4.5.2 Taxation
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Distinction between progressive, proportional & regressive taxes
Progressive tax = where higher income households pay a higher percentage of their income in tax than lower income households
Regressive tax = where higher income households pay a lower percentage of their income in tax than lower income households
Proportional tax = where both higher & lower income households pay same percentage of their income in tax
Definition of FDI
Foreign Direct Investment
Financial investment from other countries
either buy an existing business
or sets up a new business
ie. Mercedes buys a car parts company in Tunisia = FDI into Tunisia
ie. Apple establishes new factory in China = FDI into China
The economic effects of changes in direct & indirect tax rates on other variables: incentives to work
Which tax would effect this: income tax - direct tax
How would it effect:
Income tax increases → less disposable income → less incentive to work
Disincentivise to work due to big jumps in tax rates: earning a bit more money → in a new threshold for taxation → charged for higher taxes from income
To improve this:
can have more tax rates / increase tax thresholds to not loose so much each time your income increases
Note: average UK person wage = £30000/year
The economic effects of changes in direct & indirect tax rates on other variables: income distribution
Which tax would effect this: income tax - direct tax
How would it effect:
Progressive income tax helps to redistribute income from high income earners to low → decrease income inequality
To further decrease income inequality, can add another band beyond 45% so can tax more from rich / lower wages which requires to pay 45% so more ppl can pay this tax → more tax revenue
The economic effects of changes in direct & indirect tax rates on other variables: Real output & employment
Which tax would effect this:
income tax - direct tax
corporation tax - direct tax
1) Income tax increases → disposable income decreases → consumption decreases → AD decreases → real output (GDP) decreases → income decreases → production from firms decreases → demand for labour decreases → employment increases
2) corporation tax increases → profits firms decreases → less money spent on capital goods → investment decreases →…(same as above)
The economic effects of changes in direct & indirect tax rates on other variables: The Price Level
Which tax would effect this:
income tax - direct tax
VAT - indirect tax
Increase VAT (now 20%) → tax on g&s on producer increases → cost of production on firms increases → SRAS decreases & profits decreases → in order to preserve their profit levels, firms raise the prices they charge consumers → general increase in price level → increase in rate of inflation → cost-push inflation (same chain of reasoning as cost-push inflation)
Decrease in income tax → disposable income increases → c increases → AD increases → price level increases → demand-pull inflation (same chain of reasoning as demand-pull inflation)
The economic effects of changes in direct & indirect tax rates on other variables: The Trade Balance
Which tax would effect this:
Tariff (ie. US puts tariffs on China)
Imports more expensive → imports decreases → (X-M) increases →AD
increases Imports more expensive → consume goods made locally → consumption increases in US economy → AD in US increases → either
GDP increases for US → production increases → employment increases
Inflation increases → some imports are not avoidable to buy (ie. laptops) → cost of living increases even further
The economic effects of changes in direct & indirect tax rates on other variables: FDI Flows
Which tax would effect this:
Corporation tax
Government cuts corporation tax in our country → firms in our country have more profits → increase FDI flow into our country as our country seems more profitable to invest in → (Ireland has lots of FDI as corporation tax is lowest - 13% compared to 25% in UK) (→ ) more firms choose to base themselves in UK (→) more firms paying UK corporation tax (→) revenue from corporation tax could increase
The Laffer Curve (Theory)
Theory argues that: If income tax rates go beyond a certain point → more tax avoidance - ie. avoid extra work, leave country, employing accountants to decrease tax paid → less tax revenue
At 100% rate of income tax:
No incentive to work → doesn’t work → no income → cannot pay income tax → no tax revenue for government at 100% rate of income tax
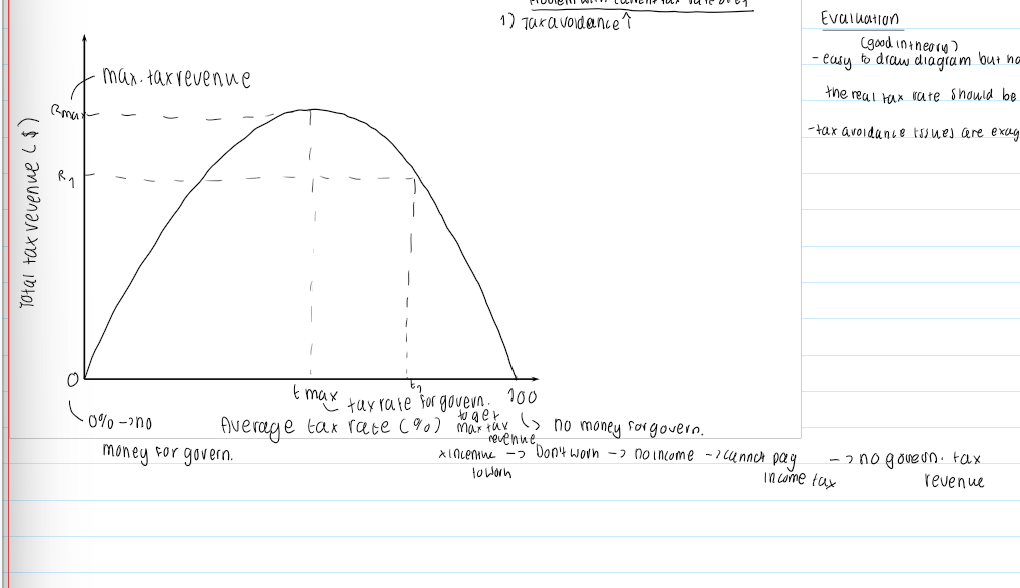
Evaluation for The Laffer Curve Theory
easy to draw diagram & understand in theory but hard for government to calculate in real-life on what the real tax rate should be to maximise tax revenue
tax avoidance issues are exaggerated
harder to employ accountant than you think → need to pay them → tax avoidance might not be a problem after all
Additional notes
Fiscal drag = in recent years income tax allowances are no longer put up by inflation - raise around £40-£60 more for UK government = stealth tax
people discouraged from working hard if their income is on boundary
UK & most countries: income tax is a progressive tax but some countries it’s proportional tax (flat rate)
VAT is a regressive tax
VAT = tax on consumer spending
Lower income spend a higher proportional of their income on consumption & have less to save
Therefore VAT takes up a bigger percentage of their income