Biology Test 5: Photosynthesis & Cellular Respiration
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/67
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
1
New cards
What are the two products of the light reactions that are needed for the Calvin Cycle?
NADPH and ATP
2
New cards
What is the pigment in chloroplasts that performs photosynthesis?
chlorophyll
3
New cards
Glucose is a ...
sugar, carbohydrate, source of quick energy
4
New cards
raw materials for Photosynthesis
water and carbon dioxide
5
New cards
role of NADPH in cellular respiration
function as a high energy electron carrier
6
New cards
Glucose is broken down into pyruvic acid during...
Glycolysis
7
New cards
What are the outputs of the Kreb's cycle
4 CO2, 6 NADH, 2 FADH2, 2 acetyl- CoA
8
New cards
The splitting of the glucose molecule is called?
Glycolysis
9
New cards
Each glucose (6C) produces how many pyruvic acid (3C) molecules?
2
10
New cards
What are the reactants (taken into) of cellular respiration?
Oxygen and glucose
11
New cards
This process releases chemical energy from sugars and other carbon-based molecules to make ATP when oxygen is present.
cellular respiration
12
New cards
What happens in the electron transport chain?
NADH and FADH2 drop off hydrogens to form massive amounts of ATP
13
New cards
Where does the Krebs Cycle take place?
mitochondria
14
New cards
Why does the third phosphate in ATP have so much energy stored in the bond?
it is highly unstable
15
New cards
original source of energy
is light from the sun
16
New cards
autotrophs
organisms that use light energy to build organic molecule from inorganic substance
17
New cards
examples of autotrophs
plants, algae, some unicellular organisms
18
New cards
heterotrophs
animals and other organisms that can't make their own food
19
New cards
examples of heterotrophs
animals, fungus, some unicellular organism
20
New cards
biochemical pathway
a complex series of reactions that perform a specific function
21
New cards
photosynthesis equation
6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy --> C6H12O6 + 6O2
22
New cards
cellular respiration equaiton
C6H1206 + 6O2 --> 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy
23
New cards
ATPase
an enzyme that breaks ATP down to ADP
24
New cards
Structure of Chloroplasts
outer membrane, inner membrane, Thylakoid w/ chlorophyll, grana, & stroma
25
New cards
Chlorophyll
Green pigment in plants that absorbs light energy used to carry out photosynthesis
26
New cards
Chlorophyll a
absorbs more blue light
27
New cards
Chlorophyll b
absorbs more red light
28
New cards
Cartenoids
includes yellow, orange, & brown pigments; allows plant to absorb more of the sun's energy
29
New cards
2 parts of photosynthesis
light dependent and light independent
30
New cards
Light dependent Reactions
Occurs in Thylakoid (membrane), converts light energy to chemical energy (ATP)
31
New cards
Photosystems I & II
clusters of pigments arranged in the thylakoid
32
New cards
stages of light dependent reactions
1: light energy is absorbed, electrons are energized, water is split
2: H+ concentration is high and diffuse across thylakoid membrane, movement triggers formation of ATP (phosphorylation)
2: H+ concentration is high and diffuse across thylakoid membrane, movement triggers formation of ATP (phosphorylation)
33
New cards
Phosphorylation
when a P is bonded with ADP, making ATP
34
New cards
Process of light dependent reactions
1. light enters the leaf & is absorbed by the photosystems
2. Water is taken into the leaf & "split" in PS2
equation: 2(H2O) ==> 4(H+) + 4(e-) + O2
3. oxygen that came from the breakdown of water is released into the atmosphere (function of oxygen is for cellular respiration)
4. electrons in the chlorophyll molecules absorb the energy (source of electrons is water)
5. as electrons are passed along (by the electron transport chain), the energy is released to form NADPH
2. Water is taken into the leaf & "split" in PS2
equation: 2(H2O) ==> 4(H+) + 4(e-) + O2
3. oxygen that came from the breakdown of water is released into the atmosphere (function of oxygen is for cellular respiration)
4. electrons in the chlorophyll molecules absorb the energy (source of electrons is water)
5. as electrons are passed along (by the electron transport chain), the energy is released to form NADPH
35
New cards
Inputs of Light dependent reactions
H2O & Light
36
New cards
Outputs of Light dependent reactions
O2, NADPH, & ATP
37
New cards
Stomata
microscopic openings in the epidermis of the leaf
38
New cards
Transpiration
process by which water vapor leaves the plant through the stomata in the leaves
39
New cards
Light Independent Reactions
AKA: Calvin-Benson cycle, Calvin cycle; occurs in the stroma, carbon fixation
40
New cards
Stroma
fluid portion of the chloroplast; outside of the thylakoids
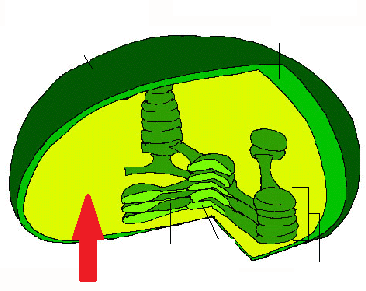
41
New cards
Carbon fixaton
carbon atoms from CO2 are bonded into organic compounds (sugars)
42
New cards
process of light independent reactions (the Calvin Cycle)
1. an enzyme combine CO2 with RuBP and results in the formation of PGA
2. PGA receives a phosphate from ATP and a proton from NADPH which results in ADP & NADP+ (these are then recycled)
3. The resulting PGAL are either used:
-by the plant cell to make other organic compounds (one of the 6 molecules of PGAL is transferred to the cytoplasms and used in the synthesis of sugars & and other carbs)
-to regenerate the 5 carbon compound from step 1: RuBP (requires more ATP)
2. PGA receives a phosphate from ATP and a proton from NADPH which results in ADP & NADP+ (these are then recycled)
3. The resulting PGAL are either used:
-by the plant cell to make other organic compounds (one of the 6 molecules of PGAL is transferred to the cytoplasms and used in the synthesis of sugars & and other carbs)
-to regenerate the 5 carbon compound from step 1: RuBP (requires more ATP)
43
New cards
RuBP
a five-carbon carbohydrate
44
New cards
PGA
a six-carbon molecule that splits into a pair of 3 carbon molecules; pair of 3 carbon molecules
45
New cards
Inputs of light independent reactions/ Calvin cycle
NADPH, ATP, CO2
46
New cards
Outputs of light independent reactions/calvin cycle
sugars
47
New cards
White light
all colors of the rainbow
48
New cards
Best light color to absorb in plants
blue & red
49
New cards
Worst light color to absorb in plants
green (it's going to be reflected so no light is absorbed)
50
New cards
Environmental Factors that affect photosynthesis
light intensity, carbon dioxide, amount of water, temperature, humidity, oxygen
51
New cards
Stages of Cellular Respiration
glycolysis, krebs cycle (citric acid cycle), electron transport chain
52
New cards
aerobic
requires oxygen to be present to complete reaction (reactants are glucose and oxygen)
53
New cards
anaerobic
no oxygen it required (reactant is glucose)
54
New cards
glycolysis
the process by which glucose is concerted to pyruvic acid (occurs in the cytoplasm, anaerobic, uses 2 ATP to produce 4 ATP & 2 pyruvic acids, but there is a NET GAIN of 2 ATP & 2 pyruvic acid)
55
New cards
oxidize
loses electron
56
New cards
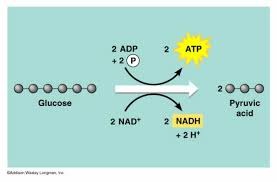
process of Glycolysis
1. glucose is converted into a 6-carbon chain, used 2 ATP which became 2 ADP
2. carbon chain is split into 2 molecules of PGAL
3. PGAL is oxidized to make two 3-carbon chain molecules
4. the carbon molecule are then concerted into 2 molecules of pyruvic acid, 4 ATP are formed
2. carbon chain is split into 2 molecules of PGAL
3. PGAL is oxidized to make two 3-carbon chain molecules
4. the carbon molecule are then concerted into 2 molecules of pyruvic acid, 4 ATP are formed
57
New cards
inputs of glycolysis
Glucose and 2 ATP
58
New cards
outputs of glycolysis
2 pyruvate, 2 ATP(net gain)
59
New cards
where does the pyruvate go?
1. pyruvic acid moves from the cytoplasm to the mitochondria
2. gives off a CO2 and combines with an enzyme (coenzyme A) to form acetyl-CoA
2. gives off a CO2 and combines with an enzyme (coenzyme A) to form acetyl-CoA
60
New cards
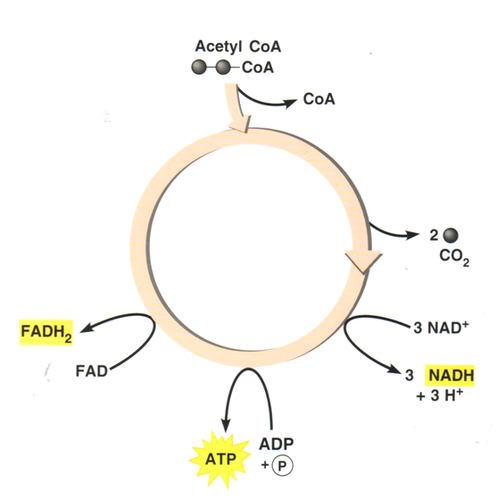
Krebs cycle
in the presence of oxygen the acetyl-CoA will go through the citric acid cycle, where it will go through a series of reactions (occurs in the mitochondria, breaks down acetyl-CoA and form ATP and CO2, electrons carriers -NAD+ & FAD- take electrons to the electron transport chain)
61
New cards
Outputs of Krebs Cycle
4 CO2, 2 acetyl-CoA, 6NADH, 2 FADH2
62
New cards
Steps of Electron Transport Chain
1. NADH & FADH₂ give up electrons that pass through the membrane from protein to protein (slowly releases energy at each stop; releases H⁺)
2. Some of the energy is used to form ATP, some is used to pump ions of H⁺ into the mitochondrion (creates a gradient that provides the energy for ATP production)
3. Final electron acceptor is oxygen (reacts with 4H and 4 electrons to form 2H₂)
4. Total of 32 ATP are made
2. Some of the energy is used to form ATP, some is used to pump ions of H⁺ into the mitochondrion (creates a gradient that provides the energy for ATP production)
3. Final electron acceptor is oxygen (reacts with 4H and 4 electrons to form 2H₂)
4. Total of 32 ATP are made
63
New cards
Inputs of Electron Transport Chain
electrons from NADH & FADH₂, oxygen
64
New cards
Outputs of Electron Transport Chain
2H₂0, 32 ATP
65
New cards
lactic acid fermentation (anaerobic)
1. 2 Pyruvic acid + NADH → 2 Lactic Acid + NAD⁺
2. NAD⁺ returns to glycolysis to form ATP
3. Lactic acid eventually goes back to pyruvic acid when transferred from the muscle cells to the liver.
4. Results in muscle fatigue
2. NAD⁺ returns to glycolysis to form ATP
3. Lactic acid eventually goes back to pyruvic acid when transferred from the muscle cells to the liver.
4. Results in muscle fatigue
66
New cards
Acoholic Fermentation (anaerobic)
1. CO2 removed from pyruvic acid leaving a 2 carbon compound
2. NADH + H+ are added to the 2 carbon compound to form ethyl alcohol (regenerates NAD+ for glycolysis = 2 ATP)
2. NADH + H+ are added to the 2 carbon compound to form ethyl alcohol (regenerates NAD+ for glycolysis = 2 ATP)
67
New cards
Photosynthesis
Food synthesized
Energy from sun stored as glucose
Carbon dioxide taken in
Oxygen given off
Produces sugars from PGAL
Requires Light
Occurs only in presence of chlorophyll
Energy from sun stored as glucose
Carbon dioxide taken in
Oxygen given off
Produces sugars from PGAL
Requires Light
Occurs only in presence of chlorophyll
68
New cards
cellular respiration
Food broken down
Energy of glucose released
Carbon dioxide is given off
Oxygen is taken in
Produces CO and HO
Does not require light
Occurs in all living cells
Energy of glucose released
Carbon dioxide is given off
Oxygen is taken in
Produces CO and HO
Does not require light
Occurs in all living cells