Chapter 4: prokaryotic cell
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Prokaryotes:
•One circular chromosome, not in a membrane
•No histones
•No organelles
•Bacteria: peptidoglycan cell walls
•Archaea: pseudomurein cell walls
•Divides by binary fission
Eukaryote:
•Paired chromosomes, in the nuclear membrane
•Histones
•Organelles
•Polysaccharide cell walls, when present
Divides by mitosis
The cell wall in prokaryotes…
•Prevents osmotic lysis (10-25 atmospheres of internal pressure)
•Determines shape (genetic characteristic)
•Made of peptidoglycan (in bacteria)
Peptidoglycan…
•Polymer of disaccharide
N-acetylglucosamine (NAG) and N-acetylmuramic acid (NAM)
•Cross-linked by short chain of aa (peptide)
•Forms dynamic, mesh-like girdle around cell
Gram Positive Cell walls have…
•Thick peptidoglycan
•Teichoic acids
•In acid-fast cells, contains mycolic acids (= waxy substance)
Gram Negative Cell walls have…
•Thin peptidoglycan
(as mono-layer)
•No teichoic acids
•Outer membrane
( LPS layer)
Gram-Positive Cell Walls contain…
•Teichoic acids – cell wall anchor
Lipoteichoic acid links to plasma membrane
Wall teichoic acid links to peptidoglycan
•May regulate movement of cations.
•Polysaccharides provide antigenic variation.
Gram-Negative outer membranes contain…
•Lipopolysaccharides, lipoproteins, phospholipids (= “LPS”)
•Lipid A (endotoxin)
•Porins (proteins) form channels through membrane (entry for molecules)
Limits size of molecules entering cell
Gram-positive Gram Stain Mechanism
•Alcohol dehydrates thick peptidoglycan
•CV-I2 crystals cannot leave
Gram-negative Gram Stain Mechanism
•Alcohol dissolves outer membrane and leaves holes in peptidoglycan.
•CV-I2 washes out
Mycoplasmas have..
atypical cell walls.
•Lack cell walls (genetic)
•Sterols in plasma membrane
provide stability
Archaea have…
atypical cell walls.
•Wall-less or
•Walls of pseudomurein
(lack NAM and D amino acids)
Flagella provide
mobility
Pilli provide
attachment.
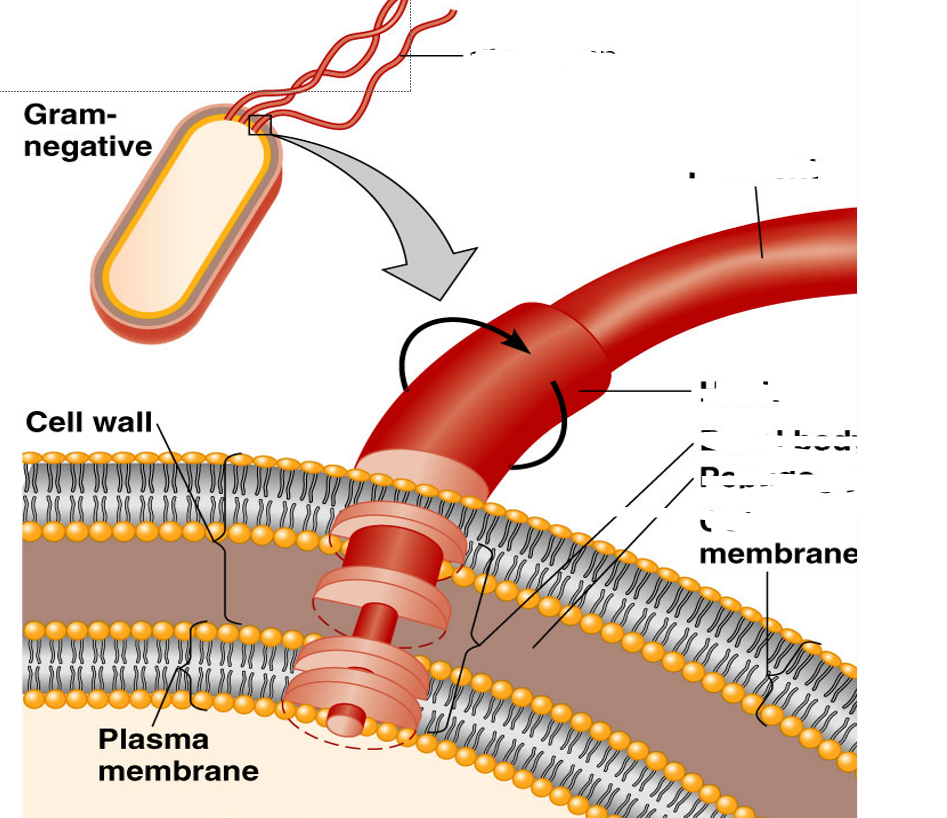
The flagella is made out of:
•Filament made of chains of flagellin
(protein subunits)
•Attached to a protein hook
•Anchored to the wall and membrane by the basal body
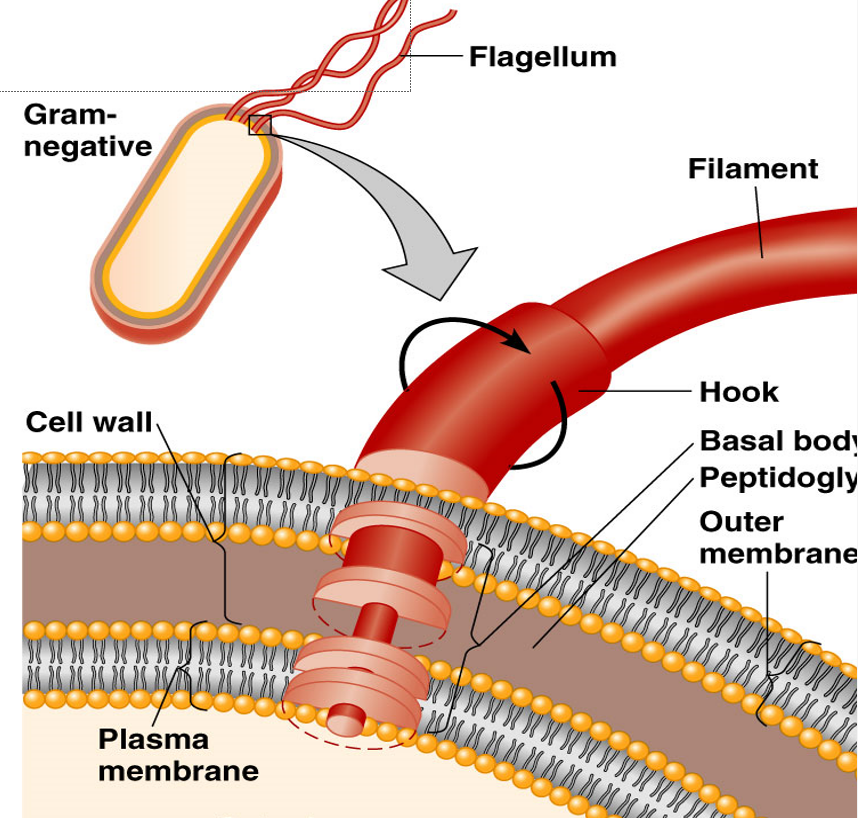
Gram negative flagella move in a
propeller motion
Different ways bacteria move to favorable conditions:
•Chemotaxis
sense chemicals
•Phototaxis
sense light intensity
•Aerotaxis
favorable oxygen concentrations
•Magnetotaxis
move along magnetic lines
How bacteria move:
Sensing: Bacteria have receptor proteins that detect stimuli in the environment.
Signal Processing: The signal alters the rotation of the flagella.
Movement Response:
Run: Smooth, straight swimming toward attractant
Tumble: Random movement or change in direction away from repellent
Axial Filaments are…
•In spirochetes
•Anchored at one end
of a cell
•Rotation causes cell
to move
glycocalyx definition
the outermost slimy, gummy, layer found outside the cell wall of many bacteria.
function of glycocalyx
•Protection Against drying out
•Against phagocytosis
•Adherence to surface (biofilm)
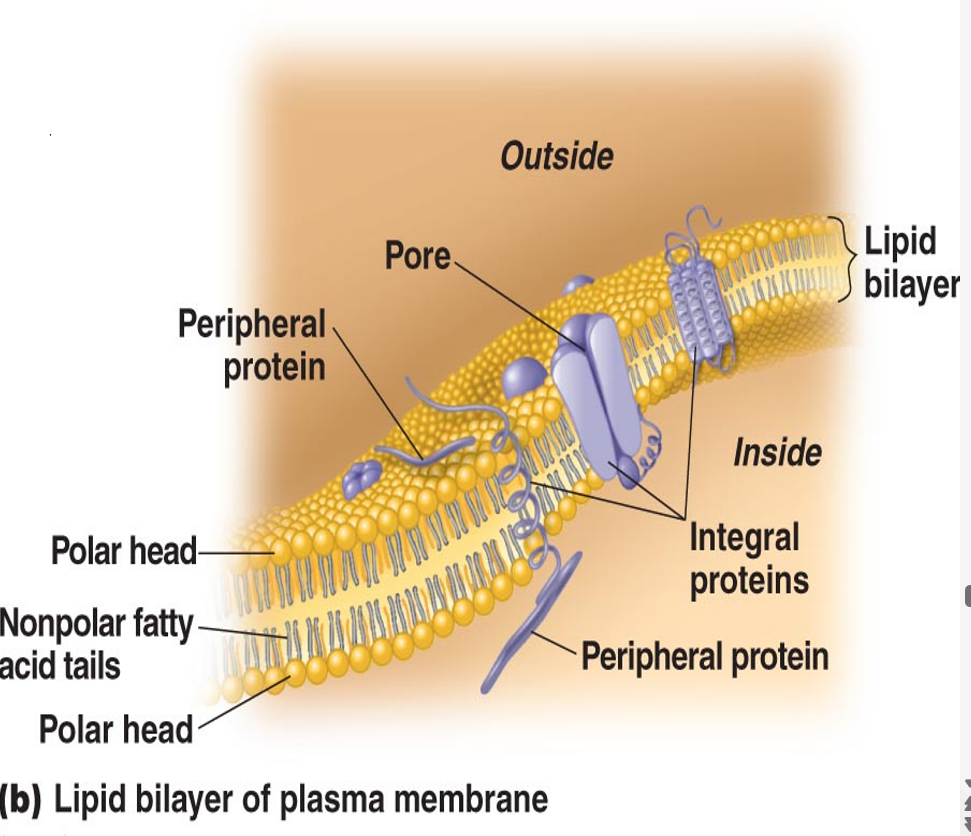
Cytoplasmic membrane function
•regulates passage into and out of cell (= transport)
made of phospholipid bilayer and proteins
Nucleoid
no histone proteins, contains genetic materiel
Ribosomes
protein synthesis
inclusion bodies (prokayrotes)
functions as internal storage for energy.
cytoplasm
gel like, 85%> water. site of metabolic activity.
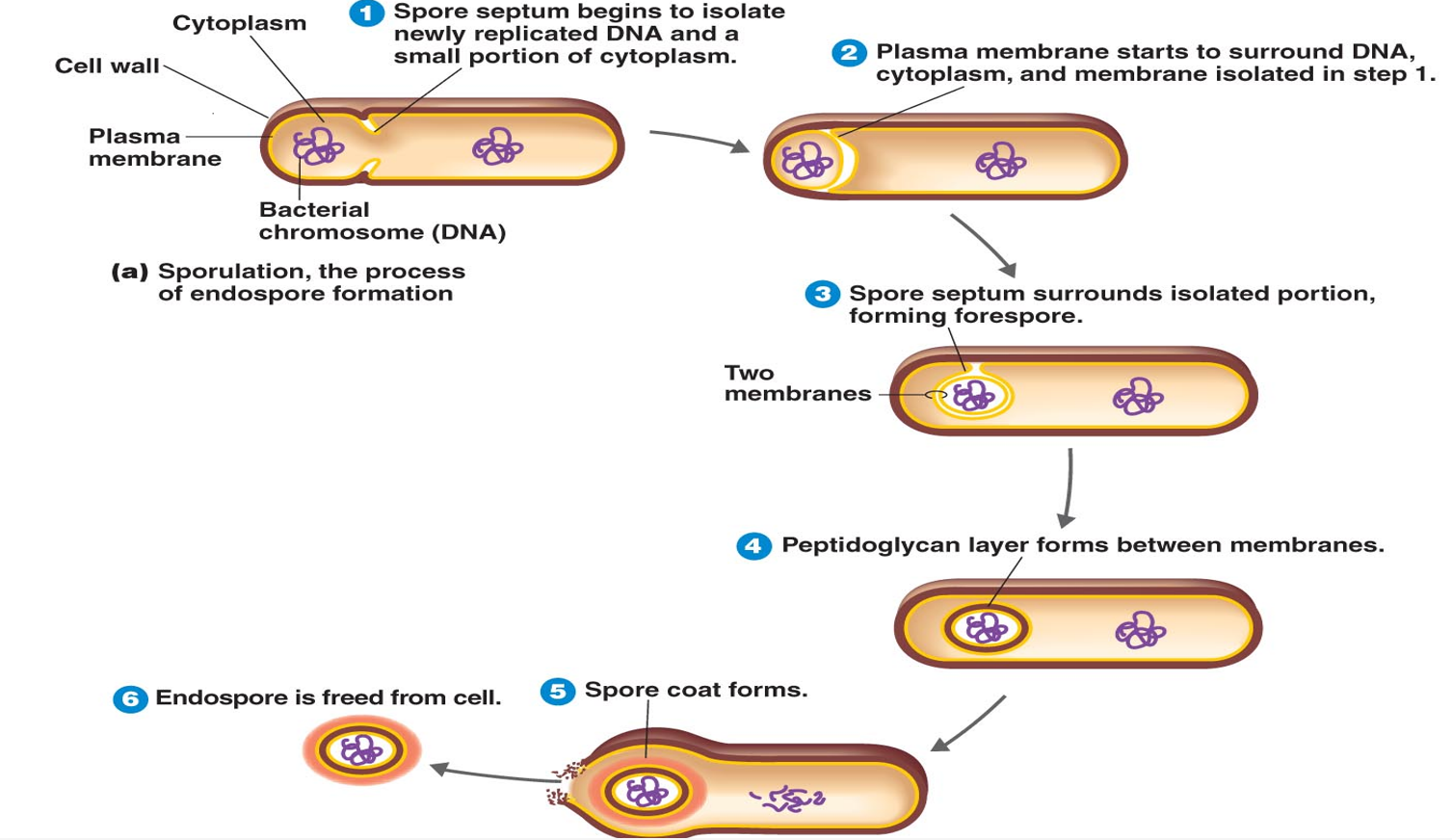
sporulation formation steps:
Copy DNA
Separate DNA into spore area (forespore)
Wrap forespore with layers (cortex + coat)
Harden and mature
Spore released (mother cell breaks open)