8: Roots FINAL
1/125
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
126 Terms
1. Anchorage
2. Absorb water and nutrients
3. Conduct water, nutrients and food
4. Produce some hormones
5. Some roots are also important storage organs.
function of roots
young portions absorb, old portions anchor
do all parts of the root absorb
swollen, enlarged roots for storage
what kind of roots do cassava and kamote have
rhizoid for attachment, no conducting tissues
do mosses have roots?
1. primary roots
2. secondary roots
3. adventitious
types of roots
adventitious roots
develop from stems, leaves, and other vegetative non-root organs
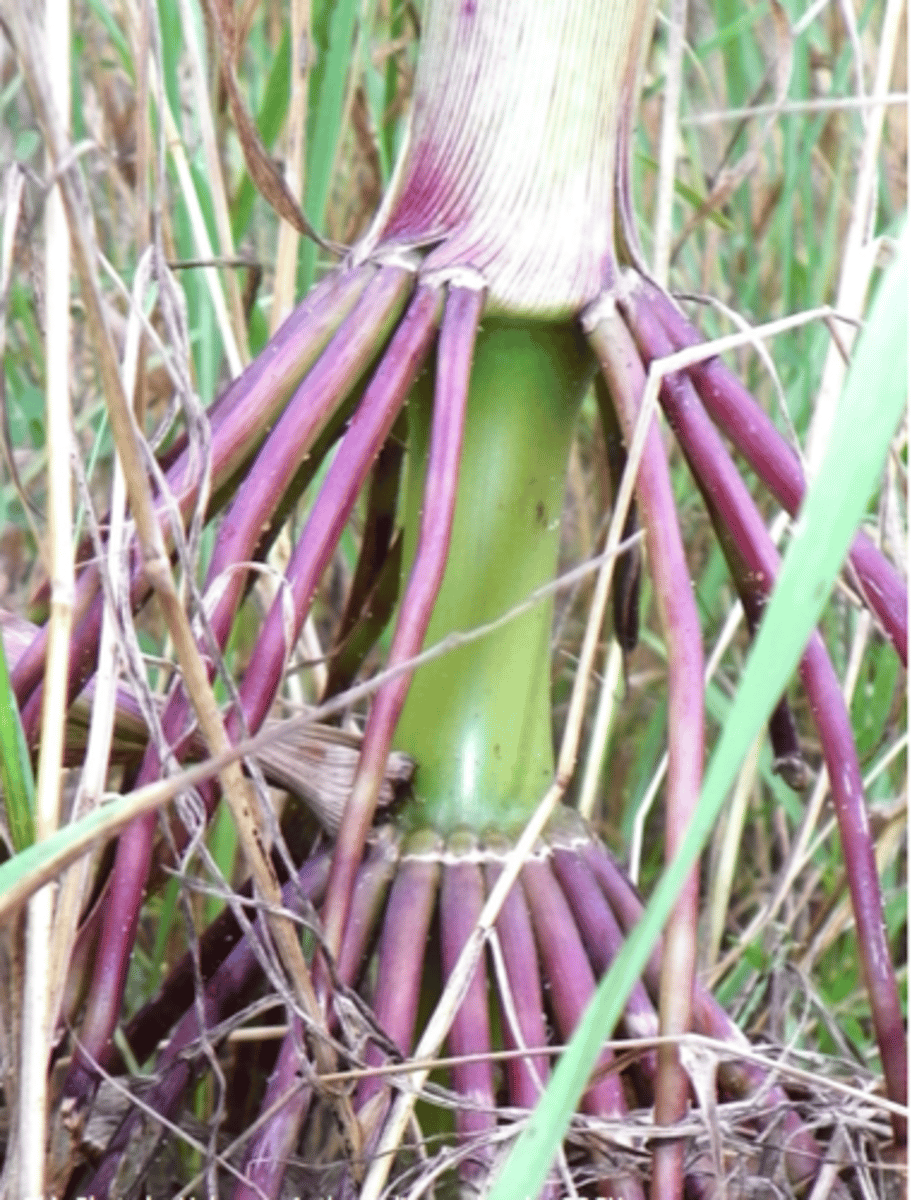
prop roots
develop from the stem

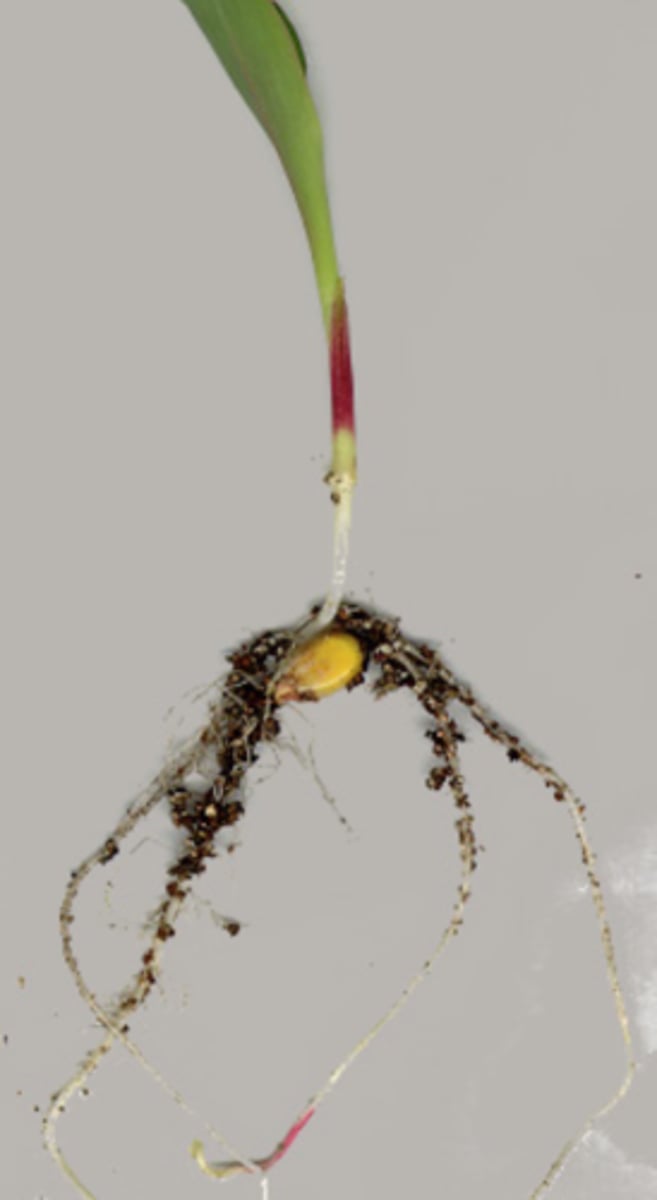
primary roots
originate from the radicle
tap root
main root + 2ndary roots
fibrous root
short-lived radicle, cant see 1 major root
radicle
primordial root
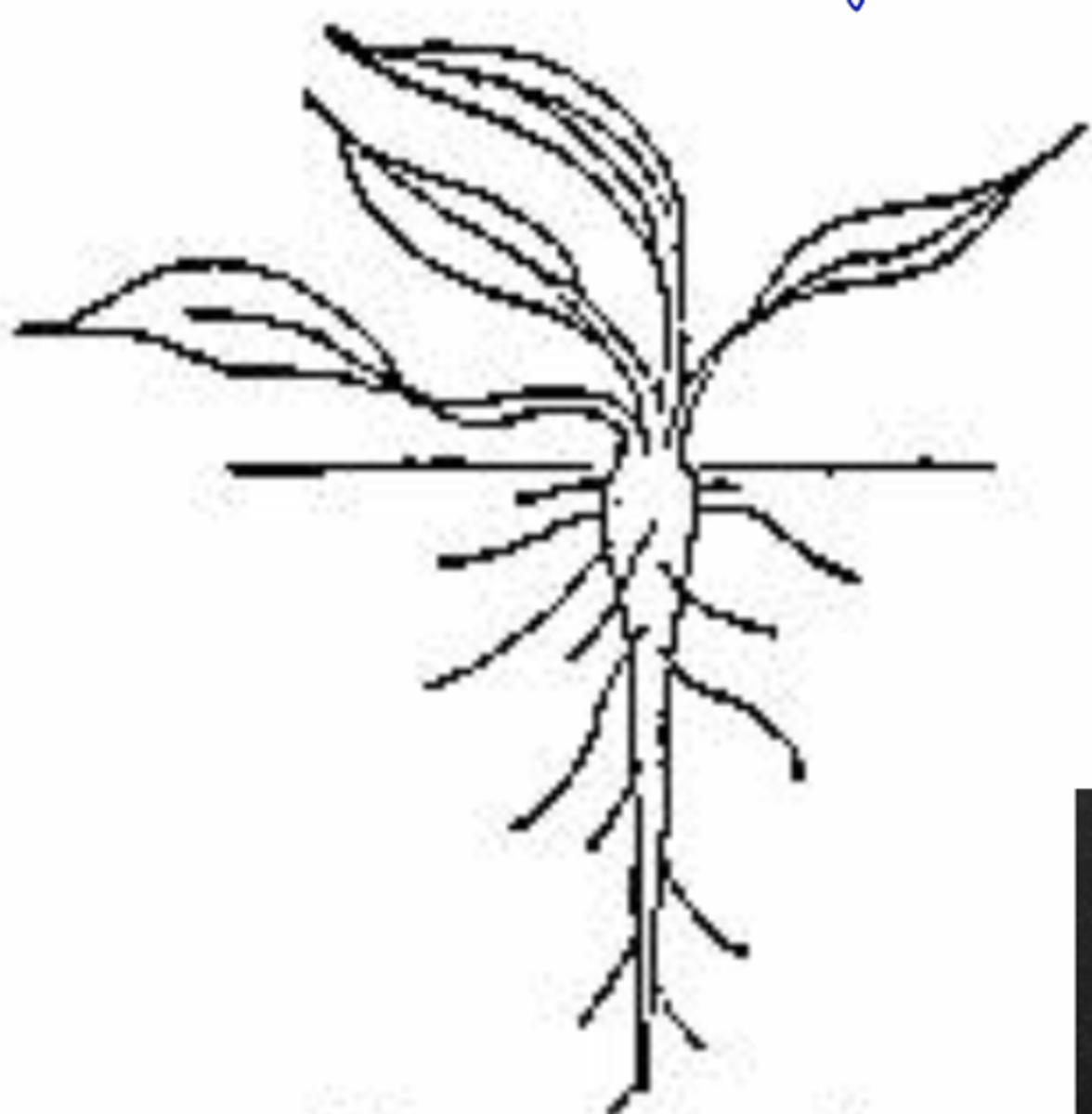
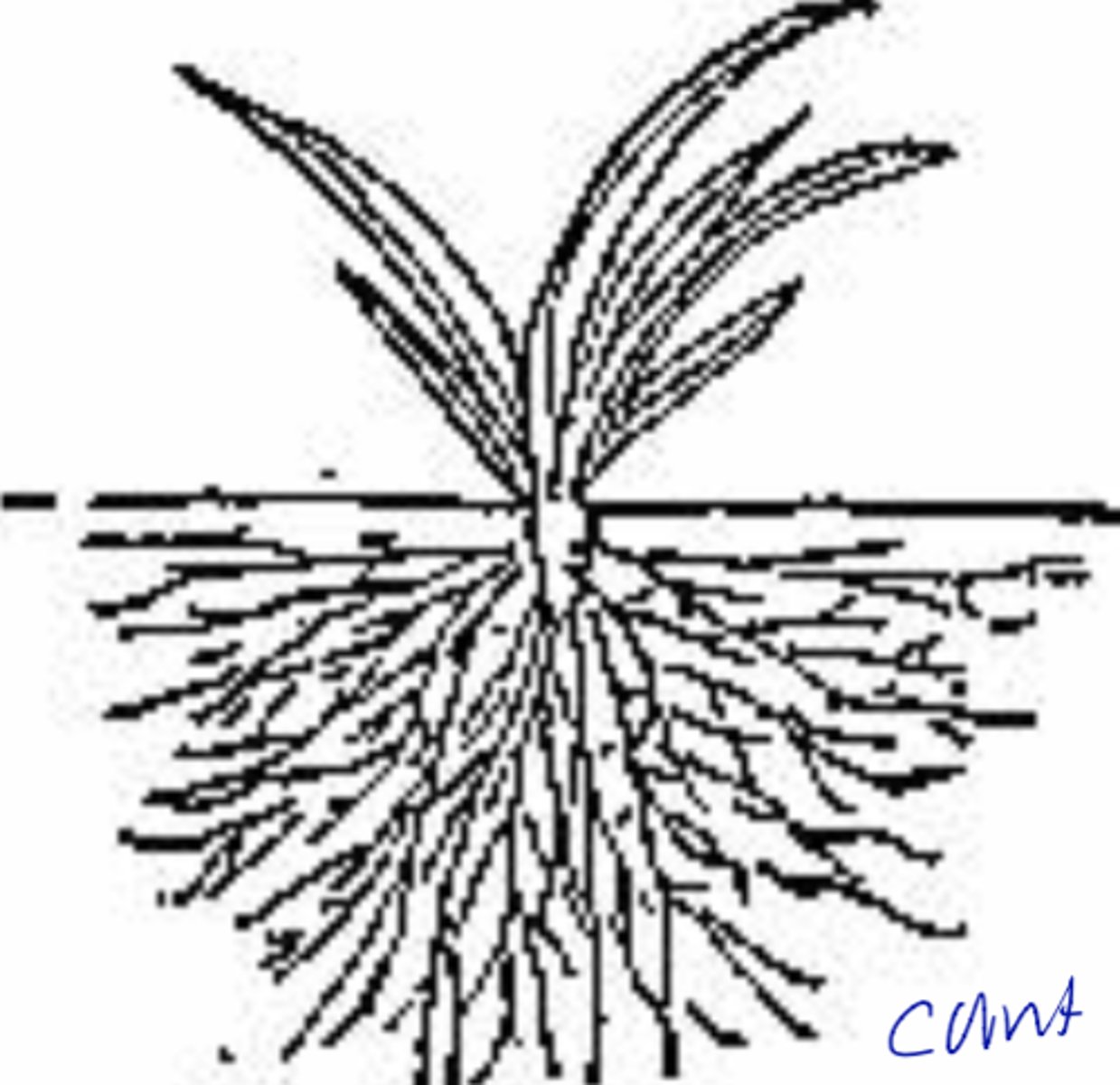
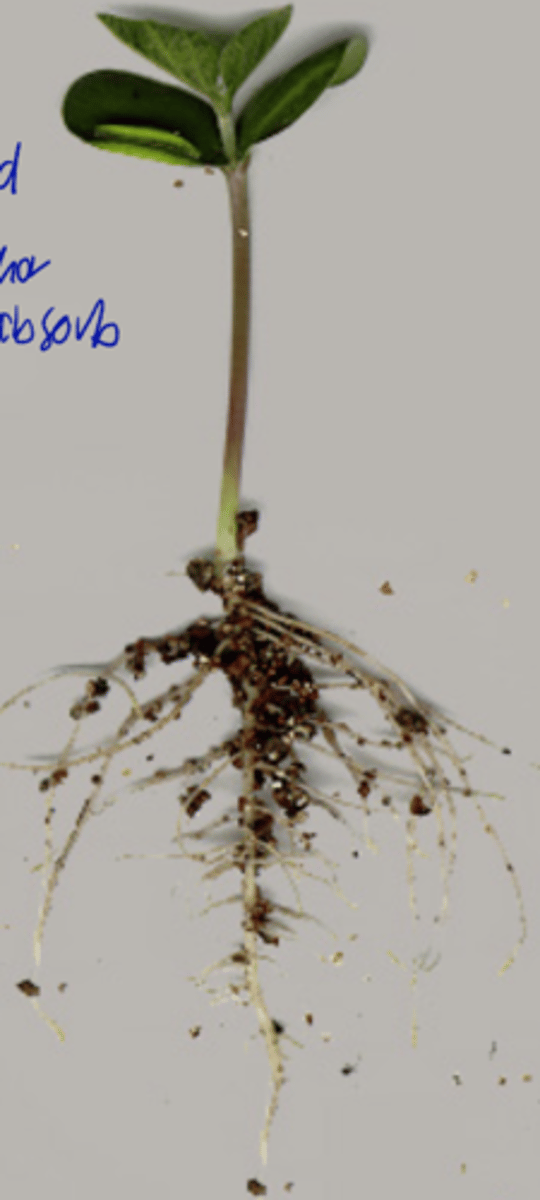
taproot system and fibrous root system
patterns of root growth
Taproot system
root growth system in eudicots, gymnosperms
taproot system
digs deep into soil; old roots sa taas for anchoring sa baba for absorption

fibrous root system
• Seedless vascular plants, monocots
• Adventitious roots
• More shallow and horizontal very seldom
• Common in dry regions

because very seldom lang rain
why do fibrous roots need to be shallow and horizontal very seldom
only from region of maturation
do roots have branches/lateral appendages
endogenously from the pericycle
how do roots arise
bidirectional; produces cells towards AND away from the axis
how does root apex produce cells
calyptrogen
root cap meristem
subterminal
location of root apical meristem
root cap
Protection and aids in penetration into the soil
Peripheral cells (and epidermal cells)
secretes mucigel
Mucigel
slimy compound
• Protection
• Lubrication
• Water absorption
• Nutrient absorption
columella
contain amyloplasts. Sedimentation of these involved in the perception of gravity by roots; positive gravitropism
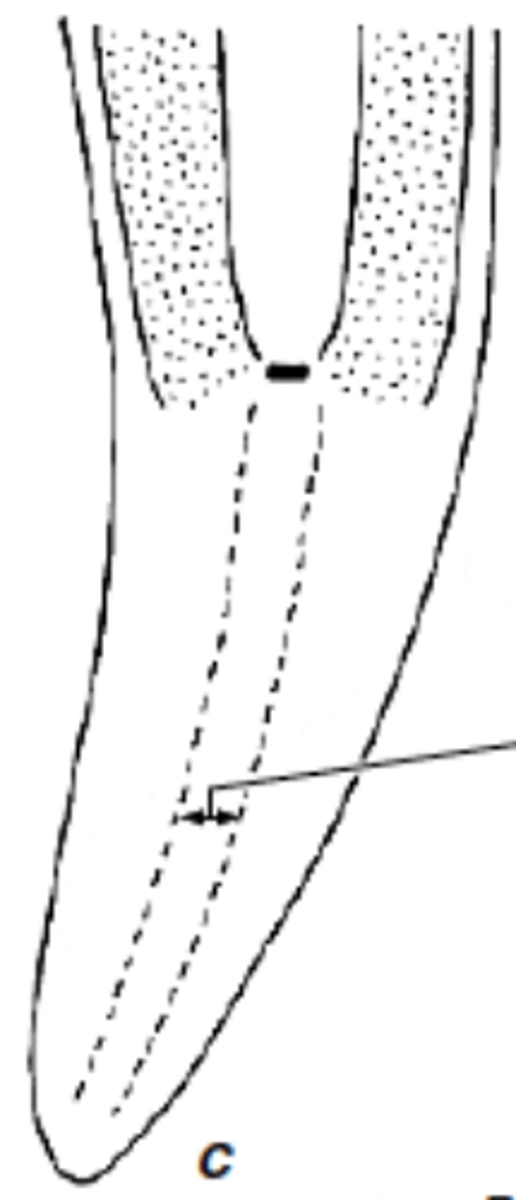
Quiescent center
- 500-1000 seemingly inactive cells
- arrested at G1 interphase
- divide once in 15-20days
- reservoir to replace damage meristems
- organizes the patterns of primary growth in roots
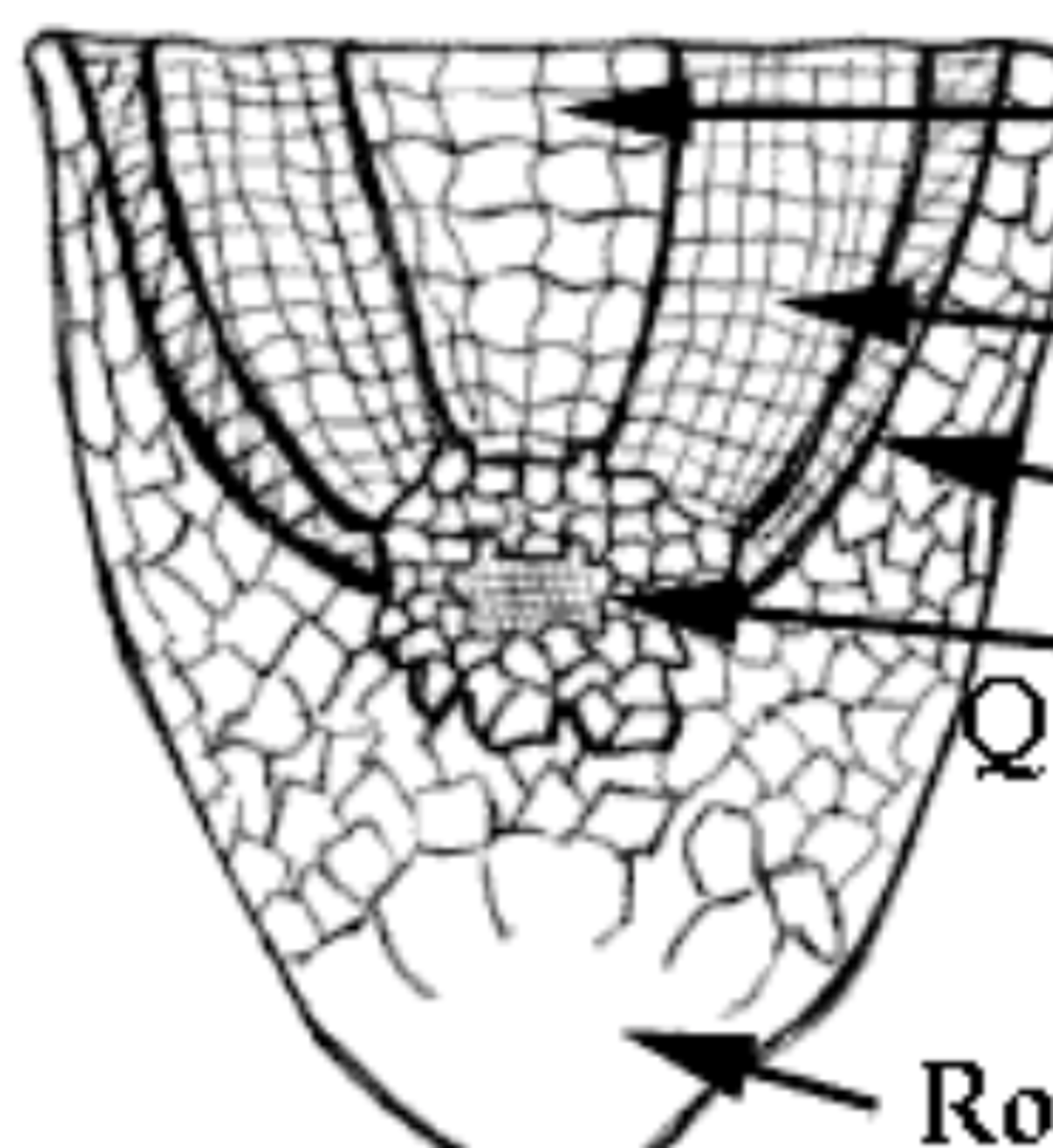
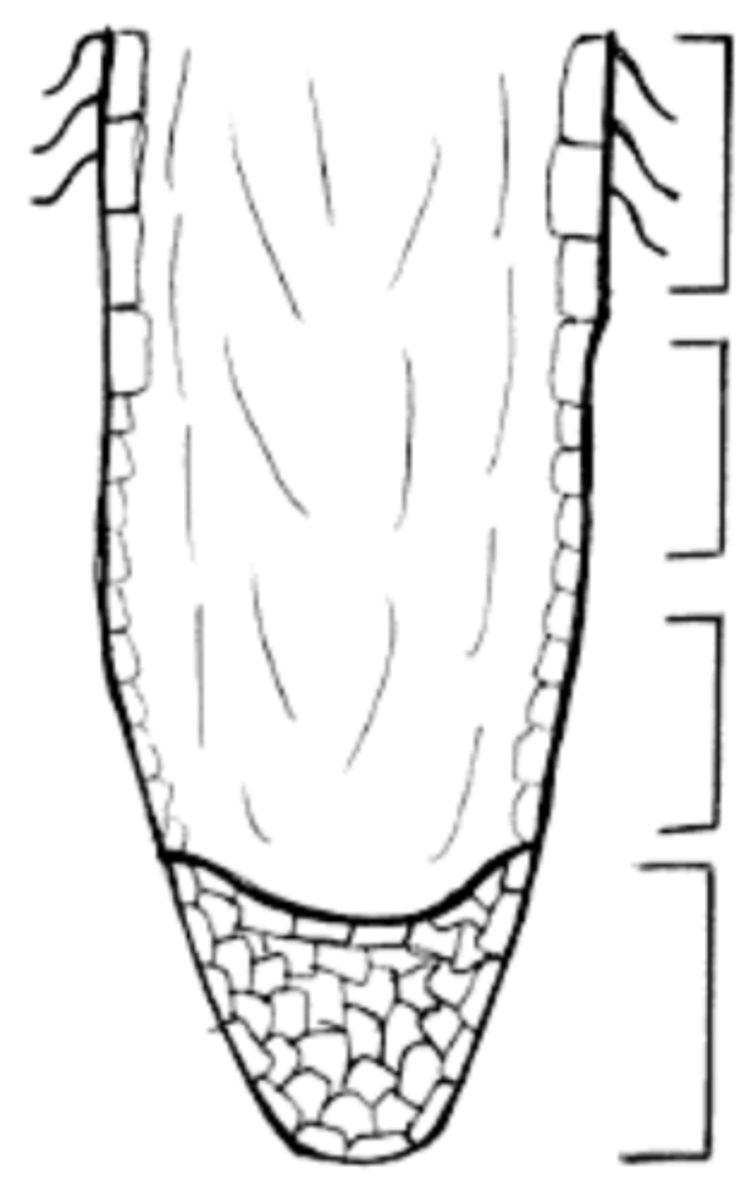
Meristem Region (region of cell division)
Region of Elongation
Region of Differentiation (maturation)
three regions of the (sub)Apical region
Meristem Region (region of cell division)
• 0.5-1.5mm behind root tip
• Area where new cells are created by mitosis
• Divide every 12-36 hours
Region of Elongation
• 4-10mm behind root tip
• Area where cells grow in length (150x)
• Long, vacuolated cells
Region of Differentiation (maturation)
• 1-5 cm behind root tip
• Root hairs
• Area where cells become specialized for different jobs, i.e. storage, protection, transport, etc.
root hairs
increase surface area for absorption
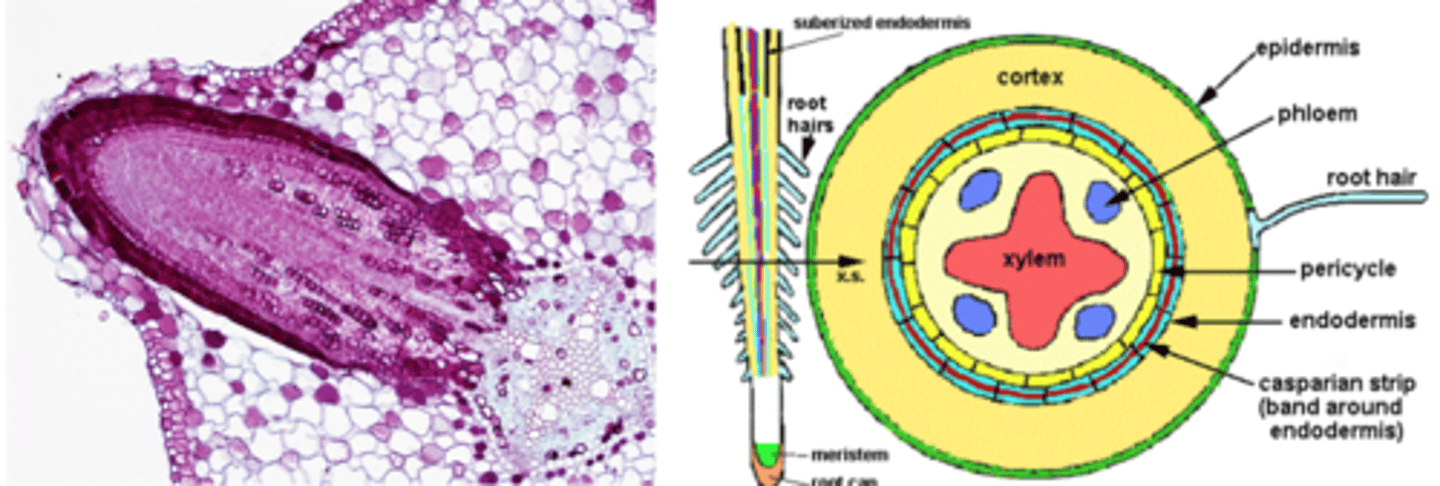
- epidermis
- cortex
- stele
which layers of the root are mature
epidermis
- protoderm
- usu. 1 cell thick
- cuticle absent
- stomata absent
- outer layer of cells, for protection and absorption
cortex
- Ground meristem
- Largest portion
- Exodermis/Hypodermis
- Parenchyma cells
- Endodermis
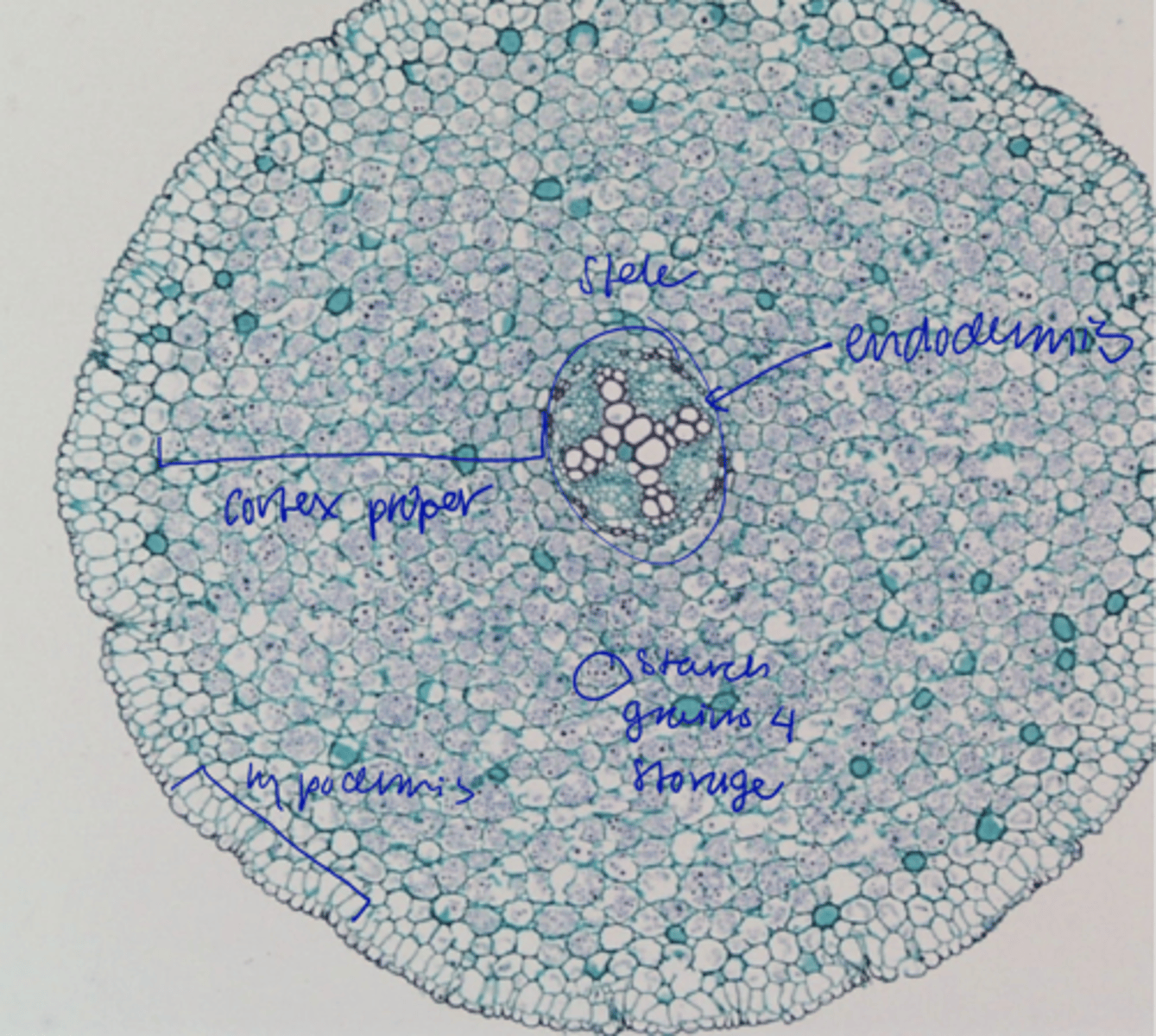
Exodermis/Hypodermis and Endodermis
which cells can the casparian strips be found
symplastic movement
movement of water & solutes thru tissues by passing thru interconnected protoplasts & their plasmodesmata
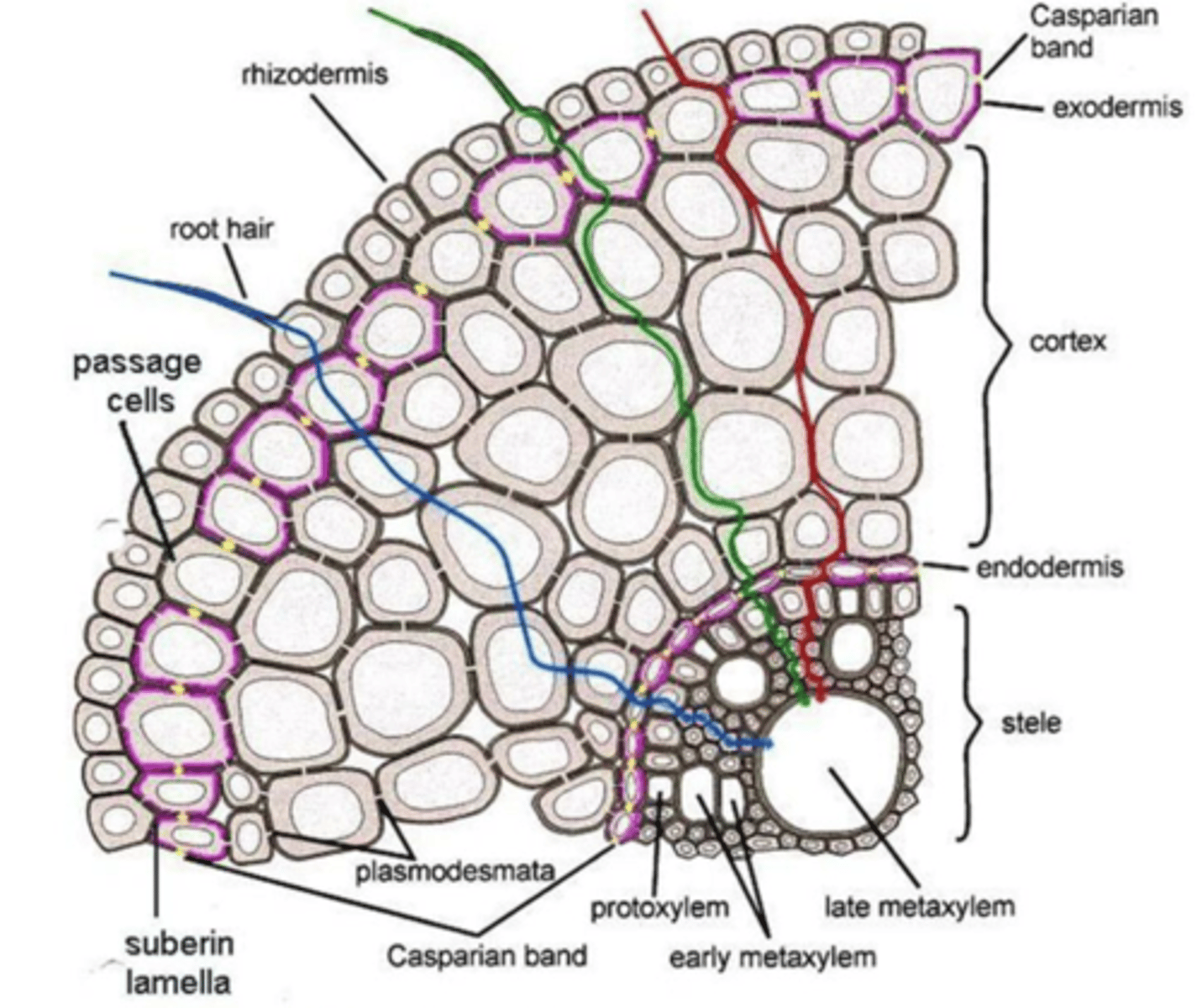
apoplastic movement
movement in the free space (cell walls & intercellular
spaces)
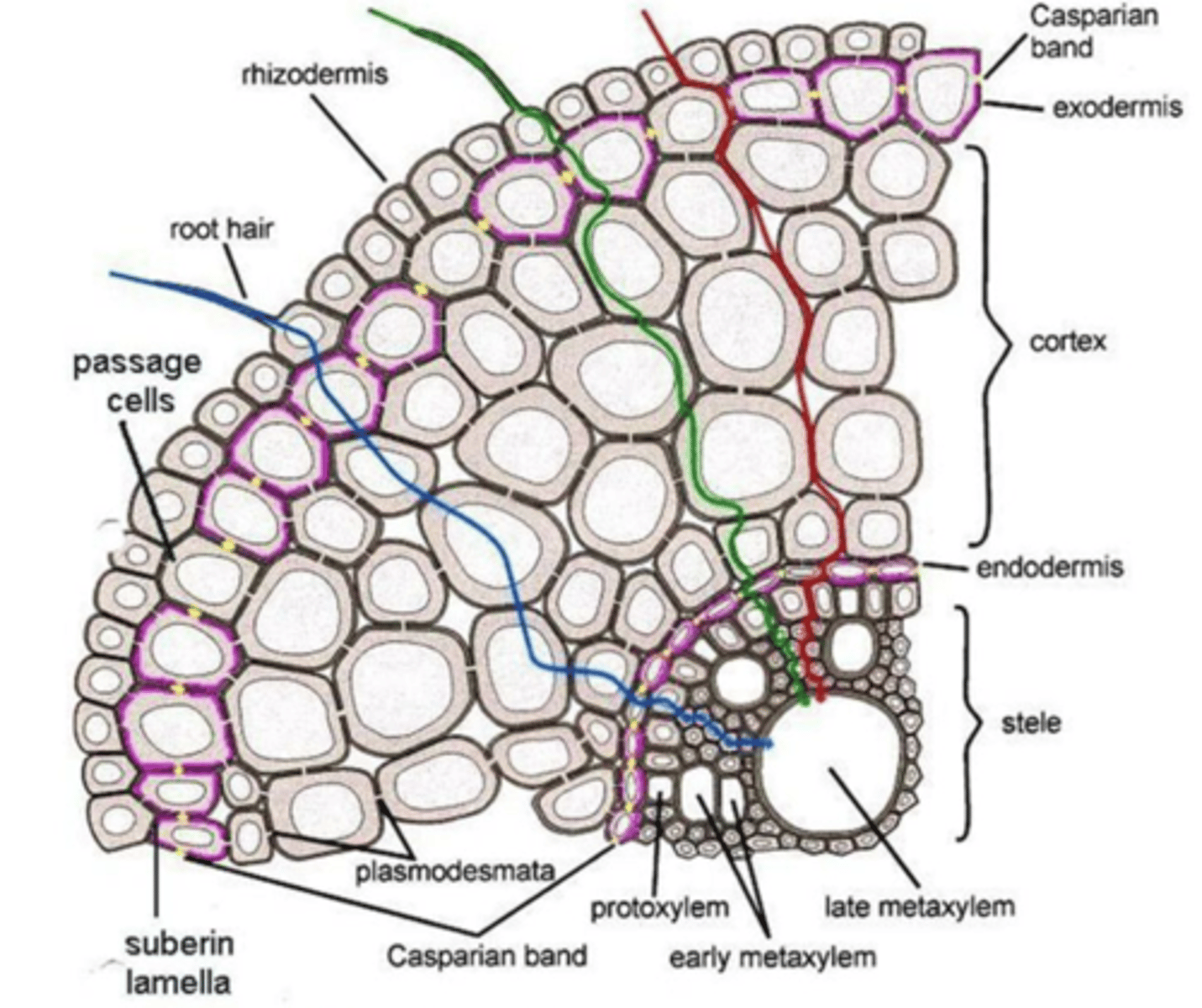
casparian strips
• Impregnated with suberin and sometimes lignin hydrophobic
• Precludes the passage of water and solutes via the tangential wall
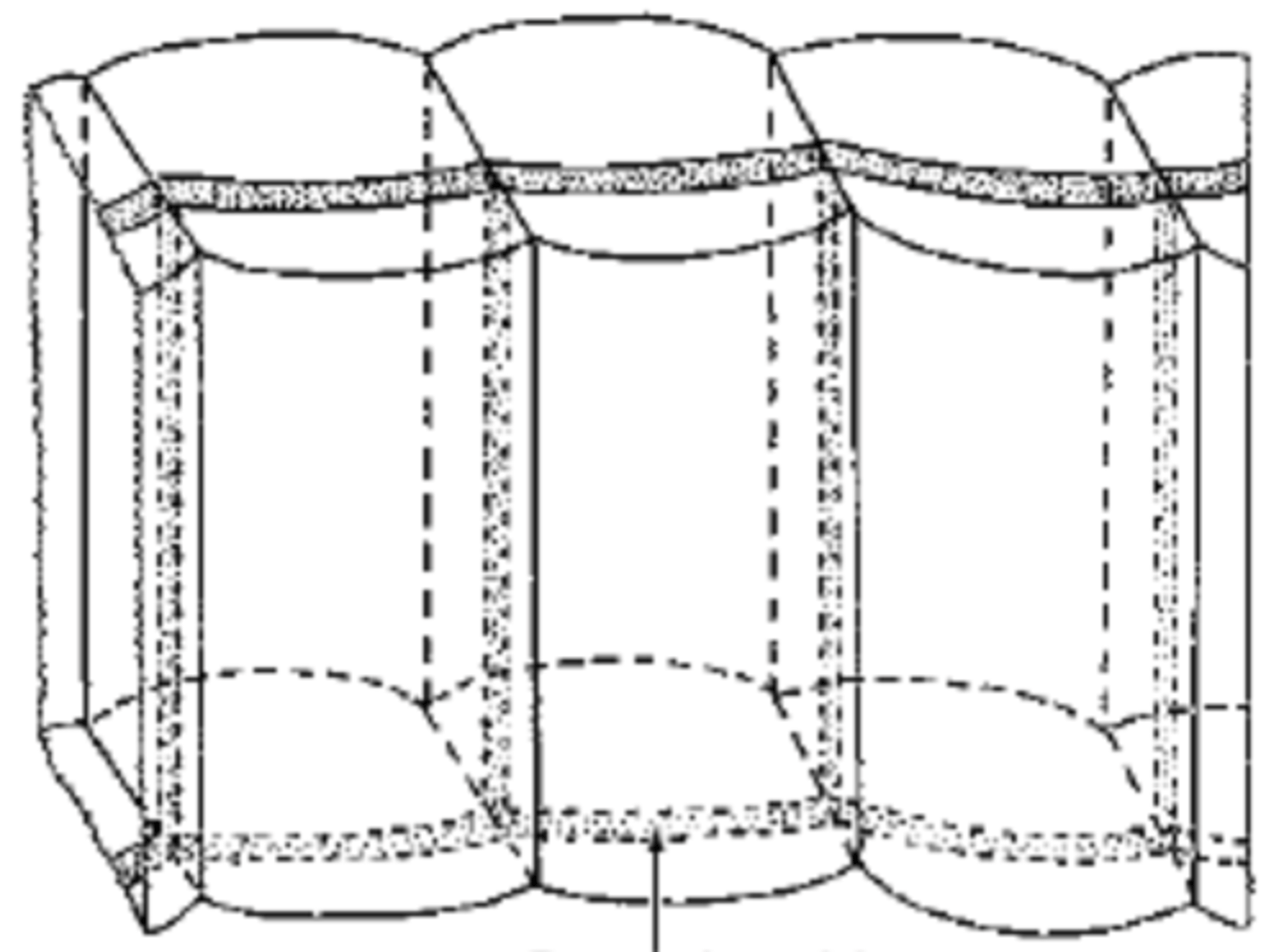
ribbon that boxes an endodermal cell; in transverse and radial wall
itsura + location ng casparian strip
endodermis
- Casparian strip diverts water & dissolved minerals into the cytoplasm of endodermal cells
- Symplastic movement
- Prevents leaks/ back flow
- Controls flow of water into the vascular cylinder
stele
• Pericycle layer
• Vascular tissues
• Pit
pericycle
• Meristematic
• Produces branch roots (secondary or lateral roots)
• Lateral appendages form endogenously
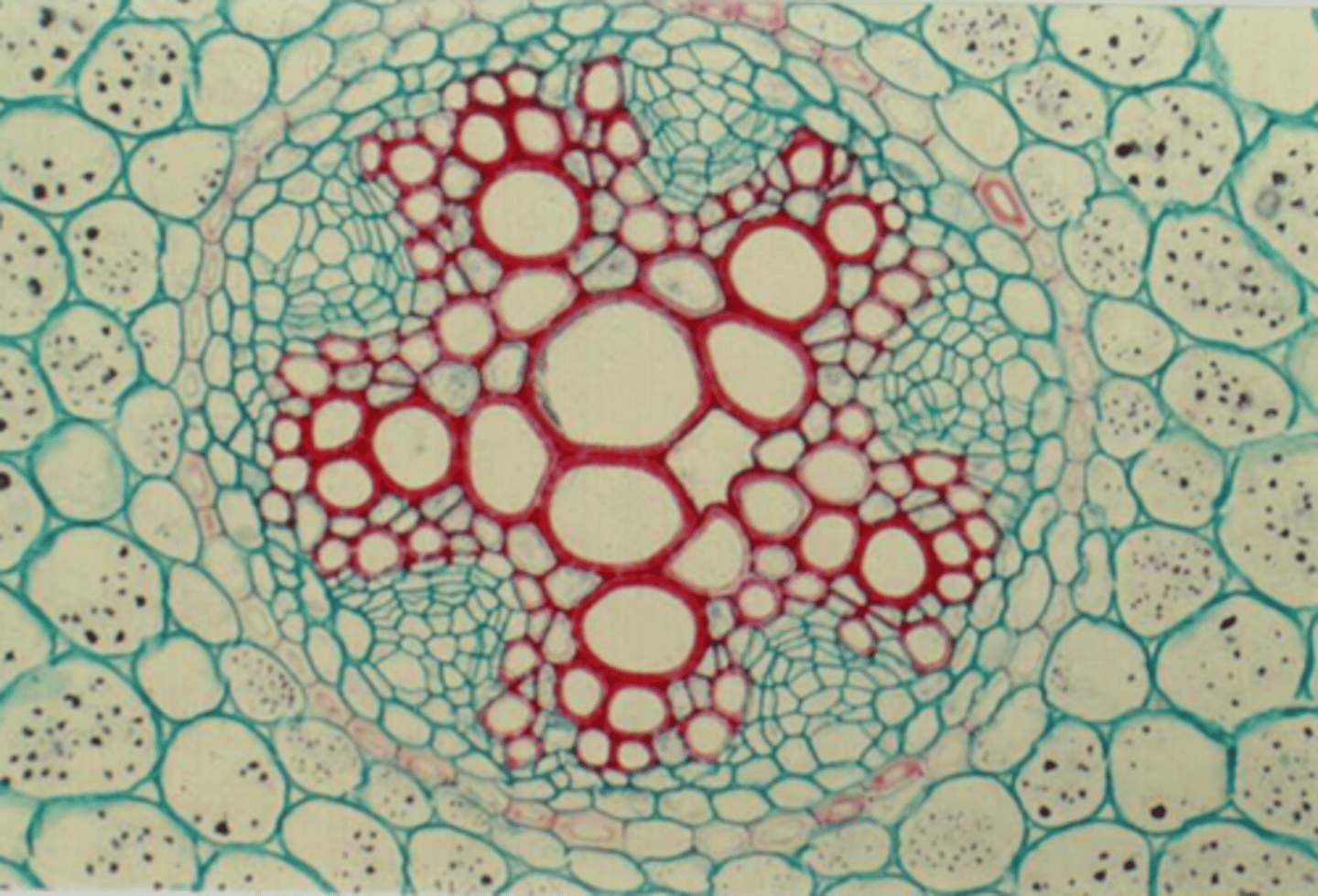
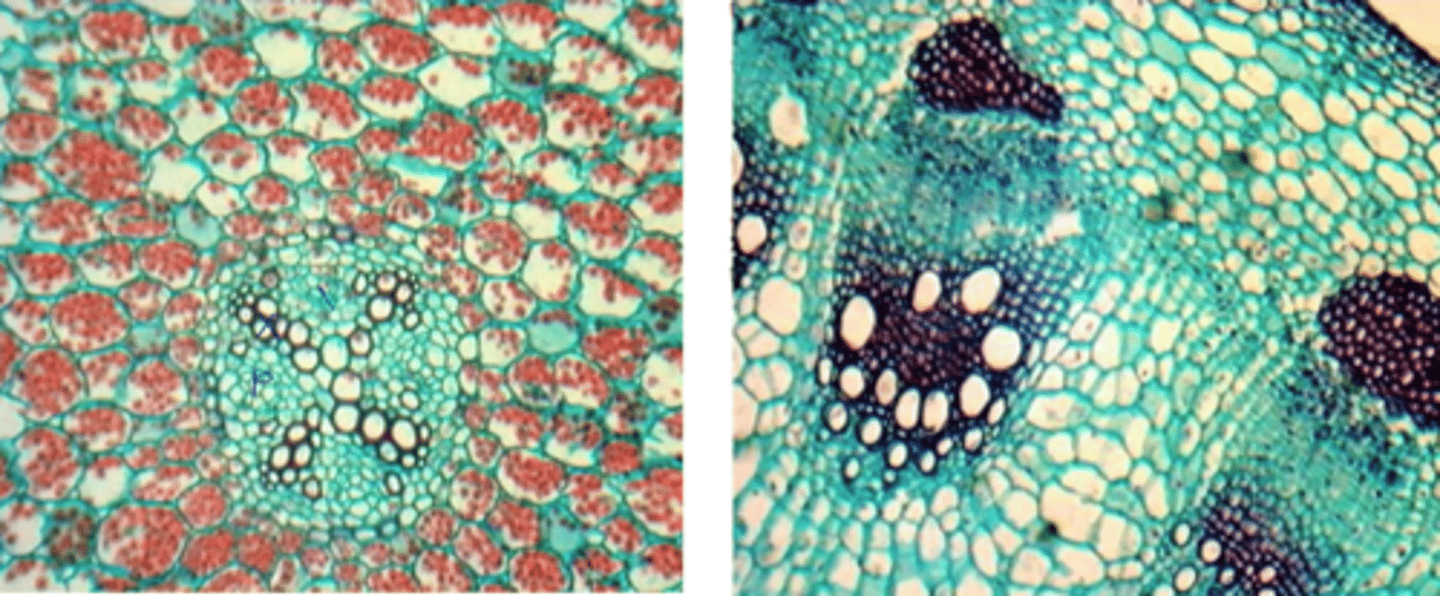
protostelic roots
- no pith
- dicots
- Procambium forms lobed, solid core of primary xylem in the center
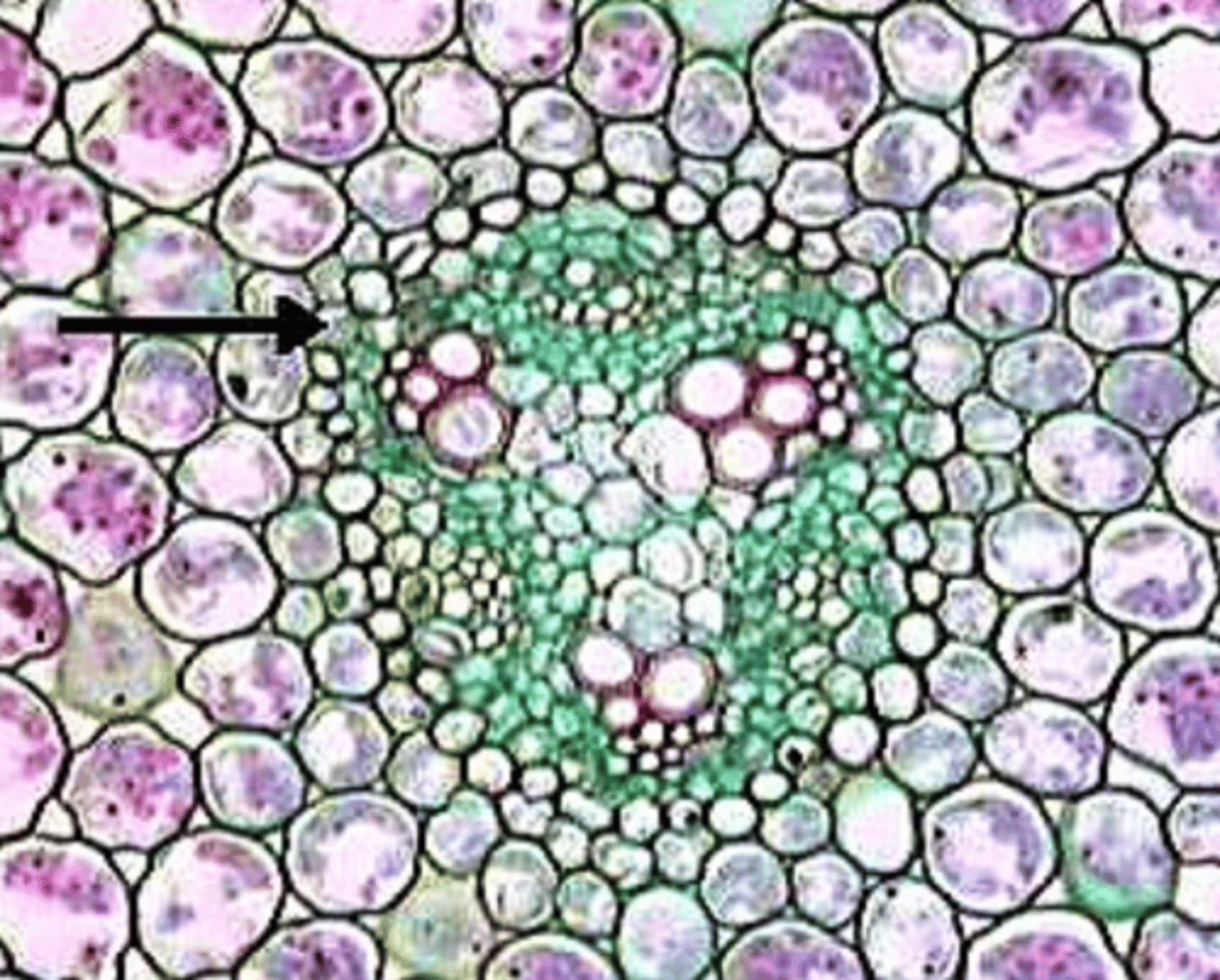
triarch
protostelic root w 3 lobes
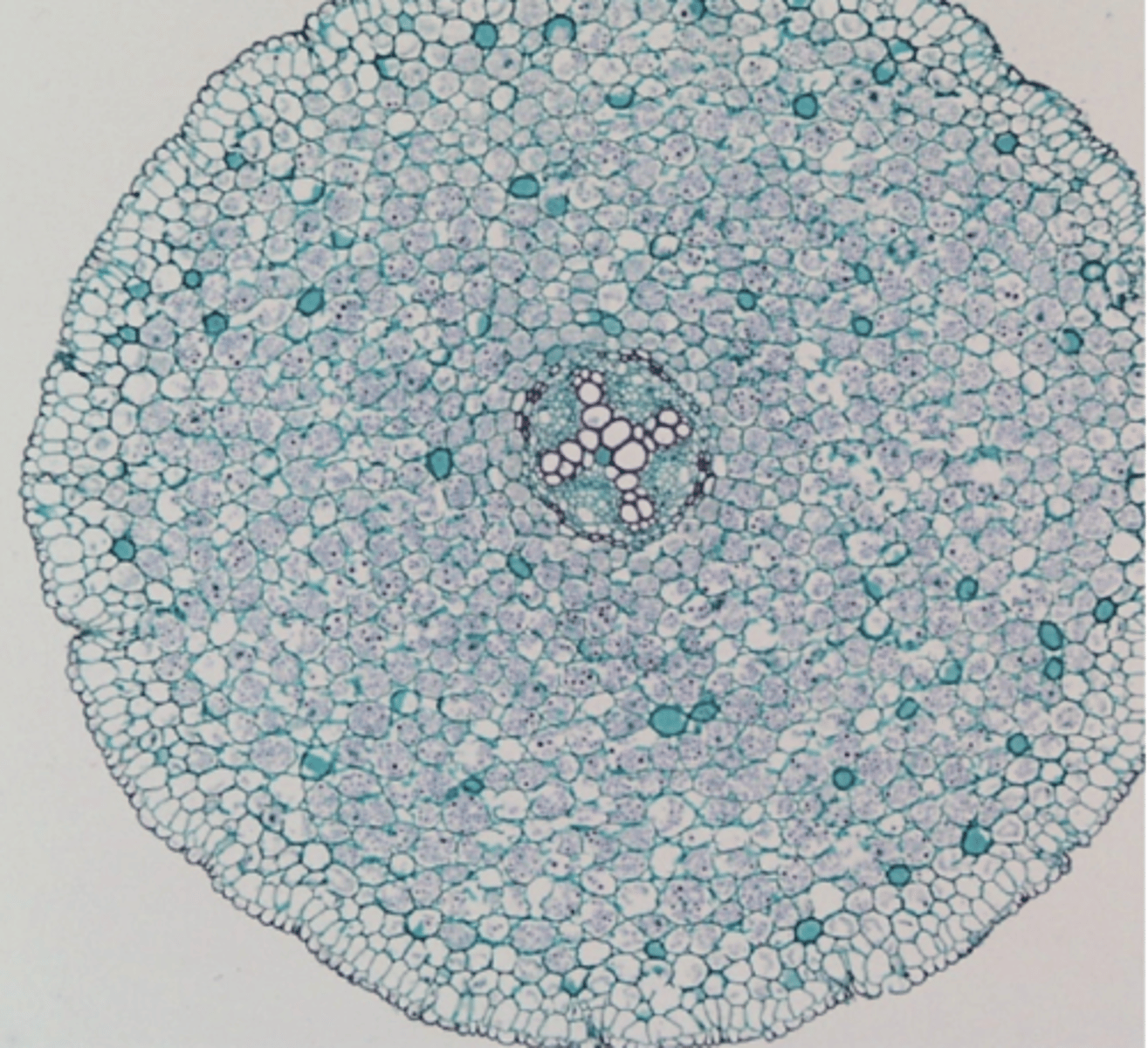
tetrarch
protostelic root w 4 lobes
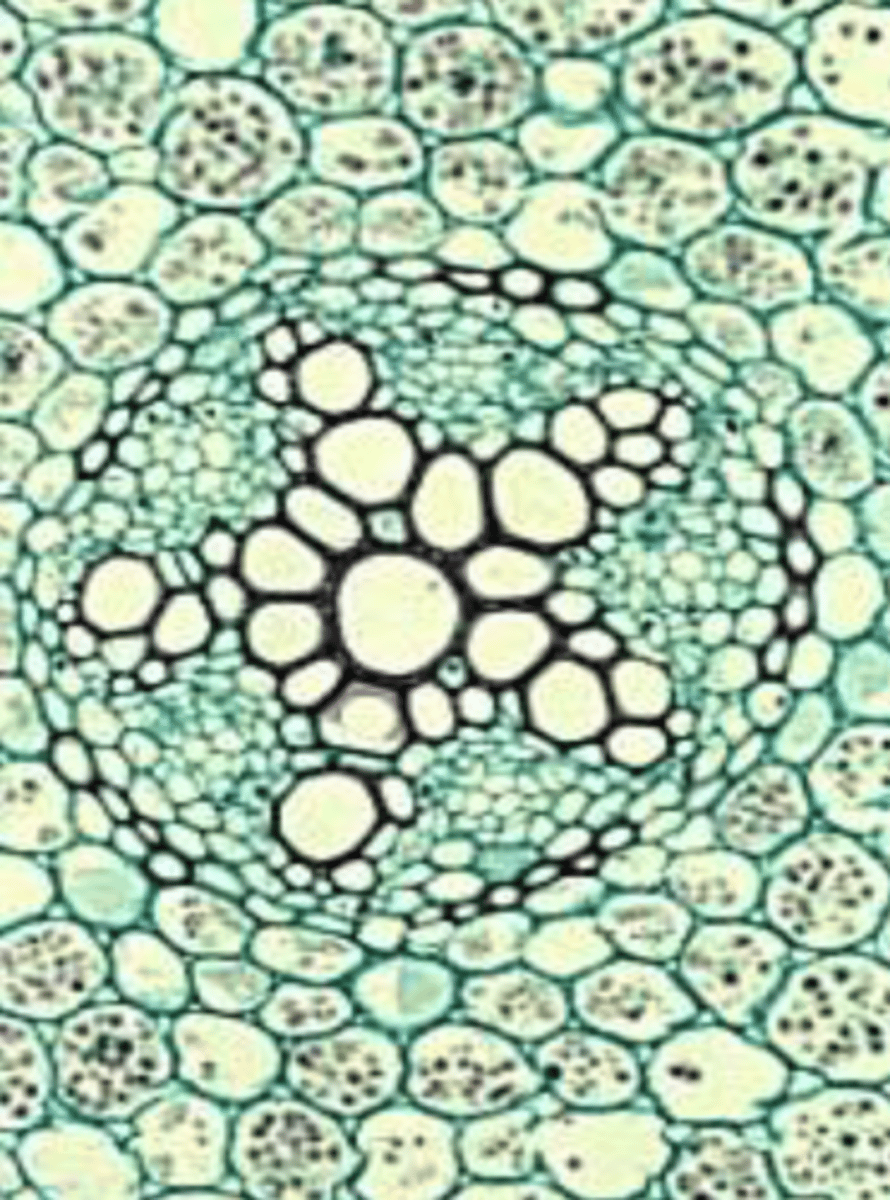
pentarch
protostelic root w 5 lobes
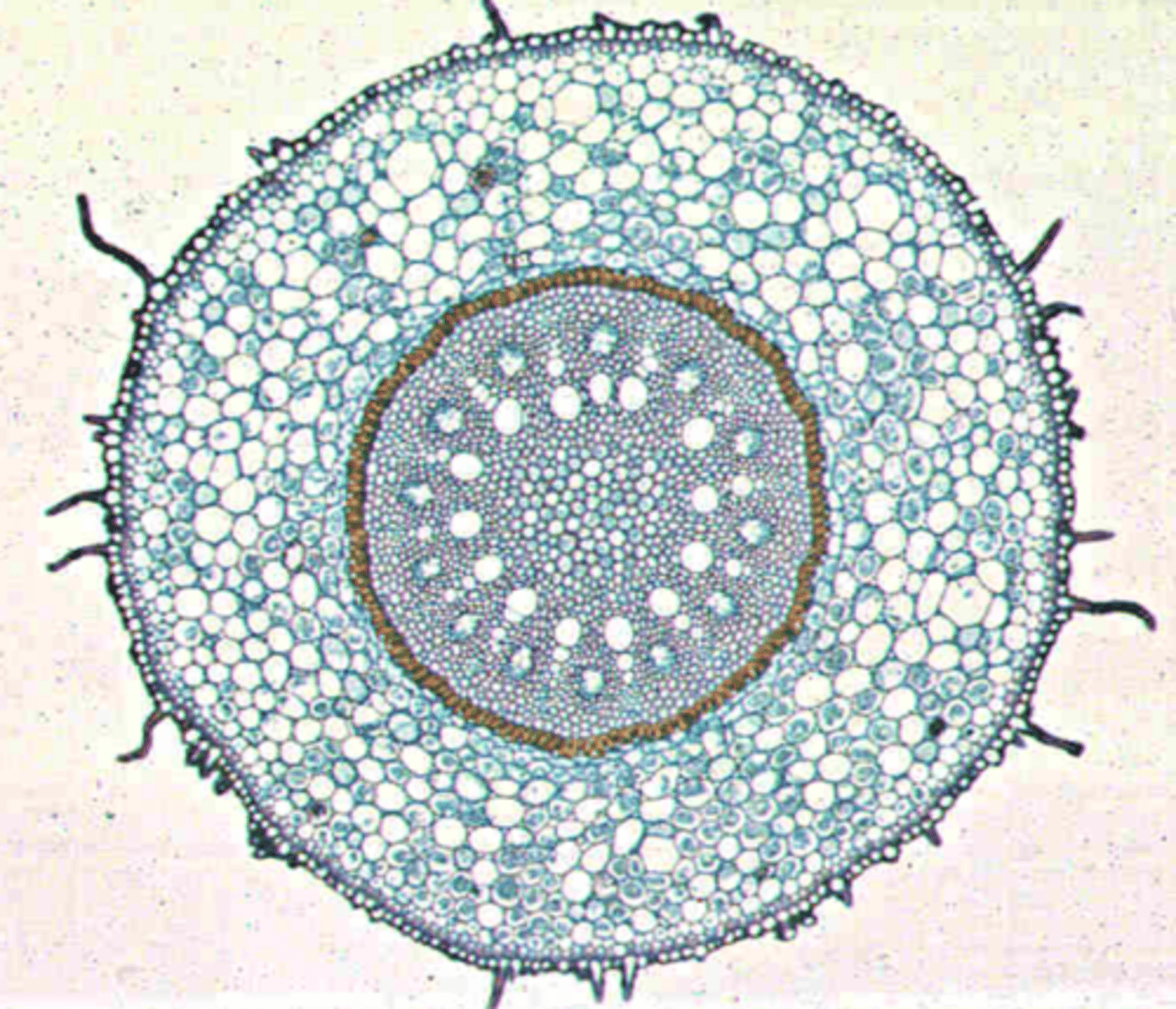
siphonostele
• roots of monocots
• A ring of vascular tissue surrounds a pith
• Polyarch - many lobes
Exarch arrangement of protoxylem
• Protoxylem differentiates from the outside
• Centripetal direction of maturation (toward inside)
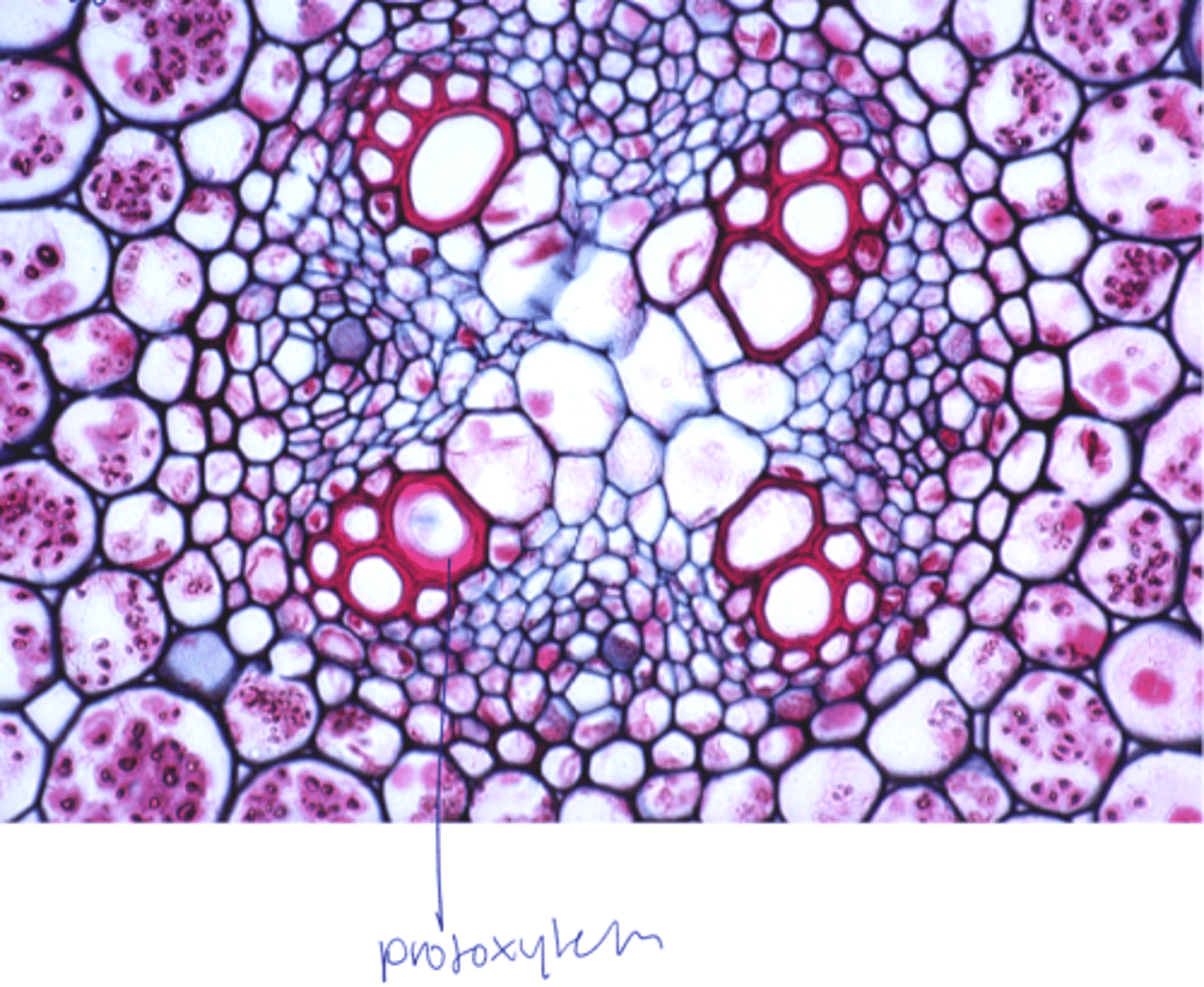
endarch
arrangement of protoxylem in stems
alternate in roots, collateral in stem
Xylem & phloem in roots vs stem
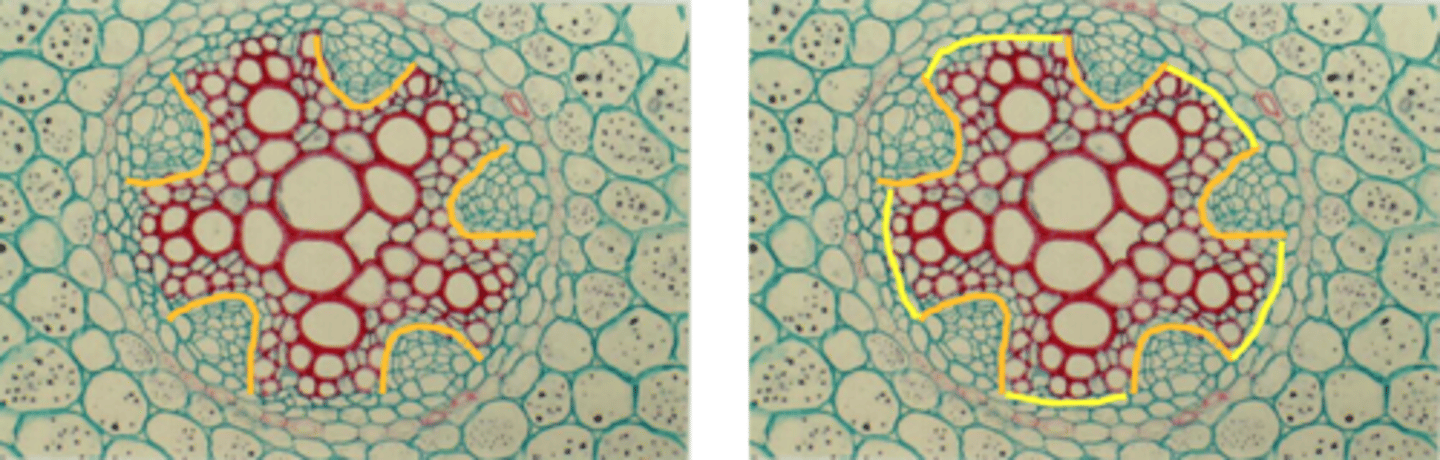
secondary growth in roots
• Usually in eudicots and gymnosperms
• Absent in monocots
1. Cambium first appears on the inner side of the phloem (orange line)
2. Cambial cells produced secondary elements
3. Pericycle cells opposite the xylem lobes (yellow lines) divide to form inner cambial cells
4. Cambial cells unite to form an undulating cambium in cross section
5. Development of secondary xylem on the inner side of phloem precedes
that of secondary xylem opposite the xylem lobes
6. Vascular become circular in cross section
steps of 2ndary growth in roots
Ferns and Monocots
Siphonosteles occur in most
root
underground organ in plants that absorbs water and minerals
1. Anchorage
2. Absorption
3. Conduction
4. Hormone Production
5. Storage Organs
Five Functions of Roots
young roots
which root has the most absorption, mainly through root hairs
Auxin
a plant hormone that promotes root formation and bud growth
moss
do not have conducting tissues and do not have a root
Rhizoids
A thin, rootlike structure that anchors a moss and absorbs water and nutrients.
primary root
the first root that emerges from a seed
lateral roots
A root that arises from the outermost layer of the pericycle of an established root.
lateral roots
branch roots
adventitous roots
Specialized roots that grow from uncommon places, such as stems or leaves.
stability, support, climbing, and clinging
Function of adventitious functions
taproot system
A root system common to eudicots, consisting of one large, vertical root that produces many smaller lateral, or branch, roots.
fibrous root system
A root system common to monocots consisting of a mat of thin roots spreading out below the soil surface.
Fibrous root system
includes adventitous roots, more shallow and horizontal for survival in dry regions
root apex
tip of the root
Calyptrogen
The meristematic cells from which produces the root cap
bidirectional
Roots are ___________ because they produce cells towards and away from the axis
True
Apical meristem is subterminal (True or False)
False
Root cap is a meristematic cell (True or False)
mucigel
A slimy substance secreted by plant root caps that eases passage of the growing root through the soil.
True
Roots do not have internodes and nodes
endogenous growth
growth of lateral roots by the pericycle
root cap
a structure that covers the tip of a root, protecting the root from injury and for penetration into the soil
Polysaccharides with vitamins, enzymes, and amino acids
Composition of mucigel
1. Protection
2. Lubrication
3. Water Absorption
4. Nutrient Absorption
Functions of Mucigel
columella cells
cells of root cap associated with sensing gravity
columella cells
contain amyloplasts for storage
500-1000 seemingly inactive cells
Quiescent center contains how many inactive cells
G1 phase of interphase
cell growth, organelle duplication, protein synthesis
15-20 days
quiescent center cells divide once in ?
quiescent center
reservoir of cells to replace damaged meristematic cells
quiescent center
organizes the patterns of primary growth in roots
subapical region
3 regions: zone of cell division, zone of cell elongation, zone of cell maturation
meristem region
The region of cell division in a root is also known as __________.
0.5 - 1.1 mm behind the root cap
how far is the meristem region from the root cap
region of cell division
area where new cells are created by mitosis
12-36 hours
meristem region divides every
True
vacuoles are small in meristem region (true or false)
region of elongation
cells become several times their original length (150x)
4-10 mm
region of elongation is _________ behind the root tip
False
Region of elongation does not have long, elongated cells
region of maturation (differentiation)
region with root hairs; area where cells become specialized for different jobs: storage, protection, and transport
root hairs
tiny hair-like epidermal extensions that increase the surface area of the root allowing it to absorbs more water and nutrients
1-5 cm behind the root tip
How far is region of maturation from the root tip
No
Can you distinguish the three regions of roots?
epidermis (root)
the outermost part of the root that protects the root and for absorption
Epidermis
region of root with non-functional stomata and absent in cuticle