Neuroplasticity and Maguire et al (2000)
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
neurons
Individual cells in the nervous system (including the brain) that receive and transmit information
neuroplasticity
The brain's ability to constantly change both the structure and function of neurons in response to life experiences or trauma; how the brain adapts throughout our lives
neurogenesis
creation of new neurons in the brain, which continues even at older ages
neural network
Interconnected neurons that work together to process information through synaptic transmission
neural pruning (synaptic pruning)
The process of eliminating connections between neurons when they are no longer used
synapses
Tiny gaps between neurons, through which impulses (messages) pass from one neuron to another
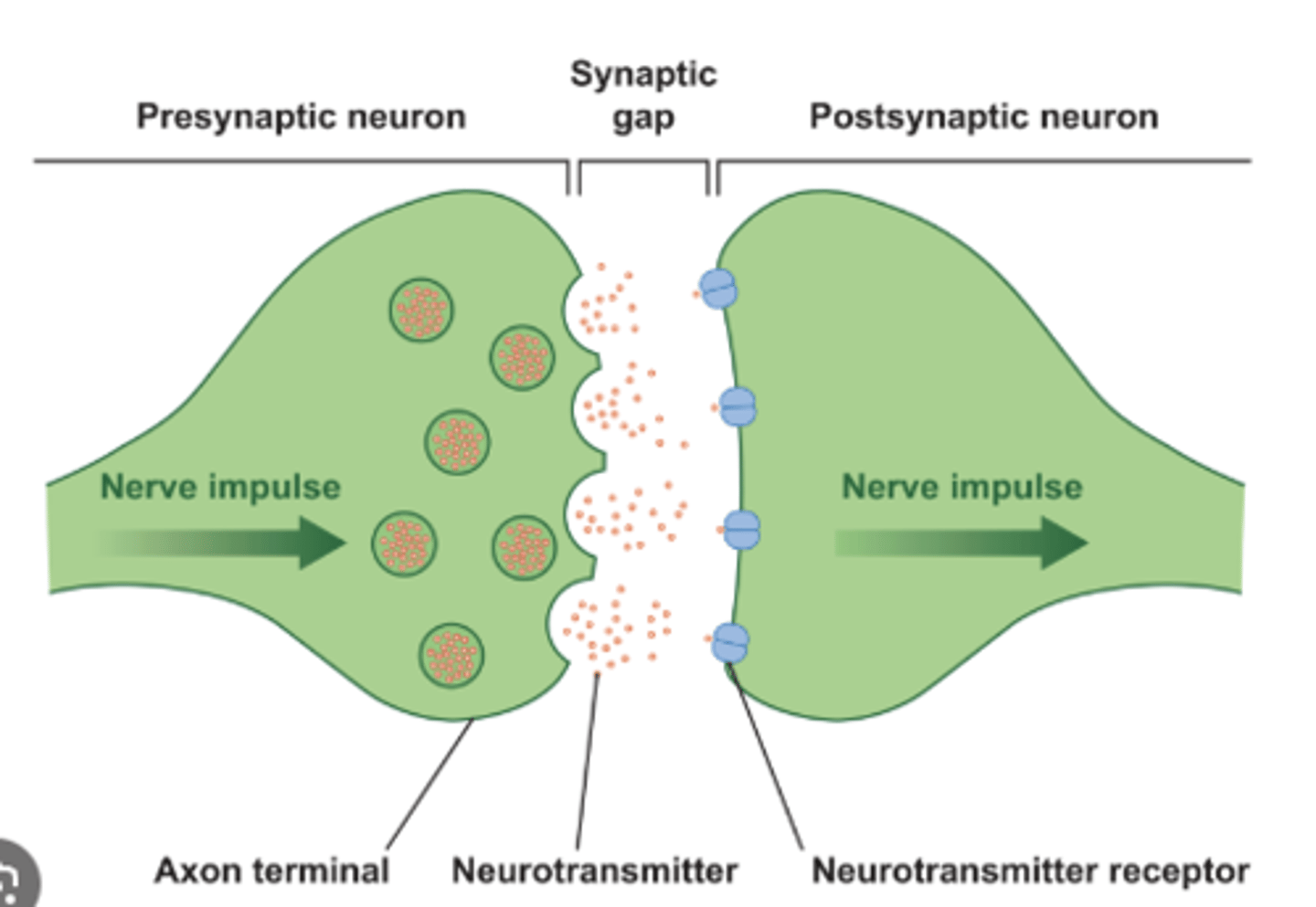
synaptic
having to do with the synapse
long-term potentiation (LTP)
A process in which synaptic connections between neurons are strengthened by repeated communication across the synapse; associated with dendritic branching and arborization
dendritic branching
New dendrites growing and branching out of a neuron and making additional connections (or traces) between neurons
dendritic arborization
Describes the dense, tree-like branching of dendrites as a neuron forms more and more connections
selective elimination
When specific synapses that have been identified as weak due to infrequent activation (use) and are then pruned
engulfment
A specific process by which microglial cells carry out selective elimination, or synaptic pruning
microglial cells
Small cells that monitor neurons and which carry out the engulfment of the synapses between neurons that are pruned due to not being used
Aim of Maguire et al (2000)
To see whether hours of spatial navigation had changed the brains of London taxi drivers and whether there was a relationship between the number of years driving a taxi and the structure of the brain
Research Method of Maguire et al (2000)
Because the Independent Variable was not manipulated by the researcher but was instead a result of changes naturally occurring during the lives of the participants, it was a natural experiment (and also a quasi-experiment, since IV was not manipulated and there was no random allocation of participants)
Procedures of Maguire et al (2000)
16 right-handed, male London taxi drivers agreed to MRI scans of their brain, which were compared with pre-existing scans of a control group of 50 right-handed men from London who had never driven a taxi before. MRI data was measured two ways: pixel counting and VBM
Controls used in Maguire et al (2000)
Single-blind study because the researcher did not know whether each scan she evaluated was from the control group or from the group of London taxi drivers
posterior
toward the back
anterior
toward the front
Findings of Maguire et al (2000)
The volume of the right posterior hippocampi in the taxi drivers was larger (more grey matter; more connections) than that of the control group's hippocampi, but the anterior hippocampi of the taxi drivers was actually smaller than those of the control group
Correlation found by Maguire et al (2000)
The number of years driving a London taxi was found to be correlated with the density of gray matter in and size of the right posterior hippocampus (the more years driving, the larger it was)
Conclusions of Maguire et al (2000)
There is evidence for neuroplasticity (the taxi driver's brain structure changed as a result of years practicing spatial navigation, growing larger in the posterior hippocampus) and localization of function (the posterior hippocampus seems to be involved when previously learned spatial information is needed, while the anterior hippocampus seems more involved when learning new environmental layouts)
hippocampus
A neural center located in the limbic system that is associated with learning and memory (including helping to transfer short term memories to long term memory)
posterior hippocampus
Involved when already-learned spatial information is accessed for navigation purposes
anterior hippocampus
Involved during learning and encoding of new environmental layouts