Cyber Analytics
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
Ransomware attacks have risen due to...
•….because the barriers to entry are decreasing
•….the operations are scalable
•….improved skillsets
Number of ransomware actors is increasing due, How?
because the barriers to entry are decreasing (through AI)
- the operations are scalable (adapt and grow)
-improved skillsets
Ransomware and AI
- Raised skill level
-Better use of English language in communications
-The skilled actors are now even better. The unskilled actors now have basic skills quickly
What attack is preferred by nation-state actors?
Ransomware
What state-sponsored activity is on the rise by Iran
malware and ransomware operations
AI as a threat
- Use of AI and ML to automate and enhance their capabilities, making attacks more sophisticated and adaptive
AI as a Tool
Using the same tools that equip attackers with advanced capabilities can also serve useful in cyber defenses.
What is IoT (Internet of Things)
a network of physical objects that can connect to the internet and exchange data
Motivations of a Cyber Criminal
• Financial Gain
• Recognition and Achievement
• Insider Threats
• Political Motivation (Hacktivists)
• State Actors
• Corporate Espionage
Nation State Actors
Might look to steal military intelligence, intellectual property, and other types of sensitive information held by government organizations, contractors, and other businesses
Foreign Intelligence Surveillance Act of 1978 (FISA)
regulates certain types of foreign intelligence collection including certain collection that occurs with compelled assistance from U.S. telecommunications companies.
What happened with FISA after 9/11
Bush II authorized a secret terrorist surveillance program (TSP) outside of FISA for collecting telephone and internet data to be used in the war on terror.
NIST Core Framework
Recover
•Identify
•Protect
•Detect
•Respond
AI vs ML
Machine learning is a subset of Artificial Intelligence
Why is ML not AI?
ML helps to create the basis of core blocks of AI but it there is much more parts to the make up of AI. AI can achieve near-human-level intelligence
Why are Virtual Machines (VMs) important?
a powerful tool for all cybersecurity professionals. The terminal allows a user
to manipulate files, create users, and run terminal programs to perform certain tasks.
Worm
Trojan
Spyware
Adware
Ransomware
Malware
There is a No "one size fits all" and security in US? (True/False)
True
Examples of sector specific privacy laws
COPPA: Children's Online Privacy Protection Act
FERPA: Family Educational Rights & Privacy Act
HIPPA: Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act
New AI Executive Order
International AI unity: 28 countries uniting for responsible AI development.
Ethical innovation drive: ensure AI innovation is matched with strong ethical practices
What is Linux?
An open-source operating system
Where is Linux Prevalent?
-500 super computers run on some variant of Linux
-84% of enterprise business runs on Linux
-Linux is used by 71.9% of all the websites whose operating system is known
-96.3% of the world's top 1 million websites were powered by Linux
-Android phones and Kindles run Linux
Why is Linux considered to be a good operating system?
extremely stable (rarely crashes)
-very fast
-less expensive
a command interpreter that allows you to type commands from the keyboard to interact with the operating system kernel
Linux shell
Displays file contents
cat
Full path from the root directory
Absolute Path
Path relative to the current directory
Relative Path
../ is an example of what kind of path
Relative Path
Steganography
writing hidden message in a way that prevents those who don't know that it is there from seeing it
What kind of security is Steganography
security by obscurity
Hashing
Algorithm that takes a block of data and returns a fixed size value.
Pros about Hashing
• Easy to compute
• Infeasible to generate
• Infeasible to modify
• Infeasible to find two different messages
Security by Obesity
a cyber approach where a system is made excessively large or complex to make it harder for attackers to find and exploit vulnerabilities.
Goals of Cryptography
○ Confidentiality: Ensuring data is accessible only to authorized users.
○ Integrity: Ensuring data has not been altered.
○ Authentication: Verifying the identity of users or systems.
○ Non-repudiation: Preventing the denial of an
Symmetric
The same key is used for both encryption and decryption
Asymmetric
Uses a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption
What type of encryption is AES
Symmetric
What type of encryption is RSA
Asymmetric
A substitution cipher where each letter in the plaintext is shifted by a certain number
Caesar Cipher
A = ? in Caesar Cipher
0
Vigenère Cipher Weakness
frequency analysis due to its repetitive key pattern, allowing attackers to determine the key length, break it into smaller Caesar ciphers
A technique used to break ciphers by analyzing the frequency of characters or symbols in a cyber text
Frequency analysis
Quantum Cryptography
encryption that uses quantum mechanics to secure data, promising theoretically unbreakable encryption.
Photons are a way to overcome speed factor of computersr
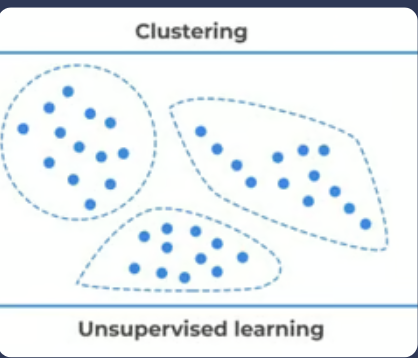
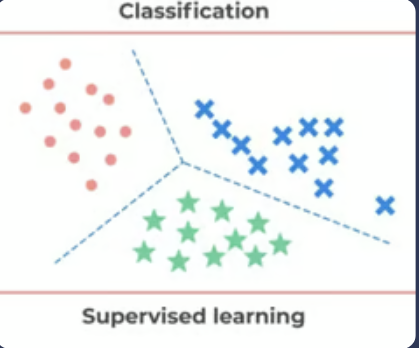
What is the difference between Supervised vs Unsupervised Learning?
Supervised learning uses labeled data, unsupervised learning identifies patterns without labels
A security system that detects and alerts administrators about potential security breaches in the network
Intrusion Detection System (IDS)
A security system that actively blocks or prevents malicious traffic in real time
Intrusion Prevention System (IPS)
Firewalls
A security device that monitors and controls incoming and out going network traffic
Access Control
a form of authorization by which you can control which users, roles, or hosts in the organization can access each segment of the network
Authentication
Verifying the identity of users or systems
network security
he broad practice of protecting computer networks and network-accessible endpoints from malice, misuse and denial
In Network Attackers
when attackers are operating within the trusted bounds of your infrastructure
Data-Centric Security
Emphasizes the security of the data itself, meaning that even if a database is breached, the data might not be of much value to an attacker
Honeypot
Decoy systems set up to attract and analyze attackers, gathering intelligence on their tactics and techniques
Wireshark
A tool for network traffic analysis, capturing and displaying data packets that are transmitted across a network
What kind of attacks include breaches, spoofing, pivoting, and denial of service (DoS)
Active
do not initiate communication with nodes in the network and do not interact with or modify network
passive
Bot traffic
Malicious network traffic generated by botnets (infected devices controlled by attackers) that can be used in DDoS attacks.
R syntax
The set of rules that define the structure of statements in the R programming language
A table-like data structure in R that allows storing different types of data in each column.
dataframes
A programming concept where a block of code is executed repeatedly based on a condition (e.g., for, while
Loops