Final Exam- Animal Health and Disease Control
1/112
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Texas State AG 3314 Spring 2025
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
113 Terms
Imunology
The study of white blood cells
Disease
Disfunction of a normal body condition.
Hematopoesis
production of white blood cells
Leukocytes
Mast cells, eosinophils, basophils, neutrophils, macrophages, dendritic, natural killer cells.
Lymphocytes
B cells and T cells
Granulocytes WBCs
mast cells, eopsinophils, basophils, neutrophils
Phagocyte WBCs
neutrophils, macrophages, dendritics
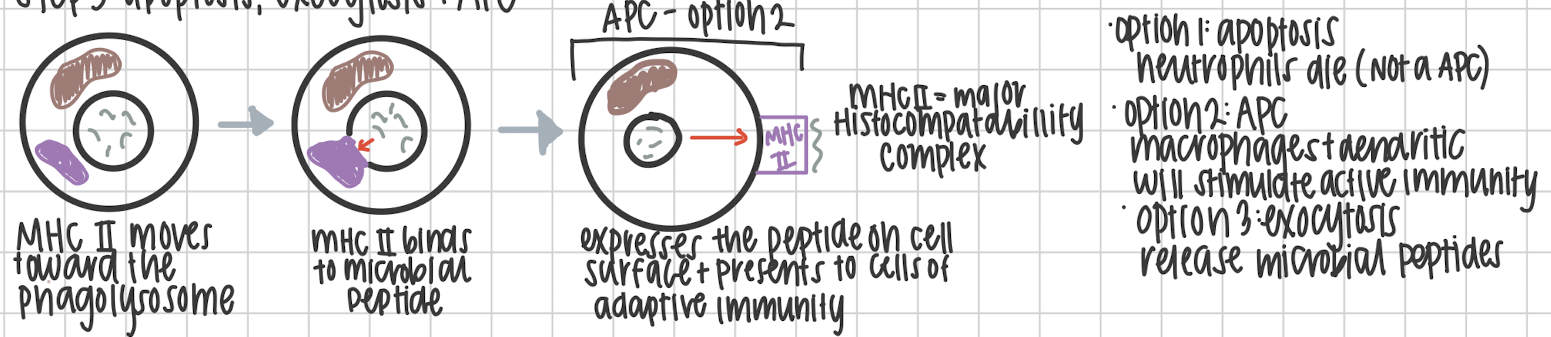
Antigen Presenting WBCs
Macrophages and dendritic
Chemokines
tells cells WHERE to GO
Cytokines
tells cells WHAT to DO
Mast Cells
Granulocyte, causes vasodilation (histamine), contains one nucleus
Eosinophil
Granulocyte, bliobed nucleus, heavily granulated, low quantities, high in parasitic response.
Basophil
Granulocyte, bilobed nucleus, heavily granulated, found in low quantities, respiratory and allergy response
Neutrophil
Granulocyte and phagocyte, 3 nuclei, most abundant WBC (50-75%), first WBC to the site of infection, major role in inflammatory response. apoptocizes and macrophage comes and engulfs.
Macrophage
Phagocyte and APC, largest WBC, great at phagocytosis, secretes cytokines and chemokines
Dendritic
Phagocyte and APC, great at activating adaptive immunity
Primary lymphatic organs
Synthesis and maturation. Bone marrow and Thymus gland.
Bone marrow is site of hematopoiesis
The medulla of the thymus gland is the site of T Cell, macrophage and dendritic cell development
Secondary lymphatic organs
Storage of mature WBCs. Spleen and lymphnode
The red pulp of the spleen is the site of storage for macrophages and dendritic. T cells stored in the white pulp.
Paracortical area of the lymphnode houses T cells, primary lymphoid follicle houses B cells
Bone marrow is the site of
Hematopoeisis
Site in thymus that develops macrophages, dendritic and T cells
Medulla
Site of spleen that stores macrophages and dendritic cells
Red pulp
Site of spleen that stores T cells
White pulp
Site of T cell storage in lymphnode
Paracortical area
Site of B cell storage in lymphnode
Primary lymphoid follicle
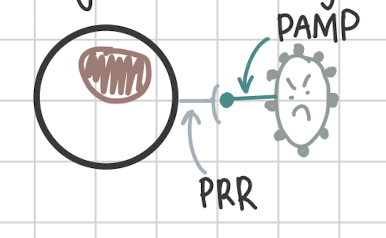
First step of Phagocytosis
PRRs on phagocytes recognize pathogens PAMP
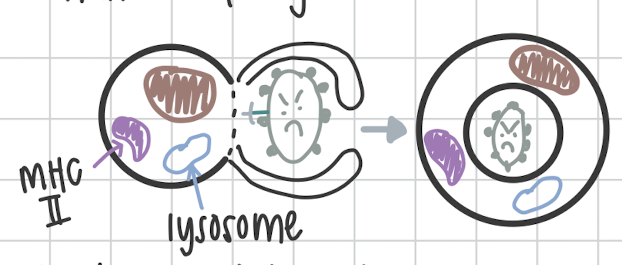
Second step of Phagocytosis
Ingestion of pathogen and formation of phagosome
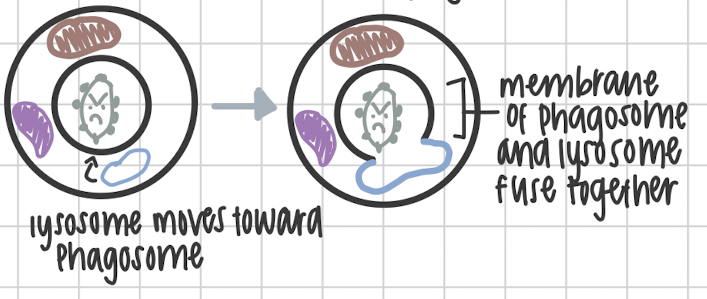
Third step of Phagocytosis
Lysosome and phagosome fuse together to form Phagolysosome
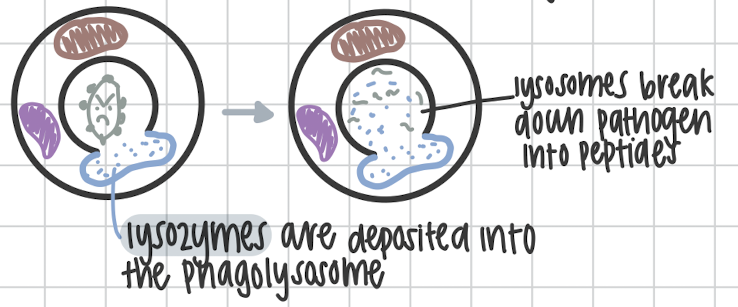
Step four in Phagocytosis
Microbial breakdown of pathogen using lysozymes
Step five in Phagocytosis
Apoptosis via neutrophils, exocytosis, or antigen presentation on the MCH II complex.
On bacteria or viruses, how do WBC recognize the pathogen?
It’s PAMP
Pathogen Associated Molecular Pattern.
How do leukocytes recognize a pathogen?
It’s PRR
Pathogen Recognition Receptors.
What is the inflammatory response?
Occurs when there is tissue damage or via a pathogen. Can result in itching, swelling, fever/heat, redness and pain. It can be acute or chronic
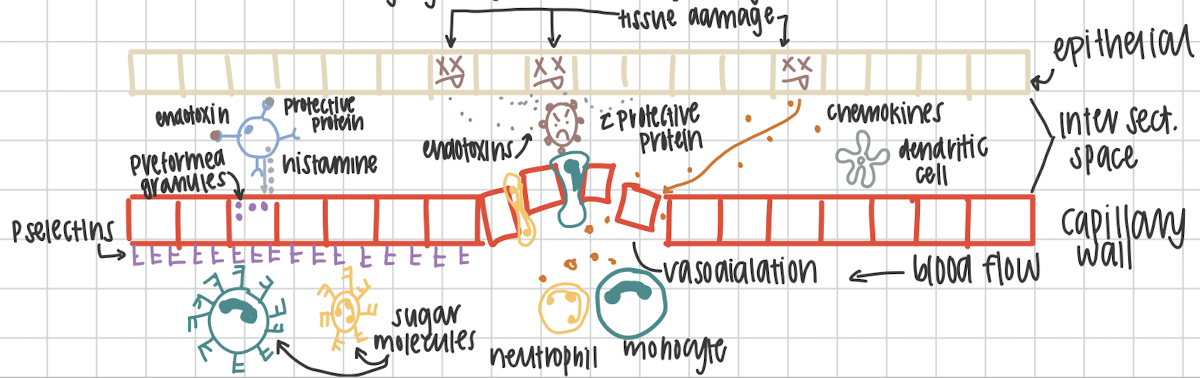
First step in the inflammatory response.
Cell damage causes cell to release signaling proteins. Pathogen releases endotoxins.Damaged cells release a protective proteins to warn neighboring cells
Second step in the inflammatory response.
Mast cell becomes activated by recognizing endotoxins or the protective proteins.
Third step in the inflammatory response.
Mast cells degranulate and release histamine that targets the capillary wall. This causes vasodilation.
Fourth step in the inflammatory response
Preformed granules in capillary cells are mobilized to cell surface to for
P-selectins
Fifth step in the inflammatory response
Chemokines that are released from damaged cells enter circulation to recruit neutrophils and monocytes (macrophages precursor. in circulation not in tissue yet)
Sixth step in the inflammatory response
Sugar molecules on neutrophils and monocytes allow for marginalization (movement) on P-selectins
Seventh step in the inflammatory response
Neutrophils and monocytes squeeze through capillary walls at vasodilation. This is called diapedesis. Neutrophils and macrophages are at site of the infection.
Eighth step of the inflammatory response
Complement system activated and is killing via MAC. Neutrophils phagocytosing pathogens and die via apoptosis. Dendritic cells are phagocytosing and presenting antigen on MHCII
Ninth and final step of the inflammatory response
Cytokines go to nearest lymphnode to activate T and B cells to trigger the adaptive immunity.
The Complement System
Three pathways: classical, alternative and lectin.
Classical pathway step 1:
Antibody on pathogen is recognized by the (non specific) FC portion.
Classical pathway step 2:
C1 recognizes FC portion of the antibody
Classical pathway step 3:
C4 binds to C1
Classical pathway step 4:
C2 binds to C4
Classical pathway step 5:
C3 binds to C2
Classical pathway step 6:
C5 binds to C3
Classical pathway step 7:
C3 and C5 are cleaved by convertase into C3b+C3a, and C5b+C5a
Classical pathway step 8:
C3b and C5b stay attached to the system, C3a and C5a become chemokines
Classical pathway step 9:
C6-C9 bind to C5b
Classical pathway step 10:
C5b→C9 break off and become MAC attack complex
MAC: membrane attack complex
Classical pathway step 11:
MAC attaches to pathogen and allows for Na2+ and H2O to enter pathogen. This causes lysis and kills the pathogen.
Alternative pathway step 1:
C3 and C5 attach directly onto pathogen
Alternative pathway step 2:
C3 and C5 cleaves into C3b+C3a, and C5b+C5a. b’s stay and a’s become chemokines
Alternative pathway step 3:
C6-C9 bind to C5b
Alternative pathway step 4:
C5b -C9 break off and form MAC.
Alternative pathway step 5:
MAC allows for Na2+ and H2O to come in and allow lysis
Alternative pathway step 6:
Macrophage phagocytosis
Lectin pathway step 1:
Lectin binds to manose molecule on a pathogen
Lectin pathway step 2:
C4 binds to Lectin, C2→ C4, C3→C2, C3→C5
Lectin pathway step 3:
C3 and C5 cleave C6-C9 bind, break off and form MAC
Lectin pathway step 4:
lysis→ macrophage phagocytizes
Antibodies
produced by plasma B cells. Consist of the heavy chain and light chain. With constant regions that determine isotope. Variable regions are the specific portion of antibody
IgG
monomer structure, most abundant, passive immunity, passes through the placenta, highest in 2nd response, good and neutralization and precipitation, opsonin.
IgA
Dimer structure, found abundantly in mucus membranes (GALT, MALT, BALT), passive immunity, passed through colostrum, good at neutralization and agglutination.
IgM
2 forms, membrane bound B cells and pentomer, highest in primary response, because it has 10 epitopes (if pentomer) and yet to gain memory, primarily agglutination.
IgE
Monomer structure, found in respiratory and GI tract, part of allergies, FCεR1 on mast cells and IgE’s recognize, essential to the parasitic response.
IgD
Monomer, membrane bound only→ B cell receptor, determines stage in B cell development.
Neutralization
Antibodies bind to pathogen, neutralized pathogen
Agglutination
Collects whole pathogens together
Precipitation
Clumping of free floating antigens
Cell mediated toxicity
IgG’s!! when cells are sick (IgG’s work with NKC) or have parasites (IgE’s work with eosinophils) used when phagocytosis isn’t an option.
B cell development
beings in the bone marrow, finishes in lymphnode to be activated. 2 stages antigen independent and antigen dependent. Remember the six stages: Happy PROfessors PREpare Interesting Notes Meticulously
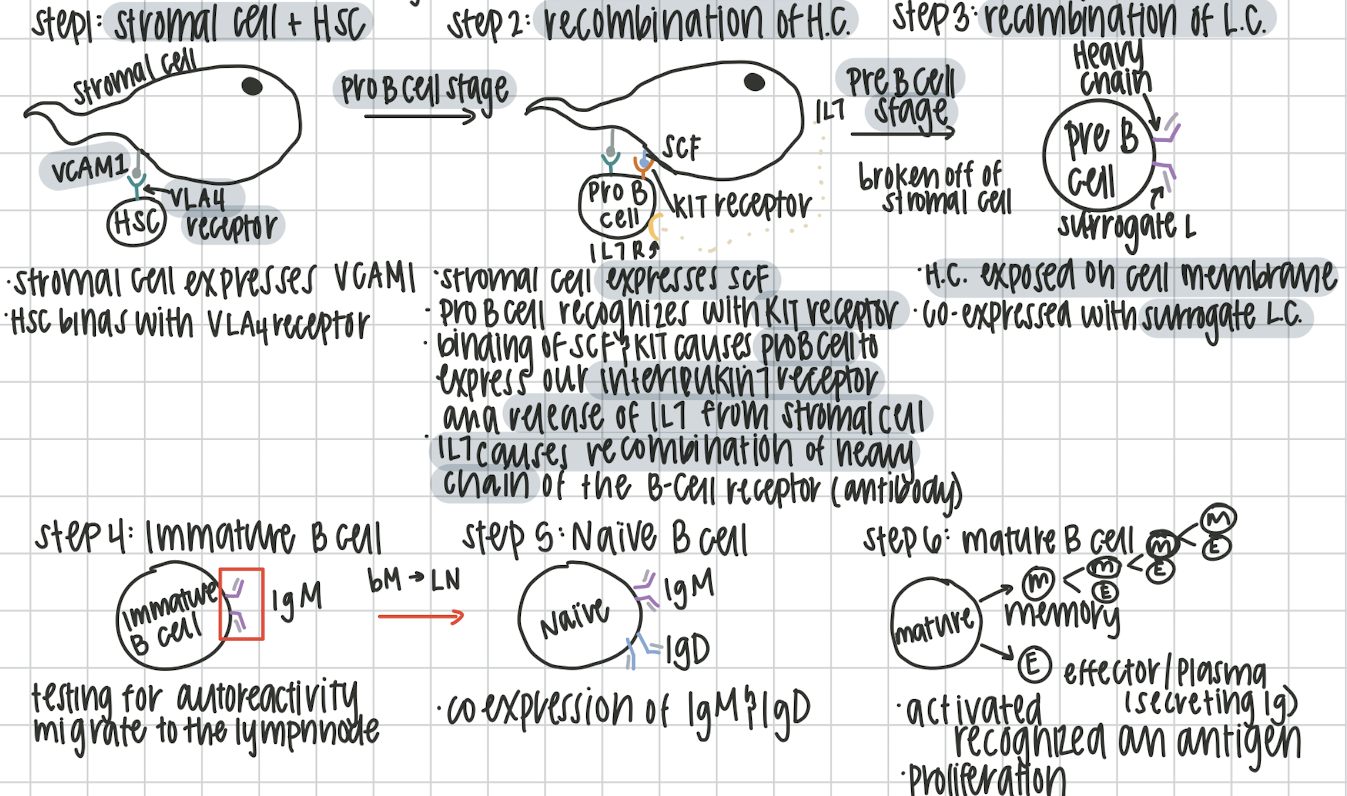
Step 1: Hematopoietic Stem Cell
Happy
Stromal cell expresses VCAM1. Hematopoietic stem cell binds with VCAM1 using its VLA4 receptor.
Step 2: Progenitor B Cell
PROfessors
recombination of the heavy chain. stromal cell expresses SCF. Pro B cell recognizes SCF with its KIT receptor. This causes the expression of IL7 receptor on Pro B cell and release of IL7 of stromal cell. IL7 causes the recombination of Heavy chain
Step 3: Pre B Cell
PREpare
After breaking off from stromal cell, the heavy chain is expressed on the cell membrane with surrogate light chain
Step 4: Immature B Cell
Interesting
Testing for autoreactivity (attacking self cells) in 2 stages.
Central tolerance autoreactivity testing
In bone marrow, testing the IgM with stromal cells, HSC and blood plasma proteins, if autorective, the surrogate L.C. recombines or apoptosis via clonal deletion or anergy
Peripheral tolerance autoreactivity testing
In spleen and lymphnode because not all self cells are in the bone marrow, tests with tissues and secreted/surface proteins. If autoreactive, apoptosis.
Step 5: Naive B Cell
Notes
Antigen dependent and now in the lymphnode. IgM and IgD are expressed
Step 6: Mature B Cell
Meticulously
Differentiation stage, into memory of effector plasma B cells
T Cell Development
7 steps: The PROud Prince Never Doubts Nobility & Majesty
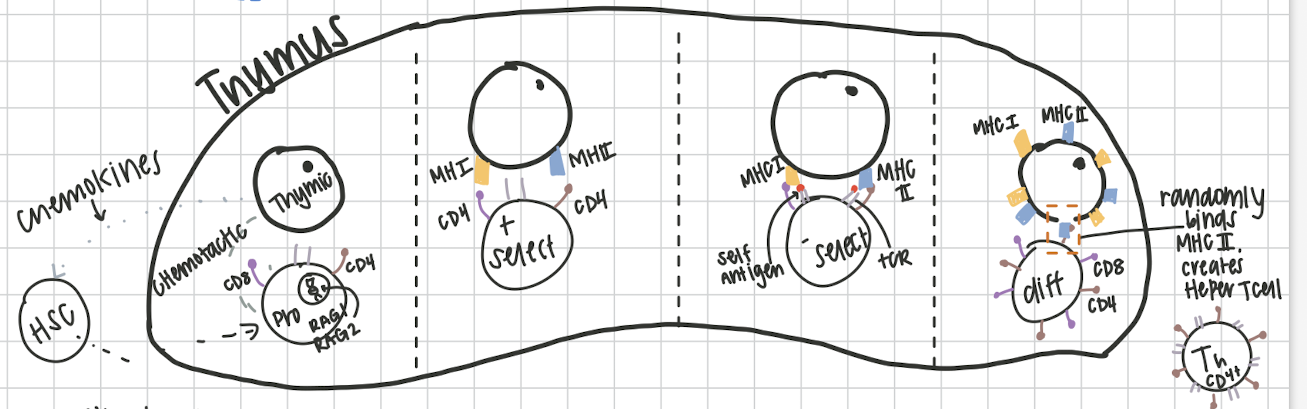
Step 1: Thymic Cells
The
Thymic cells secrete cytokines to recruit hematopoietic stem cells to thymus
Step 2: Progenitor T cell
PROud
Recombination step, chemokines act on the Pro B cell, targets RAG1 and RAG2. this creates the T cell receptor, results in cluster differentiation proteins CD8 and CD4
Step 3: Positive selection
Prince
Thymic cell presents both an MHCI and MHCII. CD8 binds to MHCI and CD4 binds to MHCII. If not recognized, to right CD/MHC results in apoptosis
Step 4: Negative selection
Never
recognition of self antigens. testing TcR against self antigens on MHC’s. If autoreactive, apoptosis
Step 5: T Cell Differentiation
Doubts
where T cells get their jobs! completely random, become helper T cell (Th) or cytotoxic T cell (Tc). If MHCI binds to CD8→Tc, if MHCII binds to CD4→Th
Step 6: Naive T cell
Nobility
Travels to secondary lymphoid organs waiting for activation
Step 7: Mature T cell
Majesty
Activated! proliferates into effector Tc or Th cells/ memory Tc or Th cells
Cytotoxic T cells
Causes apoptosis in cancerous/ infected cells by releasing granulozymes and perforins
Helper T cells
Help with activation of B cells. produce cytokines.
Th Activation
Recognition of antigen on the APC (dendritic). Th CD4 recognizes MHCII on APC and antigen
Costimulatory protein CD28 from Th binds with costimulatory receptor CD80 on APC.
Th releases IL2 and binds to their own Th IL2 receptor. Th can now proliferate into effector/ plamsa or memory Th cells.
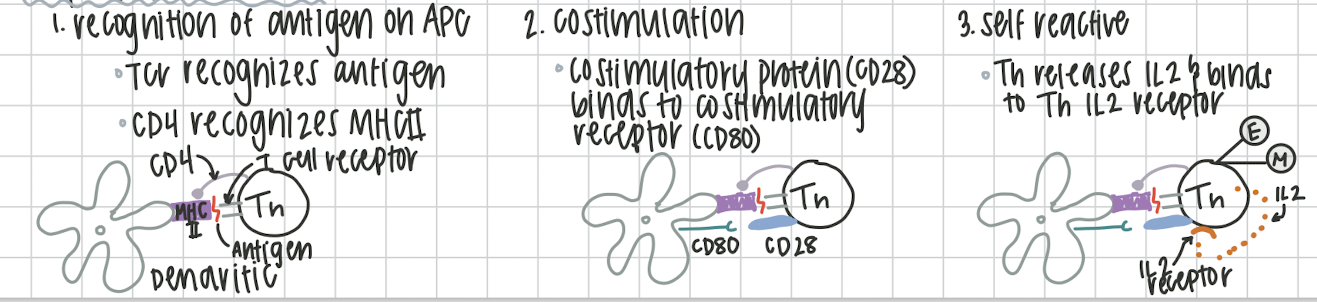
Ways B cell can be stimulated
Th dependent:
a. bind to a free floating antigen
b. APC from dendritic cell
c. B cell recognizing whole pathogen
Th independent:
requires APC from Th
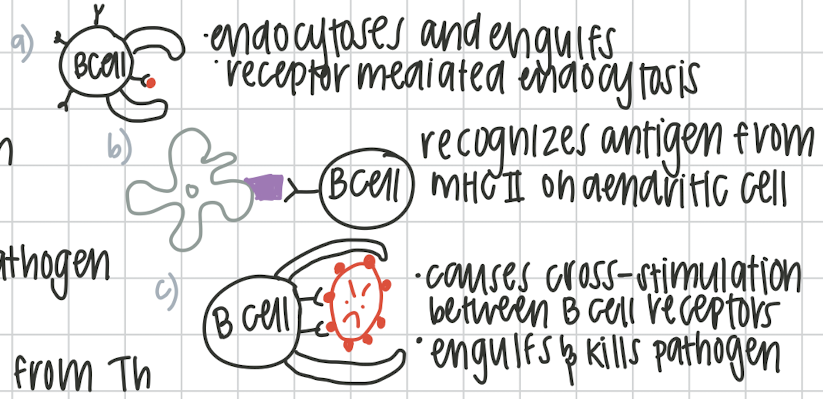
Step 1 in the humoral response
Th activation! either from recognizing antigen on APC and CD4 with MHCII on dendritic, Th CD28 binds to APC’s CD80 or, IL2 from Th released and Th’s IL2 receptor.
Step 2 in the humoral response
Naive B cell stimulation.
If nonprotein antigen: free floating antigen, whole pathogen or APC from dendritic
If protein antigen: Th stimulation
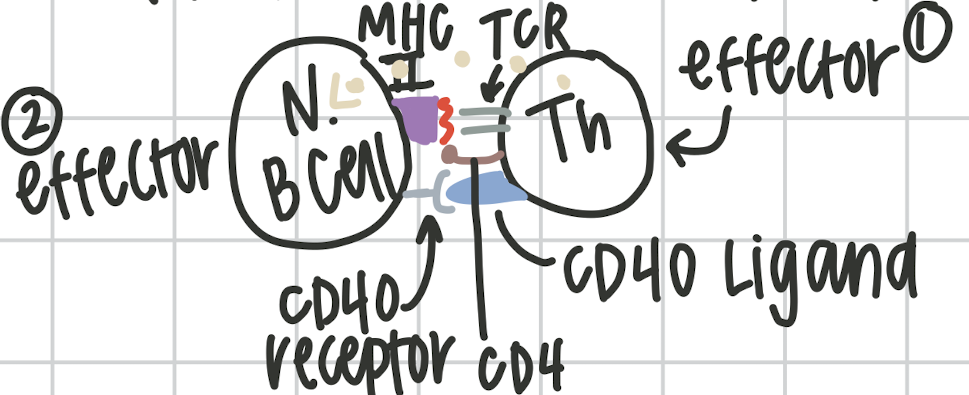
Step 3 in the humoral response
Th activates Naive B cell. ThR and CD4 recognize MHCII on naive B cell receptor. causes expression of the CD40 ligand on the Th and CD40 receptor on Naive B cell. Th releases IL5. This happens no matter what.
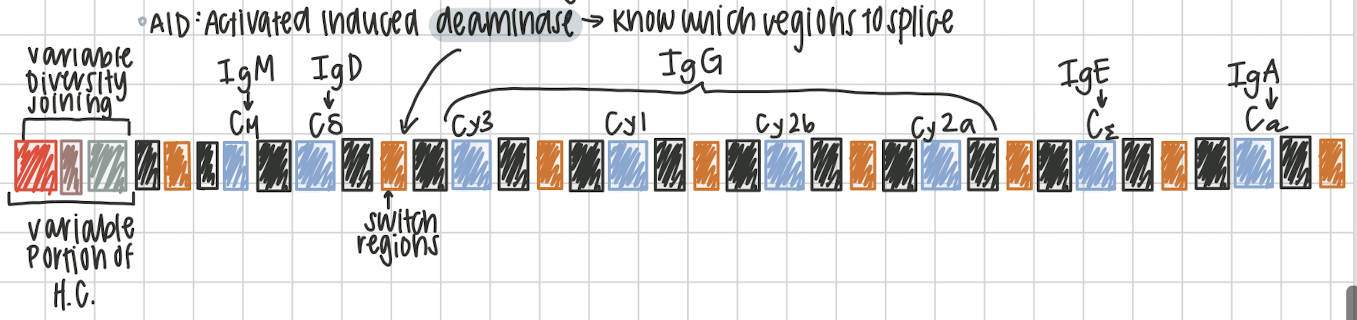
Isotope switching
process of switching IgM into variety of immunoglobulins. must encounter an antigen, irreversible process, changing the constant region on the antibody. on chromosome 14. activated induced deaminase knows which regions to splice (switch regions) variable portion of heavy chain called variable diversity joining (VDJ)
IgM → Cμ
IgD → Cδ
IgG →Cγ3, Cγ1, Cγ2b, Cγ2a
IgE → Cε
IgA →Cα
Hypermutation
Affinity maturation, natural selection for B cells, changes strength, if still not “strong enough”, B cell is killed
Cell mediated immune response
Cells helping sick cells. Key players Cytotoxic T cells (specific) NKC (nonspecific). They recognize differently but kill the same.