U of U PA School Structural and Genetic Kidney Diseases
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
How does the kidney develop?
Develops from mesopnephric tissue in renal pelvis
Ascends from pelvis to adult position
What is a horseshoe kidney?
When both kidneys remain in lower abdomen and are fused at lower poles
Usually still have 2 ureters
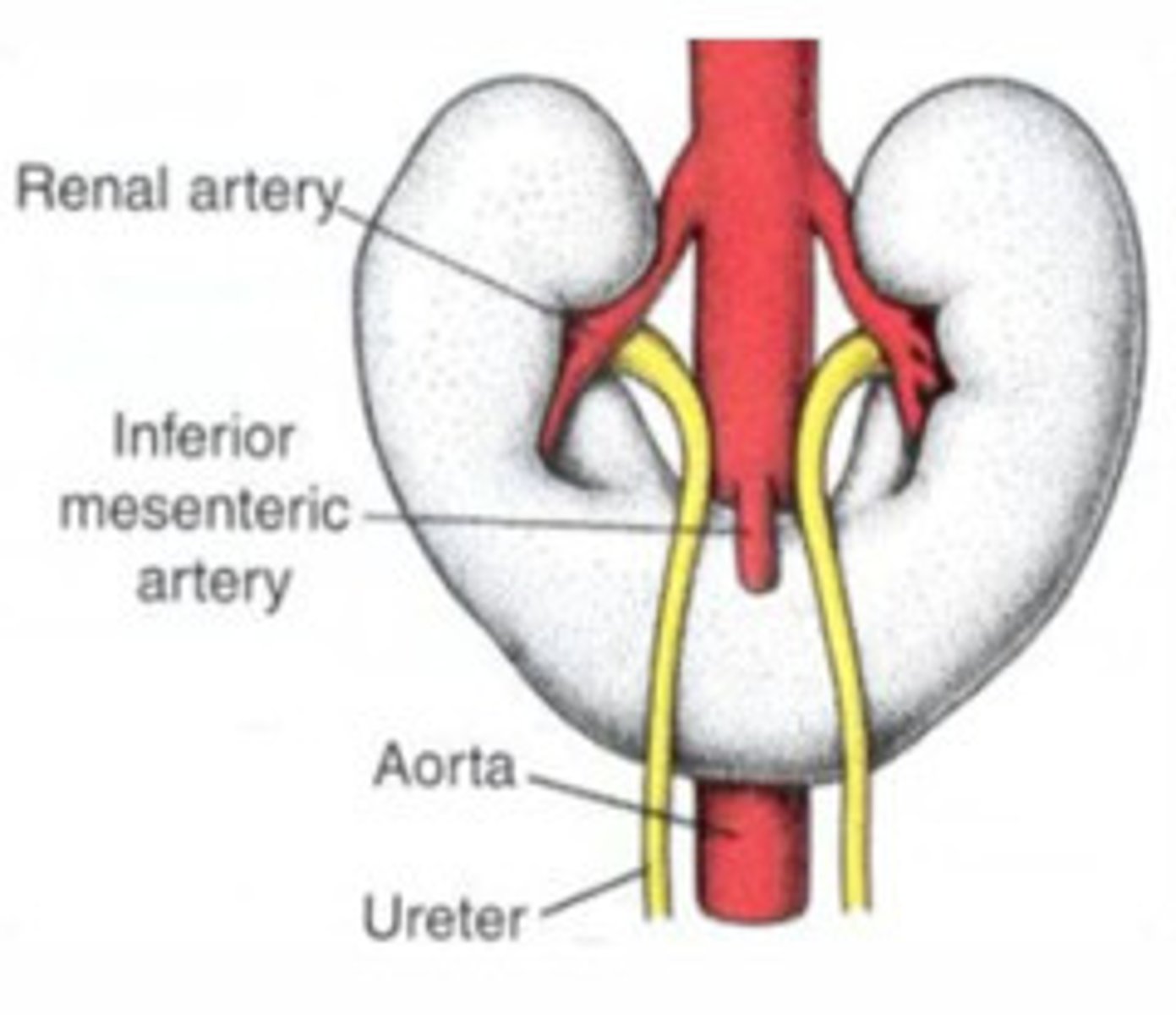
What prevents a horseshoe kidney from ascending?
Inferior mesenteric arteries
How does a horseshoe kidney present? (4)
Usually asymptomatic
Reflux symptoms
Obstructions
Stone formation
How do renal cysts change with age?
Increase in incidence
How does the cyst wall, echogenicity, septations, calcifications, and mural nodules appear on renal imaging for simple cysts?
Cyst wall - Thin
Echogenicity - Anechoic
Septations - Absent
Calcifications - Absent
Mural nodules - Absent
How does the cyst wall, echogenicity, septations, calcifications, and mural nodules appear on renal imaging for complicated cysts?
Cyst wall - Thick
Echogenicity - Internal echos from pus, hemorrhage, or protein
Septations - Present
Calcifications - Present
Mural nodules - Present
What increases the risk of complicated cysts being malignant? What imaging is needed?
Increases in modularity, septations, and vascularity increase risk of it being malignant
Need eval by contract CT or MRI
What are the two types of polycystic kidney disease?
ADPKD - Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease
ARPKD - Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease
How is ADPKD diagnosed? What isn't recommended?
If <40 years old
-3+ cysts between both kidneys
If 40-59 years old
-2 cysts in each kidney
If >60
-4 cysts in each kidney
Genetic testing expensive and not recommended
What are the renal clinical features of polycystic kidney disease? (4)
Can be silent and incidental finding on imaging
Larger cyst can cause pain or flank discomfort
Decrease GFR
ESRD based on cyst volume:kidney volume
What are the extra renal clinical features of polycystic kidney disease?
Liver cysts most common
Cysts in other abdominoperineal organs
Intracranial aneurysms that can lead to subarachnoid hemorrhage
How do liver cysts present? Who is most at risk?
Pain, early satiety, ascites, portal hypertension
More common in obese females
How should polycystic kidney disease be managed?
Delay progression to ESRD
Treat cyst infections with quinolones then aspiration if antibiotics not effective
Surgery may be needed for pain management
How should progression to ESRD be managed in polycystic kidney disease?
BP controlled to 110/70
Tolvaptan
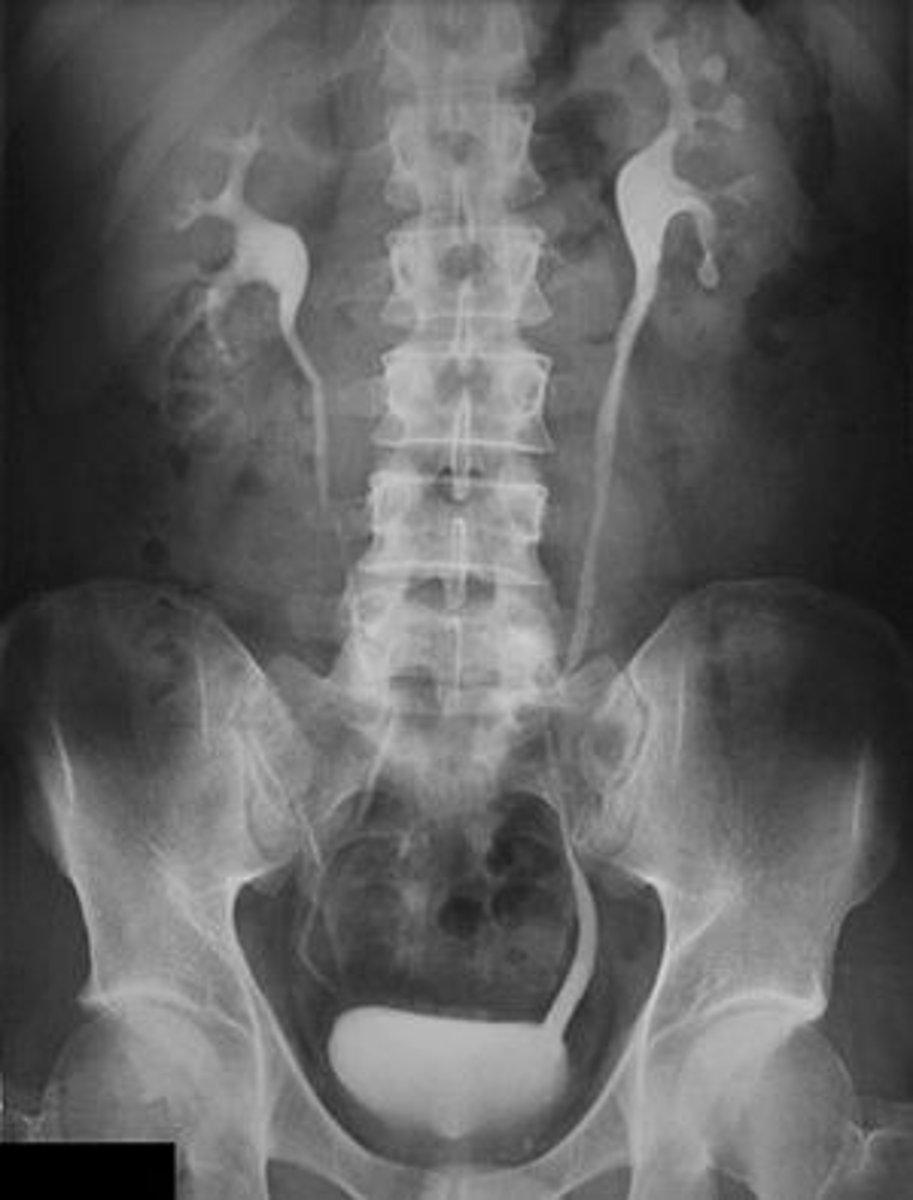
What is medullary sponge kidney?
Inherited dilation of medullary collecting duct
Prone to recurrent stones
How is medullary sponge kidney diagnosed?
Intravenous pyelogram
What is alport syndrome?
Hereditary X linked mutation in type IV collagen in basement membranes
Affects kidneys, eyes, and inner ear
How does alport syndrome present? (4)
Hematuria constant and uninterrupted from birth
CKD progressing to ESRD in adolescence to middle age
Males often have hearing loss
Ocular lesions
How do ocular lesions present in alport syndrome?
Anterior lenticonus - Rare
-Diagnostic of Alport syndrome
Temporal retinal thinning - happens in nearly all Alport
-No change to vision
What is renovascular disease?
Unilateral/bilateral:
-Renal artery stenosis
-Syndromes resulting from disease of renal arteries reducing blood flow to kidneys
What can renovascular disease cause? (4)
Renovascular hypertension
Ischemic nephropathy (decreased GFR due to decreased perfusion)
Fibromuscular dysplasia
Atherosclerosis
What is fibromuscular dysplasia (FMD)?
Medial fibroplasia of renal artery presenting as early onset hypertension between 15-50
More common in females
What is the most common cause of renovasular hypertension? What can it lead to ?
Atherosclerotic renovascular disease affecting proximal renal arteries
More common in older males
Can lead to CKD and ESRD due to ischemic nephropathy
How does renovascular hypertension happen? Why does renovascular disease cause CKD?
Activation of mechanisms to defend renal perfusion and GFR
-Associated with hypokalemia
Ischemic renal parenchyma that can lead to renal fibrosis and atrophy
When should renovascular disease be suspected? (4)
Premature hypertension
Resistant hypertension
Hypertension with hypokalemia
Rise in creatinine >30% after starting ACE/ARB
-Due to excessive drop in intraglomerular pressure and GFR
How is renovascular disease diagnosed?
Renal artery dopplers
MRA of renal vessels
Renal angiography
How is renovascular disease treated?
Medicines to treat hypertension
Revascularization
-PTCA and stenting for resistant hypertension or decresed GFR
-Always done for FMD