Animal Phylogeny and Human Locomotion Overview
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Phylogenetic tree
Diagram showing evolutionary relationships among species.
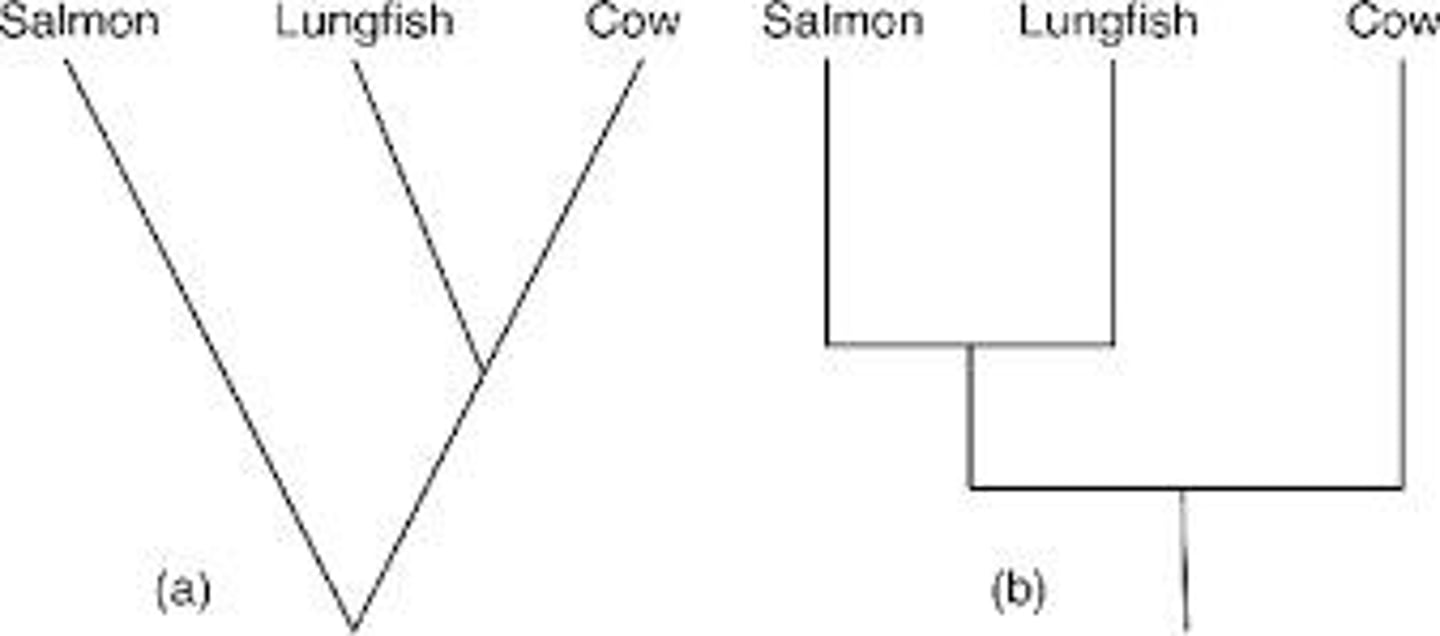
Node
Point representing a common ancestor in phylogeny.
Phenetics
Focus on overall similarities among organisms.
Cladistics
Focus on shared novel traits among organisms.
Common ancestor
Most recent species from which others evolved.
Gait cycle
Repeating sequence of limb movements in locomotion.
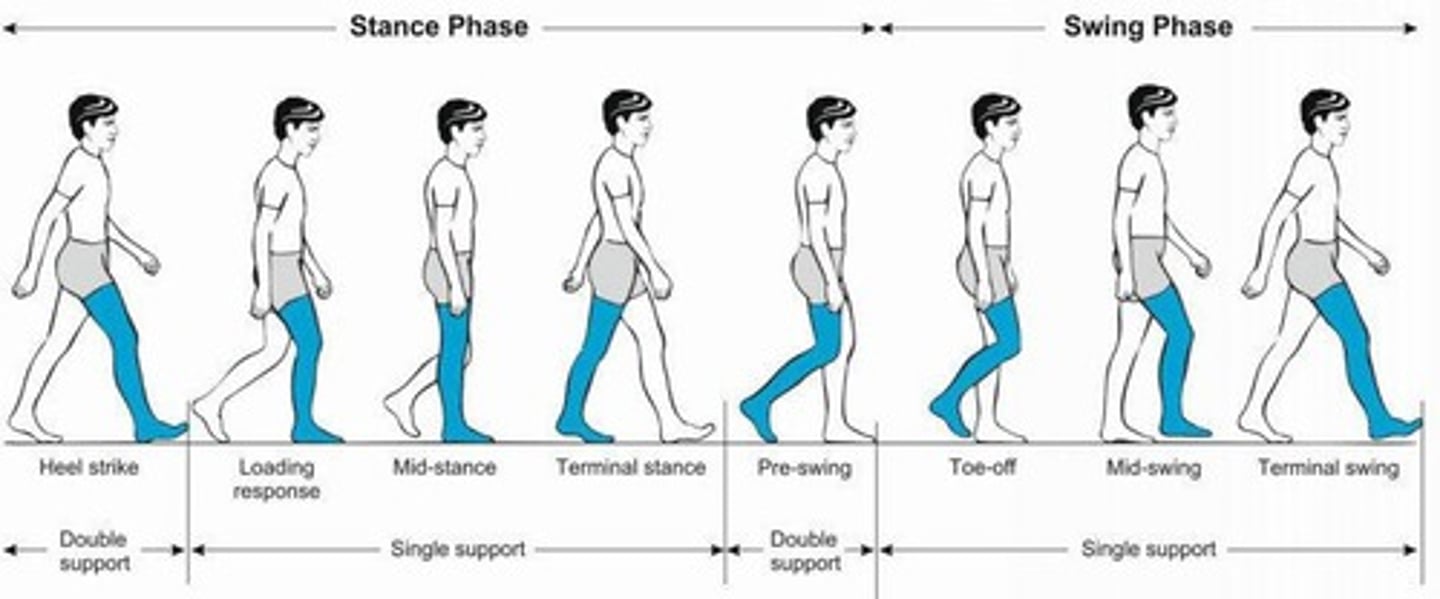
Stride length
Distance between successive initial contacts of one foot.
Step length
Distance between heel prints of opposite feet.
Stance phase
Time when foot is on the ground during gait.
Swing phase
Time when foot is in the air during gait.
Duty cycle
Ratio of stance duration to stride duration.
Ground reaction force
Force exerted by the ground in response to weight.
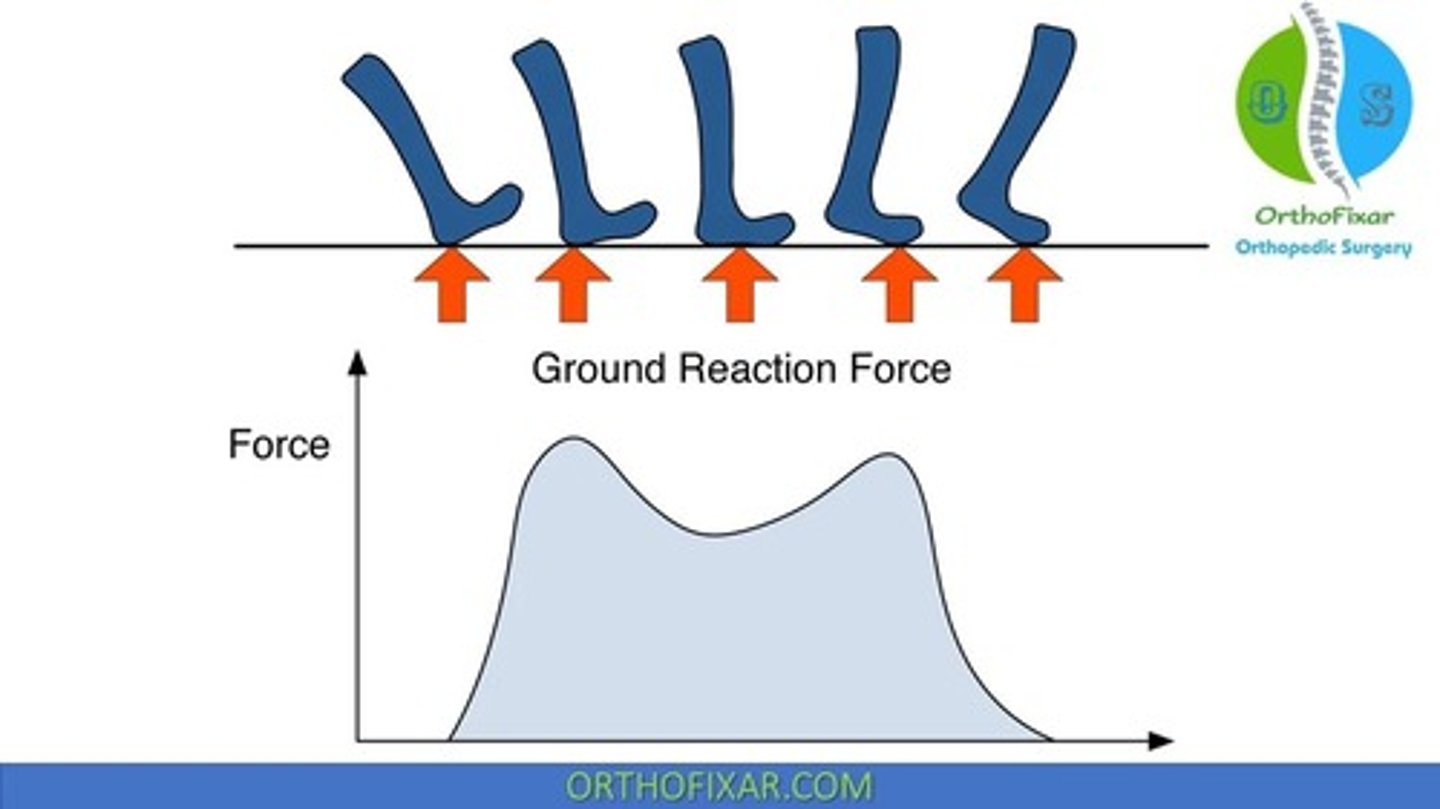
Kinetics
Study of forces involved in movement.
Potential energy (PE)
Energy stored due to height or position.
Kinetic energy (KE)
Energy of motion, dependent on velocity.
Inverted pendulum model
Model explaining energy efficiency in walking.
Spring mass model
Model explaining energy efficiency in running.
Bipedalism
Locomotion on two legs, characteristic of humans.
Pelvis adaptation
Structural changes supporting efficient upright walking.
Symmetrical gait
Footfalls evenly spaced in time during locomotion.
Asymmetrical gait
Unequal timing between footfalls of limbs.
Double support phase
Period when both feet are on the ground.
Aerial phase
Moment when both feet are off the ground.
Stride frequency
Number of strides per unit time.
Cost of transport
Energy expenditure per unit distance traveled.
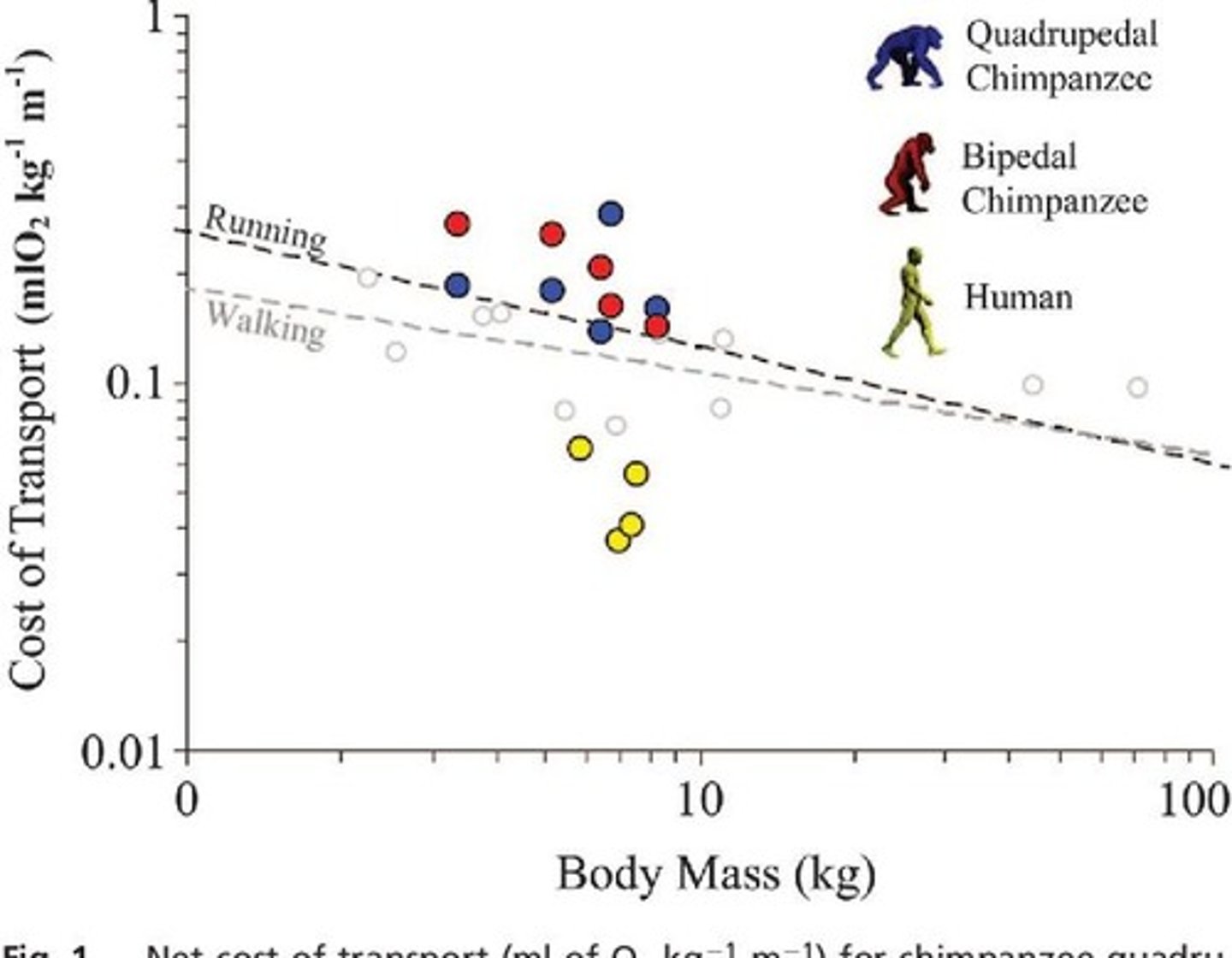
Humans vs. chimps locomotion
Humans are more energy-efficient than chimps.
Gluteus medius and minimus
Muscles stabilizing the pelvis during locomotion.
Femoral neck orientation
Angle of femur affecting center of mass stability.