Alcohol and Tobacco Use: Health Impacts and Prevention
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
Alcohol-related fatalities
Alcohol causes 60% of fatal injuries and deaths.
Binge drinking
Drinking resulting in BAC of 0.08 or greater.
Legal drinking age
Established at 21 years in 1984.
Coping motivation
Drinking to avoid personal problems.
Conformity motivation
Drinking to gain peer acceptance.
Enhancement motivation
Drinking to induce a positive mood.
Social motivation
Drinking to enhance social experiences.
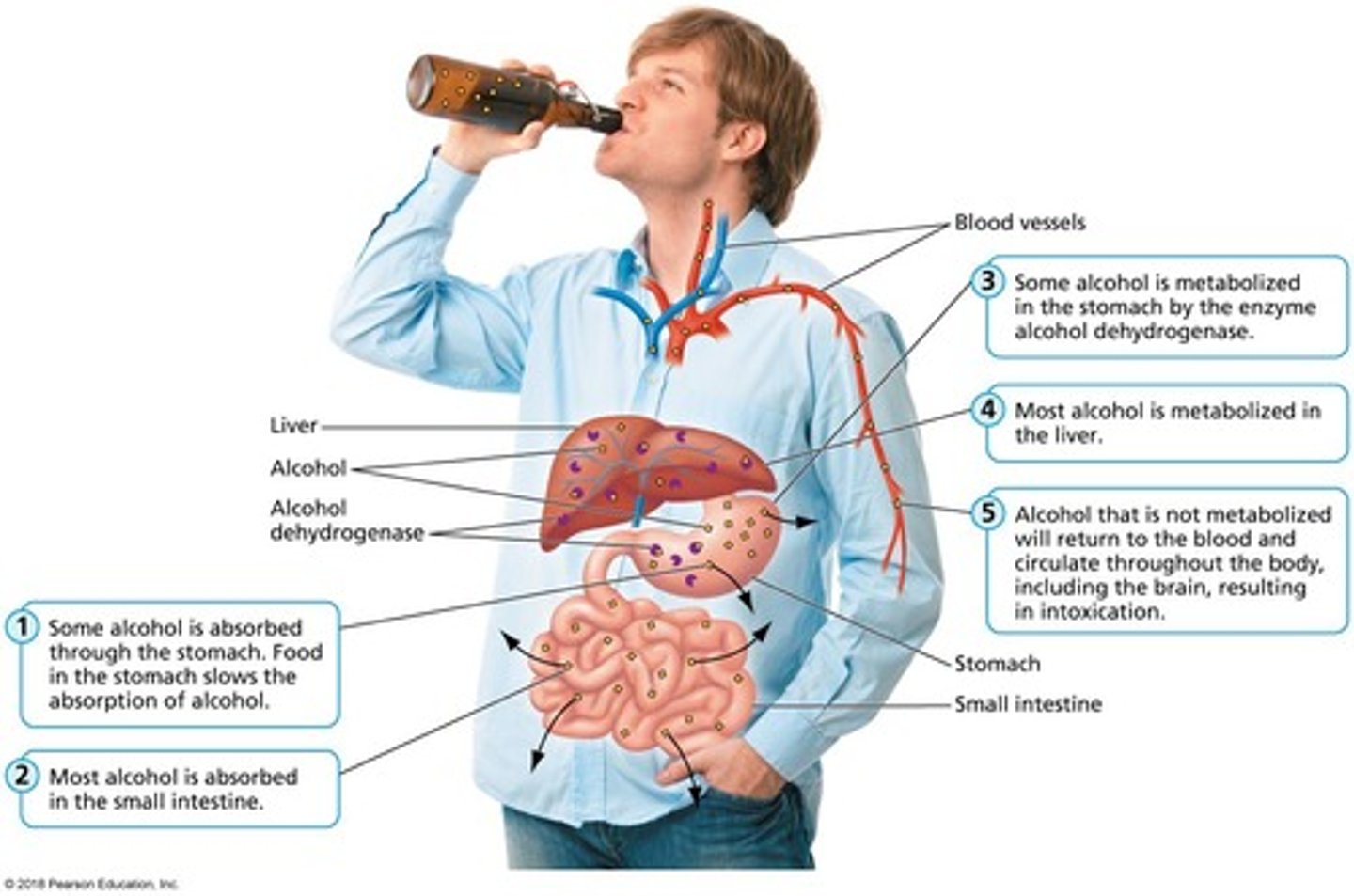
Alcohol absorption
Process of alcohol entering the bloodstream.
Ethyl alcohol
Intoxicating ingredient in alcoholic beverages.
Proof value
Measurement of alcohol strength, double the percentage.
Alcohol consumption statistics
57% of men and 47% of women drink.
College alcohol use
74.5% of college students have tried alcohol.
Secondhand smoke deaths
Responsible for 50,000 smoking-related deaths annually.
Tobacco-related deaths
One in five U.S. deaths caused by smoking.
Alcohol health effects
Includes short-term and long-term health consequences.
Alcohol abuse signs
Recognizing patterns of harmful alcohol consumption.
Tobacco use statistics
Discusses prevalence and demographics of tobacco users.
Smoking cessation strategies
Methods to help individuals quit smoking.
Smoke-free environment
Promoting areas free from tobacco smoke.
Alcohol use among youth
13% incidence of alcohol use in ages 12-17.
Alcohol and violence
Alcohol linked to increased risk of violence.
Binge drinking demographics
Most common in ages 18-24, athletes, and social groups.
Metabolism
Breakdown of food into energy.
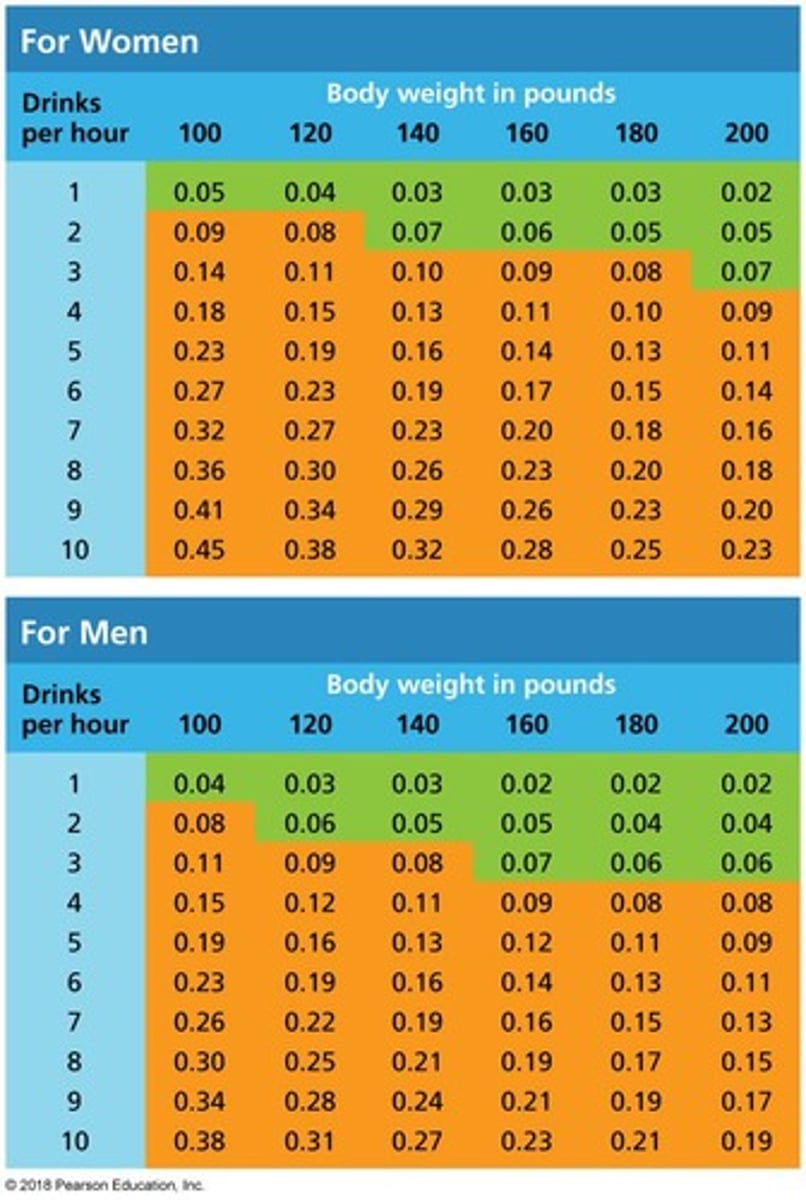
Blood Alcohol Concentration (BAC)
Alcohol amount in blood, in grams per deciliter.
Intoxication
Physical and mental impairment from excessive alcohol.
BAC of 0.08%
Legal limit for intoxication in most jurisdictions.
Symptoms at 0.03% BAC
Relaxation and exhilaration effects begin.
Symptoms at 0.06% BAC
Decreased fine motor skills observed.
Symptoms at 0.09% BAC
Slowed reaction time and poor muscle control.
Symptoms at 0.12% BAC
Loss of self-restraint and reasoning ability.
Symptoms at 0.15% BAC
Blurred vision and unclear speech occur.
Symptoms at 0.18% BAC
Difficulty staying awake and alert.
Symptoms at 0.30% BAC
Deep sleep or stupor may happen.
Symptoms at 0.50% BAC
Deep coma and risk of death present.
Immediate Effects of Alcohol
Short-term effects include dehydration and gastrointestinal issues.
Hangover
Withdrawal symptoms like headache and nausea.
Alcohol Poisoning
Dangerously high alcohol levels affecting CNS.
Signs of Alcohol Poisoning
Confusion, vomiting, seizures, slow breathing.
Fetal Alcohol Syndrome
Birth defects from maternal alcohol consumption.
Long-Term Effects of Alcohol
Linked to cancer and liver diseases.
Fatty Liver
Accumulation of fat in liver cells.
Alcoholic Hepatitis
Inflammation of the liver due to alcohol.
Alcoholic Cirrhosis
Severe liver damage from chronic alcohol use.
Health Benefits of Alcohol
Moderate consumption may reduce heart disease risk.
Drinking and Driving Statistics
Nearly 10,000 deaths in 2013 from alcohol-related crashes.
Alcohol-related deaths
1,825 students aged 18-24 die annually.
Alcohol use effects
Alters judgment, vision, hearing, reaction time.
Unplanned sexual activities
21% of intoxicated college students report this.
STDs from alcohol use
Increased risk of AIDS, hepatitis B exposure.
Sexual assault risk
Heavy drinking raises likelihood of victimization.
Alcohol abuse
Excessive drinking disrupts life and causes problems.
Alcoholism
Physical dependence causing withdrawal symptoms upon cessation.
Alcoholism symptoms
Tolerance, withdrawal, loss of control, interference with life.
Self-medicating
Using substances to cope with emotional distress.
Genetic risk factors
Family history increases susceptibility to alcoholism.
Psychological risk factors
Low self-esteem and impulsiveness contribute to alcoholism.
Peer pressure
Influence from friends can lead to alcohol abuse.
Chronic stress
Long-term stress may lead to self-medication with alcohol.
Alcoholic profiles
Five prevalent types: young adult, functional, chronic severe.
Treatment options
Includes medications, counseling, self-help groups, intensive programs.
Relapse
Returning to drinking after a period of sobriety.
- Can occur months after quitting; any smoking increases risk.
Recovery statistics
75% fully recovered 20 years post-dependence onset.
Risk reduction strategies
Pace drinking, include food, and vary activities.
BACCHUS Network
Campus advocacy group promoting responsible drinking.
Smoking-related deaths
480,000 premature deaths annually in the U.S.

College smoking statistics
25% of students have tried smoking; 2.7% daily.
Reasons students smoke
Genetics, peer exposure, weight loss desire, media influence.
Cigarette composition
50% shredded tobacco, 30% reconstituted, 20% expanded.
Additives in cigarettes
Nearly 600 additives mask tobacco taste.
Ammonia
Enhances nicotine delivery into lungs and bloodstream.
Nicotine
Psychoactive alkaloid from tobacco plant, addictive.
Carcinogenic Chemicals
Over 60 harmful substances released when smoking.
Tar
Thick brown residue from burning tobacco.
Sudden Infant Death Syndrome
Increased risk for babies of smoking mothers.
Premature Birth
Higher likelihood in babies born to smokers.
Low Birth Weight
Babies under 5.5 pounds face health risks.
Secondhand Smoke
Toxic smoke inhaled by nonsmokers nearby.
Sidestream Smoke
Smoke from burning end of cigarette or pipe.
Mainstream Smoke
Smoke exhaled by the smoker.
Health Effects of Secondhand Smoke
Includes lung cancer, heart disease, respiratory illness.
Leukoplakia
White spots in mouth, may become cancerous.
Cigars
Contain addictive and toxic substances like cigarettes.
Clove Cigarettes
No evidence of being safer than regular cigarettes.
Bidis
Not safer than traditional cigarettes.
Smokeless Tobacco
Increased cancer risk, often leads to leukoplakia.
Electronic Cigarettes
Battery-operated devices delivering nicotine vapor.
Nicotine Replacement Therapies
Includes gum, patches, inhalers for quitting smoking.
Prescription Drugs
Chantix and Zyban aid in smoking cessation.
Withdrawal Symptoms
Include difficulty concentrating, negative mood, urge to smoke.
Relapse
Can occur months after quitting; any smoking increases risk.
Support System
Essential for individuals preparing to quit smoking.