AUDIT EXAM 1
1/233
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
234 Terms
The risk to investors that a company’s financial statements may be materially misleading is called: (1:1)
Information risk.
Which of the following would be considered an assurance engagement? (1:2)
All of the choices are correct.
Which of the following best describes the relationship between auditing and attestation engagements? (1:3)
Auditing is a subset of attestation engagements that focuses on the certification of financial statements.
Jones, CPA, is planning the audit of Rhonda’s Company. Rhonda verbally asserts to Jones that all expenses for the year have been recorded in the accounts. Rhonda’s representation in this regard: (1:4)
Is not considered a sufficient basis for Jones to conclude that all expenses have been recorded.
When an auditor reviews additions to the equipment (fixed asset) account to make sure that fixed assets are not overstated, she wants to obtain evidence as to management’s assertion regarding: (1:5)
Existence.
Which of the following audit procedures probably would provide the most reliable evidence related to the entity’s assertion of rights and obligations for the inventory account? (1:6)
Inspect agreements for evidence of inventory held on consignment.
Cutoff tests designed to detect valid sales that occurred before the end of the year but have been recorded in the subsequent year would provide assurance about management’s assertion of: (1:7)
Completeness.
Independent auditors of financial statements perform audits that reduce: (1:8)
Information risk faced by investors.
When auditing an investment in a publicly-traded company, an auditor most likely would seek to conduct which audit procedure to help satisfy the valuation assertion? (1:9)
Obtain market quotations from The Wall Street Journal or another independent source.
The Sarbanes–Oxley Act of 2002 generally prohibits public accounting firms from: (1:10)
All of the choices are correct.
primary objective of compliance auditing is to: (1:11)
Determine whether client personnel are following laws, rules, regulations, and policies.
The organization primarily responsible for ensuring that public officials are using public funds efficiently, economically, and effectively is the: (1:12)
Government Accountability Office (GAO).
A determination of cost savings obtained by outsourcing cafeteria services is most likely to be an objective of (1:13)
Operational auditing.
When auditing the accounts receivable account on the Balance Sheet, an auditor’s procedures most likely would focus primarily on management’s assertion of: (1:14)
Existence.
In an attestation engagement, a CPA practitioner is engaged to (1:15)
Prepare a written report containing a conclusion about the reliability of a management assertion.
The primary difference between operational auditing and financial auditing is that in operational auditing: (1:16)
The operational auditor is seeking to help management use resources in the most effective manner possible.
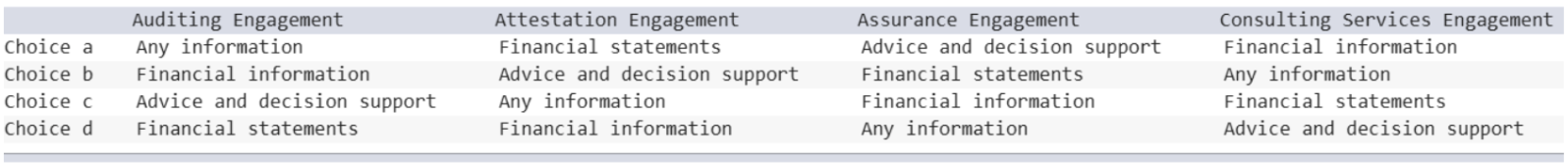
Which of the following best describes the focus of the following engagements? (1:17)
Choice d.
It is always a good idea for auditors to begin an audit with the professional skepticism characterized by the assumption that: (1:18)
A potential conflict of interest always exists between the auditor and the management of the enterprise under audit.
The Sarbanes–Oxley Act of 2002 prohibits public accounting firms from providing which of the following services to an audit client? (1:19)
All of the choices are correct.
Which of the following best describes the general contents of the first paragraph of the "Basis for Opinion" section of the auditors’ report? (2:1)
Statements identifying the responsibility of auditors and management in the financial reporting process.
Auditors’ understanding of the internal control in an entity provides information for: (2:2)
Planning the nature, timing, and extent of substantive procedures on an audit.
Which of the following opinions would be issued if auditors believed that the entity’s financial statements were not presented in conformity with GAAP? (2:3)
Adverse opinion.
Audit evidence is usually considered sufficient when (2:4)
there is enough quantity to afford a reasonable basis for an opinion on financial statements.
The evidence considered most appropriate by auditors is best described as: (2:5)
Direct personal knowledge obtained through physical observation and mathematical recalculation.
Which of the following principles is most closely associated with the auditors’ conclusion as to the fair presentation of the entity’s financial statements? (2:6)
Reporting principle.
Which of the following topics is not addressed in the auditors’ report for an issuer? (2:7)
Absolute assurance regarding the fairness of the entity’s financial statements in accordance with GAAP.
Which of the following is most closely related to the relevance of audit evidence? (2:8)
In addition to confirmations of accounts receivable, auditors perform an analysis of the aging of accounts receivable to evaluate the collectability of accounts receivable.
Ordinarily, what source of evidence should least affect audit conclusions? (2:9)
Inquiry of management
Which of the following categories of principles is most closely related to gathering audit evidence? (2:10)
Performance.
Which of the following statements is not true with respect to the performance principle? (2:11)
Auditors are required to prepare a written audit plan during the planning stages of initial audits but are not required to do so in continuing audits.
Kramer, CPA, consulted an independent appraiser regarding the valuation of fine art for a not-for-profit museum. Consultation with the appraiser in this case would: (2:12)
Be considered as exercising proper due care.
Which of the following combinations would provide the auditor the most reliable evidence? (2:13)
Choice c, external (source of evidence), more effective (of internal control)
The primary purpose for obtaining an understanding of the entity’s environment (including its internal control) in a financial statement audit is (2:14)
To determine the nature, timing, and extent of substantive procedures to be performed.
Which of the following is not related to ethical requirements of auditors? (2:15)
Professional judgment.
Which of the following recognizes that an audit conducted under generally accepted auditing standards may not detect all material misstatements? (2:16)
Reasonable assurance.
Which of the following combinations of standards and types of audits are most closely related to the activities of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board? (2:17)
Develop Auditing Standards for the audits of issuers.
Which of the following is true with respect to PCAOB inspections of accounting firms? (2:18)
PCAOB inspections review a sample of audits conducted by firms as well as the firm’s systems of quality control.
Which of the following is most closely related to the responsibilities principle? (2:19)
The auditors’ compliance with relevant ethical requirements of independence and due care.
When initiating communications with predecessor auditors, prospective auditors should expect: (3:1)
All of the choices are correct.
The company being audited has an internal auditor who is both competent and objective. The independent auditor wants to assign tasks for the internal auditor to perform. Under these circumstances, the independent auditor may: (3:2)
Allow the internal auditor to perform certain tests of internal controls.
Before accepting an engagement to audit a new client, a CPA is required to obtain: (3:3)
the prospective client's consent to make inquiries of the predecessor, if any.
With respect to the concept of materiality, which of the following statements is correct? (3:4)
Materiality is a matter of professional judgment.
Which of the following is not a benefit claimed for the practice of determining materiality in the initial planning stage of an audit? (3:5)
Being able to decide early what type of audit opinion to issue.
Which of the following statements is correct concerning analytical procedures used in planning an audit engagement? (3:6)
They typically use financial and nonfinancial data aggregated at a high level.
When applying analytical procedures during an audit, which of the following is the best approach for developing expectations? (3:8)
Comparing current-year account balances to balances of one or more comparable periods.
When planning an audit, which of the following is not a factor that affects auditors' decisions about the quantity, type, and content of audit documentation? (3:9)
The auditors’ judgment about their independence with regard to the client.
Audit documentation that shows the detailed evidence and procedures regarding the balance in the accumulated depreciation account for the year under audit will be found in the: (3:10)
Current file audit documentation.
Which of the following communications is most likely to be written before the balance-sheet date? (3:11)
An engagement letter.
Which of the following auditor concerns most likely could be so serious that the auditor would conclude that a financial statement audit cannot be conducted? (3:12)
The integrity of entity's management is suspect.
When auditing the existence assertion for an asset, auditors proceed from the: (3:13)
General ledger back to the supporting original transaction documents.
Which of the following would be considered an analytical procedure? (3:14)
Comparing inventory balances to recent sales activities.
Confirmations of accounts receivable provide evidence primarily about which two assertions? (3:15)
Existence and rights and obligations.
Which of the following conditions most likely would pose the greatest risk in accepting a new audit engagement? (3:16)
There will be a client-imposed scope limitation.
An audit engagement letter should normally include which of the following matters of agreement between the auditor and the client? (3:17)
Schedules and analyses to be prepared by the client’s employees.
When auditing Vandalay Jewelry, Costanza, CPA, was not familiar with the quality and cut of the company’s precious jewel inventory. To address this shortcoming, Costanza hired Benes, an expert in jewel valuation, to assist as an audit specialist for the inventory valuation. Should Costanza refer to Benes’s work in the audit report? (3:18)
The auditors’ report should mention the use of the audit specialist only when the audit specialist’s findings affect the auditors’ conclusions.
Prior to accepting a new audit engagement, a public accounting firm should: (3:19)
All of the choices are correct.
An auditor's permanent file audit documentation most likely will contain: (3:20)
Excerpts of the corporate charter and bylaws.
Auditing standards do not require auditors of financial statements to: (4:1)
Report all errors and frauds found to police authorities.
It is acceptable under generally accepted auditing standards for an audit team to: (4:2)
Assess risk of material misstatement at high and achieve an acceptably low audit risk by performing extensive substantive tests.
Which of the following relationships between types of analytical procedures and sources of information are most logical? (4:3)
Type of Analytical Procedure: Comparison of current account balance with expected balances.
Source of Information: Company’s budgets and forecasts
Suppose management estimated the market valuation of some obsolete inventory at $99,000; this inventory was recorded at $120,000, which resulted in recognizing a loss of $21,000. The auditors obtained the following information: The inventory in question could be sold for an amount between $78,000 and $92,000. The costs of advertising and shipping could range from $5,000 to $7,000.
A. Would you propose an audit adjustment to the management estimate?
B. Prepare the appropriate accounting entry.
C. If management’s estimate of inventory market (lower than cost) had been $80,000, would you propose an audit adjustment?
D. Prepare the appropriate accounting entry.
(4:4)
A. Yes.
B. Dr. Loss (or COGS) 12000
Cr. Inventory 1200
C. No.
D. No journal entry required.
The likelihood that material misstatements may have entered the accounting system and not been detected and corrected by the client’s internal control is referred to as: (4:5)
Risk of material misstatement.
The auditors assessed risk of material misstatement at 0.50 and said they wanted to achieve a 0.05 risk of failing to express a correct opinion on financial statements that were materially misstated. What detection risk do the auditors plan to use for planning the remainder of the audit work? (4:6)
0.10.
Auditors perform analytical procedures in the planning stage of an audit for the purpose of: (4:7)
Identifying unusual conditions that deserve more auditing effort.
Audit risks for particular accounts and disclosures can be conceptualized in the model: Audit risk (AR) = Inherent risk (IR) × Control risk (CR) × Detection risk (DR). Use this model as a framework for considering the following situations and deciding whether the auditor’s conclusion is appropriate or not appropriate.
A. Paul, CPA, has participated in the audit of Tordik Cheese Company for five years, first as an assistant accountant and the last two years as the senior accountant. Paul has never seen an accounting adjustment recommended and believes the inherent risk must be zero.
B. Hill, CPA, has just (November 30) completed an exhaustive study and evaluation of the internal controls of Edward Foods Inc. (fiscal year ending December 31). Hill believes the control risk must be zero because no material errors could possibly slip through the many error-checking procedures and review layers that Edward used.
C. Fields, CPA, is lazy and does not like audit jobs in Philadelphia. On the audit of Philly Manufacturing Company, Fields decided to use substantive procedures to audit the year-end balances very thoroughly to the extent that the risk of failing to detect material errors and irregularities should be 0.02 or less. Fields gave no thought to inherent risk and conducted only a very limited review of Philly's internal control system. (4:8)
A. Not appropriate
B. Not appropriate
C. Appropriate
Johnson & Company, CPAs, audited Guaranteed Savings & Loan Company. M. Johnson had the assignment of evaluating the collectability of real estate loans. Johnson was working on two particular loans: (1) a $4 million loan secured by Smith Street Apartments and (2) a $5.5 million construction loan on Baker Street Apartments now being built. The appraisals performed by Guaranteed Appraisal Partners Inc. showed values in excess of the loan amounts. On inquiry, Bumpus, the S&L vice president for loan acquisition, stated, “I know the Smith Street loan is good because I myself own 40 percent of the partnership that owns the property and is obligated on the loan.”
Johnson then wrote in the audit documentation: (1) the Smith Street loan appears collectible as Bumpus personally attested to knowledge of the collectability as a major owner in the partnership obligated on the loan; (2) the Baker Street loan is assumed to be collectible because it is new and construction is still in progress; and (3) the appraised values all exceed the loan amounts.
A. Do you perceive any problems with related-party involvement in the evidence used by Johnson?
B. Do you perceive any problems with Johnson’s reasoning or the appropriateness of evidence used in that reasoning? (4:9)
A. Yes
B. Yes
Analytical procedures are generally used to produce evidence from: (4:10)
Relationships among current financial balances and prior balances, forecasts, and nonfinancial data.
Auditors are not responsible for accounting estimates with respect to: (4:11)
Making the estimates.
Which of the following circumstances would most likely cause an audit team to perform extended procedures? (4:12)
The client made several large adjustments at or near year-end.
If tests of controls induce the audit team to change the assessed level of control risk for fixed assets from 0.4 to 1.0 and audit risk (0.05) and inherent risk remain constant, the acceptable level of detection risk is most likely to: (4:13)
Change from 0.25 to 0.1.
The risk of material misstatement is composed of which audit risk components? (4:14)
Inherent risk and control risk.
Analytical procedures can be used in which of the following ways? (4:15)
All of the choices are correct.
If sales were overstated by recording a false credit sale at the end of the year, where could you find the false "dangling debit"? (4:16)
Accounts receivable.
The risk that the auditors’ own testing procedures will lead to the decision that material misstatements do not exist in the financial statements when in fact such misstatements do exist is: (4:17)
Detection risk.
When completing the audit of internal controls for an issuer, the severity of an internal control deficiency depends on: (5:1)
Both the magnitude of the potential misstatement resulting from the deficiency or the deficiencies and whether there is a reasonable possibility that the company’s controls will fail to prevent or detect a misstatement of an account balance or disclosure.
Which of the following is a preventive control? (5:2)
Separation of duties between the payroll and personnel departments.
When completing the audit of internal controls for an issuer, the PCAOB requires the audit team to audit internal controls over: (5:3)
Financial reporting.
Which report would not be appropriate for a public accounting firm to provide on financial reporting controls? (5:4)
Disclaimer of opinion—significant deficiencies exist.
When completing the audit of internal controls for an issuer, AS 2201 requires auditors to test: (5:5)
Both operating and design effectiveness.
When testing a control activity’s operating effectiveness, procedures the auditor performs to test operating effectiveness would likely include (5:6)
Inquiry of appropriate personnel and reperformance of the control activity.
Effectiveness of audit procedures would be reduced by (5:7)
Performing procedures during the interim period as opposed to at the fiscal year-end date.
A material weakness is a situation in which (5:8)
It is reasonably possible that a material misstatement would not be detected on a timely basis.
If the auditor plans to assess control risk at less than the maximum and rely on controls, and the nature, timing, and extent of further audit procedures are based on that lower assessment, the auditor must (5:9)
Obtain evidence that the controls selected for testing are designed effectively and operated effectively during the entire period of reliance.
Once the auditor detects a control deficiency, which of the following steps must he or she take first? (5:10)
Evaluate the severity of the deficiency on the auditor’s control risk assessment for that assertion.
To test the operating effectiveness of a control, an audit team might use a combination of each of the following tests except for: (5:12)
Confirmation of balances.
Which of the following would probably not be considered an indication of a material weakness? (5:13)
Overproduction by the manufacturing plant.
If the auditors encounter a significant scope limitation in evaluating an issuer’s internal control over financial reporting, which of the following types of opinions on the effectiveness of the company’s internal control over financial reporting would be appropriate? (5:14)
Disclaimer of opinion.
The auditor should assess control risk for each relevant assertion by evaluating the evidence obtained from all sources, including (5:15)
All of the choices are correct.
The purpose of separating the duties of hiring personnel and distributing payroll checks is to separate the (5:16)
Authorization of transactions from the custody of related assets.
Internal controls vary significantly between organizations--depending on attributes like organization size, nature of operations, and objectives. In all systems, however, a variety of controls needs to be designed to accomplish the organization's objectives. Controls are classified as preventive, detective, or corrective (answer choices).
A. Segregation of duties:
B. A requirement to prepare bank reconciliations:
C. Maintaining backups of data:
(5:17)
A. Preventive Control
B. Detective Control
C. Corrective Control
A. Segregation of duties is a control aimed at ___ misstatement.
B. The requirement to ___ journal entries is an example of a preventive control.
C. The goal to find a misstatement that has already been made is a type of ___ control.
D. Preparing bank ___ can help detect misstatements that have been made. (5:18)
A. Preventing
B. Approve
C. Detective
D. Reconciliations
It is always a good idea for auditors to begin an audit with professional skepticism characterized by the assumption that (1:24)
A potential conflict of interest always exists between the auditor and the management of the enterprise under audit.
According to the AICPA, the purpose of an audit of financial statements is to (1:28)
Enhance the degree of confidence that intended users can place in the financial statements.
The primary objective of compliance auditing is to (1:32)
Determine whether client personnel are following laws, rules, regulations, and policies.
Performance audits usually include:
A. Financial audits.
B. Economy and efficiency audits.
C. Compliance audits.
D. Program audits.
(1:35)
B&D
The objective in an auditor’s review of credit ratings of a client’s customers is to obtain evidence related to management’s assertion about (1:36)
Valuation or allocation.
When auditing merchandise inventory at year-end, the auditor performs audit procedures to ensure that all goods purchased before year-end are received before the physical inventory count. This audit procedure provides assurance about which management assertion? (1.39)
Cutoff
When auditing merchandise inventory at year-end, the auditor performs audit procedures to obtain evidence that no goods held on consignment are included in the client’s ending inventory balance. This audit procedure provides assurance about which management assertion? (1:40)
Rights and obligations.
When an auditor reviews additions to the equipment (fixed asset) account to make sure that fixed assets are not overstated, she wants to obtain evidence as to management’s assertion regarding (1:41)
Existence.
Substantial equivalency refers to (1:43)
Permitting a CPA to practice in another state without having to obtain a license in that state.