Bio Chapter 11-13: Exam 4
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
First step of cell division
Prophase- the cell prepares for division by condensing its DNA
Second step of cell division
Metaphase- chromosomes line up and spindle fibers attach
Third step of cell division
Anaphase- chromosomes are separated by spindle fibers pulling them apart
Fourth step of cell division
Telophase- chromosomes have arrived at opposite poles, and nuclear envelope forms
Prokaryotic cell division: what is it called?
binary fission (Asexual reproduction)
What are the steps of binary fission?
DNA replication
Cell growth
Septum formation (new cell wall and membrane grow in the middle)
Cell splitting
Which is simpler? Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic chromosomes?
Prokaryotic chromosomes
Where is the chromosome found in Eukaryotic cells?
the nucleus
Where is the chromosome found in Prokaryotic cells?
an irregularly shaped area called the nucleoid, not enclosed by a membrane.
Features of Prokaryotic Chromosomes
circular, one main chromosome, loosely packed
Features of Eukaryotic Chromosomes
linear, multiple chromosomes, tightly wrapped around histone proteins
What triggers reproduction in eukaryotic cells?
growth factors, hormones, and proper cell size or DNA integrity
What triggers reproduction in prokaryotic cells?
Environmental conditions (e.g., nutrients, temperature, cell size)
sister chromatids
two identical copies of a chromosome that are formed during DNA replication
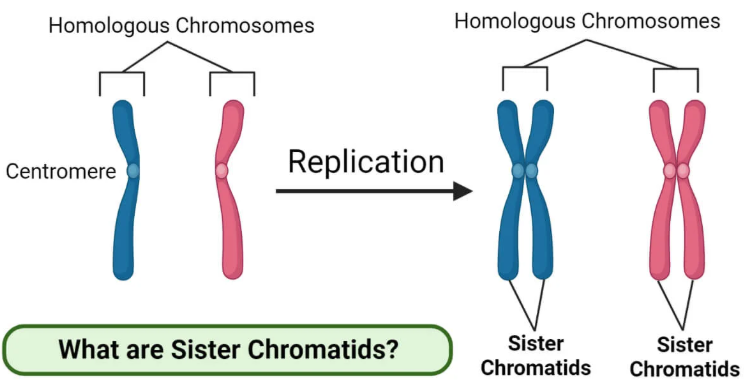
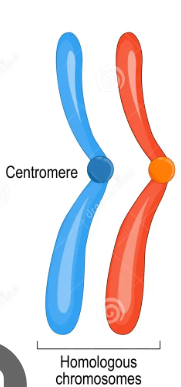
homologous pairs
two chromosomes, one from each parent, that have the same size, shape, and genes in the same locations
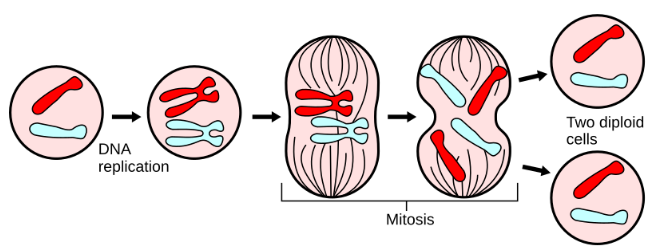
mitosis
the process of cell division, where a single parent cell divides into two genetically identical daughter cells (babies/growth and repair)
somatic cells
any cell of a living organism other than the reproductive cells
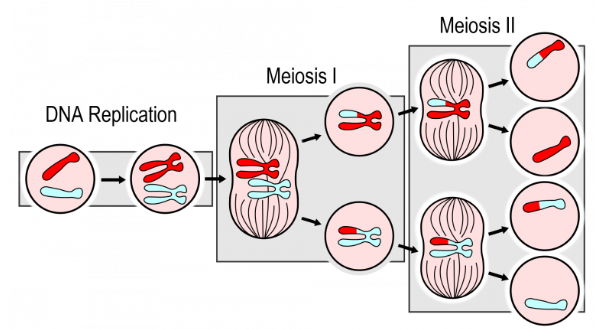
meiosis
a type of cell division that reduces the chromosome number by half, producing four genetically distinct gametes (sperm & eggs)
gametes
Mature haploid male or female germ cell (ex. sperm eggs)
What does mitosis produce?
Mitosis makes 2 identical diploid body cells for growth and repair.
What does meiosis produce?
Meiosis makes 4 unique haploid sex cells for reproduction.
3 Broad stages of cell cycle
interphase (longest stage, DNA replication)
mitosis (cell's nucleus divides)
cytokinesis (physically splitting the cell into two identical daughter cells)
Haploid
One set of chromosomes (formed through meiosis) ex. Sperm and egg cells in humans
Diploid
Two sets of chromosomes, one inherited from each parent (formed through mitosis) ex. somatic cells
What are the 3 subphases of interphase?
G1, S, and G2
What happens during interphase?
the cell grows, replicates its DNA, and prepares for cell division
What happens in G1 interphase?
the cell grows, produces proteins and organelles, and carries out its normal functions to prepare for DNA replication and division
What happens in S interphase
cell replicates its DNA, creating an exact copy of each chromosome
What happens in G2 interphase
cell continues to grow, synthesizes proteins, and produces organelles in preparation for mitosis