Arteries (5/8/2024 & 5/15/2024)
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
What makes up the circulatory system?
lymphatic system and cardiovascular system
What does the lymphatic system do
transports lymph fluid which contains WBCs that eliminate toxins and waste throughout the body
What does the cardiovascular system do?
provides tissues with oxygen and nutrients (both pulmonary and systemic circulation)
blood, vessels, and heart
What are the 3 main components of the cardiovascular system?
blood, vessels, and the heart
What is the circulatory system?
a vast network of organs and vessels that are responsible for the flow of blood, nutrients, oxygen, gases, and hormones to and from cells
In the average human, ___ gallons of blood travels through the body daily
2,000
What are the 6 main functions of the cardiovascular system?
HOMEOSTASIS
transports O2 and CO2
transports nutrients and waste
protects against disease
transports hormones
regulates temperature
Explain how the cardiovascular system transports O2 and CO2 (as one of the main functions of the cardiovascular system)
every cell requires a constant supply of O2
inhale O2, exhale CO2
3 essential processes
ventilation
diffusion
perfusion
Explain how the cardiovascular system transports nutrients and waste (as one of the main functions of the cardiovascular system)
respiratory
O2 and CO2 exchange
digestive
intestinal capillaries
nutrients to body tissues
urinary
waste materials filtered by kidneys
Explain how the cardiovascular system protects against disease (as one of the main functions of the cardiovascular system)
transports disease fighting cells to all parts of the body
fights disease
blood transports WBCs, antibodies, and proteins that defend the body against infectious diseases
fights blood loss
clotting mechanisms are also presents the protect the body from blood loss after injuries
Explain how the cardiovascular system transports hormones (as one of the main functions of the cardiovascular system)
endocrine system
glands that regulate an organs activity
control many important functions in the body
growth, development, reproduction, sleep
hormones released into the blood stream
ex: pancreas
Explain how the cardiovascular system regulates body temp (as one of the main functions of the cardiovascular system)
too high
vessels close to the skin dilate
larger surface area = more heat loss
too low
vessels close to the skin constrict
smaller surface area = less heat loss
Explain blood
a body fluid in the circulatory system that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, AND transports metabolic waste product away from those cells
What are the 4 main components of blood?
RBCs
hemoglobin
44%
WBCs
1%
plasma
liquid portion
55%
platelets
1%
Explain the heart
a muscular organ the size of a fist
the “pump” that moves blood through arteries, capillaries, and veins
What do arteries do?
transport oxygenated blood away from the heart to the cells in the body
named by location or organ it supplies
What do veins do?
transport deoxygenated blood back to the heart
What are the 2 types of veins?
superficial and deep
What do capillaries do?
facilitate the movement of blood from arteries to veins
Explain the chain of exchange from the heart, through the body, back to the heart
heart → arteries → arterioles → capillaries → venules → veins → heart
Exchange of O2 and CO2 takes place at the level of the ___
capillaries
List and describe the 3 layers of arteries
tunica intima
endothelial cells
elastic tissue
tunica media (muscle layer)
elastic connective tissue
tunica adventitia/externa
What are the 2 layers of arterioles and venules?
intima and media
List and explain the 3 layers of veins
tunica intima
endothelial cells only
tunica media
elastic connective tissue
tunica adventitia/externa
Explain valves
only in the intima of veins
permit blood flow in 1 direction
BP is lower in veins, which can allow for pooling of veins
varicose veins
most common in lower extremities
Which vessel has the thinnest walls?
capillaries
Explain the walls of capillaries
transparent
a single intima layer
allows for easy diffusion of nutrients and gas
carry blood from arterioles to venules
Explain the function of pulmonary circulation
carry deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs to get oxygenated
returns blood to heart to be transported through body
What are the trunk vessels of pulmonary circulation?
pulmonary veins and pulmonary arteries
Explain pulmonary arteries
carry deoxygenated blood from heart
begins at right side of heart
divides at T5 into right and left
Explain pulmonary veins
carry oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart
ends at the left side of the heart
right and left veins
Explain the function of systemic circulation
supplies oxygenated blood from the heart to the rest of the body
returns deoxygenated blood back to the heart
What are the trunk vessels of systemic circulation?
aorta, inferior vena cava, superior vena cava
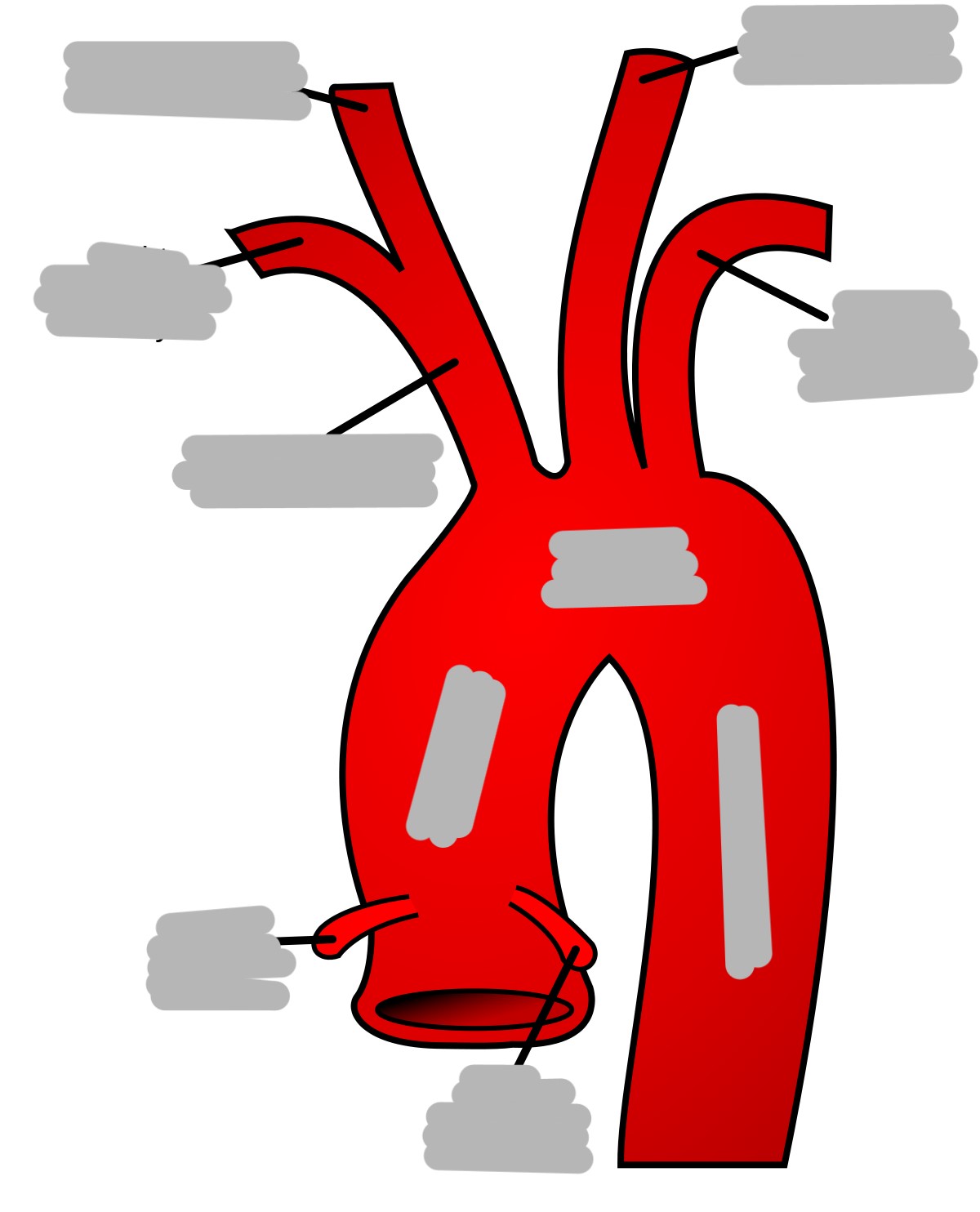
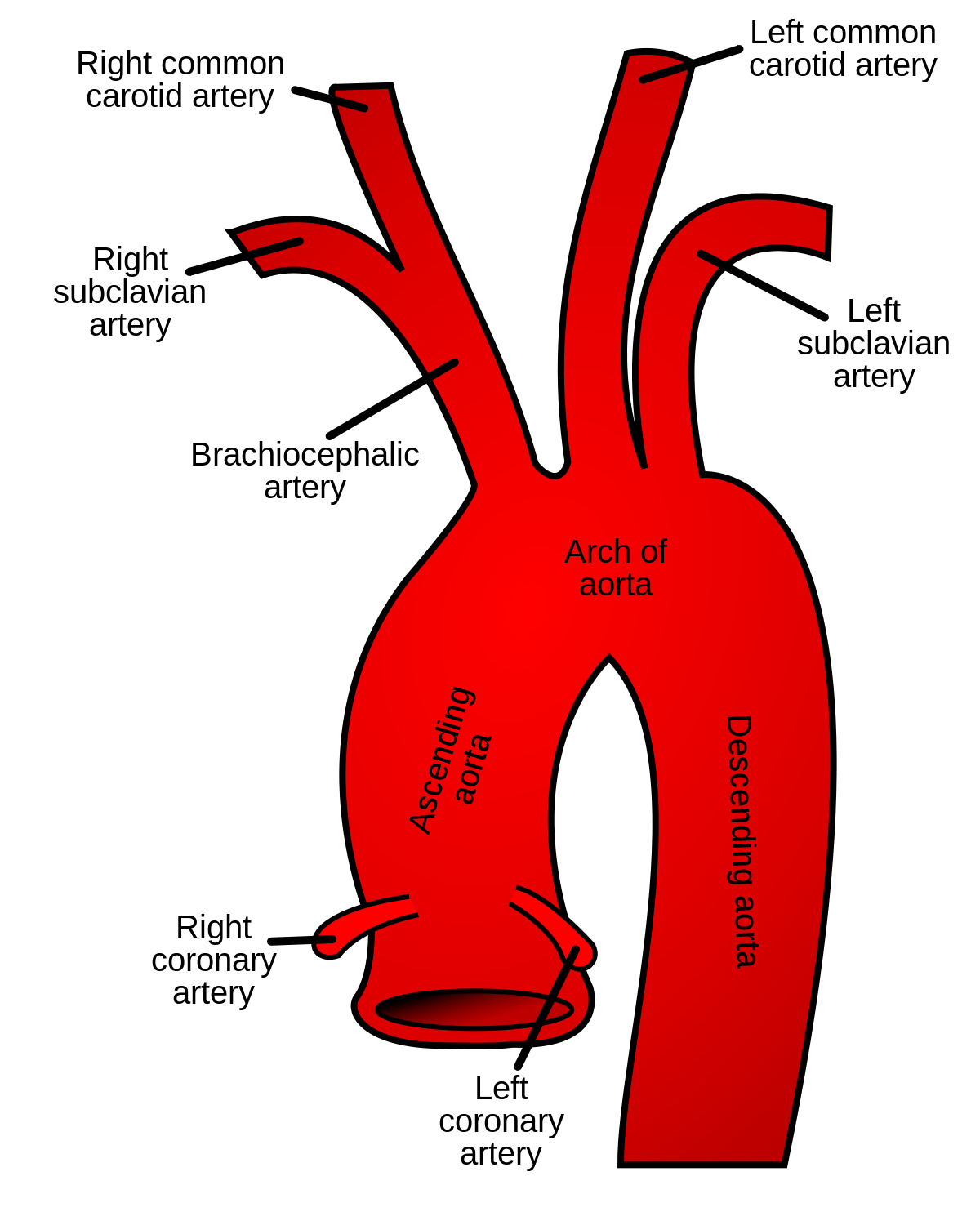
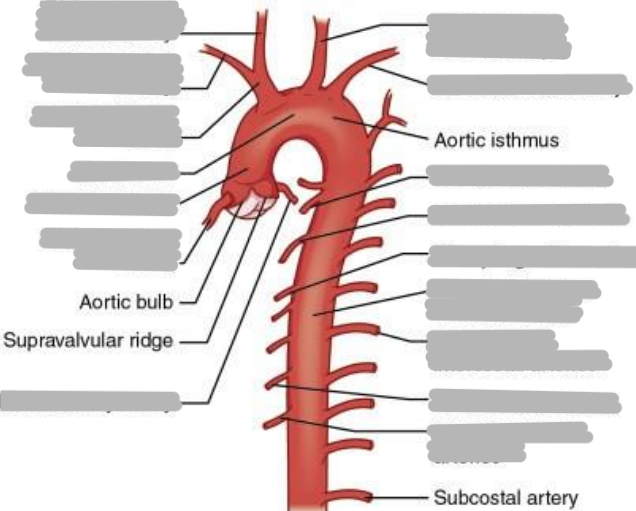
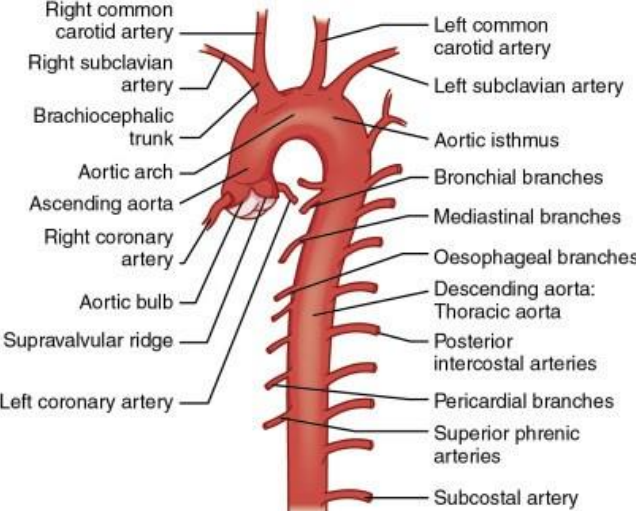
Explain the aorta (including origin and parts)
the largest artery
originates from left ventricle of the heart
contains artery branches that supply oxygenated blood to body tissues
parts:
ascending
arch
descending (thoracic and abdominal)
Explain the ascending aorta
segment that merges from the top of the left ventricle
left ventricle to T4
aortic root
2” in length
What are the first branches off of the aorta?
right and left coronary arteries (supply blood to the heart)
Explain myocardial infarct
(heart attack)
acute thrombus in the coronary arteries
What is CAD?
coronary artery disease (plaque buildup that decreases lumen size of coronary arteries)
can cause angina pectoris
Explain angioplasty
procedure done to widen a narrowed or blocked artery to increase blood flow (balloon insertion with stent placement)
Explain the location and branches of the aortic arch
begins at sternal angle
curves posteriorly and to the left
branches
right brachiocephalic artery
left common carotid artery
left subclavian artery
What is the first branch off of the aortic arch?
brachiocephalic artery
Explain the brachiocephalic artery
divides into the right common carotid artery (supplies right side of head) and right subclavian artery (supplies right shoulder and arm)
Explain the left common carotid artery
2nd branch off the aortic arch
supplies blood to the left side of the head
Explain the left subclavian artery
3rd branch off the aortic arch
supplies blood to the left arm and shoulder
Explain vertebral arteries
branches off of subclavian arteries
through transverse foramen of cervical vertebrae
merge to form one of the major cerebral arteries of the brain
Explain the thoracic portion of the descending aorta
descends along the left borders of the thoracic vertebrae
extends from T4-T12
ends at diaphragm
supplies mediastinal structures
branches:
esophageal
pericardial
intercostals
superior phrenic
bronchial
inferior phrenic
Explain the path of the blood through the circulatory system
right atrium → right ventricle → pulmonary arteries → pulmonary circulation → pulmonary veins → left atrium → left ventricle → aorta → systemic circulation
Explain aortic aneurysms
a weakening in a portion of the arteries wall
arteriosclerosis/atherosclerosis (plaque build up)
most common is abdominal level just below kidneys
Explain saccular aneurysms
involves only one side of the arterial wall
common in cerebral arteries
Explain fusiform aneurysm
involves both sides of arterial wall
common in distal abdominal aorta
Explain dissecting aneurysm
most deadly
inner layer (intima) tears and allows blood flow in the vessel
Explain old and new repair options for aneurysms
old
synthetic graft
very invasive
removal of expanded portion
graft is surgically sewn into place
new
endovascular graft
minimally invasive (go in through the femoral artery)
done in IR
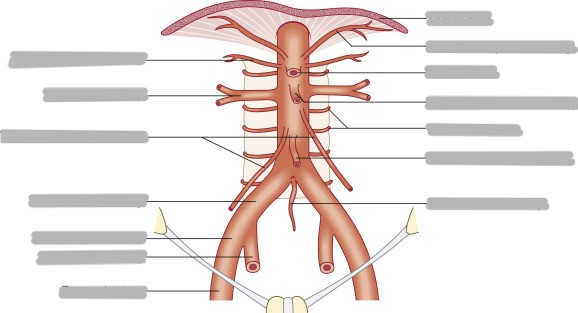
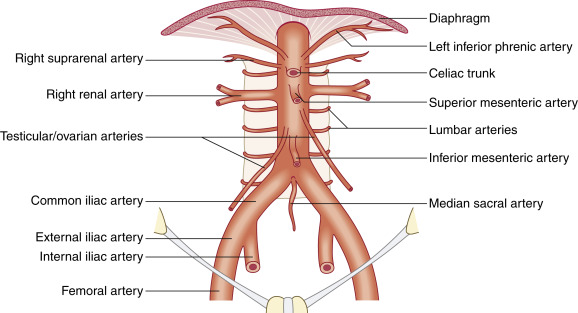
Where is the abdominal descending aorta located?
extends from T12-L4
begins at aortic hiatus and ends in a bifurcation
Are branches of the abdominal descending aorta paired or unpaired?
lateral branches are paired, anterior branches are unpaired
What are the paired branches of the abdominal aorta?
inferior phrenic
suprarenal (produce hormones to regulate metabolism, immune system, blood pressure, and stress response)
renal
gonadal
lumbar
List and explain the 3 unpaired branches of the abdominal aorta
celiac trunk/axis
supplies upper abdominal organs
liver, stomach, esophagus, spleen, ½ of duodenum and pancreas
superior mesenteric
largest single branch
at level of L1
supplies lower abdominal organs
small intestine and proximal ½ of colon
inferior mesenteric
at level of L3
supplies lower abdominal organs
distal ½ of colon, sigmoid, and rectum
What are the 3 main branches of the celiac trunk?
left gastric artery
stomach and distal esophagus
splenic artery
spleen
common hepatic artery
liver, duodenum, and pancreas
Explain the bifurcations of the terminal abdominal aorta
bifurcates into right and left common iliac artery at L4
middle sacral artery is in between the 2
bifurcates into internal and external iliac arteries at level of pelvic inlet
internal supplies genital organs
external supplies lower extremities
List the main arteries of the lower extremity in order from proximal to distal
internal iliac
external iliac
common femoral artery
popliteal
tibial
fibular
List the main arteries of the upper extremity in order from proximal to distal
subclavian
right - brachiocephalic
left - 3rd branch
axillary
once it passes the clavicle
brachial
continuation of axillary artery
artery that is compressed when taking BP
antebrachium
radial artery (pulse)
ulnar artery
dorsal and palmar arches
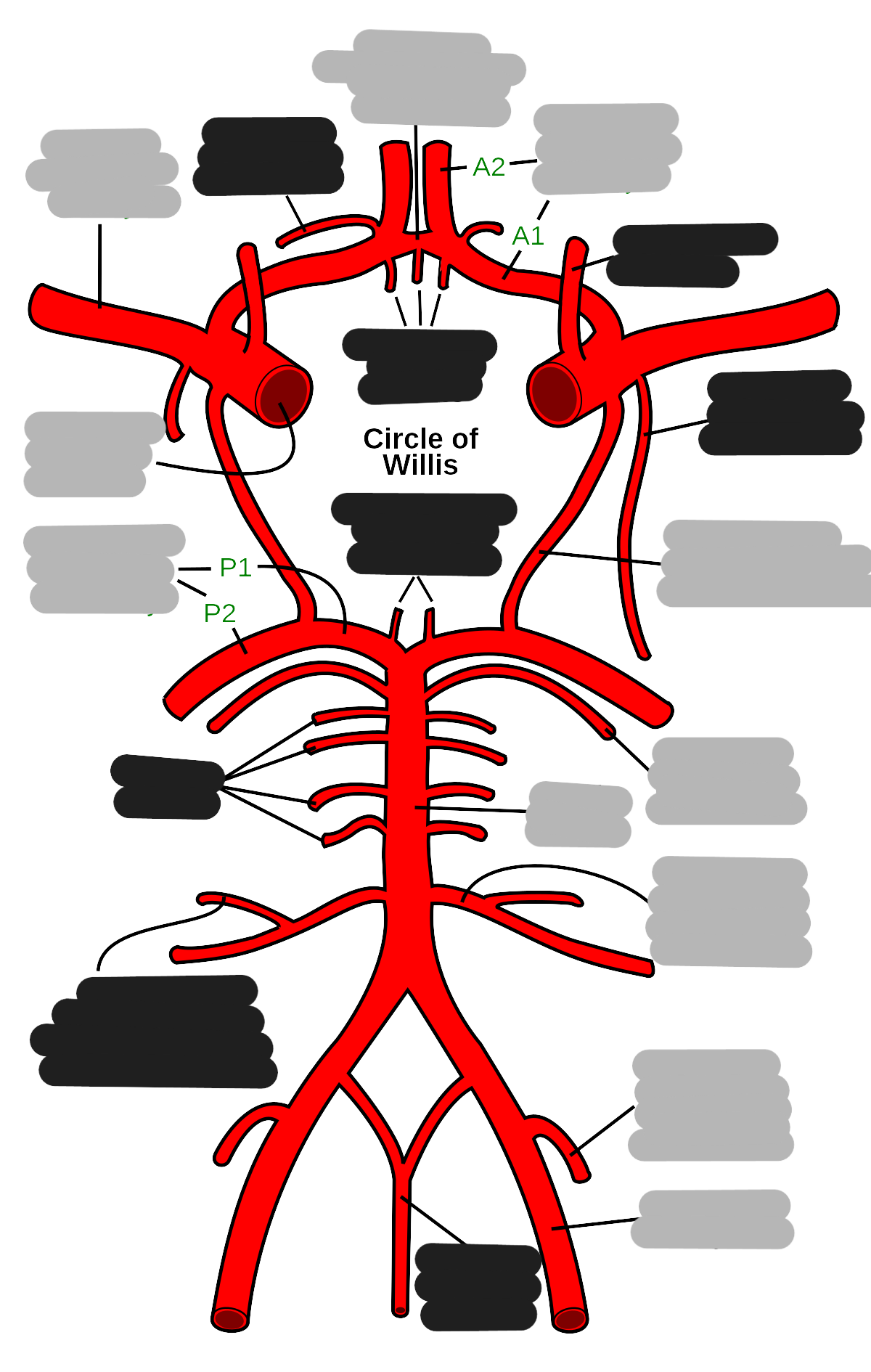
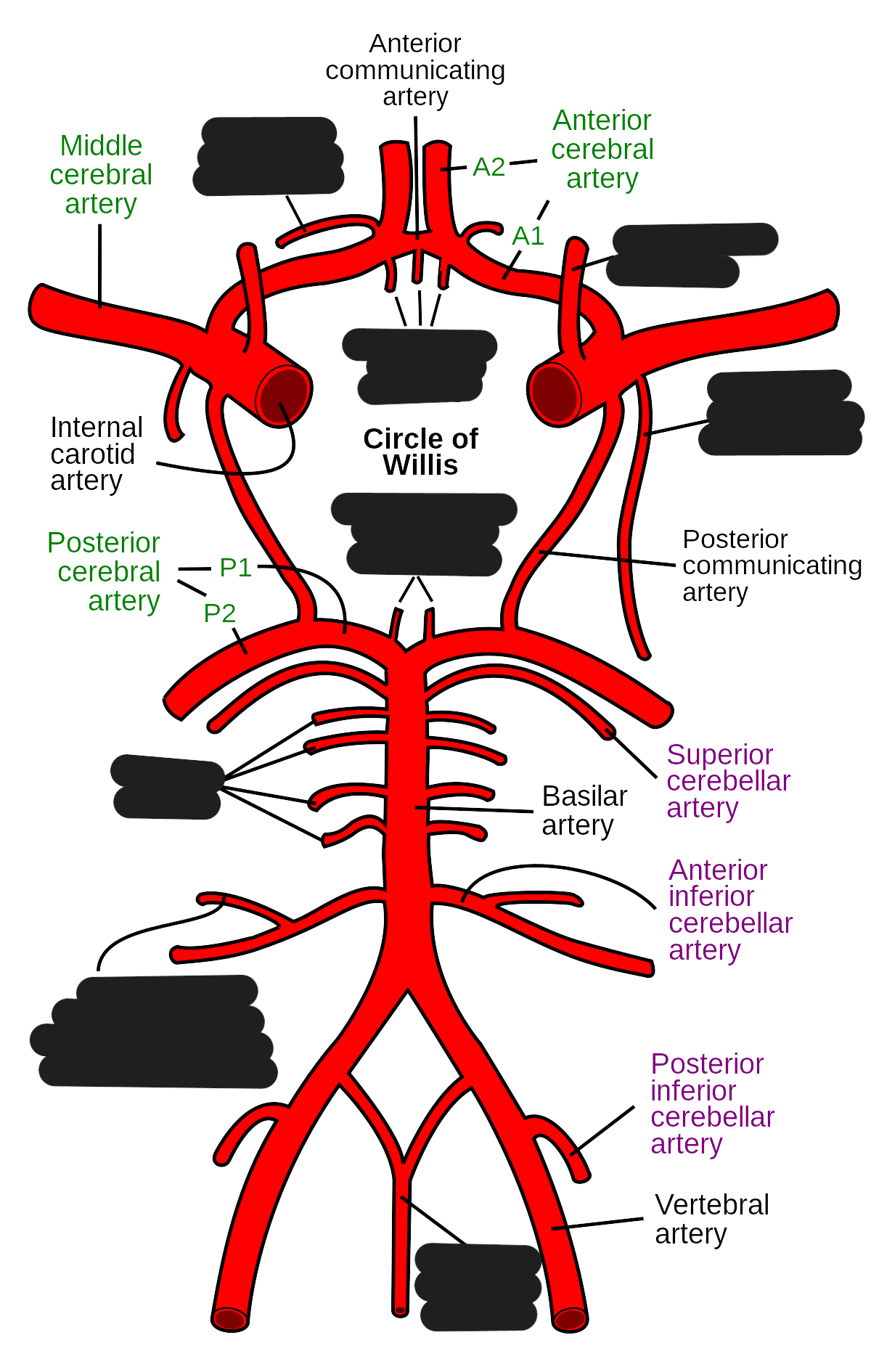
What are the 2 main arterial sources of cerebral circulation?
right and left internal carotids
supplies anterior and middle part of brain (80%)
enters through carotid foramen/canal
right and left vertebral arteries
supplies posterior part of brain (20%)
enters through foramen magnum
The internal carotids branch into:
anterior cerebral artery
smaller branch
supplies anterior and superior
middle cerebral artery
larger branch
supplies lateral
The vertebral artery is a branch of the ___
subclavian artery
Explain the location and function of the right and left vertebral arteries
through the transverse foramen of C-spine to foramen magnum and sits at the basilar portion of skull
join together to create the basilar artery
posterior cerebral arteries originate at the bifurcation of the basilar artery at midbrain and supplies the posterior part of the brain
List and explain the 2 communicating arteries
anterior communicating artery
unites cerebral arteries
posterior communicating artery
unites posterior cerebral arteries with the internal carotids
Explain the function and location of the circle of willis
the circle made up by the communicating arteries
at the inferior aspect of the brain
safeguards the brain
provides a collateral blood flow
in case of blockage in any of the major vessels (internal carotid and vertebral)
basilar artery occlusion has a high mortality rate
List and explain the 2 types of strokes
ischemic
most common
blockage of blood flow (thrombotic or embolic)
hemorrhagic
cerebral aneurysm
rupture of an aneurysm (damages cells and increases pressure)
diagnosed through CT
Explain treatment for a hemorrhagic stroke
aneurysm clipping
usually saccular
surgical procedure
remains for life
Explain treatment for ischemic stroke
medication (Tissue Plasminogen Activator) or stent placement
List the 4 types of brain hematomas
epidural
subdural
subarachnoid
intracerebral
Explain epidural brain hematomas
arterial blood leaks between the dura mater and skull to form a blood mass that presses on brain tissue
the most common cause is trauma
Explain subdural brain hematomas
venous blood vessels burst between the dura mater and arachnoid mater
leaking blood forms a hematoma that presses on the brain tissue
gets bigger and can cause gradual loss of consciousness and death
Explain subarachnoid brain hematomas
bleeding ON the brain
arterial bleeding in the space around the brain
usually happens when an irregular bulge in a blood vessel (aneurysm) bursts in the brain
Explain intracerebral brain hematomas
bleeding IN the brain
occurs when arterial blood pools in the tissue of the brain
causes include trauma, aneurysm, poorly connected veins and arteries (from birth), high BP, tumors