endoplasmic reticulum of muscle; an electrical component
storage and release of calcium ions
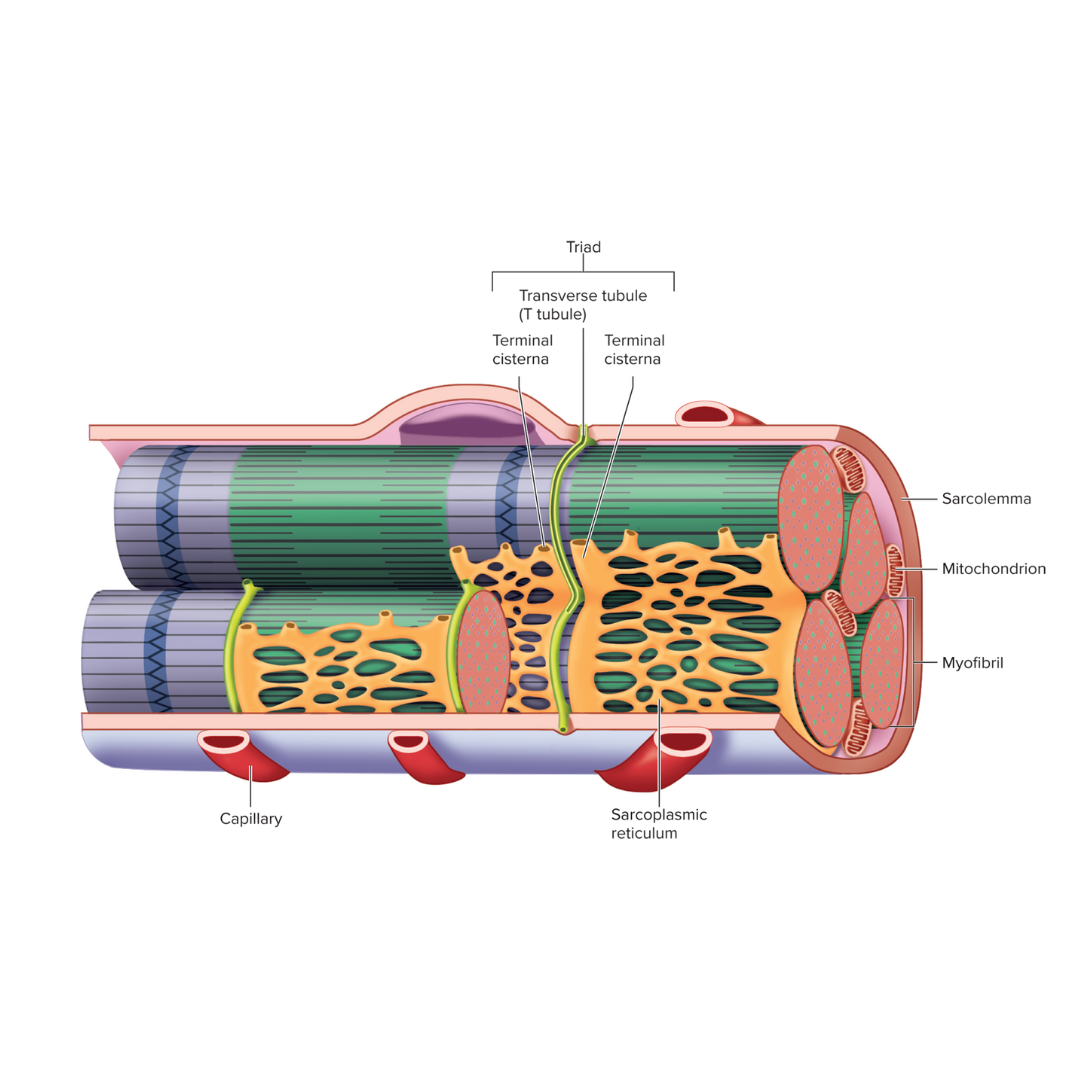
triad
9.3: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy: Fibers⚡
Two terminal cisternae (sarcoplasmic reticulum) and a T tubule between them
sarcoplasm
9.3: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy: Fibers
The cytoplasm of a muscle fiber, excluding the myofilaments.
mechanical component structures
9.3: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy: Fibers
myofibrils
myofilaments
myofibrils
9.3: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy: Fibers ⚙
bundles of protein filaments
each muscle fiber has many of these in its sarcoplasm
long threadlike structures extending the entire length of the muscle fiber
protein filaments in this interact to shorten the muscle fiber during contraction
myofilaments
9.3: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy: Fibers ⚙
Extremely fine molecular thread helping form the myofibrils of muscle; thick [term] are formed of myosin, and thin [term] are formed of actin
![<p><strong>9.3: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy: Fibers </strong><span data-name="gear" data-type="emoji">⚙</span></p><p>Extremely fine molecular thread helping form the myofibrils of muscle; thick [term] are formed of myosin, and thin [term] are formed of actin</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/52242410-608b-4efc-b549-e2332d3ceca6.png)
actin myofilaments
9.3: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy: Fibers ⚙
Thin filament of muscle fibrils
composed primarily of the protein actin
found in the sarcomeres
myosin myofilaments
9.3: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy: Fibers ⚙
Thick filament of muscle fibrils
composed of myosin molecules
found in the sarcomeres
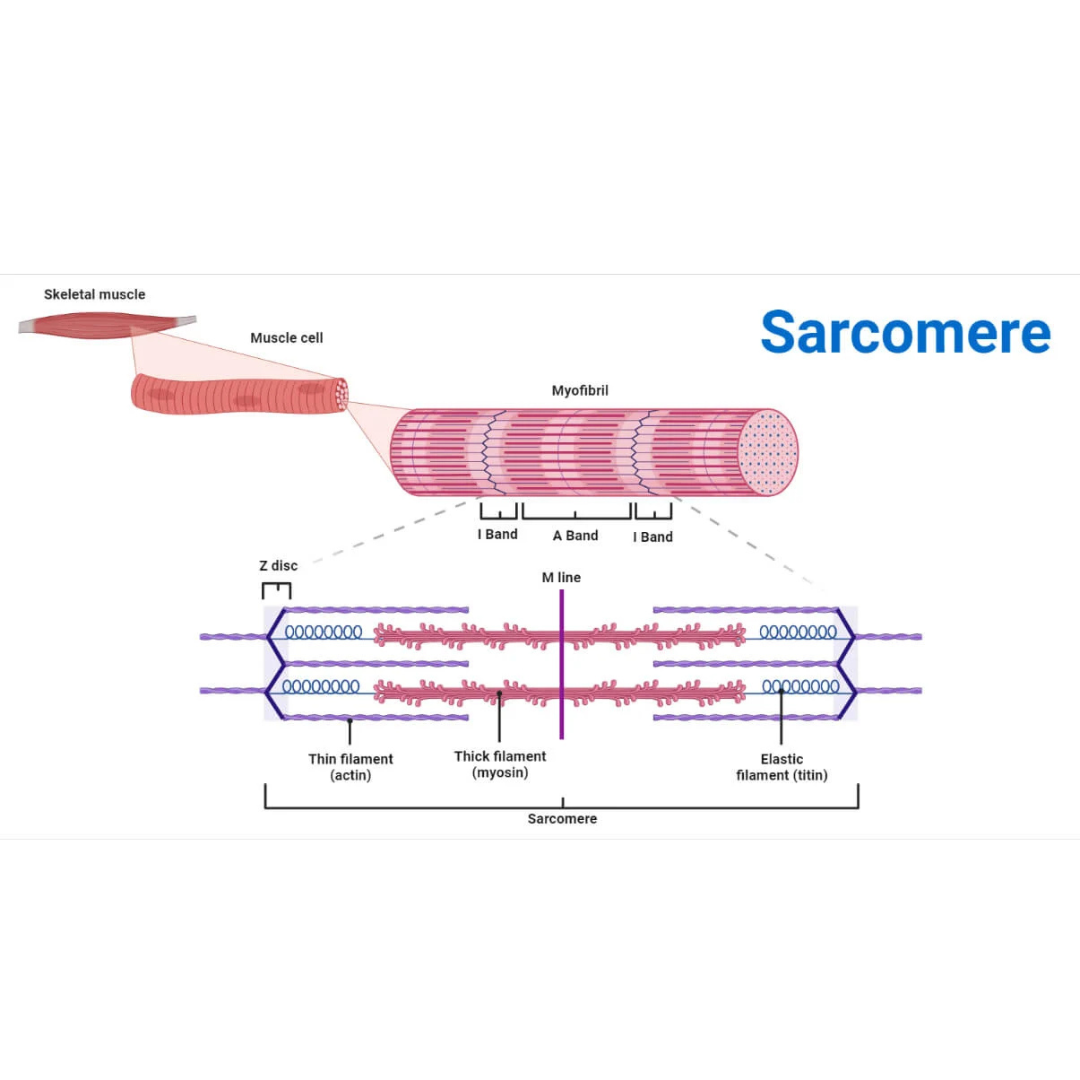
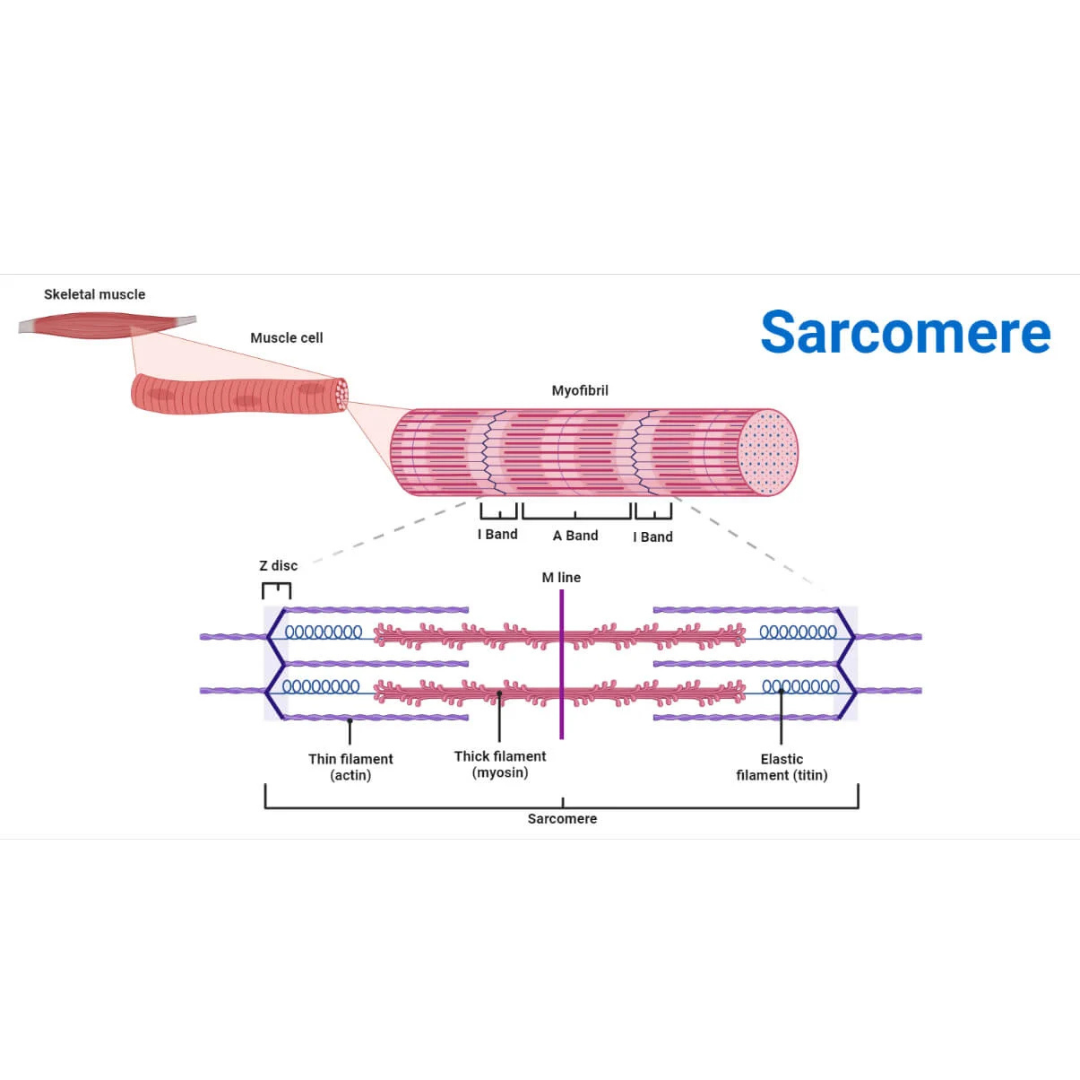
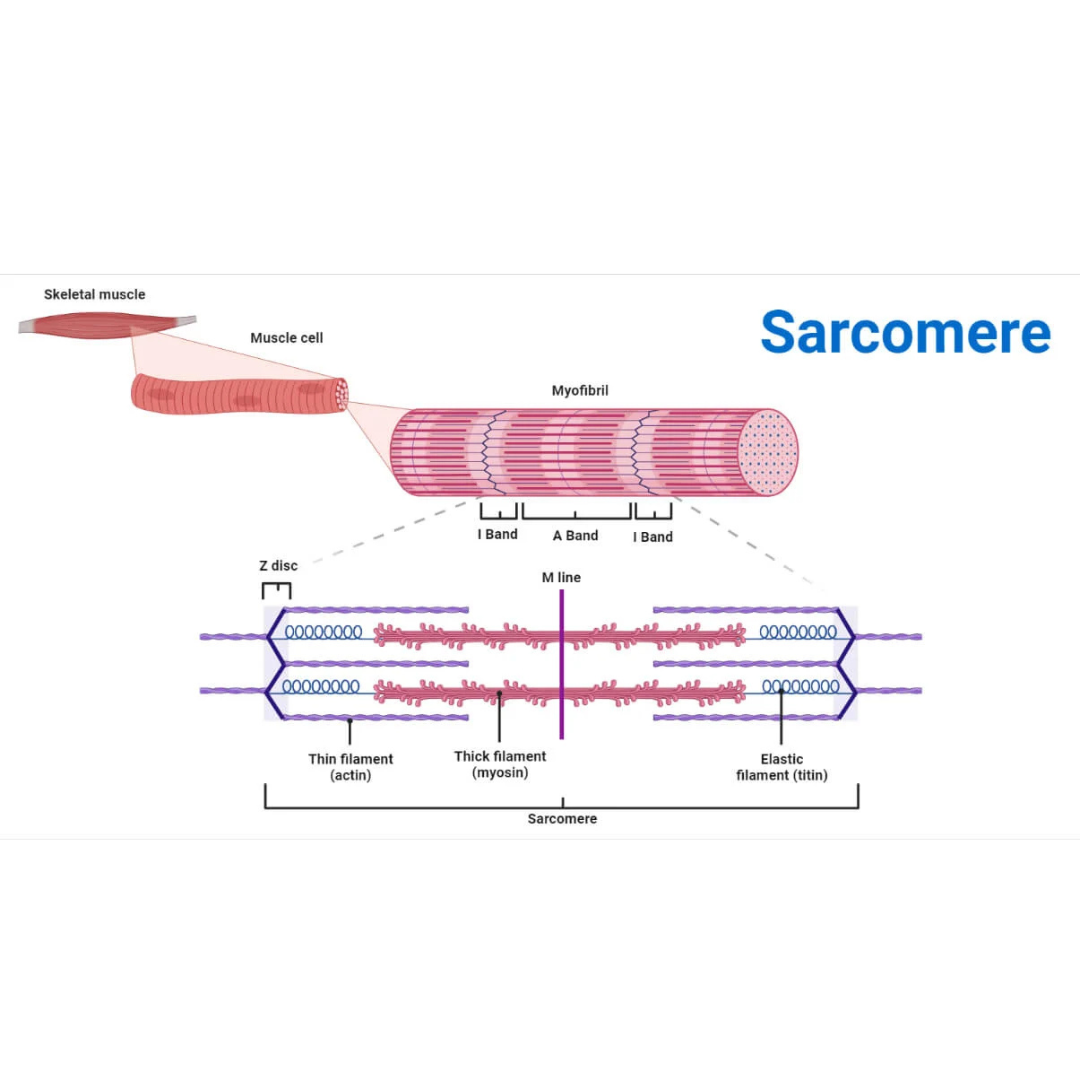
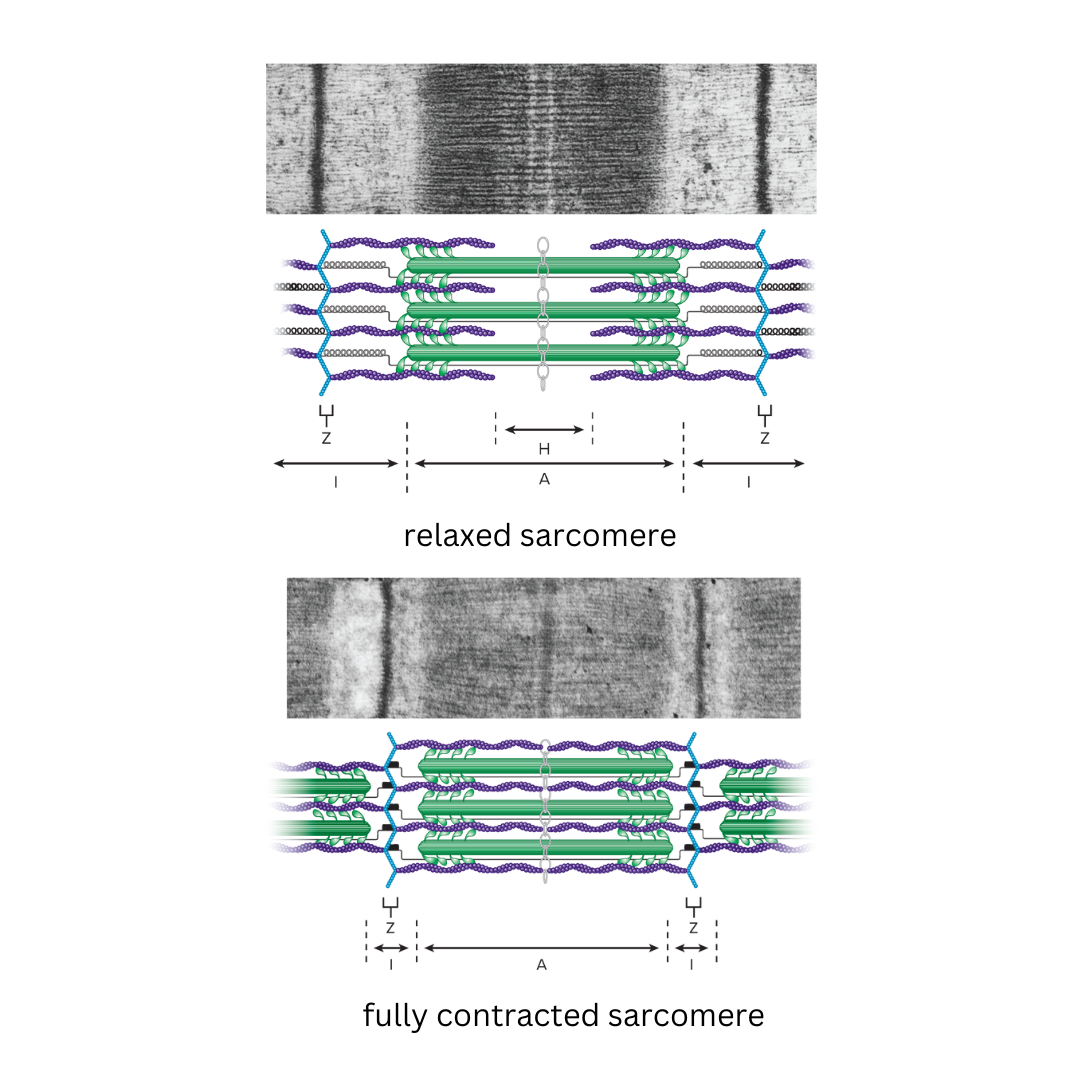
sarcomeres
9.3: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy: Fibers ⚙
structural and functional contractile unit of the skeletal muscle fiber.
Part of a myofibril between adjacent Z disks
Each one is composed of two main protein filaments—actin and myosin
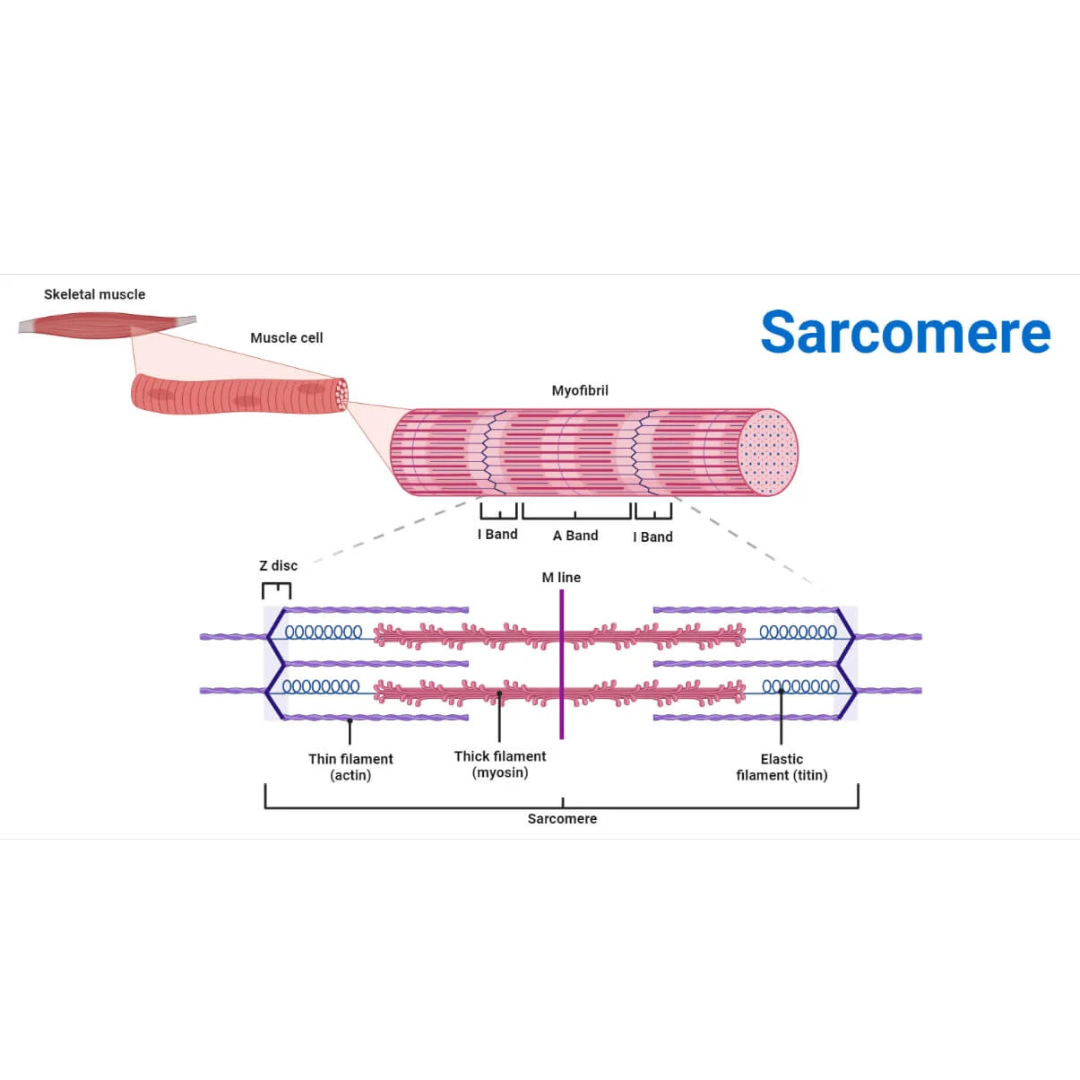
titin filaments
9.3: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy: Sarcomeres
links thin filaments to Z disks
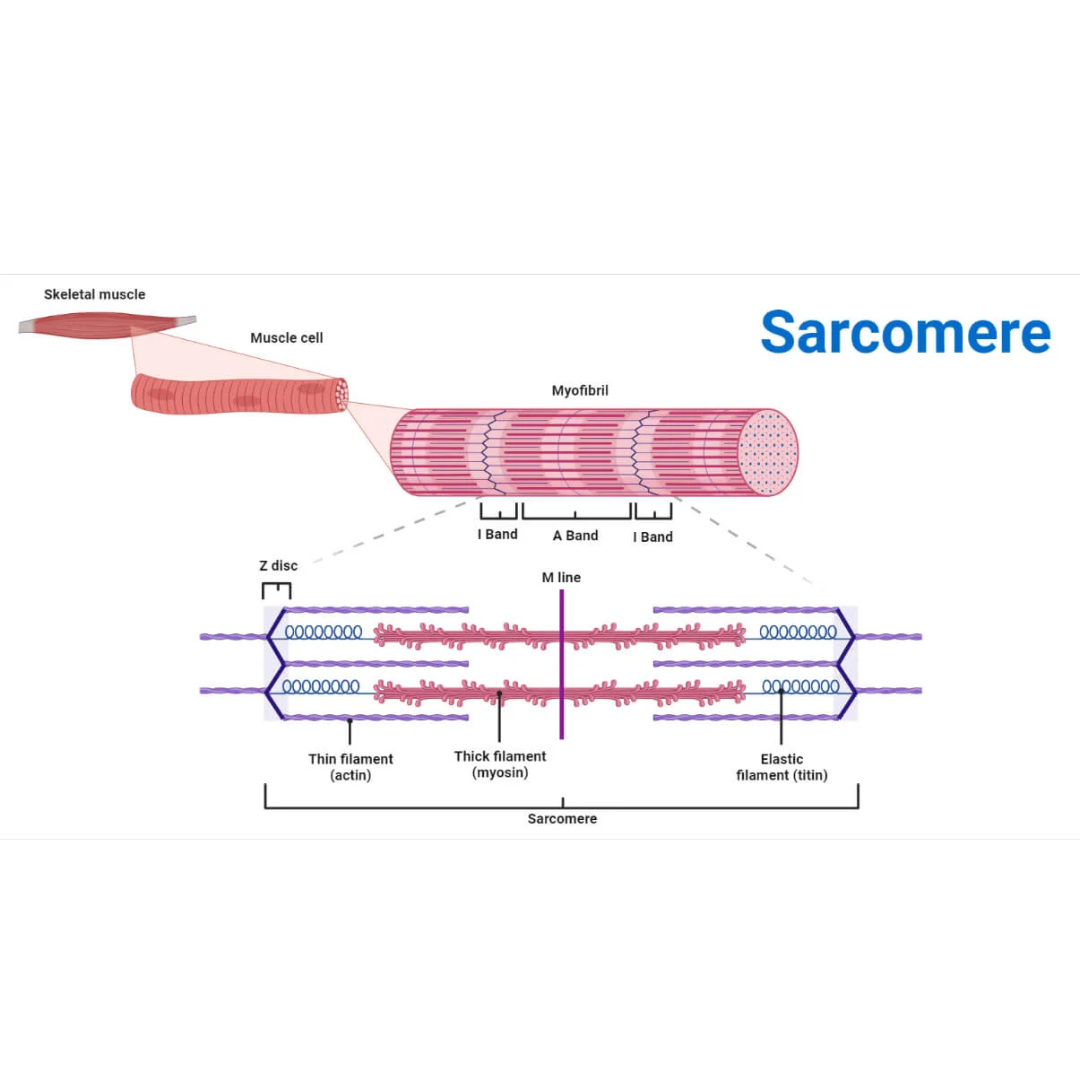
Z disks
9.3: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy: Sarcomeres
Delicate, membranelike structure found at each end of a sarcomere to which actin myofilaments attach
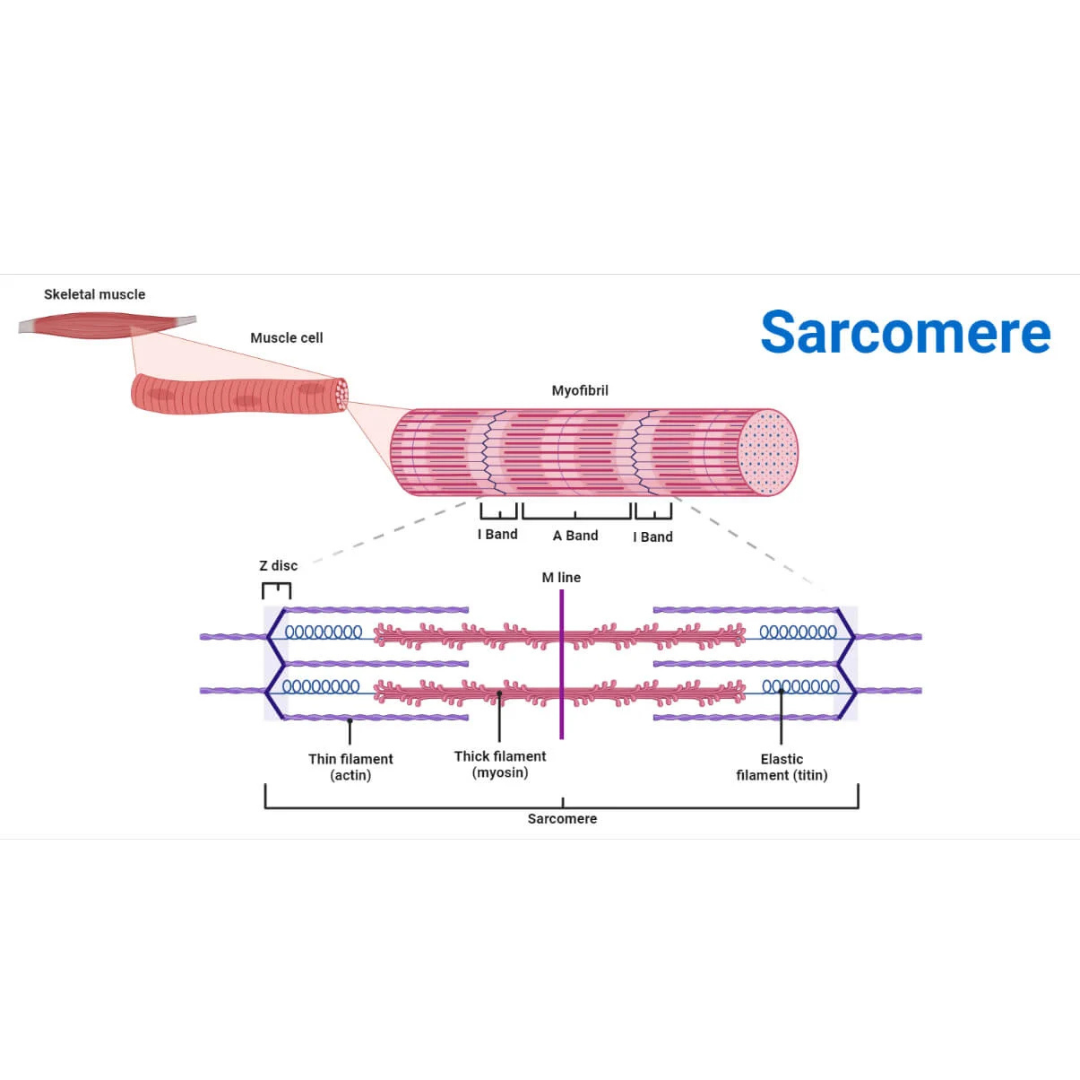
I band
9.3: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy: Sarcomeres
The area between the ends of two adjacent myosin myofilaments within a myofibril
Z disk divides this into two equal parts.
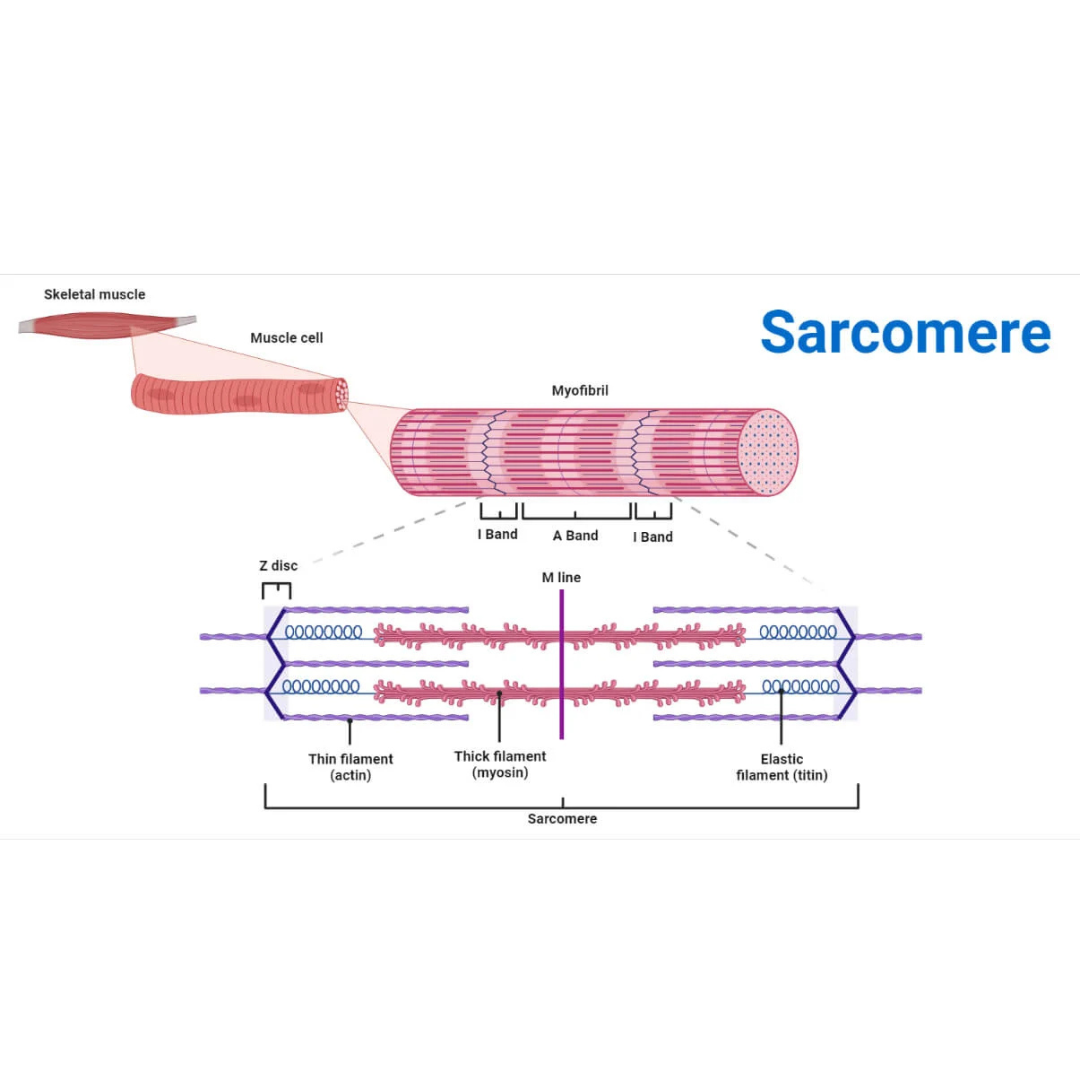
A band
9.3: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy: Sarcomeres
Length of the myosin myofilament in a sarcomere
the darker-staining band in the center of each sarcomere
contains both actin and myosin myofilaments overlapping, except in the center of the [term]
![<p><strong>9.3: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy: Sarcomeres</strong></p><ul><li><p>Length of the myosin myofilament in a sarcomere</p></li><li><p>the darker-staining band in the center of each sarcomere</p></li><li><p>contains both actin and myosin myofilaments overlapping, except in the center of the [term]</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/93fb47fd-1069-4b8c-ac6f-f143010f67a4.png)
H zone
9.3: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy: Sarcomeres
area in the center of the A band in which there are no actin myofilaments
contains only myosin
only found in relaxed muscle
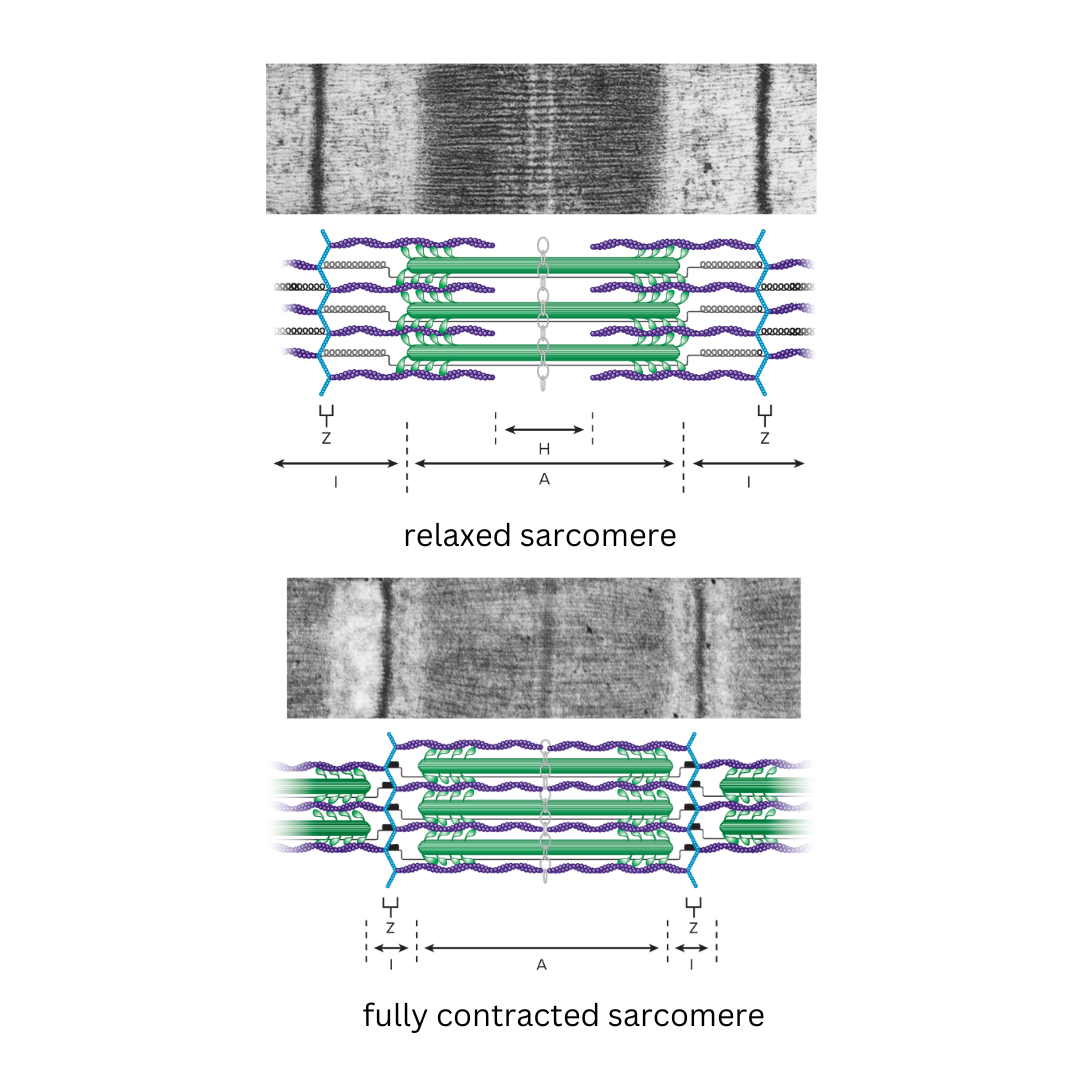
M line
9.3: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy: Sarcomeres
The line in the center of a sarcomere made of delicate filaments that hold the myosin myofilaments in place in the sarcomere of muscle fibers.
myosin head
9.3: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy: Actin Myofilaments
the part of a myosin molecule that binds to actin filaments and generates force for muscle contraction
G actin (active sites)
9.3: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy: Actin Myofilaments
Globular protein molecules that, when bound together, form fibrous actin (F actin)
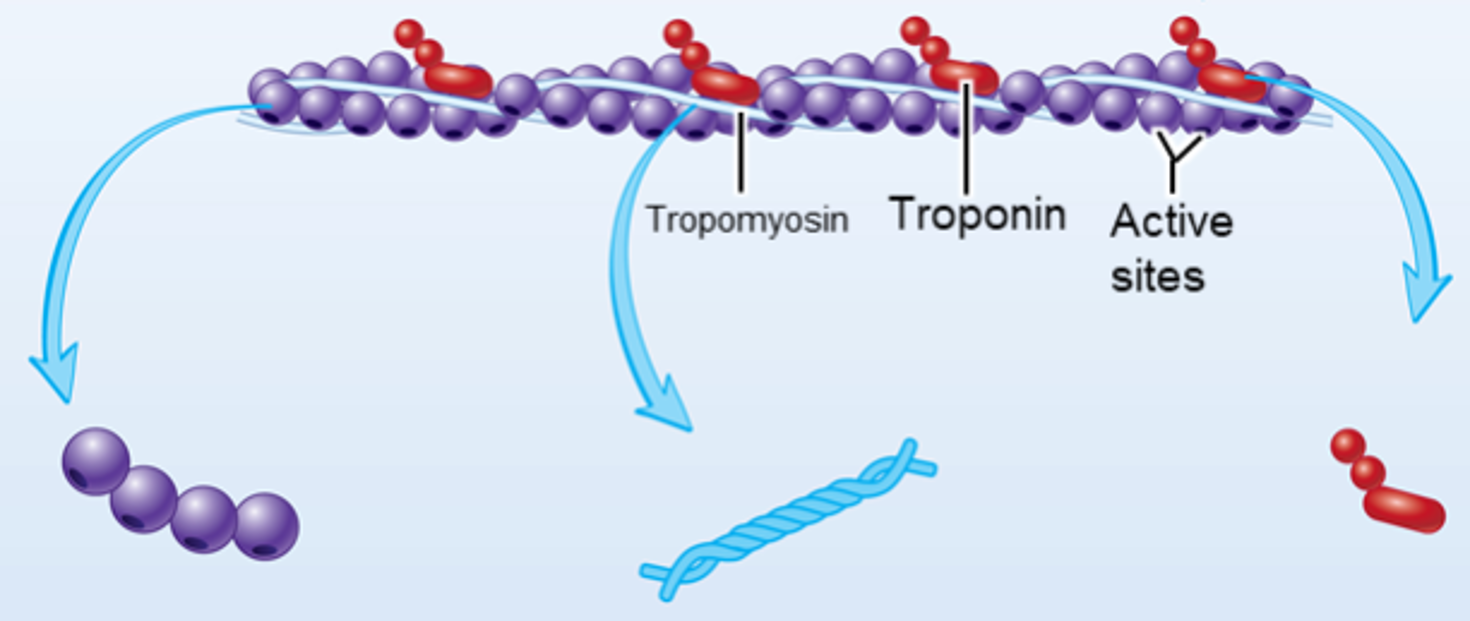
tropomyosin
9.3: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy: Actin Myofilaments
chain that goes across the surface of the actin sites, not allowing the myosin heads to hook up with the actin
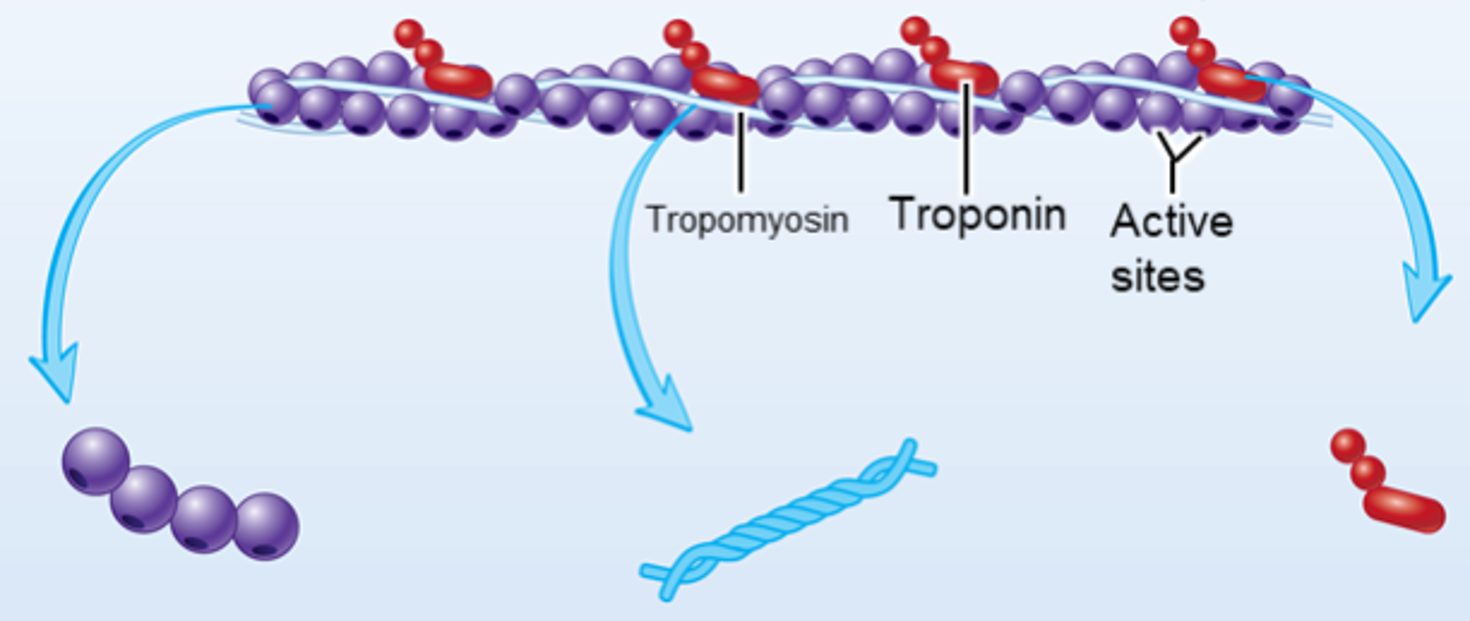
troponin
9.3: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy: Actin Myofilaments
the padlock that holds the tropomyosin (chain) in place
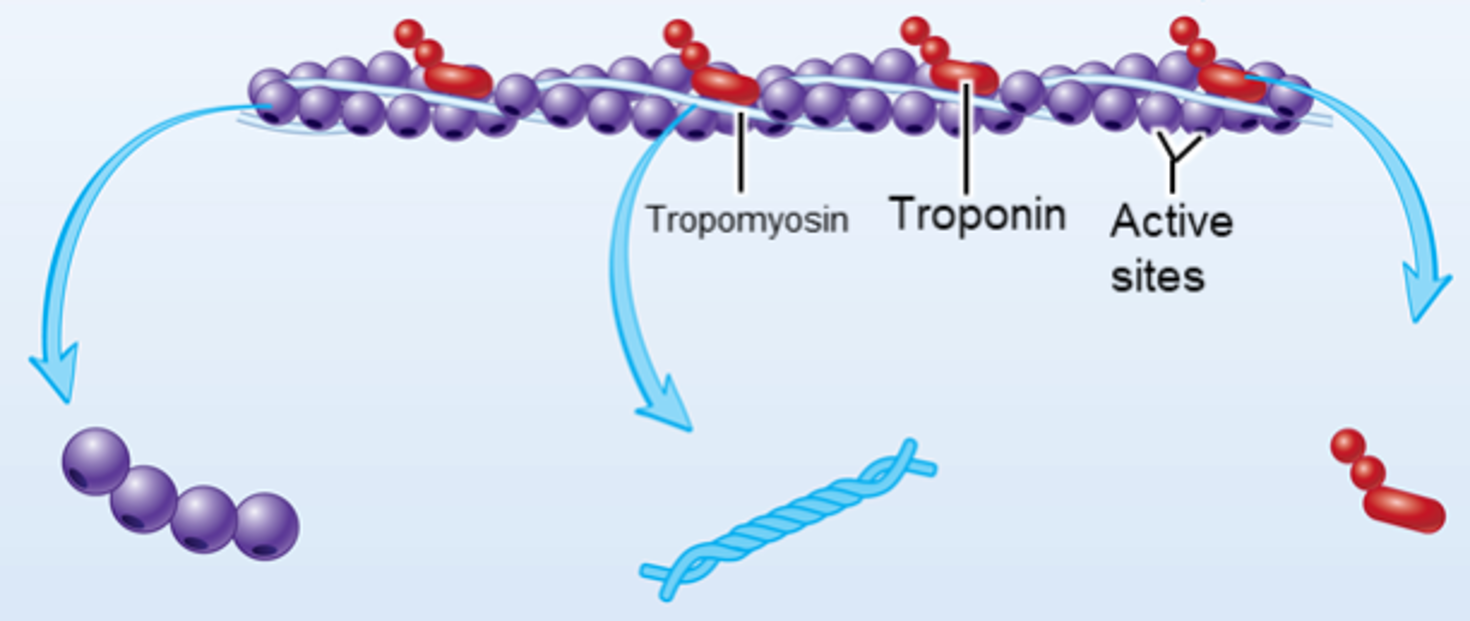
calcium
9.3: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy: Actin Myofilaments
released by the sarcoplasmic reticulum
injected through the T tubules, into the myofibrils
this mineral then binds to troponin and unlocks it, which removes tropomyosin from the actin sites, allowing the myosin heads to connect to the actin site to form a cross-bridge and undergo a power stroke, which pulls the z disks closer to the M line
sliding filament model
9.3: Skeletal Muscle Anatomy: Fibers
explains how muscles contract at a cellular level, describing the process where thin actin filaments slide past thick myosin filaments within a muscle fiber, causing the muscle to shorten and generate force, powered by the energy from ATP molecules
resting membrane potential (RMP)
9.4: Skeletal Muscle Fiber Physiology
The electric charge difference inside a plasma membrane is measured relative to just outside the plasma membrane.
ion channels
9.4: Skeletal Muscle Fiber Physiology
act as selective pores in the cell membrane, allowing specific ions to flow in and out of the cell, which in turn creates electrical changes across the membrane that form the basis of a nerve impulse
action potential
9.4: Skeletal Muscle Fiber Physiology
occurs when the excitable cell is stimulated
reversal of the resting membrane potential such that the inside of the plasma membrane becomes positively charged compared with the outside
a rapid change in the electrical charge of a muscle cell's membrane that triggers contraction
action potential phases
9.4: Skeletal Muscle Fiber Physiology
depolarization and repolarization
depolarization phase
9.4: Skeletal Muscle Fiber Physiology
phase of the action potential in which the membrane potential moves toward zero, or becomes positive.
occurs when there is a rapid influx of sodium ions into the plasma membrane
repolarization phase
9.4: Skeletal Muscle Fiber Physiology
Phase of the action potential in which the membrane potential moves from its maximum degree of depolarization toward the value of the resting membrane potential
all-or-none principle
9.4: Skeletal Muscle Fiber Physiology
When a stimulus is applied to a cell, an action potential is either produced or not. In muscle cells, the cell either contracts to the maximum extent possible (for a given condition) or does not contract.
neuromuscular junction (NMJ)
9.4: Skeletal Muscle Fiber Physiology
Specialized synapse between a motor neuron and a muscle fiber.
consists of a group of enlarged axon terminals (the end of the axon) that rests in an invagination of the sarcolemma, this contact results in an action potential
the stimulus for the action potential is the release of acetylcholine from the motor neuron
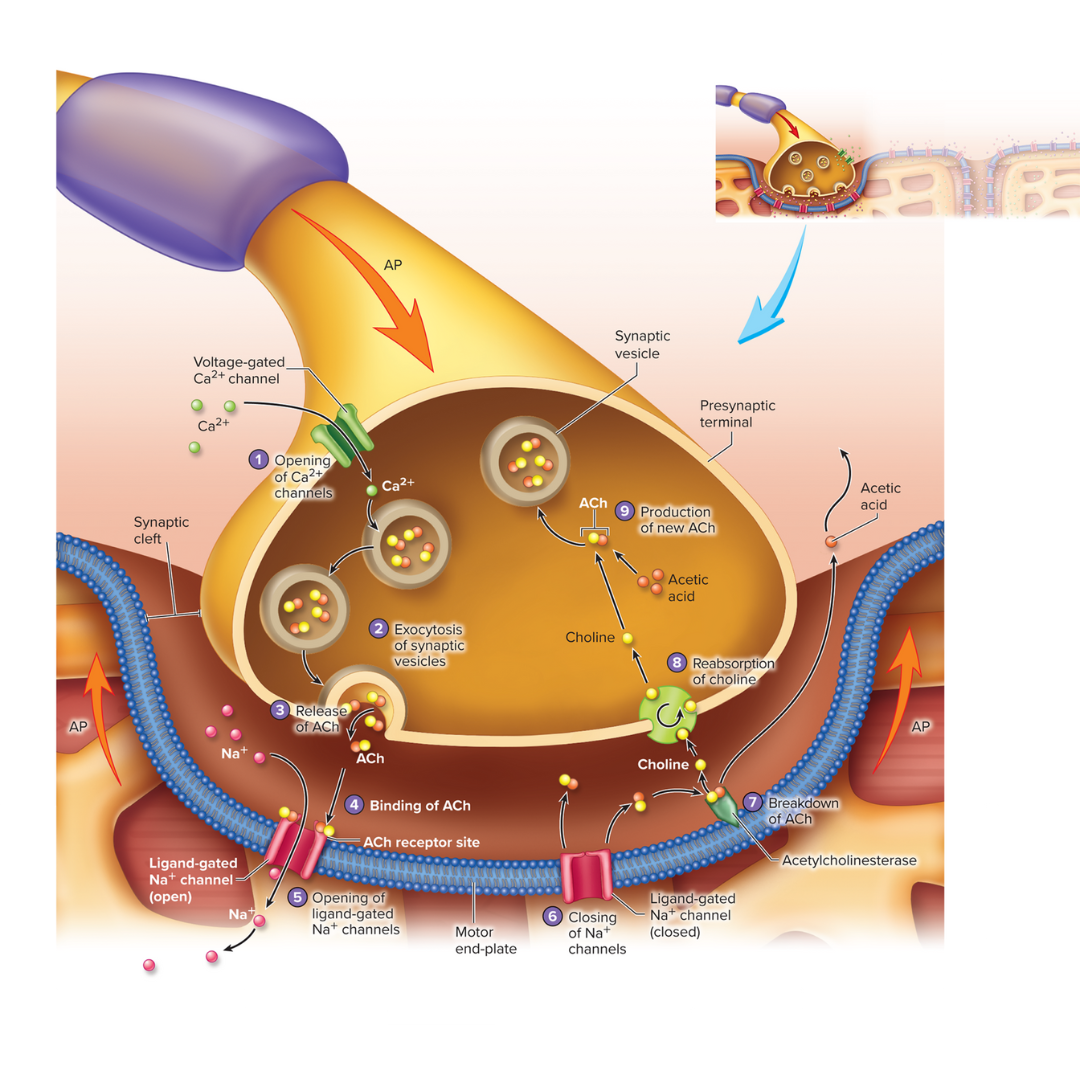
synaptic cleft
9.4: Skeletal Muscle Fiber Physiology
the fluid-filled space between a neuromuscular junction
excitation-contraction coupling
9.4: Skeletal Muscle Fiber Physiology
occurs at the triad
links the electrical component of muscle contraction to the mechanical component
the link between an action potential on the sarcolemma and the sarcomere shortening
cross-bridge movement
9.4: Skeletal Muscle Fiber Physiology
the mechanical component of muscle contraction
causes sarcomeres to shorten and the muscles to contract
requires energy from one ATP molecule for each cycle
before each cycle, the myosin head is in its resting (high-energy) position
the myosin heads connecting to the actin sites
[study this image]
![<p><strong>9.4: Skeletal Muscle Fiber Physiology</strong></p><ul><li><p>the mechanical component of muscle contraction</p></li><li><p>causes sarcomeres to shorten and the muscles to contract</p></li><li><p>requires energy from one ATP molecule for each cycle</p></li><li><p>before each cycle, the myosin head is in its resting (high-energy) position</p></li><li><p>the myosin heads connecting to the actin sites</p></li><li><p>[study this image]</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/8f119e32-7448-4818-b49a-031a49172549.png)
muscle relaxation
9.4: Skeletal Muscle Fiber Physiology
occurs when acetylcholine is no longer released at the neuromuscular junction
calcium ions are transported into the sarcoplasmic reticulum
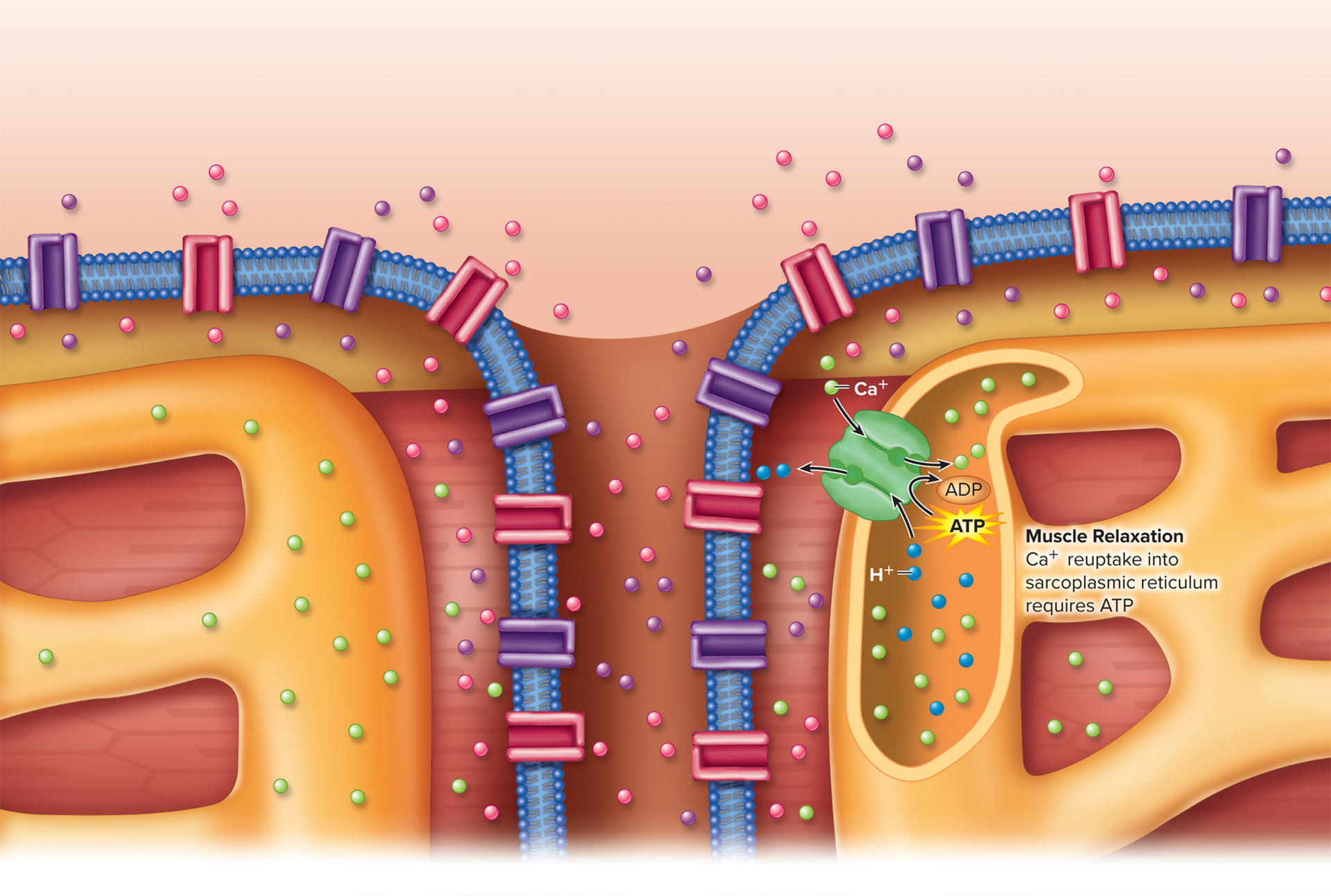
muscle twitch
9.5: Whole Skeletal Muscle Physiology
Contraction of a whole muscle in response to a stimulus that causes an action potential in one or more muscle fibers.
force of contraction
9.5: Whole Skeletal Muscle Physiology
a stimulus of increasing frequency increases the…?
Treppe
treppe
9.5: Whole Skeletal Muscle Physiology
Series of successively stronger contractions that occur when a rested muscle fiber receives closely spaced stimuli of the same strength but with a sufficient stimulus interval to allow complete relaxation of the fiber between stimuli.
wave summation
9.5: Whole Skeletal Muscle Physiology
results when many action potentials are produced in a muscle fiber
tetanus of muscles
9.5: Whole Skeletal Muscle Physiology
results from wave summation; frequency of stimulus is higher than for treppe
incomplete tetanus
9.5: Whole Skeletal Muscle Physiology
occurs when the action potential frequency is low enough to allow partial relaxation of the muscle fibers
complete tetanus
9.5: Whole Skeletal Muscle Physiology
occurs when the action potential frequency is high enough that no relaxation of the muscle fibers occurs
active tension
9.5: Whole Skeletal Muscle Physiology
tension is produced by the contraction of a muscle
as the length of a muscle fiber increases, its [term term] also increases. If stretched passed optimal length, it declines
isometric contractions
9.5: Whole Skeletal Muscle Physiology
a muscle produces increasing tension as it remains at a constant length
this is a characteristic of postural muscles that maintain a constant tension without changing their length
isotonic contractions
9.5: Whole Skeletal Muscle Physiology
a muscle produces a constant tension and shortens during contraction
this is a characteristic of finger and hand movements
includes concentric and eccentric contractions
concentric - a muscle produces tension as it shortens
eccentric - a muscle produces tension as it resists lengthening
slow twitch muscle fibers
9.6: Muscle Fiber Types
a type of muscle fiber that breaks down ATP slowly and have well-developed blood supply, many mitochondria, and myoglobin
muscle fibers used for mundane, simple tasks
dark meat
fast twitch muscle fibers
9.6: Muscle Fiber Types
break down ATP rapidly,
for powerful movements
white meat
Type IIa muscle fibers have a well-developed blood supply, more mitochondria, and more myoglobin
Type IIx muscle fibers have large amounts of glycogen, poor blood supply, fewer mitochondria, and little myoglobin
four sources of energy for ATP production in muscles
9.6: Muscle Fiber Types
conversion of two ADP to one ATP and one adenosine monophosphate (AMP) by the enzyme adenylate kinase
Transfer of phosphate from a molecule called creatine phosphate by the enzyme creatine kinase from ADP to form ATP
Anaerobic production of ATP during intensive short-term exercise
Aerobic production of ATP during most exercise and normal conditions