5. Lysosome, Endocytosis and Secretion
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
some modifications are made to carbohydrates in the ___
trans-golgi network
Trans-Golgi Network (TGN) sorting pathways
signal mediated diversion to lysosomes
constitutive secretory pathway
signal mediated diversion to secretory vesicles (for regulated secretion)
__ is the sorting compartment of the Golgi
controls __
Trans-Golgi NEtwork (TGN)
the flow of vesicles outward toward the plasma membrane
(TGN): if not added signal, proteins move on to __
this dumps lumen contents __
puts membrane proteins in __
secretory vesicles which fused with the plasma membrane (constitutive secretion/exocytosis)
outside the cell
the plasma membrane
(TGN): if a signal is present, the protein is ___
diverted
lysosomes
regulated secretion/exocytosis
lysosomes are ___ that take part in ___
cytoplasmic vesicles, degradation of macromolecules
describe internal environment of lysosomes
acidic due to a membrane pump that transports H+ in using ATP as an energy source
contents of the lysosome are ___ that work in acidic environment (__)
__ - degrades protein
__ - degrades DNA
__ - degrades RNA
__ - degrades polysaccharides
hydrolytic enzymes (degrade macromolecules)
Protease
DNase
RNase
Glycosidase
the hydrolytic enzymes of lysosomes are delivered from __
trans golgi network
the material degraded by lysosomes can be transported to the cytoplasm and used for ___
synthesis or dumped out of cell
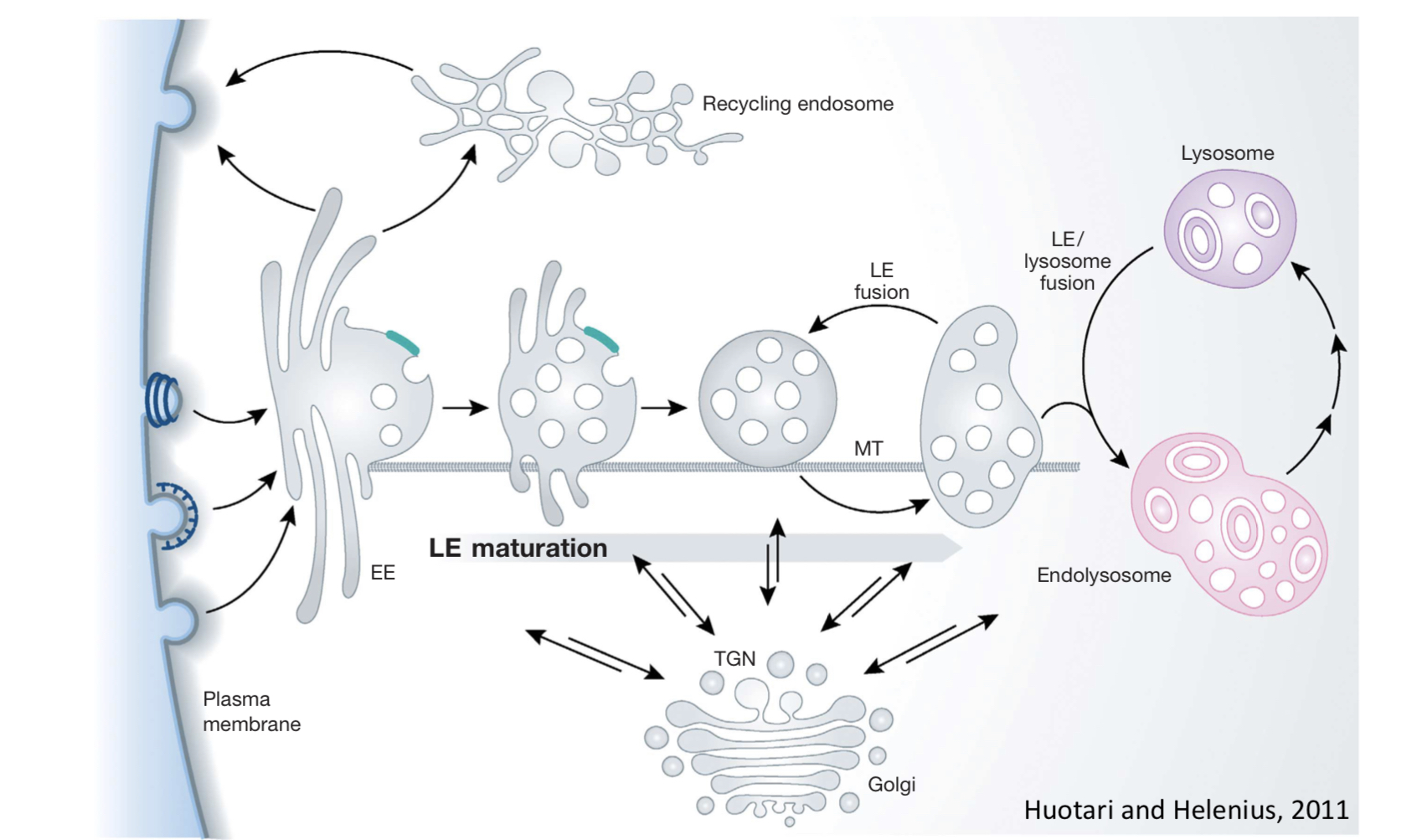
Lysosome Formation
vesicles containing lysosomal components from the ___ fuse with ___
these then fuse with existing lysosomes, creating __ and allowing the degradation of ___
these then mature again into ___, which will await another delivery from LEs
TGN; late endosomes (LEs)
endolysosomes; endocytosed material
classical lysosomes
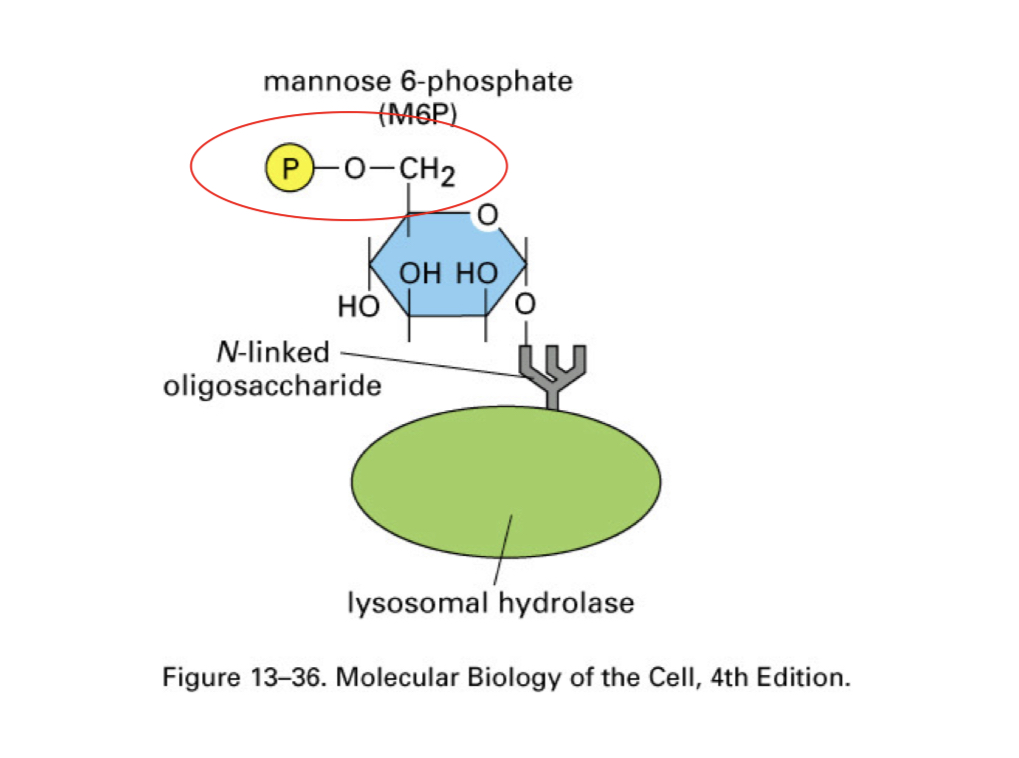
how are lysosomal proteins targeted to the LEs/Lysosomes?
a “mannose-6-phosphate” signal
PROCESS OF LYSOSOMAL PROTEINS BEING TARGETED TO LEs/LYSOSOMES
a __ in the lysosomal protein is recognized by an enzyme in the cis-golgi
a __ adds a modified phosphate mannose on the protein’s oligosaccharide tree
creates a ___ signal
this signal is recognized by a ___
__ bind to the cytoplasmic domain of this receptor, thus sorting the proteins into __
Rabs…SNARES…fusion!
in the lysosome, the pH ___
in the lysosome __ is removed so the targeting signal is no longer there
the receptor recycles back to the __
signal patch
phosphotransferase
mannose-6-phosphate signal
transmembrane Man-6-P receptor in the Trans Golgi Network
Clathrin coat and adapter proteins; vesicles destined for the late endosome/lysosome path
drops, causing receptor to release the protein
the phosphate
TGN!
what does a phosphotransferase do
its an enzyme that can transfer a phosphate group onto a target
the first coat protein discovered
Clathrin
what is clathrin made of
3 heavy chains and 3 light chains that form Clathrin triskellions
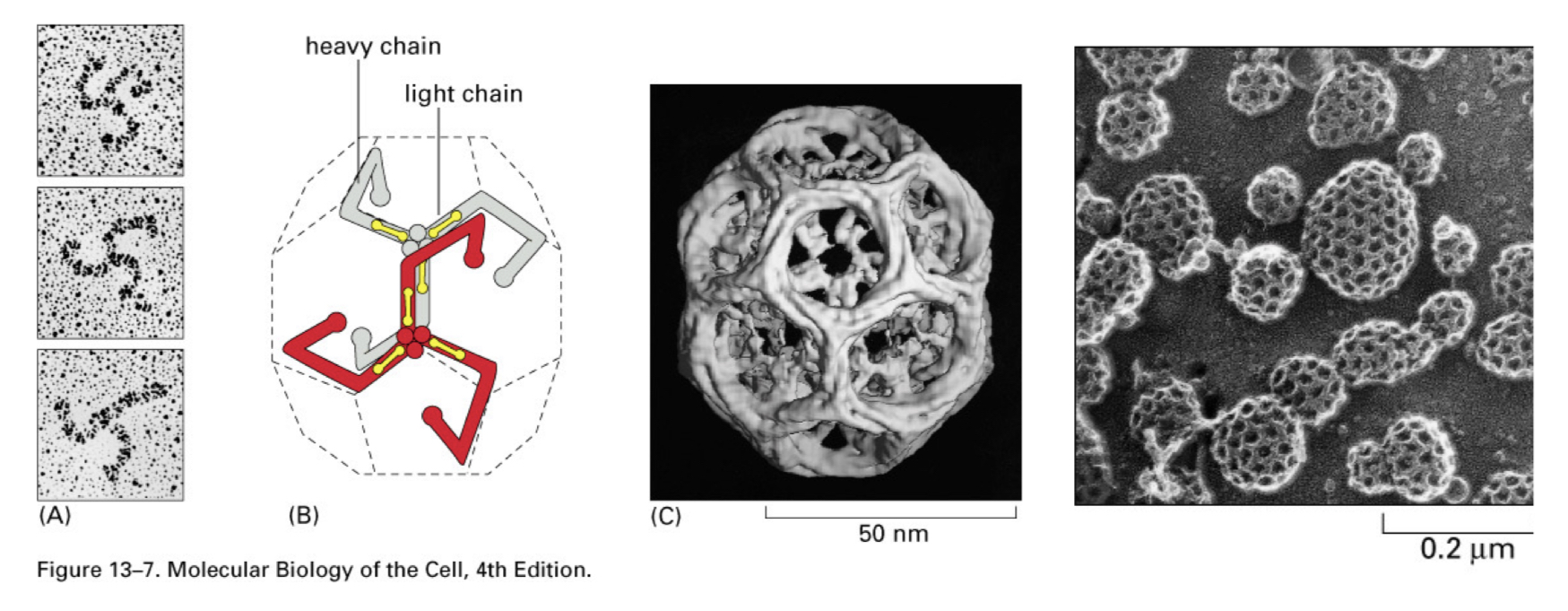
cool ability that clathrin has
can self assemble in test tube (in vitro) into polyhedral cage
clathrin forms a ___ around a vesicle
very cool looking cage
rare human genetic diseases lead to formation of inclusion bodies in cells… what does this mean?
persistent vesicles full of stuff that is normally broken down by lysosomes
what is I-cell disease
specific, severe case in which none of the lysosomal enzymes are sorted correctly to lysosomes
the multiple signal and receptor recognition events in lysosomal targeting
hydrophobic signal sequence/SRP & receptor targets protein to ER
glycosylation site (Asn-X-Ser/Thr)
ER export sequences for cargo receptors that sort lysosome proteins into COPII vesicles bound for CGN
signal patch; phosphotransferase leads to Man-6-P addition in cis-golgi
Man-6-P; Man-6-P receptors in the TGN or plasma membrane sort proteins into clathrin-coated vesicles bound for late endosomes/lysosomes
what is endocytosis
movement of materials into the cell by plasma membrane-derived vesicles
two types of endocytosis
pinocytosis (aka cell drinking)
phagocytosis
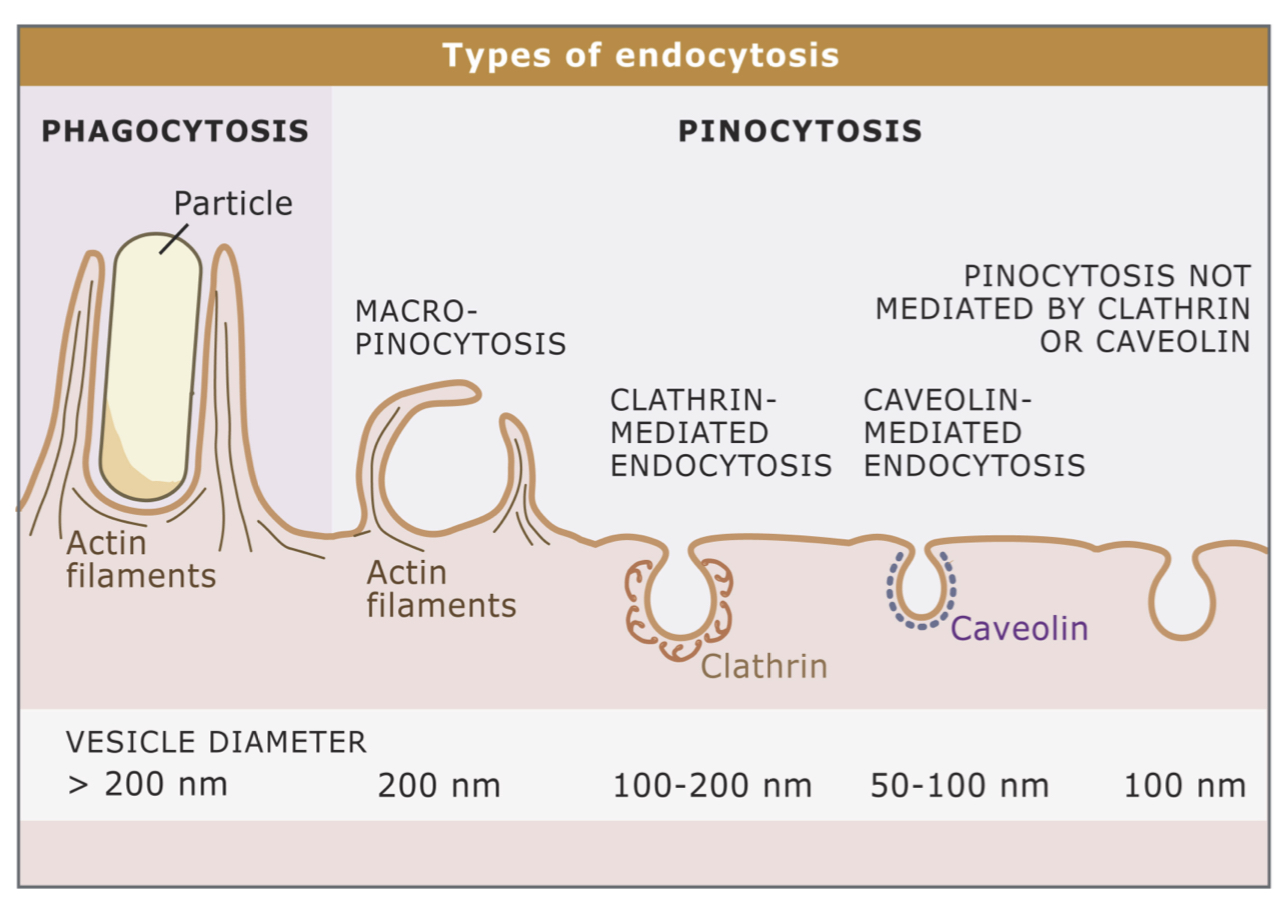
what is pinocytosis
uptake of fluids and small, soluble materials from outside the cell
what is phagocytosis
engulfment of larger solid material from outside by direct attachment
material from both pinocytosis and phagocytosis can end up in ___
lysosomes
PHAGOCYTOSIS
cell surface “zippers” around the particle to engulf it
contact of particle, bacteria, etc with __ stimulates the uptake
recognition is through ___
an outward protrusion of ___ rather than the inward budding of pinocytosis
vesicle is then closed and internalized to form a __
fusion with lysosome introduces enzymes into ___ to digest contents
used as a ___ mechanism for protists
used as a ___ mechanism for mammals
surface receptors
surface molecules on the particles, immune antibodies, or complement proteins coating it
membrane driven actin filaments
phagosome
phagolysosome
defense
defense or homeostasis
examples of how phagocytosis is used in mammals
immune cells (macrophages and neutrophils) eat and destroy bacterial invaders
used to get rid of foreign material in a wound
used to safely remove damaged, defective, or dying cells
normally cells know not to phagocytose each other
PINOCYTOSIS
“cell drinking”, but __
some is ___ and may be non-specific
brings in ___
balances the ___
some is ___ and may be specific
i.e ___
brings in soluble materials too
constitutive (constant)
nutrients and soluble macromolecules
outward flow of membrane by secretion
regulated
receptor-mediated endocytosis
two main modes of entry for pinocytosis
caveolae (small)
clathrin-coated pits (larger)
what is caveolae
small, lipid raft-based ivaginations of the plasma membrane stably coated by a protein called caveolin
with caveolae, there is no ___ so ___ is not well understood
obvious dynamic coat recruitment; budding
clathrin coated pits and receptor mediated endocytosis
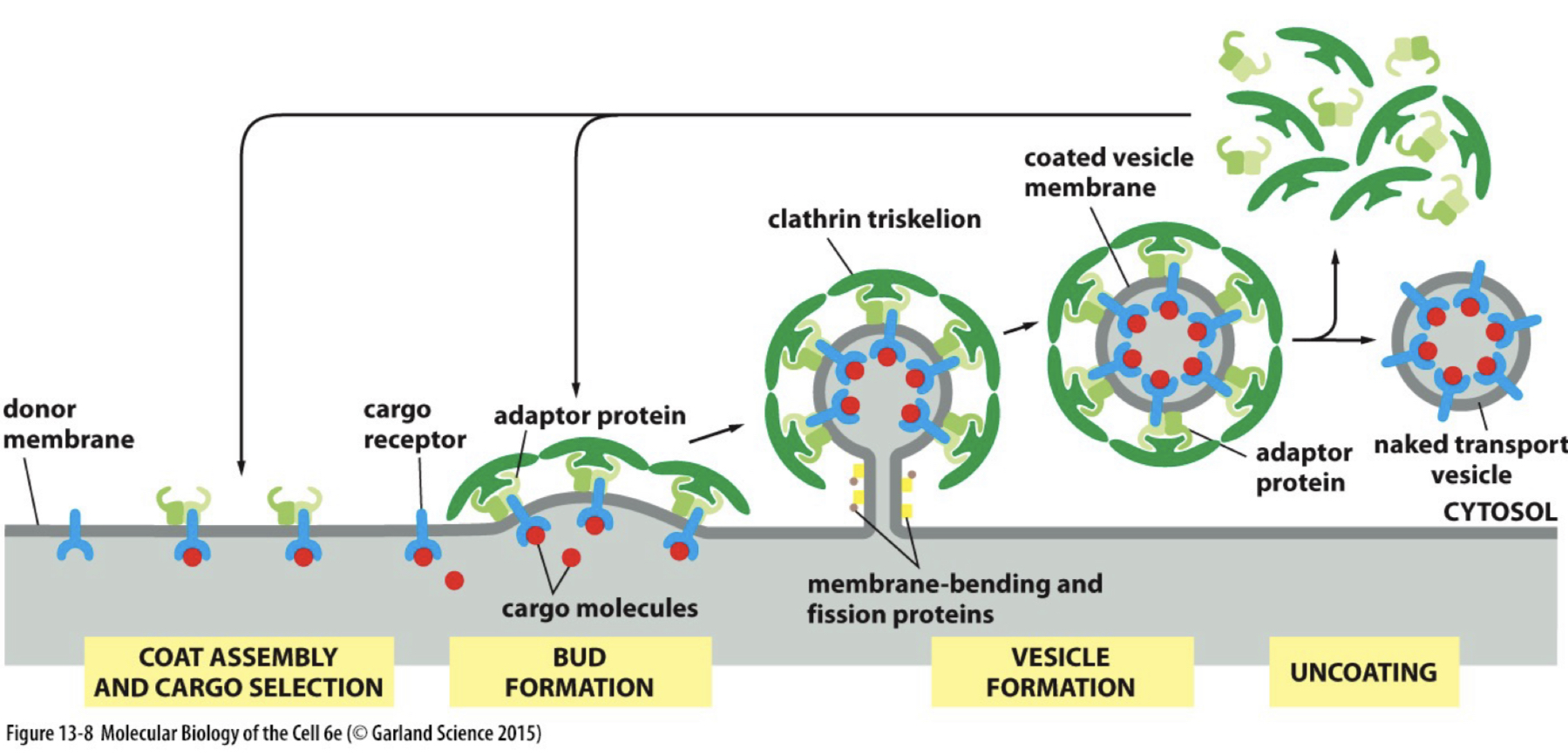
RECEPTOR MEDIATED ENDOCYTOSIS
clathrin coated-pit formation and uptake of ligands triggered by ___:
receptors associate with ___
some can associate without ligand, some only when bound
__ nucleate clathrin assembly
more receptors can continue to move in and __
clathrin assembly caused the pit to ___
non-specific membrane proteins that dont associate with coat proteins arent kept in pits and thus ___
the binding of the ligands to transmembrane receptors on the cell surface
clathrin coat adaptor proteins (AP2)
receptors, adaptor proteins, PIP2
interact with coat proteins in newly forming pits
invaginate and ultimately the vesicle is released inside the cell
arent taken up very often
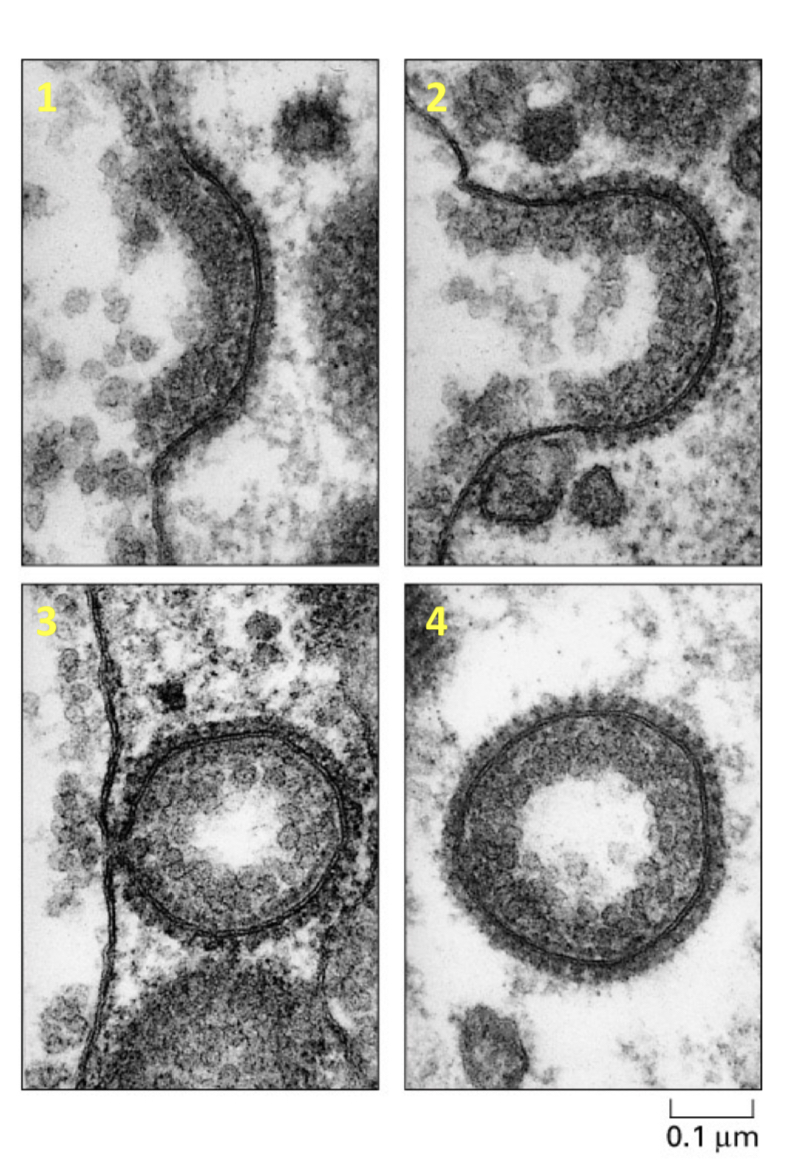
what is the early endosome
very important sorting compartment
some receptors are recycled during ___
receptor mediated endocytosis

LDL processing by cells
(Receptor Mediated Endocytosis)
___ move cholesterol from liver to other body cells
large protein + __
___ in coated pits bind LDL
internalized by receptor-mediated endocytosis
the early endosome is a sorting compartment
receptor is ___
the LDL continues on to ___
Low Density Lipoproteins (LDL)
micelle of lipid and cholesterol
LDL-Receptor
sorted and sent back to surface
lysosomes for processing
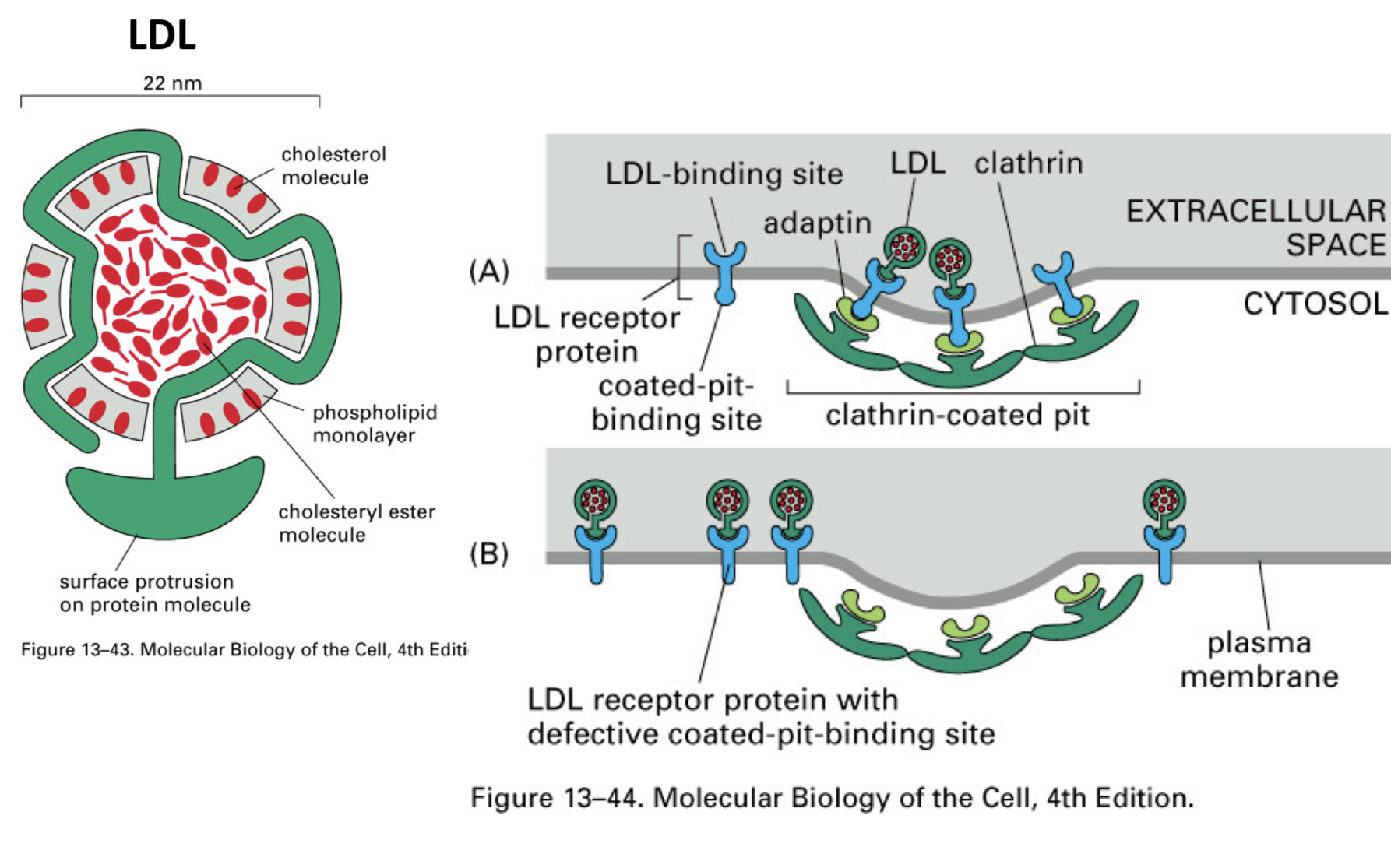
individuals with genetic disorders of cholesterol metabolism have defects in the ___
delivery machinery
if you have a defective receptor or lack on, you dont take up cholesterol efficiently leading to a high blood and low cellular concentration (hypercholesterolemia)
what is Hypercholesterolemia
high blood and low cellular concentration
some receptors can be targeted for degradation: ___ can modulate signal transduction pathway (ie RTKs)
receptor downregulaton
membrane proteins destined for degradation are ___ and targeted to ___
marked by ubiquitination; topologically distinct, intraluminal vesicles in late endosomes
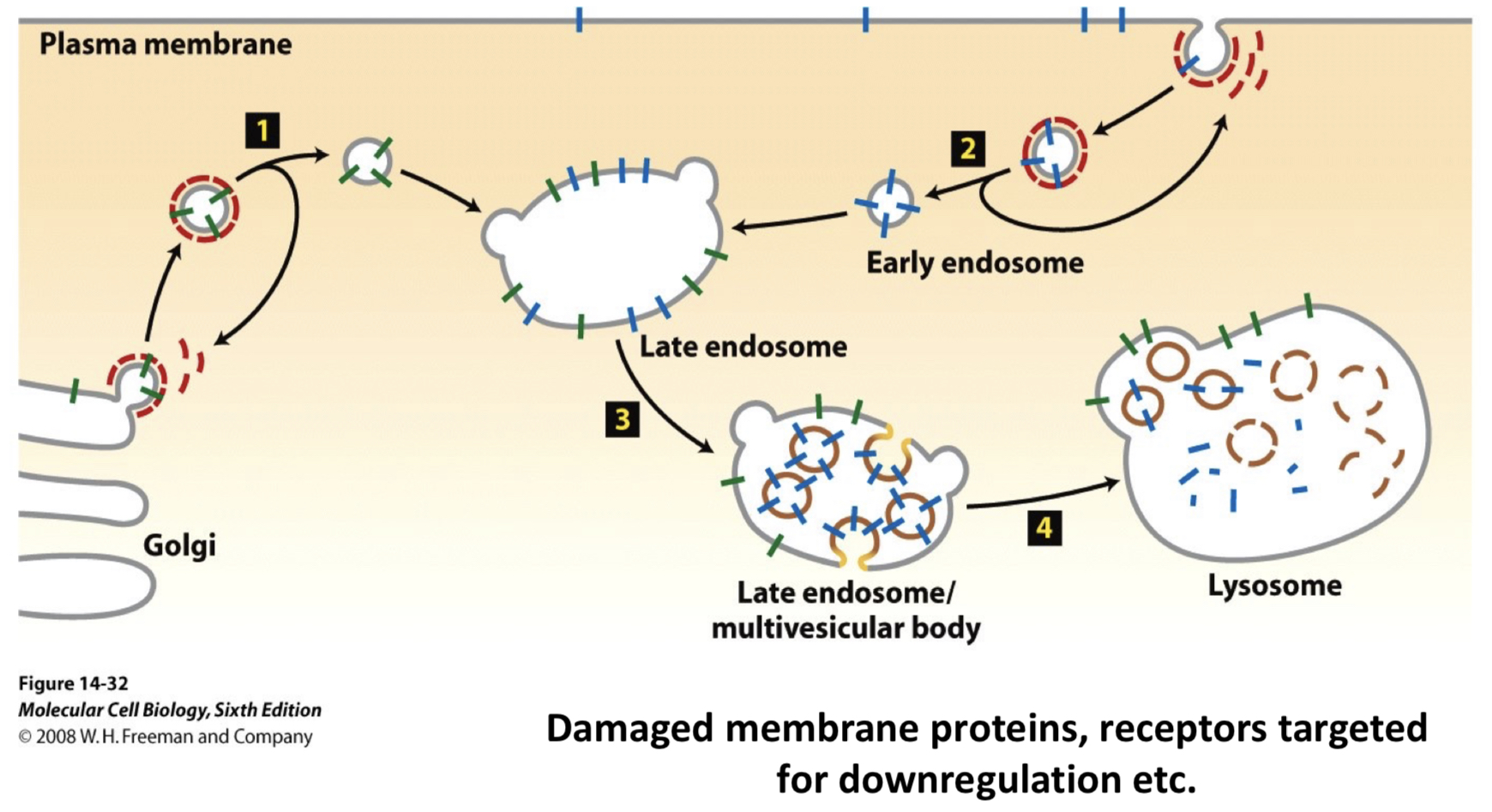
___ allow for targeted membrane proteins to be degraded while protecting other membrane proteins
basically allows stuff deep inside to be destroyed but not the stuff around it
multivesicular bodies
how are multivesicular endosomes formed
ubiquitination and ESCRT
ubiquitin group on membrane proteins allows ESCRT complex to gather up and shepherd membrane proteins into forming intraluminal vesicles
MVB
multivesicular bodies
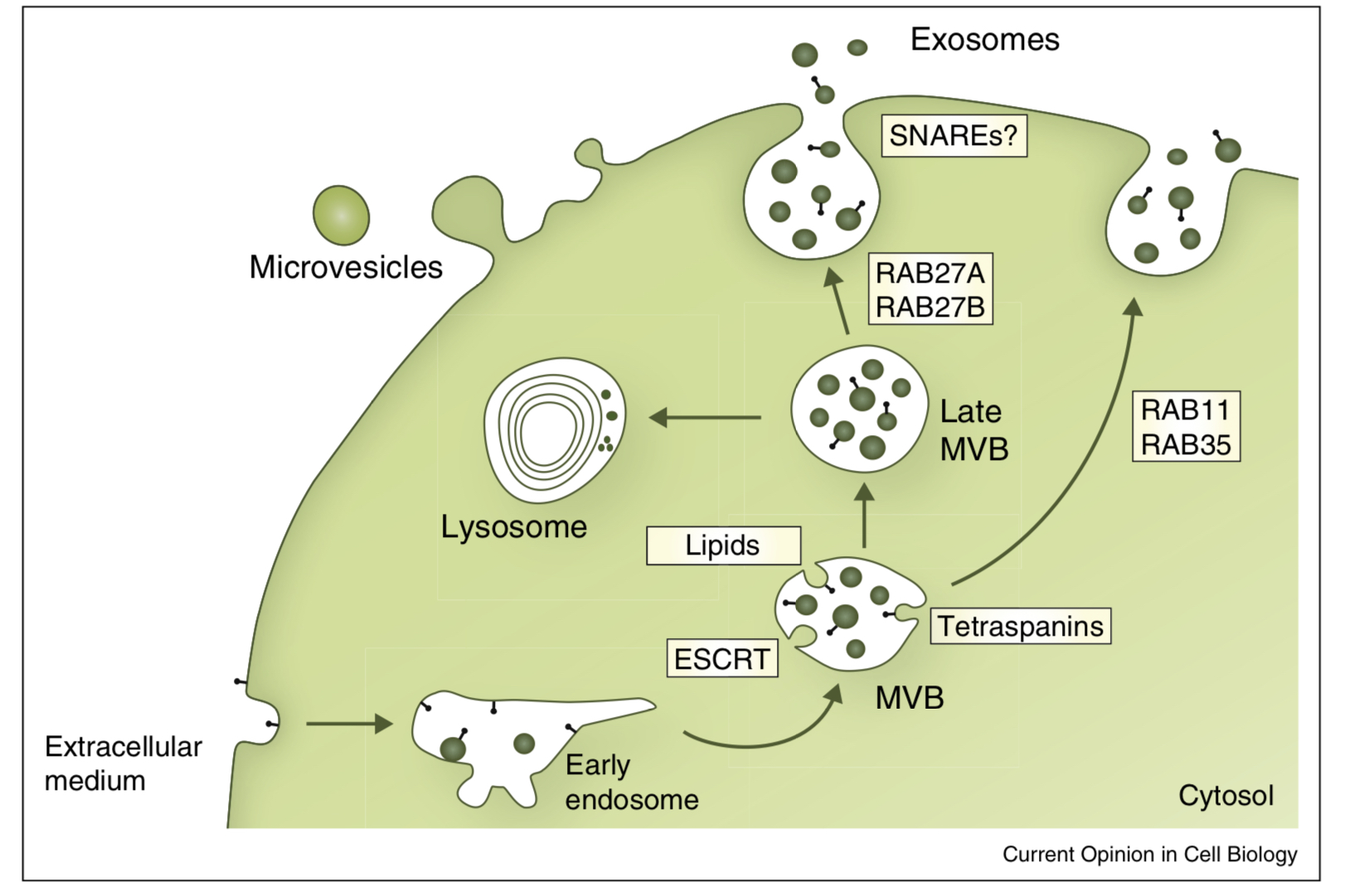
what are exosomes
extracellular vesicles that can be released from cells by fusion of MVBs with the plasma membrane
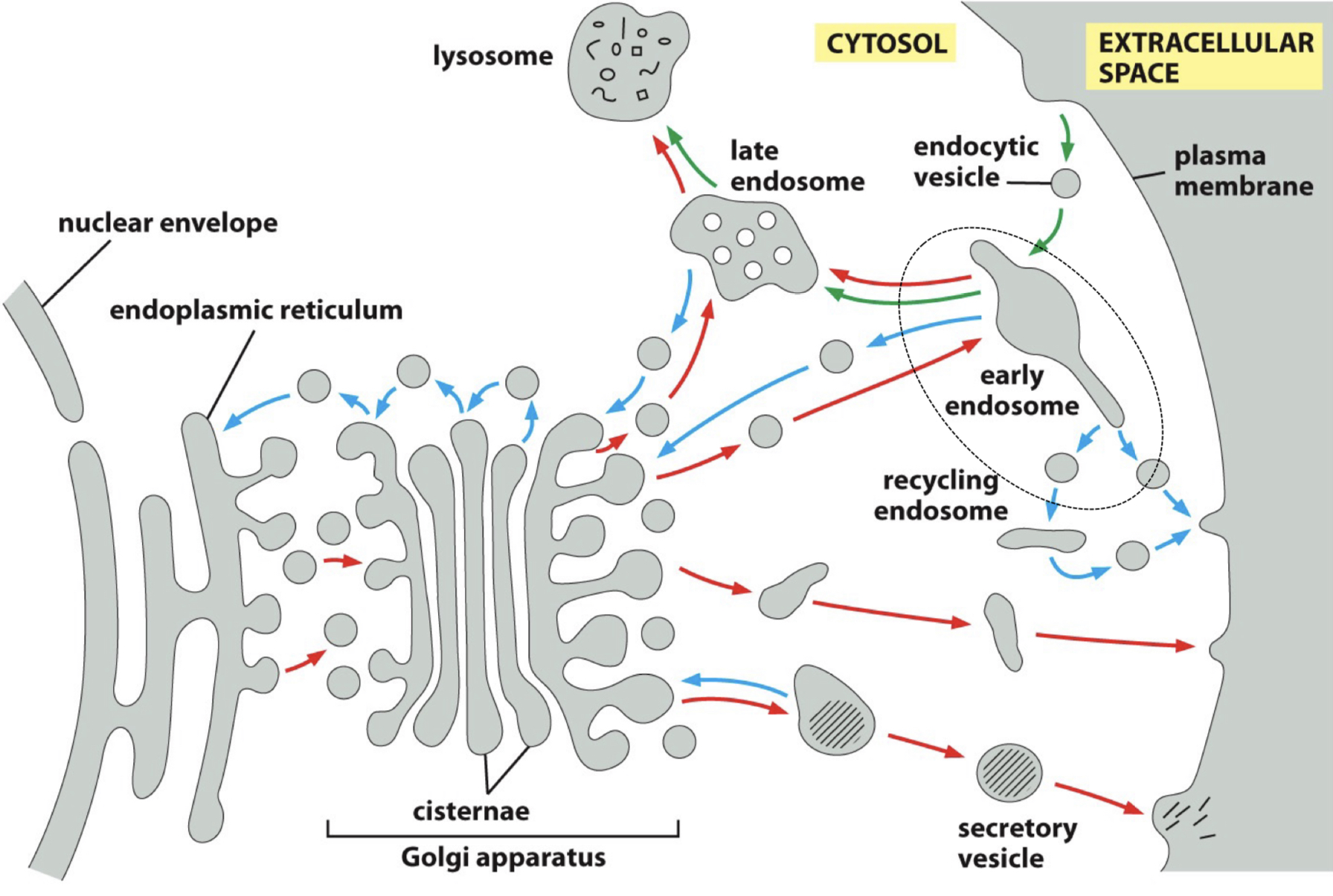
PATHWAYS TO DEGRADATION IN LYSOSOMES
Endocytosis → early endosome → late endosome → lysosome
Phagocytosis → phagosome → lysosome
Autophagy → autophagosome → lysosome
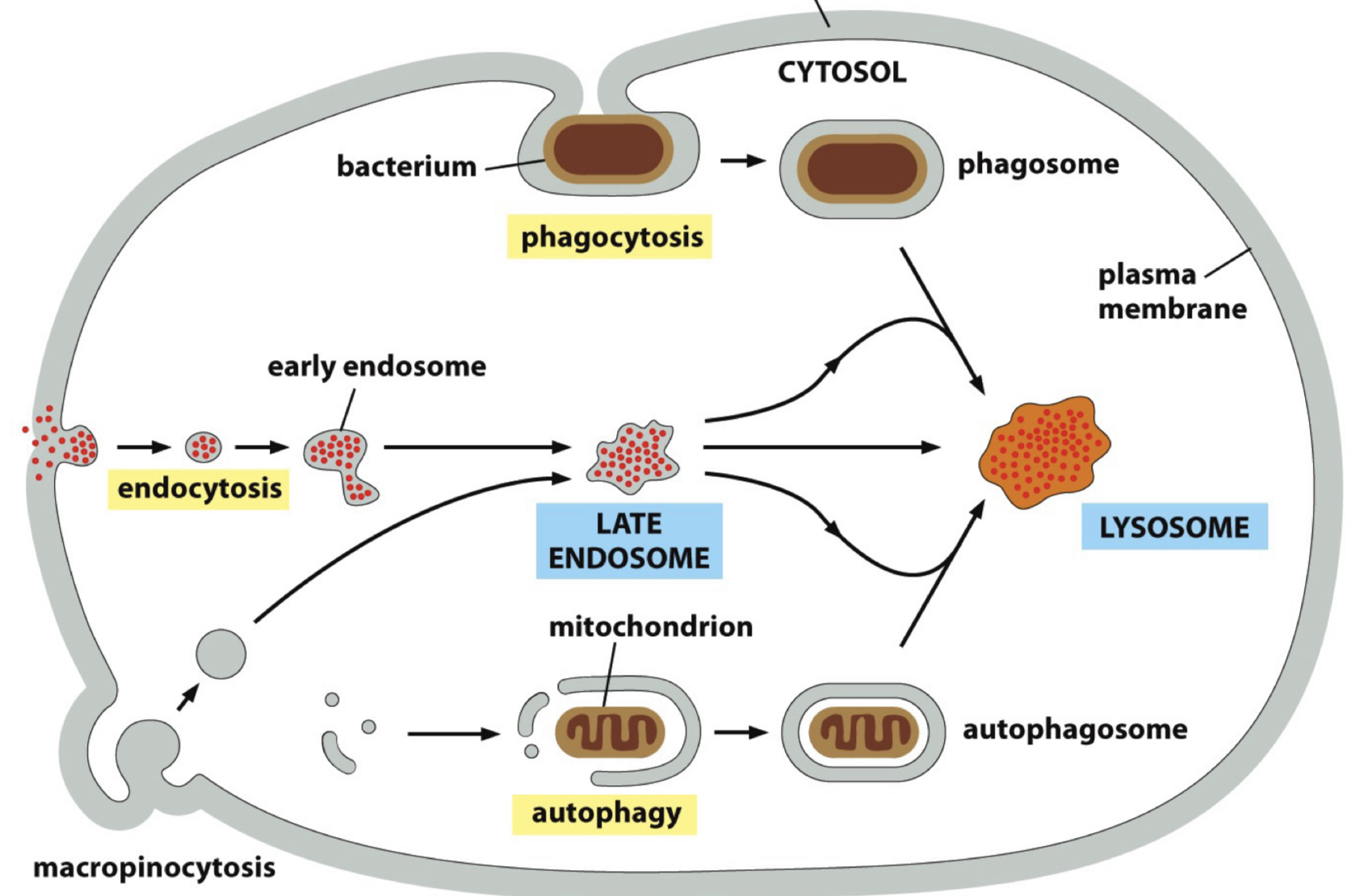
Autophagy (self eating) delivers ___
cytosolic proteins or entire organelles to lysosomes by surrounding it in double membrane
what happens during exocytosis/secretion
vesicles bud from the TGN and move to the plasma membrane
different types of exocytosis/secretion
Constitutive secretion
Regulated secretion
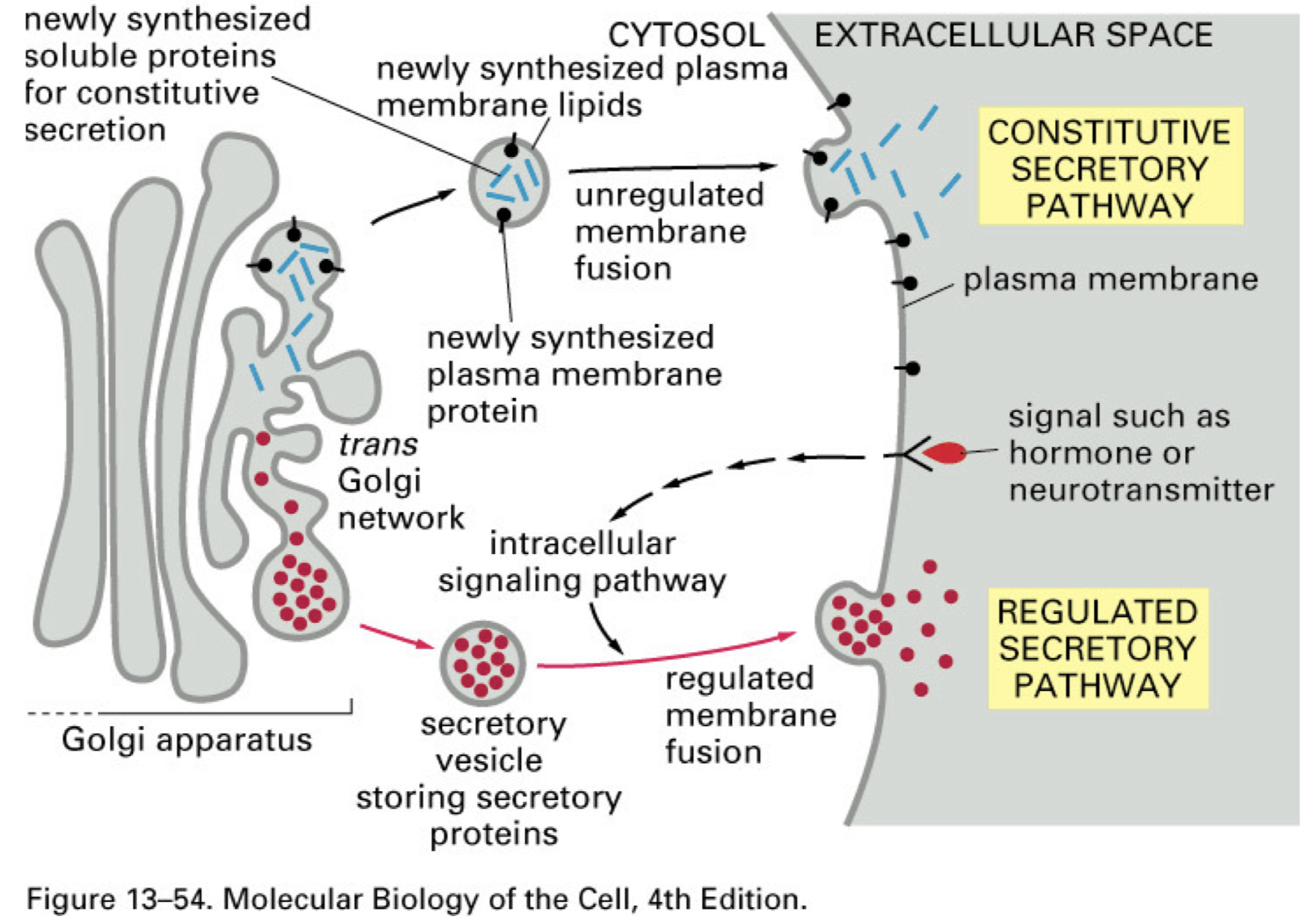
Constitutive secretion: secretory vesicles move to the plasma membrane and fuse, ___
relatively __ rate
dumping their contents outside the cell or contributing membrane proteins to the plasma membrane
constant
Regulated secretion: the vesicles are held near the membrane until ___
the secretory vesicles accumulate in the ___
when triggered by an external signal, they ___
in some cases, this is done to ___
ex: nerve impulse leads to secretion of neurotransmitter
in some cases, this is done to ___
ex: insulin causes more glucose transporter to be put on the surface
a stimulus is received and then they fuse. the signals that sort proteins for regulated secretion are not well understood but they often lead to aggregates of vesicle contents in a low pH environment
cytoplasm
fuse with the plasma membrane
release a soluble protein in the vesicle into the outside environment
put a membrane protein onto the surface of the cell
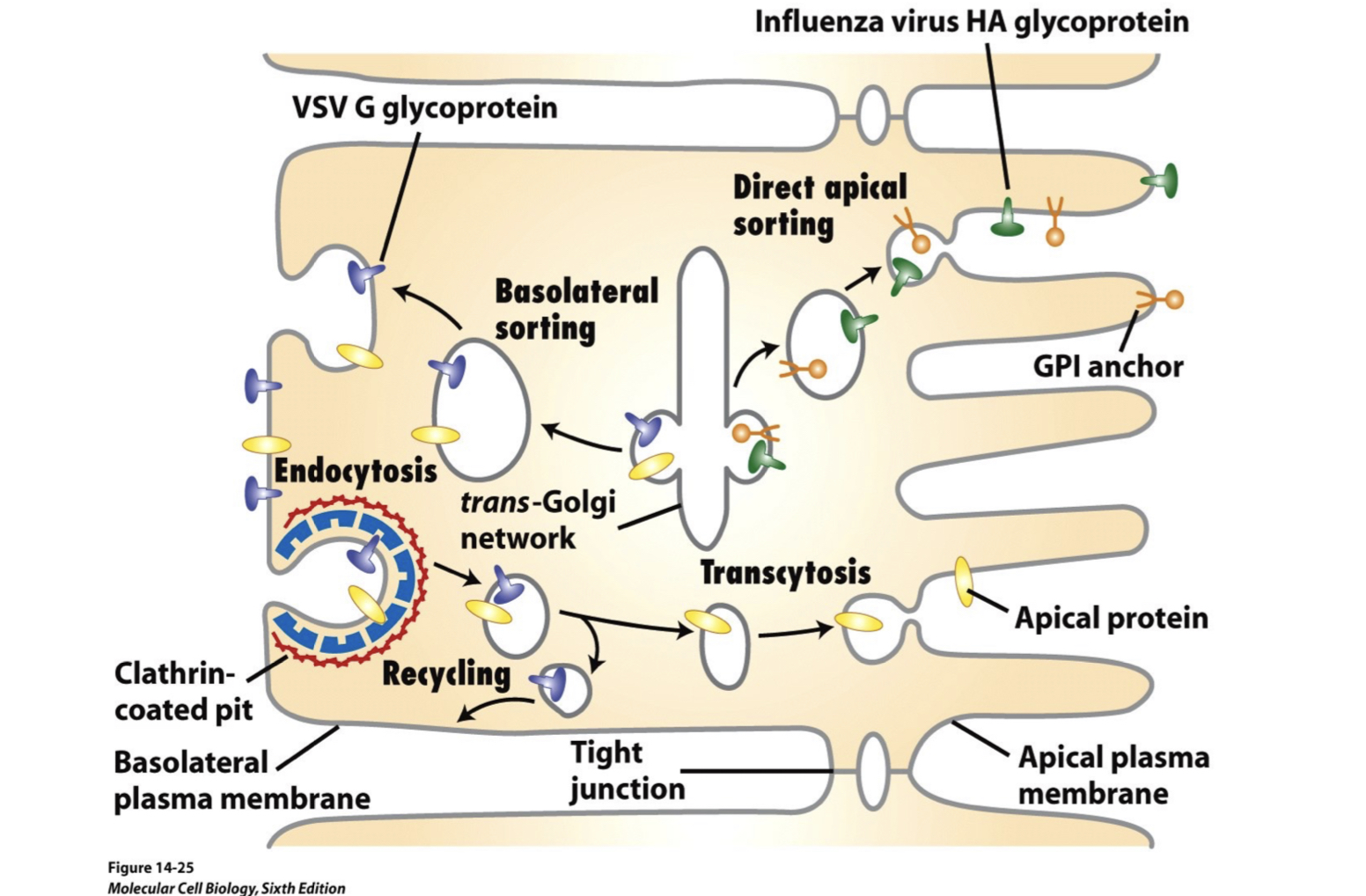
vesicles sort to different plasma membrane domains using ___
__ have been shown to act as apical signals
__ can act as apical or basal signals, based on cell type
some __ act as direct basal sorting signals
distinct __ and __ are involved in vesicle targeting between domains
a variety of mechanisms in specialized cells
N- and O- linked sugars
Glycosphingolipids and GPI-linked proteins or lipid rafts
amino acid sequences
Rabs and SNARES
OVERVIEW 1: Signals in protein trafficking in the endomembrane system
proteins are made on cytoplasmic ribosomes
if a hydrophobic start transfer sequence is made, the protein enters the ER/Golgi
Asn-X-Ser signals N-linked glycosylation
most things move to the Golgi
if a protein has an ER retention signal, it recycles back to the ER
if it does not, it goes on in the Golgi
material “moves” through the golgi apparatus by cisternal maturation
retention in the golgi is not well understood
if a protein has a lysosome signal patch it gets a Man-6-P and is sorted in the TGN to lysosomes
otherwise, it continues on to exocytic, secretory vesicles
if it is a membrane protein, it ends up in the plasma membrane (LDL receptor)
if is in vesicle lumen, it is secreted
sorting signals for regulated secretion still poorly understood
apical and basal sorting signals help organize epithelial cells
OVERVIEW 2: Secretion, Endocytosis, and Membrane dynamics
Outward flow by secretion
Membrane, membrane proteins, and soluble proteins in vesicles move from ER to Golgi to secretory vesicles to plasma membrane; Membrane and membrane proteins contribute to plasma membrane while soluble proteins are released from the cell
Some material is diverted to lysosomes by Man-6-P signal
Other material is delivered to secretory vesicles
Some vesicles travel to plasma membrane and fuse (constitutive)
Others move to plasma membrane but await a signal to fuse (regulated)
Inward flow of material through endocytosis and phagocytosis
Endocytic vesicles package soluble materials and remove membrane and membrane proteins from the plasma membrane.
Some material fuses with lysosomes for degradation
Some material is returned to the plasma membrane
Inward flowing material can also be diverted to other compartments (transcytosis)
Recycling and sorting of proteins and membrane can occur to return them to
their correct functional locations.This is a very dynamic process. The two systems must balance otherwise
you will increase the amount of plasma membrane and lose internal
membrane or vice versa.