Final: 534: Cardio Wk 7 PII
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
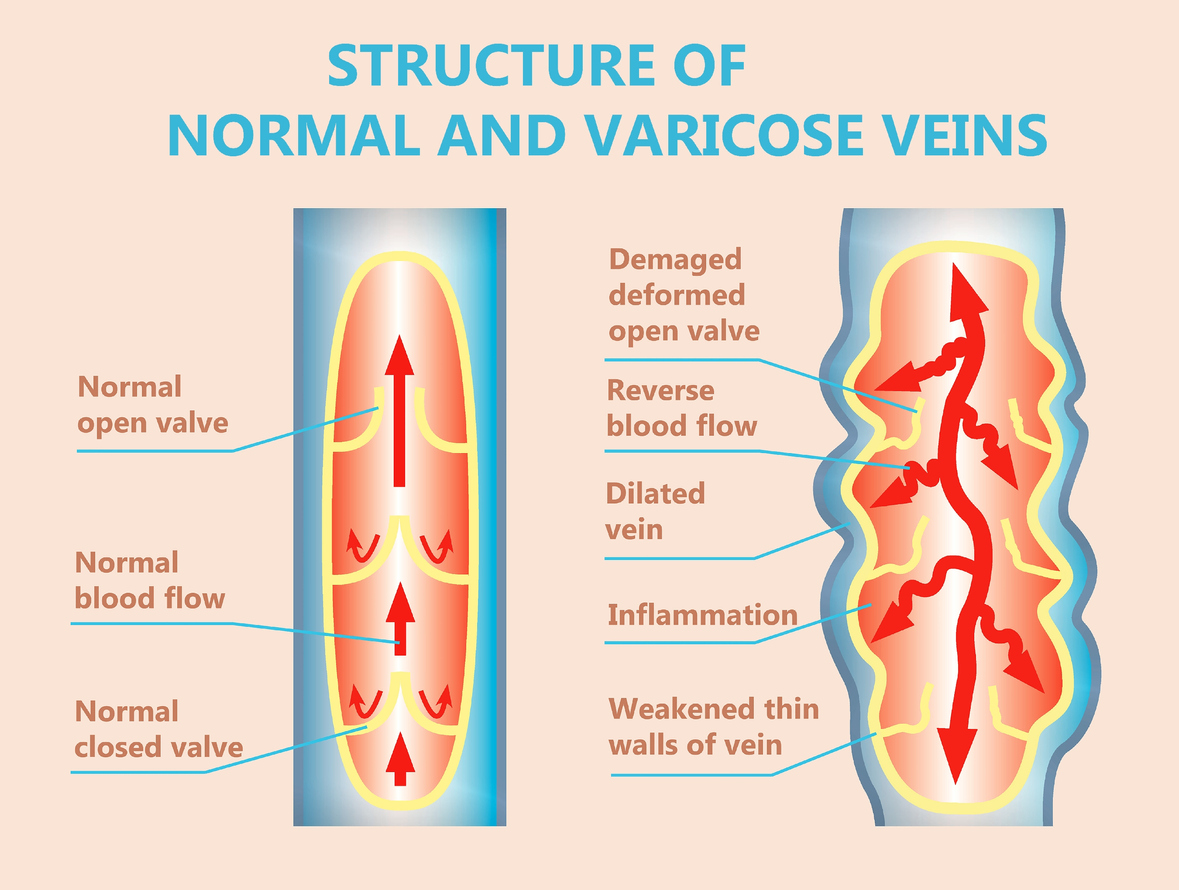
What is the pathology behind varicose veins?
Dilated, bulging, tortuous superficial veins
>3mm diameter
What is the difference between dilated intradermal veins and telangiectasias?
dilated intradermal veins
blue-green
measure 1-3 mm in diameter
No protrusion
Telangiectasias
Small at <1 mm in diameter
Dilated
spider-web pattern
What is the difference between primary and secondary varicose veins?
Primary
Origin in superficial system and 50% has + FMHX
Defective structure/function of valves of saphenous veins
Intrinsic weakness of vein wall
High intraluminal pressure
Secondary
2nd to HTN, deep-venous insufficiency or deep-venous obstruction
→ incompetent perforating veins → enlarged superficial veins
Ex: arteriovenous fistulas - varicose veins in limbs
Define chronic venous insufficiency
Consequence of incompetent veins →:
venous HTN
extravasation of fluid
blood in tissues of limb
What are some causes to chronic venous insufficiency?
varicose veins
disease in deep veins
What is the difference between primary and secondary chronic venous insufficiency
Primary
consequence intrinsic structural/functional abnl in vein wall or venous valves → valvular reflux/regurg.
Secondary
obstruction and/or valvular incompetence from previous deep-vein thrombosis.
What else can cause 2nd varicosities?
R-sided heart disease
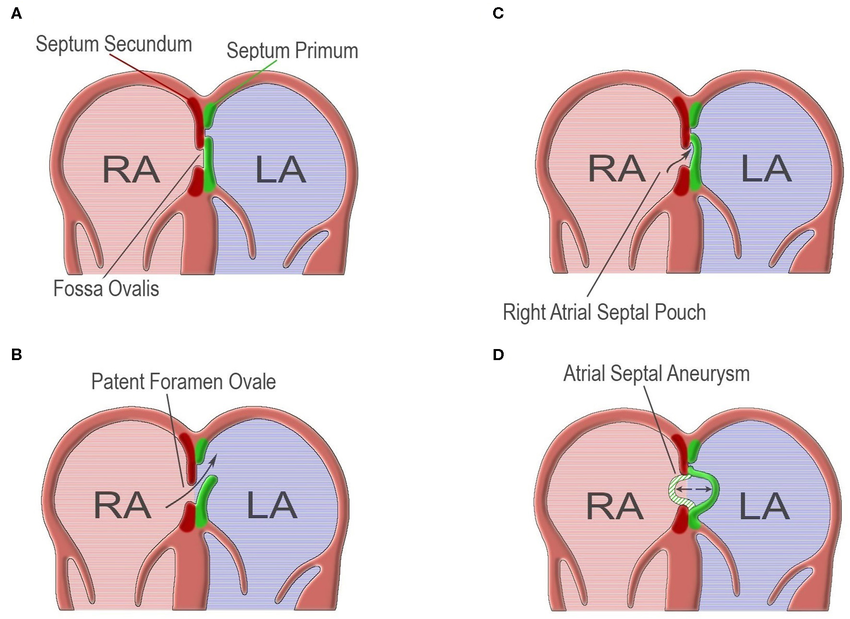
Define atrial septic defect (ASD)
Left-to-right shunt
Intracardiac holes that allows blood to transmit between chambers or spaces
Size determines R sided dilation
What is the difference between secundum ASD and primum ASD?
Secundum
MC
Occurs at fossa ovalis
Primum
Deficiency of AV canal portion of atrial septum
Always ass w/ abnl development of AV valves w
MC: cleft in mitral valve
both fixed by sx